Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Electrical Current Multiple Choice
Caricato da
Claudio FacchineiDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Electrical Current Multiple Choice
Caricato da
Claudio FacchineiCopyright:
Formati disponibili
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
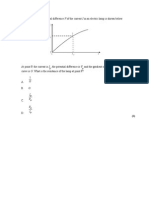
1. Which of the following is a unit for electrical resistance? A. WA2 B. AV1 C. VW2 s D. WV2 2. The work done on a positive point charge of magnitude 3.0 nC as it is moved at constant speed from one point to another is 12 nJ. The potential difference between the two points is A. 0.0 V. B. 0.25 V. C. 4.0 V. D. 36 V. The graph below shows the variation with current I of the potential difference V across a filament lamp.
3.
The resistance of the lamp when I = 1.5 mA is
. . C. 0.95 . D. 0.40 .
A. 950 B. 400 4.
The graphs below are the current-voltage (I-V) characteristics of three electrical components P, Q and R.
Which component(s) has (have) constant resistance? A. P only B. R only C. P and Q only D. P and R only
ELECTRICAL CURRENTS
COMPILED BY MARCELO PREZ M.
Page 1
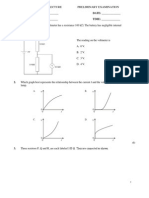
5.
Which one of the following is a correct statement about the resistance of the component?
A. For potential differences greater than V0, the resistance is constant. B. For potential differences greater than V0, the resistance decreases with increasing potential difference. C. The variation of current with potential difference is linear and so Ohms law is obeyed. D. For potential differences less than V0, the resistance is zero. 6. A conductor of constant resistance dissipates 6.0 W of power when the potential difference across it is 12 V. The power that will be dissipated in this conductor when the potential difference across it is 24 V is A. 6.0 W. B. 12 W. C. 24 W. D. 48 W. The graph shows the variation with the current I in a filament lamp of the potential difference V.
7.
Which of the following is correct regarding the resistance of the filament and its temperature as the current is increasing in the filament?
ELECTRICAL CURRENTS
COMPILED BY MARCELO PREZ M.
Page 2
8.
A resistor of resistance 1.0
is connected in series with a battery. The current in the circuit is 2.0 A. The
resistor is now replaced by a resistor of resistance of 4.0
. The current in this circuit is 1.0 A.
The best estimate for the internal resistance of the battery is
. . C. 4.0 . D. 5.0 .
A. 1.0 B. 2.0 9.
The graph shows the current-voltage (I-V) characteristic of an electrical component.
What is the resistance of the component at a potential difference V1 and how does the resistance change, if at all, between potential differences V0 and V1.
ELECTRICAL CURRENTS
COMPILED BY MARCELO PREZ M.
Page 3
10.
A battery is connected to a resistor as shown below.
The battery transfers energy transfers energy A. B. C. D.
EB
when charge Q passes completely around the circuit and the resistor
E R . The e.m.f. of the battery is equal to
ER . Q EB . Q EB ER Q EB ER Q
11.
In the circuit shown below, the cell has negligible internal resistance.
Which of the following equations is correct? A. I 1 = 2I 2 B. I 1 = 2I 3 C. I 2 = 2I 3 D. I 3 = 2I 1 12. The resistors in each of the circuits shown below each have the same resistance.
Which of the following gives the circuits in order of increasing total resistance? A. P Q S B. Q P S C. S Q P D. P S Q
ELECTRICAL CURRENTS
COMPILED BY MARCELO PREZ M.
Page 4
13. A voltmeter of resistance 50 k is connected in a circuit as shown in the diagram below.
The e.m.f. of the battery is 12 V and the resistance of the resistor is 10 k. The internal resistance of the battery is negligible. The reading of the voltmeter is A. 0.0 V. B. 2.0 V. C. 10 V. D. 12 V. 14. In the circuit below, the battery has negligible internal resistance. Lamps L, M and N which have different resistance are connected as shown.
Which one of the following is always true? A. Lamps L and N have the same current through them. B. Lamps L and M have the same current through them. C. Lamps L and N have the same potential difference across them. D. Lamps L and M have the same potential difference across them. 15. The circuit contains a battery of e.m.f. 12 V and negligible resistance.
What is the potential difference across the 25 resistor? A. 3.0 V B. 4.5 V C. 5.0 V D. 7.5 V
ELECTRICAL CURRENTS
COMPILED BY MARCELO PREZ M.
Page 5
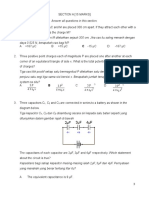
16. A resistor of resistance 50 k and a resistor of resistance 100 k are connected in series with a battery of e.m.f. 6.0 V and negligible internal resistance.
An ideal voltmeter is connected across the 50 k resistor. Which of the following is the reading on the voltmeter? A. 6.0 V B. 4.0 V C. 2.0 V D. 1.2 V 17. In the circuit below the battery has e.m.f. 6.0 V and negligible internal resistance. The three resistors each have resistance 10 . A high resistance voltmeter is connected as shown.
The reading of the voltmeter is A. 2.0 V. B. 3.0 V. C. 4.0 V. D. 6.0 V. 18. In the circuit below, resistors X, Y and Z are connected in series with a 9.0 V supply. between zero and 3000 .
Resistors X and Z are fixed resistors of resistance 3000 . The resistance of resistor Y may be varied
Which of the following gives the maximum range of potential difference V across the resistors X and Y? ELECTRICAL CURRENTS COMPILED BY MARCELO PREZ M. Page 6
A. 0 to 6.0 V B. 3.0 V to 6.0 V C. 4.5 V to 6.0 V D. 4.5 V to 9.0 V 19. In which one of the circuits is it possible to vary the current in the lamp by adjusting the variable resistor? The cell has negligible internal resistance.
20. Three resistors P, Q and R, are each labelled 100 . They are connected as shown.
The total resistance, when measured between points X and Y, is found to be 200 . What is the correct explanation for the resistance reading? A. Resistor R is zero B. Resistor R is infinite C. Resistor P is zero D. Resistor P is infinite
ELECTRICAL CURRENTS
COMPILED BY MARCELO PREZ M.
Page 7
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)Da EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ib Physics SL - Unit 4 ReviewDocumento46 pagineIb Physics SL - Unit 4 ReviewMax HudgenesNessuna valutazione finora
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Da EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- MCQN M1Documento45 pagineMCQN M1Max HudgenesNessuna valutazione finora
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsDa EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (2)
- Topic 5 Heating Currents Paper 1Documento20 pagineTopic 5 Heating Currents Paper 1felNessuna valutazione finora
- 20-DC CircuitsDocumento62 pagine20-DC Circuitsrodel.verzosaNessuna valutazione finora
- 9702 p1 Current Electricity All MCQDocumento35 pagine9702 p1 Current Electricity All MCQNafi Ul Kaysar50% (2)
- Chapter 5 Past Paper (2017-2022)Documento76 pagineChapter 5 Past Paper (2017-2022)saba falahNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuits Multiple ChoiceDocumento10 pagineCircuits Multiple ChoiceInnovate With AnweshaNessuna valutazione finora
- GibiliscoDocumento8 pagineGibiliscoChristian CuevasNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial ElectricityDocumento7 pagineTutorial ElectricityKoko Nur IzzatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Elex Post TestDocumento9 pagineElex Post TestAim HighNessuna valutazione finora
- Electricity 1Documento12 pagineElectricity 1saeed akhtarNessuna valutazione finora
- Electricity Test 2010Documento8 pagineElectricity Test 2010holaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.3 and 2.4 ElectricityDocumento17 pagine2.3 and 2.4 ElectricityAziz BakarNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Nov, David 9 Penabur 7Documento5 pagine1 Nov, David 9 Penabur 7Faber O.MNessuna valutazione finora
- Markscheme SL Paper 1Documento60 pagineMarkscheme SL Paper 1Carolina Blasco Méndez 8INessuna valutazione finora
- CH 27-30Documento69 pagineCH 27-30Richard Hammond50% (2)
- Physics Finals Rev3Documento13 paginePhysics Finals Rev3Ria MandasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Apllied Electric Circuit Objective Question and AnswerDocumento42 pagineApllied Electric Circuit Objective Question and AnswerGanesan KandasamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch5 Test3Documento10 pagineCh5 Test3chethansharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Test 5 - Potential and Circuits - BlankDocumento8 pagineTest 5 - Potential and Circuits - Blankandrey pradoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 7 (1) .4Documento7 pagineLesson 7 (1) .4jesunathan44@yahoo.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Electricity WorksheetDocumento18 pagineElectricity WorksheethumanistaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Elec Exam StandDocumento14 pagineElec Exam StandDaveyNessuna valutazione finora
- DC Electrical CircuitsDocumento4 pagineDC Electrical CircuitsAnni Lou BordiosNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.2 Resistance 91-03Documento10 pagine2.2 Resistance 91-03Murray PhysicsNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Circuits HW SolutionsDocumento10 pagineAP Circuits HW Solutionsxto07100% (1)
- Physics Quiz Chapter 20Documento4 paginePhysics Quiz Chapter 20killdevil100% (5)
- EE QuestionairesDocumento7 pagineEE Questionairesivygrace gabestpaelmaoNessuna valutazione finora
- AssignmentDocumento3 pagineAssignmentksssaNessuna valutazione finora
- PQ - Current Electricty 150Documento18 paginePQ - Current Electricty 150dongoke2019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Topic - 5 - Exam - With - AnsDocumento7 paginePhysics Topic - 5 - Exam - With - AnssamerNessuna valutazione finora
- Potential Divider QuestionsDocumento2 paginePotential Divider Questionscrackerz83100% (1)
- Tempat Belajar Infinite: Rukan Taman Meruya Blok M No. 75 Meruya Ilir Jakarta Barat 1Documento5 pagineTempat Belajar Infinite: Rukan Taman Meruya Blok M No. 75 Meruya Ilir Jakarta Barat 1infinite onlineNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics II Problems PDFDocumento1 paginaPhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNessuna valutazione finora
- AP EM FRQ-2aDocumento7 pagineAP EM FRQ-2aHansom boyzNessuna valutazione finora
- Sumulong College of Arts and Sciences: Midterm Examination 2 Semester, SY 2019-2020Documento5 pagineSumulong College of Arts and Sciences: Midterm Examination 2 Semester, SY 2019-2020Manongdo AllanNessuna valutazione finora
- 14 - 15 - H2 - Current of Electricity - Tut PDFDocumento11 pagine14 - 15 - H2 - Current of Electricity - Tut PDFeltytanNessuna valutazione finora
- f5c4 ExerDocumento3 paginef5c4 Exerjalrizal7Nessuna valutazione finora
- AEC Objective Question and AnswerDocumento35 pagineAEC Objective Question and AnswerGanesan KandasamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Objective Questions Set 01Documento19 pagineObjective Questions Set 01GAURAV GUPTANessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Circuits 1 Lecture PrelimsDocumento9 pagineElectrical Circuits 1 Lecture PrelimsGhe PataniNessuna valutazione finora
- LXL - Gr11PhysicalSciences - 24 - Electric Circuit Problems - 12aug2014Documento5 pagineLXL - Gr11PhysicalSciences - 24 - Electric Circuit Problems - 12aug2014HNessuna valutazione finora
- D. The Field Strength Is Zero at All Points Where The Potential Is ZeroDocumento3 pagineD. The Field Strength Is Zero at All Points Where The Potential Is ZeroKamran AliNessuna valutazione finora
- TRIAL STPM P2 2016 With AnswerDocumento16 pagineTRIAL STPM P2 2016 With AnswerdarwishmajidNessuna valutazione finora
- Current Electricity 3Documento13 pagineCurrent Electricity 3Mona Mohamed SafwatNessuna valutazione finora
- EE Online SAEx 2 1 PDFDocumento6 pagineEE Online SAEx 2 1 PDFJunnar Jay AbañoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5-8Documento10 pagineChapter 5-8Besu FikadNessuna valutazione finora
- Topical Test Chapter 13: Capacitor Section A: Objective (10 Marks)Documento6 pagineTopical Test Chapter 13: Capacitor Section A: Objective (10 Marks)punithaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Benchmark Exam #4 2010-2011Documento11 paginePhysics Benchmark Exam #4 2010-2011Claudia HuoNessuna valutazione finora
- DP Physics Unit 5 TestDocumento15 pagineDP Physics Unit 5 TestJoseph LAU [11D]Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7: Electricity 2003Documento12 pagineChapter 7: Electricity 2003Sobri HamzahNessuna valutazione finora
- Encircle or Write Down The Letter of Correct Answer For Each Statement (1 Point Each)Documento4 pagineEncircle or Write Down The Letter of Correct Answer For Each Statement (1 Point Each)Sonic HedgehogNessuna valutazione finora
- Xii Physics - Chapter 3 Term 1Documento64 pagineXii Physics - Chapter 3 Term 1RahulNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics 12 Worksheet Circuitry KEYDocumento3 paginePhysics 12 Worksheet Circuitry KEYIna KasimNessuna valutazione finora
- Abp - Electric Current Circuits Multiple ChoiceDocumento11 pagineAbp - Electric Current Circuits Multiple Choice羅天佑Nessuna valutazione finora
- Current and Circuits Practice ProblemsDocumento15 pagineCurrent and Circuits Practice ProblemsAnthony HuiNessuna valutazione finora
- Test 2Documento16 pagineTest 2edwardNessuna valutazione finora
- Optra Service ManualDocumento194 pagineOptra Service ManualClaudio FacchineiNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat of Fusion of The IceDocumento2 pagineHeat of Fusion of The IceClaudio FacchineiNessuna valutazione finora
- 1997 Nissan Pathfinder PDFDocumento233 pagine1997 Nissan Pathfinder PDFrodysoftNessuna valutazione finora
- Sek International School Natural Sciences Lab Report # 1 Name: Paola Facchinei Grade: 9 "D" Experiment: Structure of Some Common SamplesDocumento9 pagineSek International School Natural Sciences Lab Report # 1 Name: Paola Facchinei Grade: 9 "D" Experiment: Structure of Some Common SamplesClaudio FacchineiNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 1 - TENSION TEST OF MILD STEEL SPECIMENDocumento10 pagineExperiment 1 - TENSION TEST OF MILD STEEL SPECIMENSamiha Maysoon Nooria100% (1)
- 00 Downhole Hydraulic KTC VersionDocumento44 pagine00 Downhole Hydraulic KTC VersionaungwinnaingNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice 0Documento43 pagineMultiple Choice 0Dave SalvadorNessuna valutazione finora
- Motion Mountain The Adventure of Physics 1 of 6 22nd Edition PDFDocumento412 pagineMotion Mountain The Adventure of Physics 1 of 6 22nd Edition PDFzainikamal1975Nessuna valutazione finora
- Derivation of EaDocumento3 pagineDerivation of EaSssNessuna valutazione finora
- DOM MCQ (1-6) - RevisedDocumento112 pagineDOM MCQ (1-6) - RevisedSAURAV KOULNessuna valutazione finora
- Patent CN1488854A - Antigravity Apparatus For Spaceship-Reverse Thrust Photon RocketDocumento6 paginePatent CN1488854A - Antigravity Apparatus For Spaceship-Reverse Thrust Photon RocketVictor Von DoomNessuna valutazione finora
- Moment Curvative Relationships For Partially Prestressed Concrete BeamsDocumento12 pagineMoment Curvative Relationships For Partially Prestressed Concrete BeamsFreefirekannadigaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1790@0@104911 WlaO4PLB96z Emailing Exercises - Work and EnergyDocumento12 pagine1790@0@104911 WlaO4PLB96z Emailing Exercises - Work and Energyalirammal804Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hardy Cross Continuous Frames of Reinforced ConcreteDocumento361 pagineHardy Cross Continuous Frames of Reinforced ConcreteCarson BakerNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 11Documento2 pagineActivity 11ProfED TVNessuna valutazione finora
- Suggested+Solutions+V1+VG MVG+Level+Test+FyANVC08+Ch+16 19+electricityDocumento9 pagineSuggested+Solutions+V1+VG MVG+Level+Test+FyANVC08+Ch+16 19+electricityEpic WinNessuna valutazione finora
- Why Is Surface Tension A Force Parallel To The Interface?: Additional Information On Am. J. PhysDocumento11 pagineWhy Is Surface Tension A Force Parallel To The Interface?: Additional Information On Am. J. PhysvishveshwarNessuna valutazione finora
- JEE Advanced Previous Year Questions, KinematicsDocumento7 pagineJEE Advanced Previous Year Questions, KinematicsAnil Kapil100% (4)
- Robotics: Chapter 1: Spatial Descriptions & TransformationsDocumento39 pagineRobotics: Chapter 1: Spatial Descriptions & TransformationsNam NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Continuous Fiber Composites - I: Reinforced Plastics (Composite)Documento3 pagineAnalysis of Continuous Fiber Composites - I: Reinforced Plastics (Composite)أحمد صدقيNessuna valutazione finora
- 1-D, WB-2Documento1 pagina1-D, WB-2Monal KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Tank Wall Design by LSM 1Documento24 pagineWater Tank Wall Design by LSM 1StrucTechNessuna valutazione finora
- Modified Cam Clay Modell (MCCM)Documento15 pagineModified Cam Clay Modell (MCCM)Jorge Hernan LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.0 Convection Heat TransferDocumento41 pagine3.0 Convection Heat Transfershariza91Nessuna valutazione finora
- Open Flower Reference ManualDocumento21 pagineOpen Flower Reference Manualjgraczyk007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Consolidation Test - 023Documento11 pagineConsolidation Test - 023nepster620533% (3)
- 4) Statement of Purpose/introduction/objectiveDocumento4 pagine4) Statement of Purpose/introduction/objectiveMuhd AdamNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Notes 5: Electromagnetic Waves in Vacuum The Wave Equation (S) For E and BDocumento33 pagineLecture Notes 5: Electromagnetic Waves in Vacuum The Wave Equation (S) For E and BZhenhua HuangNessuna valutazione finora
- Code AsterDocumento12 pagineCode Asterfabvn01_125620890Nessuna valutazione finora
- Curie-Weiss Law Wiess Theory of ParamagnetismDocumento11 pagineCurie-Weiss Law Wiess Theory of ParamagnetismShashank SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Transverse Vibrations of A Rotating Uniform Cantilever Beam With Tip Mass As Predicted by Using Beam Characteristic Orthogonal Polynomials in The Rayleigh-Ritz MethodDocumento12 pagineTransverse Vibrations of A Rotating Uniform Cantilever Beam With Tip Mass As Predicted by Using Beam Characteristic Orthogonal Polynomials in The Rayleigh-Ritz MethodHassanImranNessuna valutazione finora
- ME5521 Chapter4 4 2012Documento37 pagineME5521 Chapter4 4 2012Sebastián EspinozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tall Buildings-Secondary Effects On The Structural BehaviourDocumento15 pagineTall Buildings-Secondary Effects On The Structural BehaviourMiguel MNessuna valutazione finora
- CJC Prelim Paper 1 AnsDocumento8 pagineCJC Prelim Paper 1 Ansnewtonian_physicsNessuna valutazione finora