Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Brochure
Caricato da
joyyleeeeCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Brochure
Caricato da
joyyleeeeCopyright:
Formati disponibili
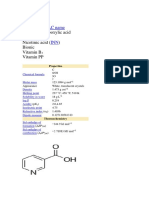
Important Physical Properties
atomic mass: 52.00 amu state at room temperature: solid melting point: 3,465F boiling point: 4,841F density: 7.15 grams/cm3 solubility: relatively water insoluble conducts heat and electricity ductile and malleable most common charge of ions that this element forms: 2+, 3+ common oxidation numbers: 6, 3 specific heat: 0.11Btu/lbmoF 4 stable isotopes atomic radius of 128 pm crystal structure:
Chromium is a hard, lustrous, steelgray metal. It forms many colorful compounds that have industrial uses. It is obtained from chromite. It is known as an essential trace element because very small amounts are necessary for human health.
Gagnon, Steve. "The Element Chromium." It's Elemental -. N.p., n.d. Web. 21 Nov. 2013.
": Uses, Side Effects, Interactions and Warnings WebMD." WebMD. WebMD, n.d. Web. 21 Nov. 2013. "Chromium." WebElements Periodic Table of the Elements. N.p., n.d. Web. 21 Nov. 2013.
Name: Chromium Symbol: Cr Mass: 52.00 amu
Joy Lee 11/21/13 Period 6
Origin/Discovery In the mid 18th century, analysis of Siberian "red lead" (PbCrO4, crocoite) from Siberia showed that it contained quite a lot of lead, but also a further material. Discovered in 1797 by Louis-Nicholas Vauquelin, this was identified as chromium oxide. He prepared the metal itself in the following year. Sources and Abundance Chromium is mined as chromite (FeCr2O4) ore. About two-fifths of the ores and concentrates in the world are produced in South Africa, while Kazakhstan, India, Russia, and Turkey are also substantial producers. Chromium is the 21st most abundant element, as it is obtained commercially by heating the ore in the presence of aluminum or silicon. Uses Chromium is used to harden steel. It plates the steel to produce a shiny, hard surface that is resistant to corrosion. Our bodies also use chromium in small amounts for body functions, such as digestion. Chromium compounds are important as pigments and oxidizing agents. Interesting Facts Chromium salts have been used since early times in the tanning of leather. Chromium (III) is what gives natural rubies their red color. Chromium was used in the ancient times, especially by the Chinese. Important Chemical Properties It doesnt react with air or water at room temperature, but reacts directly with halogens.
element symbol: Cr atomic number: 24 atomic mass: 52.00 amu Chromium is steel-gray, lustrous, and hard with toxic compounds. It is found as chromite ore. metal group 6; series 4 transition metals: Their general properties include electrical conductivity, luster, and malleability with other metals. Most are hard solids with high melting and boiling points. electron configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d4 2 valence electrons
Chromium is possibly safe for most people, but the rest may experience skin irritation, headaches, dizziness, nausea, mood changes and impaired thinking, judgment, and coordination.
Chromium is likely to lose electrons. The most common ions are Cr+2 and
Cr+3.
reaction with fluorine to form chromium (VI) fluoride: Cr(s) + 3F2(g) CrF6(s) [yellow] reaction with dihydrochloric acid to form solutions containing the aquated ion with hydrogen gas: Cr(s) + 2HCl(aq) Cr2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) + H2(g) Compounds: Chromium difluoride: CrF2 Chromium sulphide: CrS Dichromium trisulphide: Cr2S3 Chromium selenide: CrSe Chromium hexacarbonyl: Cr(CO)6
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Properties Properties: Chromium ChromiumDocumento4 pagineProperties Properties: Chromium ChromiumAlodia VaniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chromium: ES 10A: Chemistry For Engineers LABDocumento10 pagineChromium: ES 10A: Chemistry For Engineers LABKristabelle PrincipeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry of ChromiumDocumento27 pagineChemistry of ChromiumFebrian IsharyadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel ChromiumDocumento12 pagineSteel ChromiumVishalNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry of ChromiumDocumento47 pagineChemistry of ChromiumFebrian IsharyadiNessuna valutazione finora
- ChromiumDocumento29 pagineChromiumjosevitorromualdoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Research Project On 5 Elements of The Periodic TableDocumento28 pagineChemistry Research Project On 5 Elements of The Periodic TableRanjitha RaviproluNessuna valutazione finora
- ChromiumDocumento24 pagineChromiumstallone21Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chromium - WikipediaDocumento29 pagineChromium - WikipediaBhumikNessuna valutazione finora
- Cerium: 1. Devina Dwi Astari 2. Marchia Marthalena MarintaDocumento13 pagineCerium: 1. Devina Dwi Astari 2. Marchia Marthalena MarintaastariNessuna valutazione finora
- Material Individu DanyDocumento15 pagineMaterial Individu Danydanial 96Nessuna valutazione finora
- Per TableDocumento12 paginePer TableSreekumar C PillaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Study of Constituents of An AlloyDocumento18 pagineStudy of Constituents of An AlloyMohammed Anis RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Non Ferrous Metals FinalDocumento89 pagineNon Ferrous Metals FinalAstilbe AlairNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1material Chemistry and Corrosion NotesDocumento25 pagineUnit 1material Chemistry and Corrosion NotesmessmessNessuna valutazione finora
- Group II CationsDocumento23 pagineGroup II CationsMike Daven LaderaNessuna valutazione finora
- AluminumDocumento18 pagineAluminumAkniet RysbekovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basma K 2Documento5 pagineBasma K 2Anonymous j5JiMo55cNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Extra ClassDocumento7 pagineChemistry Extra Classjuan barrettNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 1b - Identification of MaterialsDocumento9 pagineExperiment 1b - Identification of MaterialsSeth Aboagye JnrNessuna valutazione finora
- Inorganic & Organic Chemistry: Submitted By: Muhammad Faizan REG NO. 2020-CH-271Documento7 pagineInorganic & Organic Chemistry: Submitted By: Muhammad Faizan REG NO. 2020-CH-271Zeeshan Abid BhattiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mercury (Element)Documento15 pagineMercury (Element)zidaaanNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet 1 SolDocumento2 pagineSheet 1 SolsaitamavioletNessuna valutazione finora
- 12th Biology Gene Replacement NotesDocumento49 pagine12th Biology Gene Replacement NotesAbishek DhinakaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry For Engineers CompilationDocumento164 pagineChemistry For Engineers CompilationRevlemmor SarmientoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Importance of Iron in Our Daily LifeDocumento38 pagineThe Importance of Iron in Our Daily Lifelamia97100% (1)
- PresentationSlides CombinedDocumento147 paginePresentationSlides Combineddiwash ghimireNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter5 (1) ChemistryDocumento14 pagineChapter5 (1) ChemistryO and A Level TutorNessuna valutazione finora
- Angel CondensadaDocumento6 pagineAngel CondensadaAsnipah Dilaos MustapahNessuna valutazione finora
- Metal & PlasticDocumento53 pagineMetal & PlasticbreighamNessuna valutazione finora
- Nature of MaterialsDocumento20 pagineNature of MaterialsBALBIDO John LesterNessuna valutazione finora
- Boron FamilyDocumento52 pagineBoron FamilyTol Ralph SabNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Metals PDFDocumento6 pagineBasic Metals PDFTanvirNessuna valutazione finora
- Answers To Materials and Heat Treatment Board Exam Review QuestionsDocumento3 pagineAnswers To Materials and Heat Treatment Board Exam Review Questionsrex tanongNessuna valutazione finora
- Metals Summary Notes GuideDocumento7 pagineMetals Summary Notes GuideRohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Elements Info. GoodDocumento59 pagineElements Info. GoodSaid Alauddeen FaiszNessuna valutazione finora
- University of Northeastern Philippines: Iriga City, Camarines SurDocumento31 pagineUniversity of Northeastern Philippines: Iriga City, Camarines SurZudotaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cuestionario Antecedentes Práctica 2 QuímicaDocumento4 pagineCuestionario Antecedentes Práctica 2 QuímicaISAC VALENTIN GONZALEZ HORTANessuna valutazione finora
- Fact Box: 22412 ChemspiderDocumento9 pagineFact Box: 22412 ChemspiderDion TriNessuna valutazione finora
- ChromiumDocumento20 pagineChromiumSherey FathimathNessuna valutazione finora
- Mercury (Element)Documento23 pagineMercury (Element)vinothenergyNessuna valutazione finora
- Higher Understanding of CarbonDocumento10 pagineHigher Understanding of CarbonSulav gairheNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel IronDocumento6 pagineSteel IronVishalNessuna valutazione finora
- HNC Unit 3 - Engineering Science LO3 - Explore The Characteristics and Properties of Engineering MaterialsDocumento7 pagineHNC Unit 3 - Engineering Science LO3 - Explore The Characteristics and Properties of Engineering MaterialsNoel JenningsNessuna valutazione finora
- Investigatory ProjectDocumento9 pagineInvestigatory ProjectShourya RaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3 Metals and Metal Working Processes: OverviewDocumento17 pagineLesson 3 Metals and Metal Working Processes: OverviewNadjer C. AdamNessuna valutazione finora
- Applications of Transition Elements & PolymersDocumento10 pagineApplications of Transition Elements & Polymerssprabesh111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Additional ElementsDocumento7 pagineAdditional ElementsRoselyn BunquinNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 2 MaterialDocumento22 pagineLab 2 MaterialMon LuffyNessuna valutazione finora
- Mee-Əm) Is A Chemical Element Which Has The Symbol CR and Atomic Number 24. It Is The FirstDocumento2 pagineMee-Əm) Is A Chemical Element Which Has The Symbol CR and Atomic Number 24. It Is The FirstMichelle VanceNessuna valutazione finora
- Matter (Group 3) - ChemistryDocumento16 pagineMatter (Group 3) - Chemistry044 Nabila Hanin FitrianiNessuna valutazione finora
- Document 32Documento17 pagineDocument 32rik.sengupta.08Nessuna valutazione finora
- Amta5 1 Identifying Metals and Their Physical PropertiesDocumento104 pagineAmta5 1 Identifying Metals and Their Physical PropertiesJason Lid-ayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemi Presentation 2Documento25 pagineChemi Presentation 2teddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Amta5 1 Identifying Metals and Their Physical PropertiesDocumento104 pagineAmta5 1 Identifying Metals and Their Physical PropertiesKrishnamoorthi VenkatesanNessuna valutazione finora
- Synthesis and Characterization of CR (III) Oxide (Cr2O3) : Lab Report (4a)Documento5 pagineSynthesis and Characterization of CR (III) Oxide (Cr2O3) : Lab Report (4a)Falak NazNessuna valutazione finora
- HQTNDocumento38 pagineHQTNAusuNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 Metals & Non TheoryDocumento60 pagine8 Metals & Non TheorySARANGMUMBAINessuna valutazione finora
- How Is Mercury Used Today? Chemistry Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Chemistry BooksDa EverandHow Is Mercury Used Today? Chemistry Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Chemistry BooksNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 TH STSODocumento6 pagine9 TH STSOKesanam Sp50% (2)
- Chapter 1Documento51 pagineChapter 1Shiela May DelacruzNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 8 Elements and SubstancesDocumento6 pagineCHAPTER 8 Elements and SubstancesLi Lian KwangNessuna valutazione finora
- Origin and Chemical Evolution of The EarthDocumento244 pagineOrigin and Chemical Evolution of The EarthElma SmrikoNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm b108-Aluminium-Alloy Permanent Mold CastingsDocumento18 pagineAstm b108-Aluminium-Alloy Permanent Mold CastingsEldennisNessuna valutazione finora
- A Timeline On Atomic StructureDocumento8 pagineA Timeline On Atomic Structureashley ciaNessuna valutazione finora
- 313 Chemistry Eng Lesson21Documento26 pagine313 Chemistry Eng Lesson21Tanuj KafleNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 9 OutcomesDocumento3 pagineScience 9 Outcomesapi-263902873Nessuna valutazione finora
- 页面提取自-Chemistry for the IB Diploma Coursebook, 2nd EditionDocumento1 pagina页面提取自-Chemistry for the IB Diploma Coursebook, 2nd EditionEshowbooks EbooksNessuna valutazione finora
- 5124 w07 QP 3Documento16 pagine5124 w07 QP 3Sudibyo GunawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Element Ball ProjectDocumento3 pagineElement Ball ProjectCarolina CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Questionnaire Science 7 - 2nd QuarterDocumento2 pagineTest Questionnaire Science 7 - 2nd Quartertrexia autidaNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Convert Atomic Percent To Weight Percent and Vice VersaDocumento5 pagineHow To Convert Atomic Percent To Weight Percent and Vice VersaAli Khalil100% (3)
- Chapter 4 The Structure of The Atom Worksheet 1Documento2 pagineChapter 4 The Structure of The Atom Worksheet 1Joy LeannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Two: The Geology of Ethiopia and The HornDocumento62 pagineChapter Two: The Geology of Ethiopia and The HornOliyad Bulto100% (1)
- Chapter1-Matter and MeasurementsDocumento19 pagineChapter1-Matter and MeasurementsToman Chi To Lam100% (1)
- 10 Average Atomic Mass-SDocumento5 pagine10 Average Atomic Mass-S776pmsfq2fNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Five Kingdom Classification: StructureDocumento23 pagineUnit Five Kingdom Classification: Structurekaladhar reddyNessuna valutazione finora
- INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Part 3Documento71 pagineINTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Part 3Triphon Gyle BalidiongNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantitative ChemistryDocumento56 pagineQuantitative ChemistryMuddamsetty ArunkalyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Chemistry Chapter 4 Homework 4-2 AnswersDocumento8 pagineModern Chemistry Chapter 4 Homework 4-2 Answersaxnybeapd100% (1)
- Chapter - 3: Atoms and MoleculesDocumento15 pagineChapter - 3: Atoms and Moleculesuma mishra0% (1)
- Atomic Model Project RubricDocumento3 pagineAtomic Model Project RubricJaclyn DuggerNessuna valutazione finora
- Kompilasi Reading ComprehensionDocumento25 pagineKompilasi Reading ComprehensionirniNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.3.5 Practice - Atomic Structure (Practice)Documento11 pagine2.3.5 Practice - Atomic Structure (Practice)damarionbryant46Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Data BookletDocumento22 pagineChemistry Data BookletIsaline GurneNessuna valutazione finora
- C289Documento22 pagineC289Gato SesaNessuna valutazione finora
- AjgDocumento9 pagineAjgTanuja MagarNessuna valutazione finora
- A Level Chemistry Notes Bilal Hameed As Books As-Book-1Documento300 pagineA Level Chemistry Notes Bilal Hameed As Books As-Book-1Abdullah Bin TariqNessuna valutazione finora
- Science7 - SLM - Q1 - M2 - V1.0 - CO Released 08032020Documento36 pagineScience7 - SLM - Q1 - M2 - V1.0 - CO Released 08032020anne abadiezNessuna valutazione finora