Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Be Syllabus&Scheme Old
Caricato da
vagoliyoTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Be Syllabus&Scheme Old
Caricato da
vagoliyoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
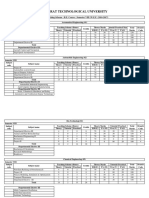
TEACHING SCHEME B.E. FIRST YEAR TEACHING AND EXAMINATION SCHEME (C,M,E,EC/IC,CE,CHEM.,ENV.RU. PL.)(ANNUAL PATTERN) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------SUB.
NAME OF TEACHING SCHEME EXAMINATION SCHEME NO. SUBJECT THE. PRACT. THEORY HOURS SESS. T/W TOTAL MARKS MARKS MARKS ---------------------------------------------------------------------------101 Maths I & II 3 100 4 50 -150 102 Surveying 2 2 100 3 50 50 200 103 Engg. Mech. 2 1 100 3 50 25 175 104 Strength of Materials 2 1 100 3 50 25 175 105 Engg. Materials 2 100 3 50 -150 106 Engg. Drg. 3 4 100 4 50 50 200 107 Heat Power 2 1 100 3 50 25 175 108 Elect. Circuit & Electronics 2 1 100 3 50 25 175 109 Workshops 2 -50 50 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------18 12 800 400 250 1450 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------B.E. (ELECTRICAL) SEM.III SUB. NAME OF TEACHING SCHEME EXAMINATION SCHEME NO. SUBJECT THE. PRACT. THEORY PRACT. SESS. T/W TOTAL MARKS MARKS MARKS ---------------------------------------------------------------------------301 Mathematics III 4 -100 -50 -150 302 Network Analysis 4 4 100 50 50 25 225 303 Linear Electroni 4 4 100 50 50 25 225 304 Elect. Power 1 4 -100 -50 -150 305 Thermal & Hydro 4 2 100 -50 25 175 lic prime movers ---------------------------------------------------------------------------TOTAL 20 10 500 100 250 75 925 --------------------------------------------------------------------------B.E. (ELECTRICAL) SEM.IV SUB. NAME OF TEACHING SCHEME EXAMINATION SCHEME NO. SUBJECT THE. PRACT. THEORY PRACT. SESS. T/W TOTAL MARKS MARKS MARKS ---------------------------------------------------------------------------401 Mathematics IV 4 -100 -50 -150 402 Int. Electronics 4 2 100 50 50 25 225 403 Elect.Machine-I 4 4 100 50 50 25 225 404 Elect.Meas. & 4 2 100 50 50 25 225 Instrument 405 Control Theory 4 2 100 -50 25 175 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------TOTAL 20 10 500 150 250 75 1000
B.E. (ELECTRICAL) SEM.V SUB. NAME OF TEACHING SCHEME NO. SUBJECT THE. PRACT. THEORY MARKS
EXAMINATION SCHEME PRACT. SESS. T/W TOTAL MARKS MARKS
---------------------------------------------------------------------------501 Elect. Power II 4 2 100 -50 25 175 502 Elect. of Elect. 4 4 100 50 50 50 250 Design 503 Electromagnetics 4 100 -50 -150 504 Power Electronic 4 4 100 50 50 25 225 Devices&Circuits 505 Business organiz 4 100 -50 -150 ation & project planning -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
B.E.Electrical Sem. VI ---------------------------------------------------------------------------SUB. NAME OF TEACHING SCHEME EXAMINATION SCHEME NO. SUBJECT THE. PRACT. THEORY HOURS SESS. T/W TOTAL MARKS MARKS MARKS ---------------------------------------------------------------------------601 Elec.Machine II 4 4 100 50 50 25 225 602 Elect.Power 4 100 -50 -150 Utilization 603 Microprocessors 4 2 100 50 50 25 225 Digitl.Electro. 604 Computer Prog- 4 2 100 50 50 25 225 ramming Techniqe 605 Energy Conserv- 4 2 100 -50 25 175 ation and Renew able sources. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------20 10 500 150 250 100 1000 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------B.E.Electrical Sem. VII ---------------------------------------------------------------------------SUB. NAME OF TEACHING SCHEME EXAMINATION SCHEME NO. SUBJECT THE. PRACT. THEORY HOURS SESS. T/W TOTAL MARKS MARKS MARKS ---------------------------------------------------------------------------701 Elect. power 4 2 100 50 50 25 225 system design 702 Elect.Mich.III 4 2 100 50 50 50 250 703 Switch Gear & 4 2 100 50 50 25 225 Protection 704 Indu.Instrumen- 4 2 100 50 50 25 225 tation 705 Elective paper I 4 2 100 50 50 25 175 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------20 10 500 150 250 100 1150 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------B.E.Electrical Sem. VIII ---------------------------------------------------------------------------SUB. NAME OF TEACHING SCHEME EXAMINATION SCHEME NO. SUBJECT THE. PRACT. THEORY HOURS SESS. T/W TOTAL
MARKS MARKS MARKS ---------------------------------------------------------------------------801 Elec.M/c.design 4 4 100 50 50 50 250 802 interconnected 4 2 100 50 50 50 250 power system 803 Commissioning of 4 2 100 50 50 25 225 Electrical Equip. 804 Elective paperII 4 2 100 50 50 25 225 805 Project&seminar 4 --50 -100 150 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------16 14 400 250 200 250 1100 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
B.E. I - SEMESTER II (C,M,E,EC,IC,CE,CH.,TT) ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS AND ELECTRONICS -----------------------------------------------------------------------------Teaching scheme Examination Scheme ----------------Theory Practical ------------------------------------------------Theory Paper Marks
----------------------------------------------------------------(Hours) (Hours) Hours Marks Sessional T.W. Pra./Viva Total 2 1 3 100 50 25 175 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------D.C. Circuits : Ohm's Law, resistance calculations, resistance combinations, effect of temperature upon resistances and insulators. Power and energy relationship in electrical, thermal and mechanical system units. ______________________________________________________________________________ Batteries : Types, constructions and maintenance. Electrostatics : Concept of electric charge and electric field, coulomb's law, electric field intensity. Electric potential, Dielectric stress and breakdown, capacitor charge and discharge of a capacitor. Electromagnetics : Magnetic circuits, series/parallel magnetic Magnetic materials permeability, hysteresis. circuit calculations.
Electromagnetic induction, statically & dynamically induced e.m.fs. Eddy current and eddy current losses. Growth and decay of current in inductive circuit. Alternating currents : Single phase voltage and current sources - phasor diagram - properties of
R,L and C series and parallel circuits. Power and power factor and energy, current locus in R-L-C circuits. Polyphase circuits : Generations of two and three phase voltages, 3 phase connection voltage, current and power relationship in balanced three phase circuits. Measurement of power in three phase circuits. Electronics : Vacuum Tubes : Diodes, triodes, tetrodes, pentodes, construction and characteristics, semiconductor devices. P-N junction diodes. Zener diodes. Transistors, their construction and characteristics. Rectifiers, amplifiers, oscillators, C.R.O. and its applications. Basic working principles of telephone, radio and television. Suggested Books : 1. 2. 3. 'Electrical Technology' by B.L. Theraja 'Electrical Technology' by Dr. S.L. Uppal 'Introduction to Electric Circuits' by Aler Ruwanowitz (John & Wiley)
E-302 NEWTORK ANALYSIS ----______________________________________________________________________________ Teaching Scheme Exam Scheme ------------------------------Theory Practical Theory Hrs. Sessional Prac. T.W. Total 4 4 marks 3 marks marks marks 100 50 50 25 225 ______________________________________________________________________________ (1) Network topology definitions, tie set & cut set tables source
transformation dot conveation principles of duality. (2) Network equations :- Mesh/loop current and node voltage equations for coupled circuits. (3) Initial conditions in elements, proceduce for evaldating conditions. analysis initial
(4) Solution of circuit equations by replace transform transient analysis of R-L, R-C Circuits R.L.C. Circuits. (5) Waveform synthesis, initial & final value theorems. (6) Network theorems thevenin, nontons, super position millman reciprocity & max.power transfer. (7) Impedance function - concept of complex freq. transform impedance * transform circuits. (8) Network functions for one part & two parts, calculation of network functions, poles & zerox. Time comain behaviour. (9) Two-ort parameters :- relationship of two port valiables; admittance, impedance, transmission and hybrid parameters. Relationship between parameter sets. Series parallel combinations of two port networks. (10) Properties of positive real function, necessary conditions. Basic synthesis procedure. Practical / Term work shall be based on the subject. Book (1) Network analysis - M.E. Van Veikenbery. (2) Network analysis - G.K. Mit (3) Network synthesis - M.E. Van Veikenbery. (4) Network analysis Rao and sufficient
E-303 Teaching Scheme --------------Theory Hours 4
LINEAR ELECTRONICS Marking scheme --------------Examination Scheme __________________ Pract. T.W. Sess. 50 25 50
Practical/Lab hours 4 Paper 100
(1) P.N. Junction diode :- Rectifier diode, switching diode, breakdown diode, varactor diode solar cells, phot detector, light emilting diode. (2) Rectifying circuit and D.C. power supplies :- Half, full wave and bridge rectifiers and their analysis. Principles of 3 phase recrtifiers & filters ckts. diode as clipper and clampers zener diode as a voltage
regulater. (3) Transistor :- Basis transistor amplifier CB,CE,CC characteristics and analysis and phot transistors. configuration
(4) Transistor biasing and thernal stability :- Stability factors, collector to base bias emiltor bias valtage devider bias, bias compensation. (5) Transistor heat heat dissipation :-heat sink and thermal dissipation. (6) Transistor to parameter ckts:- General idea of h parameter and their application in each configurations of amplifiers. (7) Low and high frequency resporse of transistor amplifier. (8) Negaline feedback amplifiers :- voltage shunt, voltage series, amplifier. (9) Transistor oscillators and maltivibration :- effect of position feedback, R.C. phase oscillator & wier bridge oscillator, Transistor as a switch. Transistors as multivibrators (astable, bistable, monostable) (10) Transistor amplifiers :- Class A, class B & Push-pull amplifier. (11) Field effect application. Books : (1) (2) transistors :- types & their characteristics and
Electronics Devices and circuits ; An introduction by Allen Moffasudd Pretic holix India. Solid state Electronic Devices :- Ben G Streetway (ch.No.5&4) Prentice hell of India.
E-304 Teaching scheme Theory 4
Electrical Power 1 Examination scheme Practical T.W. Sess. __ __ 50
Practical
Theory 100
(1) Conventional methods of Generation - Thermal, Hydro, Diesel and Nuclear power plants. - equipment layout of the above plants. - station auxiliaries & their arrangements,cooling system etc. (2) Distribution (A.C. & D.C. both): types and comparisions of Distribution systems - insulators used in transmission & Distribution system-various types of poles used-construction detail of distribution system-under ground cables, Its types and construction lying & fault detection - calculation of capacitance and insulation resistance.
(3) Mechanical design of transmission line :----------------------------------------Sag calculation - supports at equal and unequal levels - stringing chart - preparation of Sag templets. (4) Substation : Equipments and layout of busbar. (5) Generation and distribution econimics : Cost of generating stations fixed, capital and running cost - running charges - tariffs - load curve-demand factor - Diversity of load - D .F., Plant factor - capacity factor - Connected load factor - load duration curve - integrated load duration curve. (6) Consideration of efect of low power factor : Advantage of power factor improvement - methods of improving p.f. - The most economical p.f. (7) Neutral Earthing : Introduction - Isolated neutral - earth neutral. system-solid, Resi.,Reactance, Arc suppression coil, voltage transformer & earthing transformer earthing systems. (8) Equipment earthing - plat earthing, pipe earthing & substation earthing. _____________________________________________________________________________ Industrial visits to power station and substations. _____________________________________________________________________________ Ref. :(1) Elect. power by Dr. S.L.Uppal (2) Transmission & distribution by H. Cotton (3) Coarse in electrical power by Sahwny & Bhattnagar. B.E. II Semester - III (Electrical)
E - 305
Thermal and hydraulic prime movers
_______________________________________________________________________________ Teaching scheme Examination scheme Theory Practical Theory Paper sessional T.W. Pra. Total 4 2 100 3 50 25 175 _______________________________________________________________________________ (1) Steam turbines, classification velocity diagrams, their performance, losses governing condensors (2) I.C. Engines :- Classification, fuels, cooling, lubrication, their performance. (3) Gas turbines - Cycles, specific output and efficiency and improvement methods. (4) Air motors and compressors - Working principles and operation. (5) Hydraulic prime movers - Dynamic behaviour, fluid velocity triangles, their
work done, efficiency water wheels and their classification, hydraulic turbines and their classification, hydraulic tuebines and their classification, working principle and performance, Draft tube, governing and characteristics. Note : Term work shall be based on the above syllabus. Reference books (1) Hydraulic machines - R.C. Patel and A.D. Pandya (2) Heat Engines - Ballency
401 Teaching scheme
B.E.II, SEMESTER IV (C,M,E,EC,IC,EE,CHEM ) MATHEMATICS - II
Theory Hrs. Pract.Hrs. Tutorial | Theory paper marks Sessional T.w. Tota l 4 | 3 hrs. 100 50 150 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------1. Functions of complex variable Angle functions, cauchy-Riemann equations, Harmonic functions, orthogonal system, complex potential function, determination of conjugale function, confermal transformation, standard functions, bilinear transformation, Line integral, properties of complex integration, cauchy's theorum and cauchy's integral formula. 2. Laplace transform Introduction, definition, transforms of elementary functions, propoertiesof laplace transform, important theorems, Note on partial fractions, inverse laplace transforms, Applications to the solution of ordinary linear differential equations and simulations linear equations with constant coefficiants.
3.
Finite differences and difference equations : Finite differences, interpolation - Newton's and Lag formulae, difference equations with constant coefficiants. Solution of ordinary and partial differential equations with boundary conditions by finite difference method. Numerical methods Introductio, solution of algebraic and transcen equations by Newton-Raphson method false position method and iterative method, Numerical differentiation and integration, Numerical methods to solve first first degree, ordinary differential equations-Taylor and methods.
4.
5.
Vector calculus Vector function of a single sealer variable, differentiation of vectors,simple applications to plane motion, sealer and vector point functions.Del applied to sealer point function (gradient),Divergence of a vector point function,level of a vector,second order expressions, line integrals,surface integrals,theorem and sloke's theorem without proof. Reference books 1. 2. 3. 4. Chandrika prasad : Chandrika Prasad Grewal B.S. Mathematics for Engineers Prasad Mudranalaya, Allahabad : Advance Mathematics for Engineers Prasad Mudranalaya, Allahabad : Higher Engineering Mathematics, Khanna Publishers, Delhi
Warlikar & Warlikar : A text book of applied Mathematics Poona Vidyarthi Griha Prakashan, Poona
402 INTEGRATED ELECTRONICS ---------------------------------------------------------------Teaching scheme Exam scheme Theory Practical Paper sess. Pract. T.w. Total 4 2 100 50 50 25 225 ------------------------------------------------------------------Operation Amplifierl; Introduction, Block diagram representation of a typical op amp, Analysis op amp Ic, Circuits, Types, designations, packages pin configurations and power supplies. Ideal op amp, equi. circuit, open loop op amp configurations of Diff. inv. and non-inv. amplifiers op amp feedback amplifiers - inv. & Non.inv. closed loop gain, analysis diff. Amplifier analysis, Diff. amp with one, two & three op amp. Op amp parameters - offset voltages and currents, bias current, driff, PSRR, CMRR offset nuiling methods. AC performance :- Bandwidth, slew rate and fiq.response. OP Am applications: DC & AC amplifiers, peaking, summing scaling and averaging amplifiers, instrumentation amplifier, Diff. input and diff. outputamplifier, v to I and I to V converters, Integrater, differentiator comparator, Non-linear amplifier, phase shift oscillator, wein bridge oscillator, square, triangular and sawtooth save generater, voltage
controlled oscillator. Zero crossing Introduction to analogue simulation.
detector
window
detector.
Active filters :- basic low & high pass filters. Band pass & notch filters. 555 timer IC, Monostable, bistable, astable operations, their industrial applications. Phase locked loop :- operating principle, 565 Ic, basic applications. Voltage regulators : Three terminal regulator ICs, basic block schematic78 x x & 79 x x series Adjustable output voltage regulator LM 317, LM 340 and LM 337 series power supply ICs. their use and basic design considerations for designing regulator power supplies. Power amplifier IC. - LM 380 Basic logic gates, truthable Boolean algebra, Karnaugh map, Simple basic combinational logic circuits, Flip, flops - S.R, D-types, J.K. & Master slave. Books : (1) Op Amp and Linear integrated Circuit technology by Ramakant A gayakwad, prentice Hall India (2) Operational Amplifiers and Linear integrated circuits by - Robert F. Conghlin Frederick F. Driscoll Prentice Hall India (3) Applications of Analog integrated circuits. by - Sidney Soclof. Prentice Hall India (4) Digital Electronics - An introduction to theory and practice. by William H. Gothmen, Prentice Hall India E.403 Elect. M/C. I Teaching cheme ---------------------Theory hours Pract/Lab hours 4 2 Marking scheme ----------------------Examination Scheme ----------------------Paper Sess. T.w. Oral. Total 100 50 50 50 250 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------D.C. Machine : Principle of D.C. Generator and motor, construction, types of generator, E.M.F. equation, voltage build up process, critical resistance and speed characteristic of generator, performance equation and efficiency, effect of armature reaction on terminal voltage. D.C. Motor : Type of motors, Torque equation, characteristics, losses and efficiency, starting & speed control, Armature reaction and communication. Transformer : Construction and principle of single phase transformer operation at no load and on load, vector diagram, equivalent circuit, losses and efficiency, regulation determination of regulation & efficiency by direct load test and indirect test method. Alternator : Construction and principle of operation, E.M.F. equation, distribution and pitch factor, armature reaction, synchronous
impedance, voltage regulation, regulation by syn.Imp. method, synchronising. Poly phase induction motor : Rotation magnetic field, construction, type of motors, principles of operation, vector diagram, torque and power equation performance calculation. Electrical Technology Books : B.L. Theraja Vol.II A/c. Machine By M.G. Say D.C. Machine by Clayton
E.404 Elect. Measurement and instruments ---------------------------------Teaching -----------Theory 4 I. Scheme --------Practical 2 Exam. scheme ----------------------Theory Pract. T.W. Sess. 100 50 25 50
Units and dimensions : In S.I. systems meas. of absolute values of current and resistance, standard batteries. Characteristics of instruments-Definitions - true value - Accuracy precision-error-sensitivity and resolution.
II. Instruments : P.M.M.C. - M.I. Electrodnamic - Electrostatic - induction and rectifier instrument for measurement of current voltage, power frequency and resistance, Induction type energy meters. III. Instrument transformers - Construction and principle of work-error characteristics-design considerations and testing. IV. Power factor meter-frequency meter-synchroscope-maximum demand metermess. of VAH & VARH. V. Measurement of low, mediam & high resistances.
VI. A.C. & D.C. potentio meters and their applications. VII. A.C. bridges : Characteristic equation meas. of self inductance by max well's Hay's Anderson's and oweri's bridge. Measurement of capacitance by Desauty and schering bridge. Meas of Freq. by Wien's bridge.
VIII Magnetic measurements : Determination of B.H. curve. A.C. magnetic testing. T.W. will be based on above syllabus reference books. (1) Elect. Meas. & Meas. Instruments : E.S. Golding (2) Elect. & Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation - A.K. Sawhney.
E.405 Control Theory Teaching scheme ------------------------Theory Practical 4 2 Examination Scheme -----------------------------Theory Hrs. Sessional T.W. Total marks marks 100 3 50 20 175 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------(1) Introduction : Open loop and closed loop control system. Servomechanism. Laplace transformation. (2) Mathematical models of Physical systems : Differential equations of electromechanical system transfer function analogous systems. Block diagram reduction techniques signal flow graph. Meson's gain formulae, application transfer function of D.C. and A.C. Servomotors, synchros, technogenerator, gear trains. (3) Time response analyst : standard test signals, time response of first order and second order control sytems time domain Specifications steady state error and error constants componensation methods. (4) Stability : Concept of stability, necessary conditions Hurwitz criterion routh criterion, relative stability analysis applications to control systems. (5) Root Locus techniques : Root locus concept, construction of root locus, determination of reative stability. (6) Frequency response analysis : Introduction Correlation between time and frequency response, polar plots bode plots
phase margin gain margin. Nyquist stability criterion asessment of reative stability Term work/practical shall be based on the subject. Reference books : (1) Control systems engineering I.J. Nagrath/N. Gopal (2) Modern control system, Ogath
E.501 Electrical Power - II --------------------Teaching scheme Examination scheme -----------------------------------------------Theory Practical Theory Theory Pract. T/W. Sess. Total 4 hrs 2 hrs. 3 hrs 100 20 50 175 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------(1) Line constants : Inductance of 1-phase, two-wire line and composite conductor lines, inductance of 3-phase spacing, with and without transposition, double circuit line, bundled conductors. resistance and skin effect. Capacitance of 1-0 and 3-phase transmission line. Effect of earth, on transmission line capacitance. (2) Representation of power systems components :- One line diagram and impedance/reactance diagram, per unit system representation. (3) Performance of transmission lines : performance calculation of short line, medium line by nominal T and TT method. Evaluation of A,B,C, D constants longg transmission lines rigorous solution interpretation of the long line equation ferranti effect equivalent circuit. (4) Power circle diagram : receiving end and sending end power circle diagram. Universal circle digram. (5) Symmetrical fault analysis : Transients on a transmission line, short circuitof an unloaded and loaded synchronous machine, reactances of a synchrnonus machine, Bus impedance matrix. Algorithm for short circuit studies. (6) Symmetrical components : Symmetrical component transformation phase shift ioin star-delta transformers, sequence impedances of power system components/sequence networks of a power
system. (7) Unsymmetrical fault analysis : Symmetrical component analysis of unsymmetrical faults, like L-G, L-L, L-L-G faults. Bus impedance matrix method. References : (1) (2) (3) (4) Elements of power system analysis -- Stevenson Modern power system analysis -- Nagrath & Kothari Electric3al power -- D3r. S.L. Upal A course in electrical power -- Soni, Gupta and Bhagtnagar.
E.502 Elements of Electrical design ----------------------------Teaching scheme Examination scheme ---------------------------------------------------Theory Practical Theory Theory Pract. T.W. Sess. Total 4 hrs 4 hrs 4 hrs 100 50 50 50 250 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------Magnetic circuit : Basic principles of magnetic circuits. B-A1 curves calculations of MMF fir air-gap and teeth, real and apparent flux-density, effect of saturation flux-density distribution, calculation of magnetising current, fieldformm, Carter's fringe curve, flux-plotting air-gap flux distribution factor actgual fluxdistribution factor. Electromagnets : Types and design of magnet coils. design of flat faced, circular magnet, horse shoe and plunger type magnets, design of magnetic clutches.
Transformmers & choke coils : Design of small single-phase transformers, design of welding transformers, Design of variable gap choke coils for 1-phase and 3-phase. Armature windings: Types of d.c. and a.c. windings simplex lap and wave d.c. armature winding dummy coils, equilizer connections. A.c. windings : Singllayer, concentric, hemitropic, whole coil and mush winding, double layer, intergral and fractional pitch winding. Design of starters and fiels regulators : Design of starters for d.d. shunt and series motors, induction motors, graphical method for calculation of resistance steps. Design of resistance for starters, Design of field regulators for d.c. shunt motor and generators. Design of loading rhoeslats design of heating elements automatic starting of d.c. and a.c. motors. theory and circuit diagrams of push-button starters i.e. DOL star delta, rotor-resistance starters. Use of contactors in control circuits.
Term work
: Term work is based on above syllabus. At least five design problems and drawings should be done in the laboratory to enhance the knowledge, industrial visit should be arranged.
Reference Books : (i) A course in Electrical machine design - A.K. Sawhney (ii) Performance and design of A.C. machine - H.G. Say (iii) Performance and design of D.C. machine - Clayton
E.503 Engineering Electromagnetics ---------------------------Teaching scheme Examination scheme --------------------------------------Theory Pract. Theory Theory Sess. Pract/T.w. Total 4 hrs -3 hrs 100 50 ----150 --------------------------------------------------------------------------Vector analysis : Vector algebra-Cartesian c-ordinate system, vector components-unit vectors. Dot & cross product, circular, cylindrical & spherical Co-ordinate system-transformation of systems. : Coulomb's law-electric field intensity field of n-point charges- field due to line charge, continuous volume charge and sheet charge.
Coulomb's law
Gauss's law and Divergence : Electric flux density - Gauss law-application digergence - Maxwell's first equation. Vector operator and digergence theorem. Energy & potential: Energy in moving a point charge in electric fieldpotential & potential difference - potential gradient- the dipole. Conductors, Dielectrics & capacitance : Current & current density continuity of current - conductorsand semiconductorsdielectric - capacitance. Poisson's & Laplace's equations : Poisson's & Laplace's equations. Magnetic Field : Riot savert's law-Ampere's law-curl-strokes theoremmagnetic flux and flux density-magnetic potential derivation of magnetic field's laws.
Magnetic forces, Haterials & Inductance : Force on moving charge and differential current element-Nature of magnetic materialspermeability-boundary condition-magnetic circuit and inductance. Faraday's laws : Faraday's laws, Maxwell's equations in point form and
integral form. Uniform plane wave: Wave motion in free space and dielectrics - The pointing sector - Propagation in conductors - skin effect Reflection of uniform plan waves. Transmission lines of audio,radio and UMF frequences. Text books : (1) Engineering Electromagnetics - William Hayt Jr. (2) Elements of Engineering Electromagnetics- N.Narayan Rao
E.504 Power Electronic Devices and circuits ------------------------------------Teaching scheme Examination scheme --------------------------------------Theory Pract. Theory Theory Pract. T.w. Sess. Total 4 hrs 4 3 hrs 100 50 25 50 225 --------------------------------------------------------------------------(1) Thyristors : Construction, working principles and operation characteristics, Turn on and turn off methods. Series and parallel operation, di/dt and dv/dt calculations, snubbercircuit. Construction, operation and characterics. Diac and UJT,PUT triggering circuits for thyristors and triacs.
(2)
(3) Basic controlled rectifier, Half wave and full wave controlled rectifier single phase circuits with resistive and inductive loads. Free wheeling diode. Three phase full wave bridge controlled rectifier. (4) AC full wave phase control circuits for thyristor and triac with resistive and inductive loads, their analysis. Zero volage switching. (5) Thyristor voltage choppers, Jone's chopper for DC motor drive, operation and design of Jone's commutation circuit. Transistor chopper circuit. (6) Single phase and three phase full bridge line commutated inverter circuits; parallel capacitor commutated inverter circuit their analysis. PWH inverters; Mc Murray inverter - its operation and design. Mc Murray - Bedford inverter. Commutation methods and design of commutation principle of cycloconverter. (7) Speed control of D.C. motors : by armature current control armature voltage control, VDR method, saturable reactor method. Chopper speed control. Thyristor dc motor starter. (8) Speed control of AC motors : Variable voltage variable frequency control, variable current, variable frequency control. Slip of power recovery control - Chopper control of rotor circuit of slip ring induction motor. Comparison of DC & AC drives
& AC drivers & their choice. * 1. 2. 3. 4. E.505 Books of references : Power electronics and controls by Samir K. Datta Prentice Hall India, New Delhi Industrial & power Electronics by - Harish C. Rai Umesh Publications, Delhi Thyristor Engineering by H.S. Berde Khanna publications Delhi Power Electronics by - Ramshaw B.E. Semester V (Electrical) Business organisation and project planning -----------------------------------------Teaching Scheme --------------Theory Lab/Pract. Examination scheme ------------------------------Theory Sess. Pract. T.W. Total hrs. marks 4 3 100 50 150 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------1. Production : Division of labour Efficiency of labour Scale of production. Economics of scale. Special importance of small-scale industries in developing countries like India.
2. 3.
Natural income and its pleasurement : Different national income concepts. Forms of Business organisation : proprietorship, partnership and joint stock company. Tjere special features and process of formation. Management : Basic elements of process of management (its functions) systems approach to management. Evolution of management thought and principles.
4.
5.
Personnel management : Functions of personnel department and status of personnel manager. Manager planning and administration: recruitment, selection and placement, training and development. Industrial relations. Marketing management : Modern concept of marketing. Marketing mix. Market segmentation. Product mix and product planning. Sales forecast and techniques of forecasting sales. Financial management : Capital requirements for different purposes sources of finance. Capital budgeting process. Evaluation of alternatives investment opportunities. Techniques of evaluating investment proposals. Break-even analysis. Basic information about balance-sheet and profit and loss account.
6.
7.
8. Cost Accounting: Aims of cost accounting. elemeitsn fo cost depreciation and methods of calculating depreciation. Overhead costs and methods of allocation of overhead costs.
9. Enterpreneurship Development and Project Planning : (a) Enterpreneur as a dynamic agent of charge. Special importance of enterpreneurship development in a developing country. (b) Enterpreneual characteristics : Development of enterpreneurial triats. Enterpreneurial motivation skills required by an enterpreneur. (c) Need for efficient supports systems : Project formulation, infrastructural facilities, finance etc. (d) Preparation of project report : its stages - selection of product, project planning, investment decision, price-cost relationship, appraisal etc. Appraisals of a project in terms of technical feasibility, commercial feasibility, financial feasibility and overall managerial feasibility.
E.601 Electrical Machines - II -----------------------Teaching scheme Examination scheme -------------------------------------------------------------Theory Pract. Theory Paper Sess. Pract/ Term Total marks hrs marks oral work marks marks 4 4 100 3 50 50 25 225 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------1. Transformers : -----------Polyphase transformers - Polarity - star/star, star/delta. delta/delta, delta/zigzog, termimal marking, nonerchatures, vector diagram, phase grops, parallel operation, scott connection, teetiery winding, auto transformers testing of transformers - efficiency - transierts in transformers - voltage regulation - off load and on load top changers. 2. Induction motors : ---------------Principle of operation - basic equations - vector digaram - exact equivalent circuit - torque/slip characteristics - performance calculations - circle diagram - high torque motors - speed control and starting of 3-ph. induction motors - testing of I.M. as per IS-325 submercible motors linear induction motor and stepper mototrs. 3. A.C. Commulator motors : ---------------------Types of winding emf by transformer and rotation action - action of commutator as frequency convertor. Effect of emf injection - sources pf emf injection - T/S relation with injected emf equi. circuit and vector diagram. Regulating shunt and series commulator machines, Scharge commulator motor, its characteristics and performance. 4. Single phase commutator motor : ----------------------------Types - torque and mech. power equ. - vector diagram and compensated series motors - operation on a.c. and d.c. 5. Repulsion motors : ---------------General principle - brush position vector diagram - starting and speed control. 6. Single phase induction motor : ---------------------------Double field theory equivalent circuit experimental determination of motor parameters - methods of starting. Term work will be based on syllabus. will be engaged for practical aspects. Reference books 1. A.C. M/CS by - M.G. Say
2. Elects Comm. motors by - Wiaylor 3. Elect. Technology Vol. II by B.L. Theraja
E.602 Electrical Power Utilization -----------------------Teaching scheme Examination scheme -------------------------------------------------------------Theory Pract. Theory Paper Sess. Pract/ Term Total marks hrs marks oral work marks marks 4 100 3 50 150 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------1. Electric Drives : Factors effecting selection of motors - running starting, speed control, breaking - mechanical features enclosures, bearing noise load equilization - temp. rise, size of motor applications. 2. Electrical Traction : ------------------Types - various traction system - track electrification - traction motor-locomotivestramways and trolleys- types of speed time characteristics - mechanism of train movement-tractive effect specific energy consumption - control of a.c. and d.c. motors starting- series parallel control - regenerative breaking methoding control.
3.
4. 5.
6.
Electric heating and welding : Types of heating - requirements - resistance heating - induction heating- Arc furnaces - dielectic heating - type of welding resistance and arc welding. Electrolytic process : Principles - applications - types refining of metals, electrodeposition chemical and power supply. Illumination : Nature of light - production of light - difference types of lamps-lighting calculations - reflectors - factory lighting, street lighting - flood lighting. Economic aspects : load factors, maximim demand, diversity, utilization factor load curves- base load and peak load - fixed and running cost depreciation tariffs - types and problems - causes of lows pf - methods of pf improvement - economics of pf improvement - choice of equipments. Reference of books : 1. Utilization of electric energy - By E.D. Teylor Orient Langman 2. Electric power - by - Soni, Gupta and Bhattnager
E.603 Micro Processor & Digital Electronics ------------------------------------Teaching scheme Examination scheme -------------------------------------------------------------Theory Pract. Theory Paper Sess. Pract/ Term Total marks hrs marks oral work marks marks 4 2 100 3 50 50 50 225 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------1. Digital Electronics : ------------------Number system : Binary, octal and hex number system and their conversions, binary arithmatic, representation of negative numbers and binary codes. Combinational logic circuits : Sum of product and product of sum form of representation, karnaugh map method of reduction of logic expressions, design of combinational logic circuits such as BCD to sevent segment decoder, arithmatic logic circuits. Five and six variable karrough map. Digital IC's : (74LS244 & 74LS245) buffer, (74LS138 & 74LS156) (decoder), (74LS148) (encoder), (74LS373) latchi, study of their functional diagram and application code converters, registers and counters, shift registers
and counters (74 & 54 series). Logic families : Introduction to TTL, CMOS, I2 and ECL logic families and their comparative study. 2. Microprocessors : --------------(a) Orgenisations microcomputer and microprocessor architecture. Architecture of 8085 MPU. (b) Instruction formation and assembly language programming concept. Addressing modes. Study of 8085 instruction set. simple programs using instruction of 8085. (c) Memory orgenisation : Types of memories characteristics of memories. Expanding memory size. Reference books : 1. Modern digital electronics - R.P. Jain, T M H Publication 2. Microprocessor Architecture Programming and Applications with 8085/8080A - Goankar, Wiley Eastern Limited. 3. Digital Electronics - An introduction to theory and practice - by Gothmen. - Prentice Hall of India Publication. Term work shall be based on the above topics of the syllabus.
E.604 Computer Programming Technique -----------------------------Teaching scheme Examination scheme -------------------------------------------------------------Theory Pract. Theory Paper Sess. Pract/ Term Total marks hrs marks oral work marks marks 4 2 100 3 50 50 50 225 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------Introduction : introduction to digital computer, input/output peripherals, memory, interpreter, compiler. Programming with FORTRAN - 77 : Constants variables and expressions, Arithmatic statements, input and output statements transfer of control, GO TO IF statement, subscriptive variables. Use of DO statements, formats, functions and specification statements, use of subroutine. DATA, SAVE and COMMON statements. File processing. Programming with 'C' : Data type variables, operators, expressions, bit operations,. control structures, functions, pre-processor, Header files conditional inclusion, recurssion, pointer and arrays, structure unions, bit fields type definitions, files. Term work shall be based on the syllabus. Reference books : ---------------
1. 2. 3.
Introduction to FORTRAN - By K.D. Sharma The 'C' Programming - By Kerningham and Ritchie Programming in 'C' - by E. Balaguru Swami
E.605 Energy conservation and Ronewable Energy sources -----------------------------------------------Teaching scheme Examination scheme -------------------------------------------------------------Theory Pract. Theory Paper Sess. Pract/ Term Total marks hrs marks oral work marks marks 4 2 100 3 50 25 225 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------1. Energy situation : Non-conventional renewable energy source, potential of renewable energy sources. 2. Solar radiation, terrestrial solar radiation radiation balance, generalised transmission scattering by atmosphere, absorption of solar radiation, direct solar radiation. 3. Low temperature solar radiation collector, flat plate collectors, optical characteristics of the absorber and the cover, HWB collector model, low temp. applications of solar energy solar swimming systems, solar drying, basic drying parameters. Design calculation of solar drier; solar heat pump, solar refrigeration and air conditioning. 4. Solar thermal generation. 5. Photovoltaic energy conservation 6. Wind energy, tidal and ocean thermal energy conversion. Geothermal energy conversion. 7. Energy conservation - energy audit approches at unit level, industrial engineering approches for conservation such as p.f. improvement. Power factor controller, selection of electrical drives and their rating, high efficiency motors, voltage regulation, maintenance and lubrication of drives, vibration reduction in transmission and distribution losses, lightning system with good design illumination systems, efficient electrical drives for fans, pumps, compersors and refrigeration system; domestic and industrial load shedding.
8.
Use of computers in energy audit - calculation and costing; project cost evaluation by ROI, payback terms - Energy balance and organization for energy management. Conservation measures and diagnostic review. Reference books : 1. Renewable energy sources and conservation technology By- N.K. Bansal, Kleemann and Meliss published by TAta McGrawhill Publ.Co. Ltd., New Delhi Term work shall be based on syllabus.
E.701 Electrical power system design -----------------------------------Teaching scheme Examination scheme -------------------------------------------------------------Theory Pract. Theory Paper Sess. Pract/ Term Total marks hrs marks oral work marks marks 4 2 100 3 50 50 25 225 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------1. 2. 3. A.C. and D.C. L.T. distribution design for both underground and overhead lines. - Kelvin's law - Lamp flicker. H.T E HT and UHT line design - Electrical design, mechanical design, reduction of tower footing resistance. Sub station design :- Bus bar arrangement, bus bar design layout of diff. scheme - station earthing, metering and protection scheme, insulation coordination - equipment. H.V. D.C. transmission :- merits and demerits, one line diagram operation and control, application. Town and rural electrification.
4. 5.
Term work : Design and layout of power system project based on above syllabus. Visit : Students are required to visit different S/S and transmission system, town and rural electrification scheme to observe actual layout, working and protection scheme provided.
Books :
(1) Electrical power system design - M.V. Deshpande Tata Mcgrawhill publishers (2) Electrical power - Soni, Gupta and Bhattnagar (3) Electrical power - S.L. Upal
E.702 Electrical Machines III -----------------------------------Teaching scheme Examination scheme -------------------------------------------------------------Theory Pract. Theory Paper Sess. Pract/ Term Total marks hrs marks oral work marks marks 4 2 100 3 50 50 50 250 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------1. Alternator : Types of alternators - construction - EMF equation of polyphase winding-effect of harmonics on EMF - Armature reaction in cylindrical and salient pole machine - two reaction theory - equivalent circuit of cylindrical & salient pole machines, voltage equation input/output equations - condition for maximum power - synchronizing of alternators and division of load - operation of alternators on infinite bus - electrical load diagram - synchronizing power and torque - regulation of alternator by synchronizing impedence, mmf, simple AT, ZPF & AIEE method. - Sudden short circuit of alternator. 2. Synchronous motor : Principles of reversibility - voltage equation - phasor diagram - electrical and mechanical power equ. - 'V' curves and 'O' curve - circle diagram - starting - synchronous condensor. Auto synchronous motor : Construction - principle of operation - different connection scheme for excitation and its equivalent a.c. current - performance by circle diagram. Induction machines : Unbalance operation of induction motor regulators (single and three phase) Special machine : induction
3.
4.
5.
Amplidyne, metadyne, balancers, boosters, welding machines. 6. Testing of d.c. machines : Losses in d.c. machines - efficiency - different method of testing - regererative testing of series and shunt machines - separation of losses by different methods.
Term work : Laboratory practicals will be carried out on above syllabus. Reference books : (1) (2) (3) (4) E.703 Switch gear and protection -----------------------------------Teaching scheme Examination scheme -------------------------------------------------------------Theory Pract. Theory Paper Sess. Pract/ Term Total marks hrs marks oral work marks marks 4 2 100 3 50 50 25 225 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------Switchgear : (1) Theory of circuit interruption Physics of arc phenomena properties of arc Arc interruption theories (2) Circuit constants in relation to circuit breaking Circuit breaker rating - circuit constants and circuit conlitions restviking voltage - transient characteristics of restiviking voltage Expression for R.R.R.V. - Factors affecting the restriking voltage characteristics, current chopping interruption of small inductive currents capacitor switching. (3) Theory and practice of convertional circuit breakers Automatic switching - Air break circuit breaker, oil circuit breakers, single and multi-break construction - performance of circuit breakers minimum oil circuit breakers, air - blast circuit breakers. Interruption methods - voltage distribution in oil circuit breakers with arc control devices - modification of circuit breaker duty by shunt resistors comparative merits of different type of convetional circuit breakers Auto reclosures and fuses. (4) Recent development in circuit breakers Modern trends - vacuum circuit breaker, SF6 circuit breaker and D.C. circuit breakers. (5) Testing of circuit breakers Performance & Performance & A.C. machines A.C. machines Design of d.c. machine - Clayton design of a.c. machine - M.G. Say - Garik - Kostenko
High voltage testing - short circuit testing of C.B. - direct testing and indirect testing of circuit breakers. Protection : (1) Introduction : Requirements of protective systems, primary backup and auxiliary protection essential requirements of protective systems basic terminology. Method of discrimination. (2) Operating principles and constructional features of electromagnetic relays Classification of relays, principle, types of electromatnetic relays theory of induction relay torque - various types of induction relays. (3) Relay application and characteristics : General equations of equation for electromagnetic relays, over current relays, instantnesus over current relays, plag setting and time multiplier setting in induction disc relays - directional relays, differential relays distance relays etc. applications. (4) Apparatus protection scheme : Generator protection, transformer protection. feeder protection bus zone protection carrier protection. (5) Testing and maintenance of protective gear : Classification of relay testing general methods of testing protective gear current transformer test - potential transformer tests. (6) General principle of static relays and their applications and future prospectus Laboratory work shall be based on the above theory Note : The students should be taken to power stations and substations to show actual equipments used in field and their operation and performance. Reference books : (1) Power system protection and switchgear - B.Ravichranath - M.Chander (2) Switchgear and protection - S.S. Rao (3) Art and scrence of protective relaying - Masson
E.704 Industrial Instrumentation -----------------------------------Teaching scheme Examination scheme -------------------------------------------------------------Theory Pract. Theory Paper Sess. Pract/ Term Total marks hrs marks oral work marks marks 4 2 100 3 50 50 25 225 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------1. Transducers : Principles, general characteristics - elect. design characteristics, static and dynamic performance characteristics. Strain gauge transducers and load cells, force, weight and torque measurements. Piezo electric transducers - piezo electric elements Piezo electric accelerometers and other applications Displacement measurement - capacitive, inductive and redstive type transducers and other methods for linear and angular displacement measurement Transducers and measurement system for pressure , flow and level. Thermometry - resistance temperature detectors, thermocouples and thermisters and their circutries. Humidity and moisture sensing elements and their measurement techniques. Neuclear radiation delection and measurement, voltage and current transducers 2. 3. 4. Spectophotometers, gas - chromatography, thermal conductivity meters, viscosity and SP gravity measurement Recorders : X - Y, strip chart and circular type graphic recorders indicating, recording and controlling instruments, multichannel recorders. Single processing, filtering and analysis : Spectrum analyser -
Reference books : (1) Instrumentation : Devices and systems By C.S. Rangan, G.R. Sarma, V s V. Mani (2) Mechanical and Industrial measurements by - R.K. Jain (3) Industrial Instrumentation by - Patranabis (4) Measurement systems : Application & Design by - E.O. Doeblin (5) Instrument transducers - An introduction to their performance & design - Hermanh K.P. Neubert (6) Practical instrumentation transducers
by - Frank J. Oliver
E.705 B.E. Sem VII (E)
Elective paper - I : High voltage engineering ------------------Teaching scheme --------------Theory Pract. Examination scheme -----------------------------------------------Theory Paper Sess. Pract/ Term Total marks hrs marks oral work marks marks 4 2 100 3 50 50 25 225 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------!1. Break down mechanism of gases :- townsends break down characteristic, gas discharge characteristic, townsend's criterion of breake down, streamer theory of break down, corona, Paschein's law. 2. Break down mechanism of liquids :- Various liquid dielectrics, reconditioning of dielectrics oil, theories for conduction and break down for commercial oil. Break down mechanism of solids :- Intrinsic break down, Electro mechanical break down, thermal break down, erosion break down, electrochemical B.D. Treeing & tracking, internal discharges, varicus solid dielectrics; Generation of high voltage : High voltage D - C & A - C generation at power frequency and high frequency - impulse voltage generation. Measurement of H.V.D.C., HVAC and implise voltages. Testing :- non destructive testing - three electrode system for sold & liquid dieelectric testing - Meas. of insulating resistance, dielectric constant by schering bridge, Earthing and sheilding - partial discharge meas. - R F measurement destructive testing of insulators, bushings, cables, transformers, CBs, LA impulse testing -
3.
4. 5. 6.
Term work :- Lab. Practicals & study will be based on syllabus. Ref. books :- (1) High voltage engineering (2) Extra high voltage AC transmission engineering - R.K. Begamudre (wiley Eastern) (3) Elect. Measurement & Meas. instruments. - Golding E.W. (ELBS)
E.705 Elective paper - I : Microprocessor Interface, Programming & Application. ( Microprocessor group) --------------------------Teaching scheme Examination scheme -------------------------------------------------------------Theory Pract. Theory Paper Sess. Pract/ Term Total marks hrs marks oral work marks marks 4 2 100 3 50 50 25 225 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------1. Subroutine and stack operations for PUSH - FOP and CALL - RETURN instructions of 8085. 2. 3. Design of delay routines and their uses in designing counters, flashing lights, trafic signals. Memory interfacing and mapping, Data transfer schemes, peripheral interfacing of parallel and serial devices. For I/O operations. Use of programmable peripheral interfacing devices - 8155, 8255, USART 8251 - RS 232 port. Interfacing of simple LEDs, 7 segment display LEDs, keys. Key debounce techniques / keyboard / display interfacing using 8279. Interrupts : Multiple interrupts, device polling, vectored interrupts, 8085 interrupts enabling, disabling and masking of interrupts, EI and DI instructions of 8085. Interrupt controller 8259, programmable timer / counter 8253 and DMA controller 8257. Interfacing Data converters : A to D converter - dual slope and successive approx. types, sample and hold circuit, analog multiplixor, VCO. Interfacing of e.g. ADC 0800 multiplexor AM3705, S/H LF 398, ADC 0808/AD 0809, ADC 0816, ADC 1210/DCA 1211 and similar. D to A converter : R - 2 R ladder network type DAC, DAC interfacing e.g. DAC 0800. Generation of waveforms using DAC. Realization of A to D converter using D to A converter. DAC and ADC specifications. 6. Applications of microprocessor based systems for measurement of electrical qualtities, protective relays; firing control of SCr, triac; process control systems as temperature, flow etc. Term work shall be based on the above syllabus. Ref: - (1) Fundamental of microprocessors and microcomputers by - B.Ram. Dhanpat Rai & Sons. (2) Microprocessor with applications in process control by - S.I. Ahson, Tata - McGrawHill (3) Microprocessor and Architecture & Programming by - R.Gaonkar (4) Introduction to microprocessors 3rd edition by - A.P. Mathur Mc Graw Hill.
4.
5.
E.801 Electrical machine design --------------------------Teaching scheme --------------Theory Pract. Examination scheme -----------------------------------------------Theory Paper Sess. Pract/ Term Total marks hrs marks oral work marks marks 4 2 100 3 50 50 50 250 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------1. General Aspects : Insulating materials & classification - Heating of electrical machines - cooling of transformers & rotating machines electrical & Magnetic loading - output co-efficient - factors affecting size of machines 2. Transformer design : Output equation - optimum design considerations with a view to core loss, copper loss & weight of active materials - variation of output & losses with linear dimersions - design of core - selection of type of winding & its design - window space factor & dimensions design of yoke & overall dimension - leakage reactance & resistance of winding - regulation - mechanical forces - No load current - change of parameters with frequency - temperature rise - design of cooling system. 3. Induction motor design : output equation - main dimenrsions - stator winding - stator slots ... shape & area - stator core & teeth - LMT rotor design - air gap length calculations - selection of rotor slots design of rotor bars & end ring - harmonic torques & reduction of harmonic torques - rotor winding design for would rotor - design of rotor teeth & core. Calculations of no load & short circuit - circle diagram - diepersion co-efficient 4. Design D.C. machines : output equation - selection of number of poles, core length & armature diameter - pole proporation & profile - length of air-gap. Armature design - choice of winding - no. of conductors & slots - slot diamersions - arm. voltage drop - design of arm. core. Design of field system - design of interpole, commulator & brushes calculations of losses and efficiency. 5. Design of synchronous machines : output equation - main dimersions short circuit ratio & its consideration - air gap length - shape of pole face - arm. design - armature winding - slots - LMT & stator core calculation of arm.resistance & reactance - design of rotor - design of pole & pole winding - short circuit characteristic & performance evaluation Term work : Atleast design of 3 machines will be done by students & relevant deisgn report as well as drawing sheets in full size will be submitted as term work. Sketches of components & parts of designed machines will be drawin in sketch book & submitted as part of term work. Books : (1) A course in electrical machine - A.K. Sawhney (Dhanpatrai & Sons) (2) Perf. & design of a.c. machines - M.G. Say (ELBS) (3) Performance & design of d.c. machines - Clayton (ELBS)
E.802 Inter Connected power system ---------------------------Teaching scheme --------------Theory Pract. Examination scheme -----------------------------------------------Theory Paper Sess. Pract/ Term Total marks hrs marks oral work marks marks 4 2 100 3 50 50 50 225 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------1. General system modelling - per unit system - power transfer through transmission - universal circle diagram - MVAR control - voltage control methods. 2. Load flow study : Introduction - Network model formulation - formation of bus admittance matrix - load flow problem - approximate load flow solution - shipley inverson method - Gauss siedel method - Newton Ruphson method - comparision. Economic operation of power system : Economic operation of generators within the plant - transmission losses as function of plant generation. Economic distribution of load between plants co-ordinating transmission losses - Kron's method of evaluating loss co-efficient - penalty factor Algorighom of different schemes. - Automatic load dispatching. Load frequency control : Introduction - Single area control of frequency - modelling of turbine governor, turbine & generator - steady state analysis - principle of frequency control - flat frequency, selective, tie line control methods. Power system stability : Stability problem - classification - power angle characteristic - steady state & transient state stability & their limits. Dynamics of synchronous machines & swing equation - synchronizing power co-efficient - equal area criterion of stability & its application critical clearing time & angle - numerical solution Visit : Students are required to visit LDC for power control study. Reference books : (1) Modern power system analysis - Nagarth & Kothari (Tata Mcgraw Hill) (2) Power System Analysis - Stevenson (Mcgraw Hill) (3) Electrical Power System - C.L. Wadhva (Wiley Eastern)
3.
4.
5.
E.803
Commissioning of Electrical Equipments -------------------------------------Teaching scheme --------------Theory Pract. Examination scheme -----------------------------------------------Theory Paper Sess. Pract/ Term Total marks hrs marks oral work marks marks 4 2 100 3 50 50 25 225 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------1. Preparation of atternator prior to putting in to commercial service : Preparation & drying out of alternator winding - insulation resistance measurements - HV test - measurement of temp. of winding - alt. protective gear tests - earth leakage protection, phase sequence & synchronizing - starting time & pick up of load - neutral point earthing. Parallel operation of alternator : load sharing - voltage control - p.f. control - sharing of KVA & freq. control - interconnection. Alternator troubles : instability & loss of field - alternator instability - heating & cooling of windings - wear & troubles of slipring, bearings unbalance rotor & transient torques tec instrument transformer palarities. Commissioning of circuit breakers : fire precaution - oil & compound filling - insulation resistance - H.V. test - mechanical operation & adjustment - relaytests. Relay setting - fuses - preliminary operational tests - purpose of CBs. short circuit - rating of CBs - factors preventing the reforming of arc in CBs. - time for fault clearing Term work : laboratory work based on above syllabus. Visits : Industrial visit should be arranged to enhance the practical knowledge. Books for reference : The commissioning of Electrical Plant RCH richardson (Chapman & Hall)
2.
3.
4.
E.804 Elective Paper - II : (power group) ------------------Power System Operation & Control
Teaching scheme --------------Theory Pract.
Examination scheme -----------------------------------------------Theory Paper Sess. Pract/ Term Total marks hrs marks oral work marks marks 4 2 100 3 50 50 25 225 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------1. Economic operation in generating plant : optimal unit commitment using dynamic programming (D.P.) method - Reliability & security constraints UC table - start up condition. Hydrothermal co-ordination. 2. 3. 4. 5. Load frequency control : Frequency control of two area system. Power system short circuit study : short circuit study of unsymmetrical fults - Algorithm - bus impedence matrix method. Power system stability study : stability study of multimachine system. Neutral grounding : Effictively grounded system - ungrounded system resonant grounding - methods of neutral grounding - generator neutral breaker - grounding practice. Insulation co-ordination & over voltage protection : volt-time curve over voltage protection - ground wires - surge protection of rotating machines and transformers. Load flow study : Newton Raphson method - voltage control profile - use of regulating transformer - decoupled load flow problem - fast decoupled load flow study - voltage control method. Term work : Laboratory work will be based on above syllabus. Visit : Students will be required to visit substations, power stations to enhance practical knowledge. Books : (1) Modern Power System Analysis - Nagrath & Kothari (TMH) (2) Electrical Power System - C.L.Wadhwa (Wiley Eastern)
6.
7.
E.804 (Electrical) Sem.VIII Elective power - II : (Microprocessor group) Advanced Microprocessors ---------------------------
Teaching scheme --------------Theory Pract.
Examination scheme -----------------------------------------------Theory Paper Sess. Pract/ Term Total marks hrs marks oral work marks marks 4 2 100 3 50 50 25 225 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------1. Microprocessor Evolution : Common microprocessor types - dedicated controllers - bit slice processors and general purpose CPUs. Introduction to 8086, 8088, 80286, 80386 & 80486 CPUs. 2. Architecture and programming of 8086 : Organisation of 8086 - memory, registers, addressing modes, programming of 8086 - stack operation, string operation and I/O operations. Bus structure and timing, MUX mode operation, 8086 interrupts. Microprocessor based system developments aids; monitors, editor, operating system, interpreter, file manager, linker loader/locator, compiler, macros. 8086 : System hardwares & connections - instruction study of 8086 and additional programming techniques. Micro controllers : Concept of single chip microprocessor. Study of 8031/8051, 8096, 7810 microcontrollers. Micro controller application hardwares. Term work : T/w based on above syllabus Books : (1) Introduction to microprocessors - A.P. Mathur (TMH) (2) Microprocessor and interfacing - Programming and hardware - Douglass V. Hall (McGrawHill) (3) Design with microcontrollers - John B.Peatman (McGrawHill)
3.
4. 5. 6.
E.805 Project & Seminar ----------------Teaching scheme --------------Theory Pract. 4 2 Examination scheme -----------------------------------------------Theory Paper Sess. Pract/ Term Total marks hrs marks oral work marks marks 3 50 100 150
---------------------------------------------------------------------------A student is required to select a topic relevent to any of the subjects studied during his course of B.E. (Elect.) He will prepare seminar report & will deliver a talk on his work. He will then carry out elobarated project work based on his seminar. The project may be either design & fabrication work or a review work or a simulation of problem on computer or a detailed study of engineering units like power plant, electrical installation etc. A detail project report will be submitted, as term work.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Namh ShivDocumento1 paginaNamh ShivvagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Murd HaniDocumento1 paginaMurd HanivagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Bhram Ni LimpDocumento1 paginaBhram Ni LimpvagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Tano TunahDocumento1 paginaTano TunahvagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- NirjariDocumento1 paginaNirjarivagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- TrilochanayDocumento1 paginaTrilochanayvagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- DibangarayDocumento1 paginaDibangarayvagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Chakar Chand TandavamDocumento1 paginaChakar Chand TandavamvagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- As Bar Din Janki MataDocumento1 paginaAs Bar Din Janki MatavagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Tum Upkar Sugrivahi KinhaDocumento1 paginaTum Upkar Sugrivahi KinhavagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Krupa KaroDocumento1 paginaKrupa KarovagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Man Kram Bachan Dhyan Jo LaaveDocumento1 paginaMan Kram Bachan Dhyan Jo LaavevagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hanumat Se Hi Sarv Sukh KarahiDocumento1 paginaHanumat Se Hi Sarv Sukh KarahivagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- Meli Mukha MahiDocumento1 paginaMeli Mukha MahivagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Shree RamDocumento1 paginaShree RamvagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Tumharo Mantra BibhishanDocumento1 paginaTumharo Mantra BibhishanvagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Jay Jay GujaratDocumento1 paginaJay Jay GujaratvagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Jay Saraswati MataDocumento1 paginaJay Saraswati MatavagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Life Without Limits 2Documento31 pagineLife Without Limits 2Kalpesh PrajapatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Vidhyavan Guni AtiDocumento1 paginaVidhyavan Guni AtivagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Jay MatajiDocumento1 paginaJay MatajivagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- 01082016Documento20 pagine01082016vagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Jai HanumanDocumento1 paginaJai HanumanvagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mid - Int Circlar For Sem-12 Winter 2016Documento1 paginaMid - Int Circlar For Sem-12 Winter 2016vagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- 2140909Documento3 pagine2140909vagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- BE6Documento17 pagineBE6vagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Power SystemDocumento3 pagineElectrical Power SystemPatel Keyur NNessuna valutazione finora
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Ramanjuam Magic Square PDFDocumento15 pagineRamanjuam Magic Square PDFvagoliyoNessuna valutazione finora
- New PDFDocumento16 pagineNew PDFkapiljoshi007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gujarat Technological University: Draft Teaching Scheme: B.E. Course: Semester VIII (W.E.F.: 2016-2017)Documento15 pagineGujarat Technological University: Draft Teaching Scheme: B.E. Course: Semester VIII (W.E.F.: 2016-2017)DeveshPrajapatiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Semantic Red Effect: Processing The Word Red Undermines Intellectual PerformanceDocumento12 pagineThe Semantic Red Effect: Processing The Word Red Undermines Intellectual PerformanceWwwanand111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Responsory From GroveDocumento14 pagineResponsory From GroveAlessandra RossiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Tale of The Man of Lawe 1000059498 PDFDocumento340 pagineThe Tale of The Man of Lawe 1000059498 PDFjurebieNessuna valutazione finora
- Resume AnkitaGhoshalDocumento6 pagineResume AnkitaGhoshalabcNessuna valutazione finora
- My Own True NameNew and Selected Poems For Young Adults, 1984-1999Documento95 pagineMy Own True NameNew and Selected Poems For Young Adults, 1984-1999Arte Público Press100% (1)
- Constructing More Extended Formal Proofs: - For A Given Argument As A Sequence of Statements, Each Is Either A Premise ofDocumento10 pagineConstructing More Extended Formal Proofs: - For A Given Argument As A Sequence of Statements, Each Is Either A Premise ofariel lapiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Vocabulary Acquisition Paul Nation 1989Documento139 pagineVocabulary Acquisition Paul Nation 1989juanhernandezloaizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading-Comprehension - Stalin GuañunaDocumento3 pagineReading-Comprehension - Stalin GuañunaSTALIN JESUS GUA�UNA CHICAIZANessuna valutazione finora
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- SsDocumento22 pagineSsruqia95aribNessuna valutazione finora
- Body Image and The Media EssaysDocumento6 pagineBody Image and The Media EssayskbmbwubafNessuna valutazione finora
- Subject: PRF192-PFC Workshop 05Documento13 pagineSubject: PRF192-PFC Workshop 05Quoc Khanh NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment Meg 004 (14 15)Documento1 paginaAssignment Meg 004 (14 15)bubli234100% (1)
- 9th Grade Math Vocabulary 1683069284Documento2 pagine9th Grade Math Vocabulary 1683069284BABY MARIE APASNessuna valutazione finora
- (Final) LHS ML Information System User's ManualDocumento111 pagine(Final) LHS ML Information System User's ManualHarold Paulo MejiaNessuna valutazione finora
- GRADE 5 - First Mastery Exam: Pointers in MathDocumento1 paginaGRADE 5 - First Mastery Exam: Pointers in MathJocelyn Villacorta DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Grammar Tick ( ) A, B, or C To Complete The SentencesDocumento3 pagineGrammar Tick ( ) A, B, or C To Complete The SentencesAndre SilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Like Most Philosophy Dissertations Crossword ClueDocumento4 pagineLike Most Philosophy Dissertations Crossword ClueWritingServicesForCollegePapersAlbuquerqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Annotated-Script 20and 20part 201Documento3 pagineAnnotated-Script 20and 20part 201api-592414054Nessuna valutazione finora
- Parallelism Lesson PresentationDocumento29 pagineParallelism Lesson PresentationMa. Luz CalvoNessuna valutazione finora
- VTK Dot NET Wrapper Install GuideDocumento7 pagineVTK Dot NET Wrapper Install GuideShaofan QiNessuna valutazione finora
- Name:Mr - Sarawut Moontima ID:5631301107 Section:01 Date: DueDocumento17 pagineName:Mr - Sarawut Moontima ID:5631301107 Section:01 Date: DuePongsatorn TammavaragornNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Sanskrit Periodicals: Newspapers and Magazines in India & AbroadDocumento7 pagineList of Sanskrit Periodicals: Newspapers and Magazines in India & Abroadkngane8878Nessuna valutazione finora
- Python Apprentice SampleDocumento51 paginePython Apprentice SampleAlexNessuna valutazione finora
- Blueback Language ActivitiesDocumento1 paginaBlueback Language ActivitiesZola SiegelNessuna valutazione finora
- Rohit Dvclub 130422125508 Phpapp02Documento20 pagineRohit Dvclub 130422125508 Phpapp02Sam HoneyNessuna valutazione finora
- Songs of Robert BurnsDocumento596 pagineSongs of Robert BurnsJane CourtNessuna valutazione finora
- Negotiation Skills HandbookDocumento29 pagineNegotiation Skills Handbookashokteam100% (1)
- Table of English Tenses PDFDocumento3 pagineTable of English Tenses PDFViviarvi100% (1)
- Error Analysis Perspectives On Second Language Acquisition PDFDocumento2 pagineError Analysis Perspectives On Second Language Acquisition PDFPatricia50% (4)
- International Journal of Applied Linguistics & English LiteratureDocumento7 pagineInternational Journal of Applied Linguistics & English LiteratureAyad HammoodNessuna valutazione finora