Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
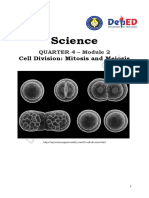
Chapter 3 Cell Division
Caricato da
Nurul FasihahCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chapter 3 Cell Division
Caricato da
Nurul FasihahCopyright:
Formati disponibili
BIOLOGI
SELANGOR MATRICULATION COLLEGE
SB016 / DB015
CHAPTER 3
CELL DIVISION
3.1 The concept of cell division a) Explain cell division. State the importance of cell division in living organisms.
Key points: cell division - new cells are reproduced from old ones - enables organisms to grow and reproduce - parent cells divide equally into two daughter cells - cell division in eukaryotes involves karyokinesis and or cytokinesis. cell division important in living organisms - responsible for growth of organisms replacement - repair - reproduction
3.2 The cell cycle a) Explain the stages in cell cycle. [Emphasize on interphase]
Key points: cell cycle - sequence of stages that a cell passes through between one cell division and the next - interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis - interphase is resting phase between successive mitotic divisions - interphase is longest stage 90% of cycle cell duplicates genetic material - at G1, metabolic activities - transcription and translation - cell increases in size - at S phase, DNA synthesis - then G2 - at G2, cell produces new proteins, synthesize microtubules mitosis (M) after G2 is followed by cytokinesis (C) - complete cell cycle is G1, S, G2, M and C.
BIOLOGI 3.3 Mitosis
SELANGOR MATRICULATION COLLEGE
SB016 / DB015
a) Describe the four stages of the mitotic cell division. b) Explain the behavior of the chromosomes at each stage.
Key points: four stages of the mitotic cell division - prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase - at prophase, chromatin begins to condense - each chromosome consists of 2 identical [or sister] chromatids - nucleolus disappears - mitotic spindle begins to form and is complete at the end of prophase - at metaphase, the centrioles have moved to opposite poles of the cell - chromosomes line up at metaphase plate - at anaphase, the centromeres separate contraction of spindle fibres pull the sister chromatids to opposite poles - at telophase, spindle fibres disappear - chromosomes uncoil - nucleus begins to form at each pole
c) Describe briefly the cytokinesis process. Key points: cytokinesis process - division of the cytoplasm - separate daughter nuclei - may begin before or after mitosis is completed - in animal cells, cytokinesis begins with cleavage furrow in plant cells, vesicles are formed at equator that fuse to form a cell plate
d) Compare cell division in animal and plant. Key points: cell division in animal and plant similarity - differences due to absence of centriole in plant cells different in that asters are formed only in animal cells difference in cytokinesis processes difference in tissues involved in cell division and their location[
e) State the significance of mitosis. Key points:
significance of mitosis - growth of organism - cell replacement - asexual reproduction - maintaining genetic stability - regeneration in some organisms
BIOLOGI 3.4 Meiosis
SELANGOR MATRICULATION COLLEGE
SB016 / DB015
a) Explain the position and changes of the chromosomes at each stage.
Activity: Meiosis I includes these phases _____________________ while Meiosis II includes these phases____________________. 5 sub-stages In early in Prophase I are the
_______________________________________.
prophase,
leptotene,
chromosomes first appear as ___________________.
At zygotene, the homologous
chromosomes seem to ________________________. By pachytene, the chromosomes have ______________________________. Each homologous chromosome is seen as
___________________________. While, at prophase II, the chromatin ________________ again. As in prophase I, spindle fibre formation ______________ and the centrosomes
_________________________________. At metaphase I, the bivalents _________________ at the _________________. While, a metaphase II, the chromosomes ____________________________________. At anaphase I, the bivalents ______________ and ______________________. Each chromosome still has 2 sister chromatids, attached at their centromeres; the centromeres do not separate in anaphase I. While, at anaphase II, the centromeres of sister chromatids _____________________________. At telophase I, the chromosomes _________________. Cytokinesis occurs with the formation of ________________in animal cell or __________________ in plant cell. interkinesis or interphase II, no DNA replication occurs. At
While, at telophase II, the
chromosomes also ____________________. Cytokinesis also occurs with the formation of ________________in animal cell or __________________ in plant cell. _______________________ and ________________________ reforms. The nucleolus Cytokinesis
separates the cells and produces _______________________.
BIOLOGI
SELANGOR MATRICULATION COLLEGE
SB016 / DB015
b) Define chromatid, synapsis, bivalent, tetrad, chiasma, crossing over and centromere Activity: _____________________ are the daughter strands of a duplicated chromosome which are joined by a single centromere. A _________________ is a region on a chromosome that joins two sister chromatids. ___________________ is the pairing of two homologous chromosomes that occurs during meiosis. During the prophase of meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair and form synapses. The paired chromosomes are called ________________. The ___________________ have two chromosomes and four chromatids, with one chromosome coming from each parent. Exchanged of genetic material between homologous chromosomes, is called ___________________________. The point at which crossing over takes place is a ____________________.
c) State the significance of meiosis. Activity: Meiosis is important in keeping the ______________________ across generations. If meiosis did not occur, the chromosome number would _______________________ over the generations. Meiosis ensures that ___________________ contains only 1 member of each _______________________ so that when they combine, a __________________ is produced. Meiosis produces ___________________, the source for evolution. ___________________in meiosis I results in variation because it produces gametes with new
______________________. environment.
Genetic variation allows a species to ______________ to the
BIOLOGI
SELANGOR MATRICULATION COLLEGE
SB016 / DB015
d) Compare meiosis and mitosis.
Activity: Both meiosis and mitosis are ___________________ processes. preserves the ________________________, meiosis will But, while mitosis the
_____________
chromosome number.
Mitosis involves only __________ nuclear division or
_________________, but meiosis involves ____________ nuclear divisions. In mitosis, homologous chromosomes remain _____________, while in meiosis homologous chromosomes _______________________. _____________________ does not occur in mitosis; but in meiosis, crossing over occurs in_________________. Since there is no crossing over in mitosis, ________________ are not formed. But in meiosis
________________ are formed. Duplicated chromosomes _____________________ in metaphase in mitosis. But in meiosis, ______________ line up at the equator in metaphase I. In mitosis, ________________ separate to form daughter chromosomes in anaphase. While in meiosis, ______________________ separate in anaphase I. In mitosis, ___________________ are are produced; In mitosis, while the in meiosis, cells are
____________________
produced.
daughter
____________________l to each other and to the parent cell.
But in meiosis, the
daughter cells are ___________________________ to each other or to the parent cell. In mitosis, the centromeres separate in anaphase. But in meiosis, ______________ remain intact during anaphase I. ________________. The _________________ only separate in
Mitosis may occur in ____________, _______________ or
polyploidy cells. But meiosis occurs only in ______________ and ___________ cells. Mitosis occurs during the formation of _______________ and _____________ spores. But meiosis occurs in the formation of _______________ and ______________ spores.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Cell's Life Cycle: Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory ManualDocumento6 pagineThe Cell's Life Cycle: Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory ManualJan Edward Abarientos MandaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Agri-21Documento8 pagineFinal Agri-21regielabutong24Nessuna valutazione finora
- PACKET Cell Cycle - MitosisDocumento7 paginePACKET Cell Cycle - MitosisSawin HainiNessuna valutazione finora
- Las in Science 12Documento3 pagineLas in Science 12Richez VillaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4-The Cell's Life CycleDocumento4 pagineModule 4-The Cell's Life Cycle10. Briol AlvinNessuna valutazione finora
- GB - 1st Quarter - wk3 - PDFDocumento20 pagineGB - 1st Quarter - wk3 - PDFHeaven LeighNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Division: Mitosis and MeiosisDocumento18 pagineCell Division: Mitosis and Meiosislouisse veracesNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell DivisionDocumento12 pagineCell DivisionLeona TittleNessuna valutazione finora
- MODULE 4 Sec2Documento13 pagineMODULE 4 Sec2Tanalgo JPNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis Teacher NoteDocumento4 pagineMitosis Teacher NoteJonathan JayakrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Cycle and Division: Phases, Significance of Mitosis and MeiosisDocumento8 pagineCell Cycle and Division: Phases, Significance of Mitosis and MeiosisAlbert Jade Pontimayor LegariaNessuna valutazione finora
- WORKBOOK - Cell DivisionDocumento9 pagineWORKBOOK - Cell DivisionAsad AbbasNessuna valutazione finora
- Wk7 - Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis and Game To GenesisDocumento23 pagineWk7 - Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis and Game To GenesisMariam SepashviliNessuna valutazione finora
- GENBIO1MOD3Documento11 pagineGENBIO1MOD3Renzsoc JalmascoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell DivisionDocumento29 pagineCell Divisionryiss03Nessuna valutazione finora
- Student Exploration: Cell Division: Isabella Jacquin Rivas November 24, 2022Documento5 pagineStudent Exploration: Cell Division: Isabella Jacquin Rivas November 24, 2022。Poki 。Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cell DivisionDocumento49 pagineCell Divisionsharanya.10.puneet.8.karolNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity Sheet Compares Mitosis and MeiosisDocumento3 pagineActivity Sheet Compares Mitosis and MeiosisJoseph Gabriel Genuino Cruz100% (1)
- Mitosis 3rd WeekDocumento21 pagineMitosis 3rd WeekIanie GemmaNessuna valutazione finora
- MeiosisDocumento5 pagineMeiosispenn hicksNessuna valutazione finora
- REMEMBER: Interphase Is NOT A Stage ofDocumento4 pagineREMEMBER: Interphase Is NOT A Stage ofWONG LI KING MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis Song Activity SheetDocumento2 pagineMitosis Song Activity SheetArshe OmaguingNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis and Meiosis WebquestDocumento3 pagineMitosis and Meiosis Webquestapi-315693239Nessuna valutazione finora
- Class 11 Neet Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocumento11 pagineClass 11 Neet Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionViswaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1819 Level I Science Basic Question CH 1 Sec 1Documento12 pagine1819 Level I Science Basic Question CH 1 Sec 1elena123456elena123456Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cell CycleDocumento39 pagineCell CycleBuyco, Nicole Kimberly M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pathology of CellDocumento7 paginePathology of CellamanuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Cycle QuizDocumento3 pagineCell Cycle QuizCa RingorNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Assignment PDFDocumento13 pagineBiology Assignment PDFmohd mehartaj100% (1)
- Cell Cycle: Prepared By: Ms. Charis D. Juanico, General Biology 1 TeacherDocumento59 pagineCell Cycle: Prepared By: Ms. Charis D. Juanico, General Biology 1 TeacherTrisha Loise VillacampaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science8 Q4 M2Documento6 pagineScience8 Q4 M2Arabella BaldonadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Q1 GenBio1 SLKWeek4 EditDocumento9 pagineQ1 GenBio1 SLKWeek4 EditInele Ellia AgReNessuna valutazione finora
- LAB 3 and 4 - Cell Cycle and Plant TissuesDocumento7 pagineLAB 3 and 4 - Cell Cycle and Plant Tissuesدوار الشمسNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Cycle, Mitosis & Cancer ReviewDocumento4 pagineCell Cycle, Mitosis & Cancer Review33 NICASA, DENDEN S.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wk.2.module 2 .QRT.4 Mitosis & Meiosis, Phenotypic ExpressionDocumento34 pagineWk.2.module 2 .QRT.4 Mitosis & Meiosis, Phenotypic ExpressionShanikMendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell DivisionDocumento2 pagineCell DivisionSohom PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Docsity Cell Division 29Documento5 pagineDocsity Cell Division 29Jake KreidelNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Cycle and MitosisDocumento11 pagineCell Cycle and MitosisMatthew TarditiNessuna valutazione finora
- Gen Bio 1 Lesson 4Documento2 pagineGen Bio 1 Lesson 4Ric SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Cancer ReviewDocumento3 pagineCell Cycle, Mitosis and Cancer ReviewAnicia Toscano100% (3)
- Week 2Documento8 pagineWeek 2lilyrosemary.masilangNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Division Assignment#2 .123Documento3 pagineCell Division Assignment#2 .123jaeminsoftboiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson: Cell Division: Activity 1Documento3 pagineLesson: Cell Division: Activity 1Akane ForestNessuna valutazione finora
- 0 BooksDocumento20 pagine0 Bookslaraib zahidNessuna valutazione finora
- General Biology I Long Test ReviewerDocumento18 pagineGeneral Biology I Long Test ReviewerJillian GarcilanNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 4: Name: - Oliver Ryne N. Doctor - Date: - Section: - BSN 1-C - ScoreDocumento5 pagineActivity 4: Name: - Oliver Ryne N. Doctor - Date: - Section: - BSN 1-C - ScoreDoctor OliverNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Cycle and MitosisDocumento4 pagineCell Cycle and MitosisJudy TanNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.3 Cell Division, Diversity and OrganisationDocumento12 pagine1.3 Cell Division, Diversity and OrganisationMo_Bash1Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Cell Cycle (Module)Documento11 pagineThe Cell Cycle (Module)Cel Callao Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 - Gen Bio 1 - MidtermDocumento7 pagineModule 3 - Gen Bio 1 - MidtermAngel Cuacko GacmatanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis Song Paired Activity Sheet: Name - DateDocumento2 pagineMitosis Song Paired Activity Sheet: Name - Datepurplepink 127Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis and Meiosis: Comprehension QuestionsDocumento2 pagineMitosis and Meiosis: Comprehension QuestionsKareem AghaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Cycle ExplainedDocumento35 pagineCell Cycle ExplainedHimanshi ShrresthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis Mover! Cell Cycle InteractiveDocumento2 pagineMitosis Mover! Cell Cycle Interactivej jNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Division: Mitosis and MeiosisDocumento74 pagineCell Division: Mitosis and MeiosisNor HilmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Cycle: The Stages of Growth and DivisionDocumento20 pagineCell Cycle: The Stages of Growth and DivisionUzma AdnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 1 Q1 Periodical ExaminationDocumento4 pagineBiology 1 Q1 Periodical ExaminationJessie PeraltaNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity-1-Zoolab - FinalDocumento4 pagineActivity-1-Zoolab - FinalDaniel BernalNessuna valutazione finora
- Module in EnglishDocumento28 pagineModule in EnglishIannNessuna valutazione finora
- Malaysian Construction Sector and Malaysia Vision 2020Documento7 pagineMalaysian Construction Sector and Malaysia Vision 2020Nurul FasihahNessuna valutazione finora
- Tips To Save BookletDocumento9 pagineTips To Save BookletNurul FasihahNessuna valutazione finora
- Interview Guidelines For Candidates Applying To University of MalayaDocumento4 pagineInterview Guidelines For Candidates Applying To University of MalayaNurul FasihahNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 3: Formatting and Manipulating TablesDocumento2 pagineLab 3: Formatting and Manipulating TablesNurul FasihahNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Members TypesDocumento10 pagineStructural Members TypesShashank TiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Outcome SB016Documento9 pagineLearning Outcome SB016Nurul FasihahNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento4 pagineChapter 1Nurul FasihahNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer System: Hardware - StorageDocumento18 pagineComputer System: Hardware - StorageNurul FasihahNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.3.2 Generation of Dislocations: Dislocations in The First Place!Documento2 pagine5.3.2 Generation of Dislocations: Dislocations in The First Place!Shakira ParveenNessuna valutazione finora
- Modulo InglesDocumento8 pagineModulo InglesJames Mosquera GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- KG Technologies Inc Metric: K119X-DX024P-1AT-90A-C399Documento2 pagineKG Technologies Inc Metric: K119X-DX024P-1AT-90A-C399Bhushan PAwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiegel Kutter Idriss PDFDocumento1 paginaFiegel Kutter Idriss PDFAvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1: Overview of Implementation of The NSTP (Activities)Documento3 pagineModule 1: Overview of Implementation of The NSTP (Activities)RonnelNessuna valutazione finora
- U1 Presantation-MAK 032021Documento15 pagineU1 Presantation-MAK 032021MD ANAYET ALI KHANNessuna valutazione finora
- Heritageoil Corporategovernance AwDocumento68 pagineHeritageoil Corporategovernance AwbeqsNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Neutralization Titrations for Acid-Base AnalysisDocumento21 pagineApplication of Neutralization Titrations for Acid-Base AnalysisAdrian NavarraNessuna valutazione finora
- David Freemantle - What Customers Like About You - Adding Emotional Value For Service Excellence and Competitive Advantage-Nicholas Brealey Publishing (1999)Documento312 pagineDavid Freemantle - What Customers Like About You - Adding Emotional Value For Service Excellence and Competitive Advantage-Nicholas Brealey Publishing (1999)Hillary Pimentel LimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chrome Blue OTRFDocumento4 pagineChrome Blue OTRFHarsh KushwahaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Game of Thrones: George RR MartinDocumento6 pagineA Game of Thrones: George RR MartinRavi ShankarNessuna valutazione finora
- 14.marifosque v. People 435 SCRA 332 PDFDocumento8 pagine14.marifosque v. People 435 SCRA 332 PDFaspiringlawyer1234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Toyota TPMDocumento23 pagineToyota TPMchteo1976Nessuna valutazione finora
- Syntax - English Sentence StructureDocumento2 pagineSyntax - English Sentence StructurePaing Khant KyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Revised Answer Keys for Scientist/Engineer Recruitment ExamDocumento5 pagineRevised Answer Keys for Scientist/Engineer Recruitment ExamDigantNessuna valutazione finora
- Subject Object Schede PDFDocumento28 pagineSubject Object Schede PDFanushhhkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Volatility Clustering, Leverage Effects and Risk-Return Trade-Off in The Nigerian Stock MarketDocumento14 pagineVolatility Clustering, Leverage Effects and Risk-Return Trade-Off in The Nigerian Stock MarketrehanbtariqNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Review of Related Lit - 1Documento83 pagineChapter 2 Review of Related Lit - 1CathyNessuna valutazione finora
- People V Gona Phil 54 Phil 605Documento1 paginaPeople V Gona Phil 54 Phil 605Carly GraceNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic - Properties - Part 2 - by - AKansha - Karnwal - 1702453072953Documento68 paginePeriodic - Properties - Part 2 - by - AKansha - Karnwal - 1702453072953Saktipratik MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Recommendation Letter - One Young WorldDocumento2 pagineRecommendation Letter - One Young WorldNabeel K. AdeniNessuna valutazione finora
- Buckling of Thin Metal Shells 58Documento1 paginaBuckling of Thin Metal Shells 58pawkomNessuna valutazione finora
- Ra 1425 Rizal LawDocumento7 pagineRa 1425 Rizal LawJulie-Mar Valleramos LabacladoNessuna valutazione finora
- Vol 98364Documento397 pagineVol 98364spiveynolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Times Leader 04-10-2013Documento37 pagineTimes Leader 04-10-2013The Times LeaderNessuna valutazione finora
- BSP Memorandum No. M-2022-035Documento1 paginaBSP Memorandum No. M-2022-035Gleim Brean EranNessuna valutazione finora
- Madagascar's Unique Wildlife in DangerDocumento2 pagineMadagascar's Unique Wildlife in DangerfranciscogarridoNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear RegressionDocumento56 pagineLinear RegressionRanz CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Dalit LiteratureDocumento16 pagineDalit LiteratureVeena R NNessuna valutazione finora
- Ava Gardner Biography StructureDocumento5 pagineAva Gardner Biography Structuredanishfiverr182Nessuna valutazione finora