Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Dermatology Revision
Caricato da
mksharmaaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Dermatology Revision
Caricato da
mksharmaaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Impetigo contagiosa Cocci + poor Etiology hygiene & moisture or scabies & pediculosis 1- Ordinary C/P 2- Bullous : new
born staph infection may be fatal 3- Circinate : extension of ordinary 4- Ulcerative : crust & scars Complications Post streptococcal glomerulonephritis Topical antiseptics Treatment + topical antibiotics and systemic if sever
Folliculitis Stap aureus ( infection of upper part of hair follicle Follicular pustules
Sycosis barbae Staph aureus ( folliculitis of the beard area ) Follicular pustules & papules
Bacterial infections Furncle Carbuncle Infection of lower part of the hair follicle Red papules Diabetes
Erythiplas Inflammation of upper dermis ( B hemolytic stept ) Erythrematous tender swollen area with sharp border + constitutional S
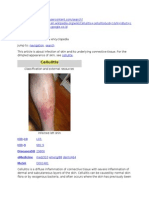
Cellulitis INF of lower dermis ( staph aureus strpt pyogenes As erythiplas but illdefined border
erythrasma Corynebactrium minutissimum ( DM )
Multiple deep boils open on surface by fistulae
Reddish brown patches in interriginous areas / Give red fluorescence with woods light
Lymphedema Same Same Same Incision & drainage + systemic AB Erythromycin Aggressive AB Topical AB and antifungal ? systemic AB
Herpes simplex HSV I : herpes libialis Aetioligy HSV II : herpes progenitalis 1- HSV I : C/P a. superficial vesicles perioroficail ulcers swollen gums & lymphadenopathy + constitutional manifestations b. recurrent attacks in lips & face less sever c. ocular type d. herpitic witlow : in fingers very painful 2- HSV II : vesicles on genitals and ulcers / if pregnant CS Complications 2ry infections / eye cimolications / CNS : encephalitis / erythema multiforme / cancer cervix Treatment Antiseptic lotions Acyclovir cream 5 times daily 5 days IDU for eye lesions Acyclovir tab 200 mg 5 X 5
Viral infections Herpes zoster Varicella Zoster virus Vesilces along distribution of a sensory nerve + local LNs enlargement leave scar give permenant immunity DANGEROUS in : Bilateral Old age Gangrenous Recurrent
Warts Human papilloma virus 1- Common warts : verroucus papules 2- Plane warts : flat topped papules 3- Filiform warts : peduculated 4- Digitiform warts : finger like 5- Planter warts : foot = tender grow inward 6- Genital warts : moist foul smelling in MM & skin Oncogenicity ( cervical cancer ) 1- Cautery : electro- cryo laser chemical 2- Podophyllon resin in alcohol : for veneral 3- Radiotherapy 4- Autosuggestion
Mollascum contagiosum Pox virus Dome shaped papule with central umblication and white chessy material if squeezed can be sexual
Eye complication ? post herpitic neuralgia 1- Topical : drying AS lotion / Acyclovir cream 2- Systemic : Acyclovir 800 mg 5 X 7 - Analgesics
Cauterization
Cause
Tinea capitis Trichophyta & microspore
1- Scaly type :child bal patch with scales 2- Black dot : hair breaks leave dots 3- Kerion : also adult with boggy swelling & pustules cicatricial alopecia 4- Favus : diffuse loss of hair with mousy odour yellow crusts cicatricail alopecia
Fungal infections Dermatophytes Tinea circinata Tinea pedis Trichophyta & Trichophyta & microspore epidermophyta
Other types 1- Tinea cruris : scrotum not involed
2- Tinea axillaris 3- Tinea barbae 4- Tinea mannum :
C/P
Annular patches with active edge and healing centre itching is common on exposed surfaces
Sodden white macerated skin with bad dour between toes
in palm 5- Tinea uguium : onchomycosis thickened greenish nails
Yeasts Pityriasis versicolor Candidiasis Malassezia furfur Candida albicans the pathogenic form of pityrrosporum orbiculare 1- Cutaneous Macule hypo or candidiasis : hyper pigmented a. Intertrigo : with fine scales in i. Axilla & groin upper chest arms ii. Eriosio In summer
interdigitalis mastocytica iii. Angular chelitis iv. Napkin dermatitis b. Paronychia : nail fold tender nail corrugated 2- Mucosalcandidiasis : oral thrush vulvo vaginitis - balanitis
Diagnosis
1- Woods :
green
DD : herald patch
Woods light gives
yellow Parker ink stain :
Treatment
2- LM 3- Culture on saburoud Topical alone is Topical antifungal 2 useless daily + systemic ( ketoconazole grisofulvin for 3 W shampoo + griseofulvin tab for 2 months
1- Tincture iodine 1% 2- Systemic antifunal in sever cases
spagitti & meatballs appearance 1-Systemic : ketoconazole 200X10 2-Topical : Na hyposulphide imidazole zinc pyrithione white field tincture iodine
1- Topical : castellani paint nystatin oint 2- Systemic : mycostatin oral drops Azoles amphotericin B in sever
Scaly erythematous lesions Psoriasis Lack of UV rays Etiology - Hemolytic infection - Hypocalcemia - Pregnancy - Trauma / psychogenic Erythematous papule with C/P shiny scales lossely adherent bleed on removal ( Auspiz )
Lichen planus - Psychological - Liver disease - Sunrays - Antimalairial gold Flat topped polyangular violaceous itchy papules with adherent scales in flexor areas with sever pruritis
Discoid Lupus erythematousus Pityriasis rosea Chronic scaly erythematous Considered exanthematous eruption in skin reaction for upper respiratory viral infection ( HHV 6-7 )
Erythematous plaques + adherent scales + dilated pilosebaceous orifices ( stippling ) + telangectesia + thin atrophic scar cicatricial alopecia in sun exposed areas
Clinical types
Treatment
1- Psoriasis vulgaris a. Skin : in extensors back b. Scalp psoriasis c. Nail psoriasis : bi;aterla pitting hyperkeratotic nail d. Flexural type : scaling is absent 2- Erythrodermic 3- Arthropathic 4- Pustular : sterile pustules 1- Local : coal tar Anthralin 0.5% - corticosteroids salicylic acid 5% calcipotriol PUVA laser 2- Systemic : for extensive psoriasis : Methotrexate retinoids cyclosporine corticosteroids PUVA oral
1- Ordinary LP 2- Actinic LP : in sun exposed area in summer 3- Mucosal : reticulate network ulcerative laesion precancerous 4- LP of the scalp : cicatricai alopecia
Herald patch ( outer erythematous zone intermediate scaly one healing center ) parallel to rib / 2ry eruption give chrismats tree appearance & jacket with short sleeves 1- Ordinary type 2- Inverted type : occur distal 3- Abortive type : only herald 4- Papular type : more elevated 5- Flexural type
1- Antihistaminics 2- Steroids & aalcylic loacally 3- Steroids retinoids and cyclosporine systemically 4- Actinic : sunscreens 0 chloroquine 200mg /day 5- Mucosal : steroids acitrtin chloroquine
1- Sun screens 2- Systemic photoprotectives ( chloroquine ) 3- Corticosteroids ( local systemic intralesional )
1234-
PT reassurance Avoid hot baths Calamine lotion Oral antihistaminics , topical corticosteroids and UVB
Eczema May be genetic in types as atopic & allergic contact dermatitis
Allergic Dermatoses urticaria
1- Contact dermatitis : a. 1ry irritant dermatitis : any individual b. Allergic contact dermatitis : type IV in genetic susceptile 2- Discoid eczema : well defined 3- Atopic eczema : genetic with FH a. Infantile : on cheeks & hands b. Childhood : on flexures c. Adult : hyperpigmentation & lichenification 4- Stasis eczema : venous insufficiency edema oozing vesiculation itching 5- Seborrheic eczema : by malassezia furfur a. Infantile type : scales on scalp & diaper area b. Aadult : from androgens on sebaceous glands
-acute eczema : erythema swelling vesicles -chronic eczema : lichenification & excoriations 1- Acute : drying antiseptic lotion & corticosteroid cream witth hydrous base systemic antihistaminics & corticosteroids 2- Chronic : local corticosteroids cream 3- Atopic : + topical immunomodulators & UVB 4- Seborrheic : antidandruff shampoo
Erythema multiforms Drug eruptions 1- Exogenous : foods as fish1- Genetic factors Allergy to the drug chocolate / drugs as penicillin 2- Infections : HSV injected or ingested / pollens 3- DRUGS : NSAIDs 2- Endogenous : infection 4- Autoimmune : SLE parasites SLE lymphoma 5- Malignancy : lymph pregnancy 1- Ordinary urticaria 1- EM minor : only 1- Urticarial & 2- Facticious : very mild limmted to skin no angioedema follow trauma or mild mucosal 2- Erythroderma ( 3- Cholinergic : itchy involvement no exfoliative dermatitis ) sensation after sweating systemic involvement 3- Photosensitive drug with wheals on scalp neck 2- EM major : extensive reaction upper chest mucosal and systemic 4- Acneform eruptions 4- Physical : either solar involvement death ( steroids ) pressure cold heat 5- Fixed drug eruption 5- Popular : due to insect bite : with sulfonamides & in infants & children / NSAIDs / fixed to the wheal then papule over it drug & site / permengnate colored macule vesicles & eruption Sudden appearance of elevated Primary lesion : iris ( target ) Acute atypical inflammatory edematous lesion varies in size lesion erythematous annukar eruptions suside after transient for few hours ring with central vesicle / in stoppage of drug mucosa : may form painful HGE bullae & erosions 1- local : cold 3- Local : compresses compresses calamine calamine lotion lotion steroids steroids antiseptics 2- Systemic : oral 4- Systemic : antihistaminic antihistaminics parentral AH oral steroids antibiotics steroids parentral 5- Major needs steroids adrenaline hospitalization and SC or IM TTT of complications
Etiology
Vitiligo Melanocytes are destroyed and disappear from epidermis due to : 1- Autoimmune : antimelanocyte AB precipitated by psycho or mechanical trauma 2- Neurogenic L melanocytotoxic substances from nerve endings 3- Chemical : melanocytotoxic substances from rubber gloves etc 4- UV rays 1234Focal vitilgo Unilateral vitilgo Generalized vitilgo Universal vitiligo
Types
ALopecia 1- Cicatricial : mechanical trauma fungal inection DLE lichen planus 2- Non cicatricial : a. Telogen : postpartum nutritional deficiency b. Anagen : cytotoxic retinoids mercury c. Familial baldness : overactivity 5alfa reductase d. Areata : genetic factors immunological actors 1- Cicatricial 2- Non cicatricail : telogen effulfium anagen effluvium androgenitic alopecia alopecia areata ( patchy marginaalis ophiasis totalis universalis )
Acne Block of follicular opening by KCs dilatation of the lower part disruption of the epithelium discharge into the dermis inflammation especially with propionobacterium acnes lead to papule pastule nodulocystic lesions
1- Mild ; comedones no papules 2- Moderate : comedones paules pustules 3- Sever : nodules & cysts
DD Tratment
DD : tinea versicolor pityriasis albapostinflammatory hypopigmentation 1- Phoyototherapy : PUVA 2- Steroids & immunomodulators 3- Surgical : punch gafting & tissue culture 4- camouflage
1- topical ; local irritants corticosteroids cream PUVA minoxidil 2- systemic : antidepressant corticosteroids
1- topical : erythromycin lotion retinoids benzyl peroxide azelic acid 2- systemic : antibiotics (tetracycline) + retinoids dapsone & steroids ( sever )
The following topics has to be studied from the department book : leprosy & protozoal infections
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Clinical Dermatology: Differential DiagnosisDocumento73 pagineClinical Dermatology: Differential DiagnosisHalim MaherNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral Dermatology: Important Oral Questions & AnswersDocumento29 pagineOral Dermatology: Important Oral Questions & AnswersMedo JTNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Topical Treatments in DermatologyDocumento18 paginePrinciples of Topical Treatments in DermatologyAnonymous OlS0WZwNessuna valutazione finora
- Dermatology Questions and AnsDocumento147 pagineDermatology Questions and AnsEl FaroukNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 5791904539871281964 PDFDocumento521 pagine4 5791904539871281964 PDFElmira RissadiqahNessuna valutazione finora
- Nelson Pediatrics Review (MCQS) 17edDocumento631 pagineNelson Pediatrics Review (MCQS) 17edGabrielle Maycock75% (8)
- Pediatric DermatologyDocumento47 paginePediatric DermatologyAmr Abualrub100% (2)
- Dermatology OSCE Pictures 1Documento208 pagineDermatology OSCE Pictures 1medt80Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dermatology Approach: Fayza RayesDocumento108 pagineDermatology Approach: Fayza RayesMinghan Shi100% (2)
- Dermatology Notes for Medical StudentsDa EverandDermatology Notes for Medical StudentsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- Dermatology - Papulosquamous DisordersDocumento34 pagineDermatology - Papulosquamous DisordersskNessuna valutazione finora
- Ichthyosis - Fitzpatrick Dermatology 9th EdDocumento26 pagineIchthyosis - Fitzpatrick Dermatology 9th EdIza Singson-CristobalNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Cases in Dermatology Modern Management of Acne Actinic Keratosis and Atopic DermatitisDocumento7 pagineClinical Cases in Dermatology Modern Management of Acne Actinic Keratosis and Atopic DermatitisJpratoNessuna valutazione finora
- CLINICAL DERMATOLOGY (NXPowerLite)Documento119 pagineCLINICAL DERMATOLOGY (NXPowerLite)api-3710926Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dermatology ReviewDocumento116 pagineDermatology ReviewJ Cheung100% (1)
- PATHOPHYS - DermatologyDocumento19 paginePATHOPHYS - Dermatologyaagioaa100% (1)
- Dermatology GuideDocumento89 pagineDermatology GuideZeljnaznanja100% (3)
- Dermatology Images (All in One Merged)Documento692 pagineDermatology Images (All in One Merged)Woo Rin Park100% (2)
- Clinical Dermatology: Carmen I Farid. MDDocumento81 pagineClinical Dermatology: Carmen I Farid. MDBahaa ShaabanNessuna valutazione finora
- Dermatology EMQDocumento4 pagineDermatology EMQislamawniNessuna valutazione finora
- 3b Dermatology PresentationDocumento73 pagine3b Dermatology PresentationOlivia Genevieve El JassarNessuna valutazione finora
- Dermatology QuestionsDocumento8 pagineDermatology QuestionsDrMubashir ShaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- 1-Dermatological Case PresentationDocumento41 pagine1-Dermatological Case Presentationnaimat007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dermatology Treatment GuidelinesDocumento33 pagineDermatology Treatment GuidelinesYoga YogaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Dermatology Assessment of A Dermatologic PatientDocumento86 pagineIntroduction To Dermatology Assessment of A Dermatologic PatientAtifNessuna valutazione finora
- Sqweqwesf Erwrewfsdfs Adasd Dhe: Dermnet NZDocumento19 pagineSqweqwesf Erwrewfsdfs Adasd Dhe: Dermnet NZkdwazirNessuna valutazione finora
- Derm - Monitoring Systemic MedicationsDocumento3 pagineDerm - Monitoring Systemic MedicationsriskhakovNessuna valutazione finora
- Viva Questions DermatologyDocumento5 pagineViva Questions DermatologyRavva0% (1)
- Dermatology FinalDocumento16 pagineDermatology FinalMelinda100% (2)
- Paraneoplastic DermatosesDocumento57 pagineParaneoplastic DermatosesMohamed Riyaz100% (1)
- Palmoplantar KeratodermaDocumento4 paginePalmoplantar KeratodermakurutalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Prometric Book 2nd EditionDocumento207 paginePrometric Book 2nd Editionsajitha100% (2)
- Complete Dermatology NotesDocumento41 pagineComplete Dermatology NotesSetlhare MotsamaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide-Dermatology 2021Documento14 pagineStudy Guide-Dermatology 2021Nasir RafieNessuna valutazione finora
- Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical DermatologyDocumento1.146 pagineAtlas and Synopsis of Clinical DermatologyAnda Madalina Zaharia100% (6)
- General Considerations For Topical PreparationsDocumento6 pagineGeneral Considerations For Topical PreparationsOccamsRazorNessuna valutazione finora
- Dermatomycosis 18th July 2021Documento120 pagineDermatomycosis 18th July 2021Sekar OktaviaNessuna valutazione finora
- Derma MegatableDocumento21 pagineDerma MegatableNicole ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Dermatology PastestDocumento26 pagineDermatology PastestMateen Shukri100% (1)
- 06 DermatologyDocumento8 pagine06 DermatologyMichael NyaataNessuna valutazione finora
- Dermnet NZ: Special Stains and TestsDocumento4 pagineDermnet NZ: Special Stains and TestsRaja Sekaran DuraiNessuna valutazione finora
- (DERMA) Revalida Review 2018Documento202 pagine(DERMA) Revalida Review 2018anonymousNessuna valutazione finora
- An Approach To The Patient With ErythrodermaDocumento42 pagineAn Approach To The Patient With ErythrodermaShakilNessuna valutazione finora
- Dermatology Board Review 2007 Part 3Documento42 pagineDermatology Board Review 2007 Part 3hifuka100% (1)
- Dermatology Quiz 2015 AnswersDocumento40 pagineDermatology Quiz 2015 Answerspoorva shahNessuna valutazione finora
- Secret PlusDocumento1 paginaSecret PlusYoga Adi0% (2)
- Phototherapy For Dermatologic ConditionsDocumento18 paginePhototherapy For Dermatologic ConditionsSeth MosebyNessuna valutazione finora
- DermatologyDocumento72 pagineDermatologyRashed ShatnawiNessuna valutazione finora
- Topical Antibiotics in DermatologyDocumento19 pagineTopical Antibiotics in DermatologyJejem Marandra EmkamasNessuna valutazione finora
- Dermatolgy - Aiims Past Questions - ProProfs QuizDocumento3 pagineDermatolgy - Aiims Past Questions - ProProfs QuizheshamNessuna valutazione finora
- Acne Vulgaris Acne Rosacea Acne Disorders: Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocumento19 pagineAcne Vulgaris Acne Rosacea Acne Disorders: Systemic Lupus Erythematosusapi-26938624Nessuna valutazione finora
- اسئلة الجلدية لهيئة التخصصات السعودية PDFDocumento24 pagineاسئلة الجلدية لهيئة التخصصات السعودية PDFDrhisham AttiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dermatology Essay QuestionsDocumento2 pagineDermatology Essay QuestionsPeter Abikoye100% (1)
- Dermoscopy in General DermatologyDocumento16 pagineDermoscopy in General DermatologyMaestro JadNessuna valutazione finora
- Dermatology Slides - Introduction To Clinical DermatologyDocumento34 pagineDermatology Slides - Introduction To Clinical DermatologyAzry Mustapa100% (1)
- Benign Skin LesionsDocumento75 pagineBenign Skin LesionsEmma Enggar SafitriNessuna valutazione finora
- Dermatology SlidesDocumento16 pagineDermatology SlidesmuhammadridhwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Dermatopathology - Classification of Cutaneous Lesions (E Zappi)Documento219 pagineDermatopathology - Classification of Cutaneous Lesions (E Zappi)Denisa VladulescuNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual of Skin Surgery: A Practical Guide to Dermatologic ProceduresDa EverandManual of Skin Surgery: A Practical Guide to Dermatologic ProceduresValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (1)
- 5 - Hypovolaemic ShockDocumento7 pagine5 - Hypovolaemic ShockmksharmaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical MnemonicsDocumento256 pagineMedical MnemonicssitalcoolkNessuna valutazione finora
- Dept Acc OrgDocumento14 pagineDept Acc OrgmksharmaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Booklist NMC 12-13Documento13 pagineBooklist NMC 12-13mksharmaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre PG MCQ by Amit Ashish - Medicine N SurgeryDocumento466 paginePre PG MCQ by Amit Ashish - Medicine N Surgerymksharmaa100% (5)
- Cover TestDocumento2 pagineCover Testmksharmaa100% (1)
- Sept Mci 2011 QuestionsDocumento3 pagineSept Mci 2011 Questionsmksharmaa0% (1)
- Papilloedema: - Circulation of Cerebrospinal Fluid - Causes of Raised Intracranial Pressure - HydrocephalusDocumento8 paginePapilloedema: - Circulation of Cerebrospinal Fluid - Causes of Raised Intracranial Pressure - HydrocephalusmksharmaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Otitis ExternaDocumento14 pagineOtitis ExternaRizkaGayoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Patient With Recurrent Oral UlcerationDocumento9 pagineThe Patient With Recurrent Oral UlcerationintanNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Skin Lesions: Presented By: Dr. Divyank A. Vankawala Jr. Resident, Dermatology Dept., NDMVPS VP Medical CollegeDocumento46 pagineBasic Skin Lesions: Presented By: Dr. Divyank A. Vankawala Jr. Resident, Dermatology Dept., NDMVPS VP Medical CollegeniveditakartikNessuna valutazione finora
- Dermatologia: Anais Brasileiros deDocumento3 pagineDermatologia: Anais Brasileiros deSango AyraNessuna valutazione finora
- Tinea Capitis: Anggota Kelompok: Suci Melinda M. Brigitha Rahmaddini NRP St. Hardianty Ayu Resky A. Juliana RamdaniDocumento27 pagineTinea Capitis: Anggota Kelompok: Suci Melinda M. Brigitha Rahmaddini NRP St. Hardianty Ayu Resky A. Juliana RamdaniSyafitri NavisyaNessuna valutazione finora
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocumento6 pagineNew Microsoft Office Word Documentabas_maytham1021Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anki Derm 2Documento4 pagineAnki Derm 2Simran SandhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Pityriasis Alba Pityriasis AlbaDocumento11 paginePityriasis Alba Pityriasis AlbaSSGeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bullous Disorders, Bacterial and Fungal Skin InfectionsDocumento95 pagineBullous Disorders, Bacterial and Fungal Skin InfectionsDeborah ChemutaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Moh - Fahri (Dermatitis Venenata)Documento5 pagineMoh - Fahri (Dermatitis Venenata)fahriitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cards+Against+Paediatric+Dermatology+-+Vickie+Wells+&+Emma+Buxton+ (v1 0)Documento146 pagineCards+Against+Paediatric+Dermatology+-+Vickie+Wells+&+Emma+Buxton+ (v1 0)Donna RicottaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: January 2014Documento4 pagineDyshidrotic Eczema: January 2014Strawberry ShortcakeNessuna valutazione finora
- LeukoplakiaDocumento12 pagineLeukoplakiaPrashant PuranikNessuna valutazione finora
- Bullous Disease of The Skin, Acantholytic Bullous Disease (Darier's Disease, Keratosis Follicularis), M 15, Scalp, NeckDocumento3 pagineBullous Disease of The Skin, Acantholytic Bullous Disease (Darier's Disease, Keratosis Follicularis), M 15, Scalp, NeckDeba P SarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2012 SLICC SLE Criteria - RheumTutorDocumento3 pagine2012 SLICC SLE Criteria - RheumTutorgkrgagNessuna valutazione finora
- EfloresensiDocumento3 pagineEfloresensiputriana safitriNessuna valutazione finora
- Derma EmergencyDocumento2 pagineDerma EmergencyAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNessuna valutazione finora
- Connective Tissue DZDocumento1 paginaConnective Tissue DZAndre GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Report Dermatitis ContactDocumento10 pagineCase Report Dermatitis ContactMuhammad Aktora Tarigan100% (1)
- SelulitisDocumento5 pagineSelulitisdnswrNessuna valutazione finora
- Epidemio-Clinical Profile of Atopic Dermatitis in Children in General Population in Parakou (Benin)Documento4 pagineEpidemio-Clinical Profile of Atopic Dermatitis in Children in General Population in Parakou (Benin)asclepiuspdfsNessuna valutazione finora
- GonorrheaDocumento9 pagineGonorrheaPencenk AzznewNessuna valutazione finora
- ImpetigoDocumento3 pagineImpetigoLauraNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric Blistering Diseases: MSU/Beaumont Health Dermatology Residency ProgramDocumento80 paginePediatric Blistering Diseases: MSU/Beaumont Health Dermatology Residency ProgramGeoRNessuna valutazione finora
- 139 Case ReportDocumento2 pagine139 Case ReportlistyNessuna valutazione finora
- Study. RSUD Soetomo Surabaya. Vol. 26. No 3. Universitas AirlanggaDocumento2 pagineStudy. RSUD Soetomo Surabaya. Vol. 26. No 3. Universitas AirlanggaKhoirunnisaSPazkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Case Book MeDioStar 2018-11Documento48 pagineClinical Case Book MeDioStar 2018-11medspa49Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 DermTerms & Dx-1Documento53 pagine2016 DermTerms & Dx-1vivekNessuna valutazione finora
- Alopecia 203Documento14 pagineAlopecia 203api-535005469Nessuna valutazione finora