Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
BIOL 3364 Clinical Biochemistry Tutorial #1 Urinalysis, Stool Analysis & Hematology
Caricato da
Helen AmmonDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
BIOL 3364 Clinical Biochemistry Tutorial #1 Urinalysis, Stool Analysis & Hematology
Caricato da
Helen AmmonCopyright:
Formati disponibili
BIOL 3364 Clinical Biochemistry Tutorial #1 Urinalysis, Stool Analysis & Hematology
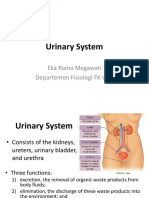
1) A- left kidney B- ureter C- urinary bladder D-urethra E- renal pelvis F- ureter G- cortex H- renal pyramid I- Bowmans capsule J- glomerulus K- Loop of Henle L- distal convoluted tubule M-medullary collecting duct N- cortical collecting duct 2) The kidneys function as biological purification plants to remove harmful toxins, metabolic wastes and excess ions from the blood. 3) The components of a urine sample from a healthy individual consists of: 96% water, 2% urea from the breakdown of amino acids and 2% of inorganic compounds (Cl-, Na+, K+, SO42-, PO42-, HCO3-) and organic compounds (creatinine and uric acid). 4) Three kidney diseases that may cause abnormal urinalysis results are: diabetes mellitus, hypertension and atherosclerosis. 5) Renal threshold is when the concentration of a substance dissolved in the blood above which the kidneys begin to remove it into the urine. When the renal threshold of a substance is surpassed, reabsorption of the substance by the proximal convoluted tubule is incomplete; thus, part of the substance is excreted in the urine. 6) A diuretic is any substance that helps in the removal of excess fluid through increased urination. 4 natural diuretics that may be found in the Caribbean diet are: tomatoes, cucumbers, eggplant and celery. 7) Anuria is the absence of urine production often caused by failure in the function of kidneys. Clean catch urine is a urine sample that is collected to be tested. This type of urine is necessary when urine is to be cultured for microorganisms as it prevents germs from the genitals from entering the sample. 8) Three commonly used means of preserving urine are: refrigeration, commercial transport tubes and use of preservatives such as hydrochloric acid or glacial acetic acid. 9) The limitations of commercial transport tubes are: pH and SG may be altered, varies with tube used; can interfere with chemistry tests (e.g., sodium, potassium, hormone, drug
assays). The limitations of acids are: unacceptable for urinalysis testing; potential chemical hazard. 10) Three components of urinalysis are: gross/physical examination, chemical screening, and sediment examination. 11) Four causes of abnormal urine colors are: rhabdomyolysis, urinary tract infection, hepatitis and acute infective cystitis. 12) Three causes of cloudy urine are the presence of bacteria, sperm and crystals. 13) The specific gravity of urine will reflect generalized renal impairment as it shows the ability of the nephron tubules to excrete solids and reabsorb substances needed for homeostasis. 14) A darker coloured urine would have a higher specific gravity. This is because specific gravity of urine is a measurement of the density of urine - the relative proportions of dissolved solids in relationship to the total volume of the specimen. As such, darker urine will always have a higher specific gravity as it is denser than lighter coloured urine. 15) 6 chemical tests routinely performed on urine using reagent strips are: glucose, bilirubin, ketones, blood, pH and protein.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Formation of urine in the kidneysDocumento9 pagineFormation of urine in the kidneysمحمد حامدNessuna valutazione finora
- UrinalysisDocumento10 pagineUrinalysisMichelle100% (2)
- Urinalysis PDFDocumento34 pagineUrinalysis PDFAzeli SiquianNessuna valutazione finora
- Target Organ Toxicity: Hematotoxicity, Hepatotoxicity, NephrotoxicityDocumento7 pagineTarget Organ Toxicity: Hematotoxicity, Hepatotoxicity, Nephrotoxicityaveen rasulNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal Function and Non-Protein Nitrogen TestsDocumento7 pagineRenal Function and Non-Protein Nitrogen TestsAndrew NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- UrinalysisDocumento120 pagineUrinalysisKate Alyssa Caton100% (1)
- Urine AnalysisDocumento30 pagineUrine AnalysisFrances SingsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Toxicity of LiverDocumento59 pagineToxicity of LiverMd Abu Eabrahim Siddique100% (1)
- Body Fluids PDFDocumento31 pagineBody Fluids PDFJustine Salvo EvaristoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture (5) Kidney Function Tests Part IDocumento33 pagineLecture (5) Kidney Function Tests Part IAmine GobranNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Text Books/Reference Books: TH TH TH TH THDocumento64 pagineList of Text Books/Reference Books: TH TH TH TH THtanmay mehtaNessuna valutazione finora
- Body Fluids BiochemDocumento31 pagineBody Fluids BiochemAlyssa PachecoNessuna valutazione finora
- CM Handouts Clinical MicrosDocumento33 pagineCM Handouts Clinical Microsrenato renato100% (1)
- International Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Invention (IJMSI)Documento8 pagineInternational Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Invention (IJMSI)inventionjournalsNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 8 Anatomy Physiology of Urinary System - TaggedDocumento27 pagineLab 8 Anatomy Physiology of Urinary System - TaggedSaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Microscopy Guide to Urine and Body Fluid AnalysisDocumento32 pagineClinical Microscopy Guide to Urine and Body Fluid AnalysispikachuNessuna valutazione finora
- DR - Layla Abd Alasattar Sadiq Laylani: PHD PhysiologyDocumento13 pagineDR - Layla Abd Alasattar Sadiq Laylani: PHD PhysiologyAkAm 33 ꪜNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab. 7Documento6 pagineLab. 7tamanranya234Nessuna valutazione finora
- IOSRPHRDocumento9 pagineIOSRPHRIOSR Journal of PharmacyNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant and human excretion systems explainedDocumento9 paginePlant and human excretion systems explainedJoy FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnostic EvaluationsDocumento17 pagineDiagnostic EvaluationsJayvadan LalparaNessuna valutazione finora
- Body Fluids: ManualDocumento90 pagineBody Fluids: ManualGhaidaa SadeqNessuna valutazione finora
- Fungsi GinjalDocumento21 pagineFungsi GinjalA1205Angelica GloryNessuna valutazione finora
- 7B Heller's Ring TestDocumento2 pagine7B Heller's Ring TestHilmond Octaviano VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To UrinalysisDocumento12 pagineIntroduction To UrinalysisfaysalhusseinfaysalhusseinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 26Documento7 pagineChapter 26jess waldenNessuna valutazione finora
- MICROSCOPIC URINE ANALYSISDocumento89 pagineMICROSCOPIC URINE ANALYSISLucia SurduNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinalysis and Body Fluids2020Documento47 pagineUrinalysis and Body Fluids2020MONFOLA100% (1)
- Recall MT Boards 2016Documento41 pagineRecall MT Boards 2016Daphne HernaezNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 5 - The Urinary System: KidneyDocumento6 pagineLab 5 - The Urinary System: Kidneymath_mallikarjun_sapNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Pathology: Urine AnalysisDocumento42 pagineClinical Pathology: Urine AnalysisRathinaKumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ratification Page: Andi Citra Pratiwi, S.PD, M.Ed Muhammad Nur Arsyad, S.PDDocumento18 pagineRatification Page: Andi Citra Pratiwi, S.PD, M.Ed Muhammad Nur Arsyad, S.PDFatmawatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Aubf Questions With AnswersDocumento16 pagineAubf Questions With AnswersFenyl Isis GuigayomaNessuna valutazione finora
- RTRMFDocumento24 pagineRTRMFAngelo MercedeNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary SystemDocumento11 pagineUrinary SystemAlan AzadNessuna valutazione finora
- Urine MetabolomeDocumento28 pagineUrine MetabolomeFlorina FloriNessuna valutazione finora
- Review in Clinical MicrosDocumento103 pagineReview in Clinical MicrosSyvelmarie Tinte100% (1)
- Lecture Notes On Chemical Pathology of UrineDocumento23 pagineLecture Notes On Chemical Pathology of UrineTaylorNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Pathology Ii. Pathology of Urinary System Lectuer NotesDocumento26 pagineMedical Pathology Ii. Pathology of Urinary System Lectuer Noteseric epahNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Excretion System IGCSE 9th GradeDocumento33 pagineHuman Excretion System IGCSE 9th GradebenunosNessuna valutazione finora
- UrinalysisDocumento3 pagineUrinalysisSusan FNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry: Spring 2022Documento77 pagineBiochemistry: Spring 2022Horn DudeNessuna valutazione finora
- ExcretionDocumento36 pagineExcretionMeet vermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lapleng Biokim Unit 5 Urine - Muhanmmad RaihanDocumento27 pagineLapleng Biokim Unit 5 Urine - Muhanmmad RaihanRaihan AlbaihaqNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To HematologyDocumento95 pagineIntroduction To HematologyAhmad Farhan Hassan0% (1)
- Urine Specimen Types and CollectionDocumento7 pagineUrine Specimen Types and CollectionRyan KadavilNessuna valutazione finora
- Identifying urine constituentsDocumento7 pagineIdentifying urine constituentsMaipha DeapatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Urine Analysis Reveals Glucose and Sediment LevelsDocumento8 pagineUrine Analysis Reveals Glucose and Sediment LevelsDewi AulyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Excretory SystemDocumento6 pagineExcretory SystemAJAYI PETERNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4Documento69 pagineModule 4punte77Nessuna valutazione finora
- BIO 156 Chapter 9 PowerpointDocumento17 pagineBIO 156 Chapter 9 PowerpointDrPearcyNessuna valutazione finora
- Swu Phinma, College of Pharmacy 2020: Wr/Urinalysis - Html#Ixzz6Zxlj RQKH /Product-Manual/3008 - 3B - UrinalysisDocumento7 pagineSwu Phinma, College of Pharmacy 2020: Wr/Urinalysis - Html#Ixzz6Zxlj RQKH /Product-Manual/3008 - 3B - UrinalysisTrex MarciiiNessuna valutazione finora
- Liver Function TestsDocumento52 pagineLiver Function TestsAhaisibwe GordonNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal Function: Clinical Chemistry IiiDocumento23 pagineRenal Function: Clinical Chemistry IiiJannica Dominique ClarosNessuna valutazione finora
- Bab IDocumento21 pagineBab IMarilahNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Yerevan Drinking Water Quality - CHSR PDFDocumento17 pagineAnalysis of Yerevan Drinking Water Quality - CHSR PDFrayNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary Stones: Medical and Surgical ManagementDa EverandUrinary Stones: Medical and Surgical ManagementMichael GrassoNessuna valutazione finora
- Key Questions in Clinical Farm Animal Medicine, Volume 2: Types, Causes and Treatments of Infectious DiseaseDa EverandKey Questions in Clinical Farm Animal Medicine, Volume 2: Types, Causes and Treatments of Infectious DiseaseTanmoy RanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal Reflections: Exploring the Marvels of Nephrology: The Intricate Ballet of Kidney Functions UnveiledDa EverandRenal Reflections: Exploring the Marvels of Nephrology: The Intricate Ballet of Kidney Functions UnveiledNessuna valutazione finora
- Hematuria, (Blood in Urine) A Simple Guide to The Condition, Related Diseases And Use in Diagnosis of DiseasesDa EverandHematuria, (Blood in Urine) A Simple Guide to The Condition, Related Diseases And Use in Diagnosis of DiseasesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Atomic StructureDocumento22 pagineAtomic StructureHelen AmmonNessuna valutazione finora
- Extra Hours August 2015 To DelDocumento1 paginaExtra Hours August 2015 To DelHelen AmmonNessuna valutazione finora
- CalculationsDocumento8 pagineCalculationsHelen AmmonNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab CalculationsDocumento6 pagineLab CalculationsHelen AmmonNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOL 3364 Clinical Biochemistry Tutorial #1 Urinalysis, Stool Analysis & HematologyDocumento2 pagineBIOL 3364 Clinical Biochemistry Tutorial #1 Urinalysis, Stool Analysis & HematologyHelen AmmonNessuna valutazione finora
- Isolate Rat Liver Cell Fractions Using Differential CentrifugationDocumento29 pagineIsolate Rat Liver Cell Fractions Using Differential CentrifugationHelen AmmonNessuna valutazione finora
- Isolate Rat Liver Cell Fractions Using Differential CentrifugationDocumento29 pagineIsolate Rat Liver Cell Fractions Using Differential CentrifugationHelen AmmonNessuna valutazione finora
- Brain Hemisphere and ControlDocumento2 pagineBrain Hemisphere and ControlHelen AmmonNessuna valutazione finora
- DNADocumento1 paginaDNAHelen AmmonNessuna valutazione finora
- BCG X Meta India M&E 2023Documento60 pagineBCG X Meta India M&E 2023Никита МузафаровNessuna valutazione finora
- CSEC Physics P2 2013 JuneDocumento20 pagineCSEC Physics P2 2013 JuneBill BobNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Test 4: Explorer's Rainforest Trip and Blind AdventurerDocumento6 paginePractice Test 4: Explorer's Rainforest Trip and Blind AdventurerKhang Nguyen TienNessuna valutazione finora
- List of As... SimilesDocumento3 pagineList of As... SimilesFara ZahariNessuna valutazione finora
- Literature Review 2.1. Shodhana A. Ayurvedic System of ShodhanaDocumento93 pagineLiterature Review 2.1. Shodhana A. Ayurvedic System of ShodhanasiesmannNessuna valutazione finora
- 677 1415 1 SMDocumento5 pagine677 1415 1 SMAditya RizkyNessuna valutazione finora
- CimoryDocumento1 paginaCimorymauza.collection12Nessuna valutazione finora
- GSP Action PlanDocumento2 pagineGSP Action PlanTen Victa-Milano100% (3)
- Maternal and Perinatal Outcome in Jaundice Complicating PregnancyDocumento10 pagineMaternal and Perinatal Outcome in Jaundice Complicating PregnancymanognaaaaNessuna valutazione finora
- HPC - 2022-JIAF - Guide-1.1Documento60 pagineHPC - 2022-JIAF - Guide-1.1Emmanuel LompoNessuna valutazione finora
- Microcontrollers vs MicroprocessorsDocumento90 pagineMicrocontrollers vs MicroprocessorsMehmet AşıkNessuna valutazione finora
- Soal EnglishDocumento7 pagineSoal EnglishRieZky RamadhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Jones 2020 E RDocumento12 pagineJones 2020 E RKAINessuna valutazione finora
- (1964) AC 763 Help: House of Lords Chandler and OthersDocumento22 pagine(1964) AC 763 Help: House of Lords Chandler and OthersShehzad HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- Calendar of ActivitiesDocumento7 pagineCalendar of ActivitiesAries Robinson CasasNessuna valutazione finora
- Communicative Approach - ChomskyDocumento4 pagineCommunicative Approach - ChomskyMiss AbrilNessuna valutazione finora
- International Human Resource Management - A Literature Review PDFDocumento7 pagineInternational Human Resource Management - A Literature Review PDFTosin AdelowoNessuna valutazione finora
- Draft Certificates Bg. Terang 306 - 7,557. 258mt Mt-2Documento5 pagineDraft Certificates Bg. Terang 306 - 7,557. 258mt Mt-2BOBY RAHMAN PURBANessuna valutazione finora
- Civet CoffeeDocumento8 pagineCivet CoffeeAn NhiênNessuna valutazione finora
- Sid The Science Kid - The Ruler of Thumb Cd1.avi Sid The Science Kid - The Ruler of Thumb Cd2.aviDocumento27 pagineSid The Science Kid - The Ruler of Thumb Cd1.avi Sid The Science Kid - The Ruler of Thumb Cd2.avisheena2saNessuna valutazione finora
- Flow Through AnnulusDocumento7 pagineFlow Through Annulusamir_hayfaNessuna valutazione finora
- Academic TranscriptDocumento6 pagineAcademic Transcriptapi-450491493Nessuna valutazione finora
- How The Government Was Formed After Prophet MuhammadDocumento48 pagineHow The Government Was Formed After Prophet MuhammadMUSALMAN BHAINessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4-Historical RecountDocumento14 pagineChapter 4-Historical RecountRul UlieNessuna valutazione finora
- Michigan History-Lesson 3Documento4 pagineMichigan History-Lesson 3api-270156002Nessuna valutazione finora
- HDPS 1303 - 930425105424Documento6 pagineHDPS 1303 - 930425105424Cheryl LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Page - 1Documento18 paginePage - 1Julian Adam Pagal75% (4)
- AntimonyDocumento72 pagineAntimony沈益Nessuna valutazione finora
- Benchmark Evidence BasedDocumento11 pagineBenchmark Evidence BasedPeterNessuna valutazione finora
- Sector:: Automotive/Land Transport SectorDocumento20 pagineSector:: Automotive/Land Transport SectorVedin Padilla Pedroso92% (12)