Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Optics Cheat Sheet
Caricato da
Aakash AkronosCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Optics Cheat Sheet
Caricato da
Aakash AkronosCopyright:
Formati disponibili
High School Physics - Core Concept Cheat Sheet
17: Geometric Optics
Key Physics Terms
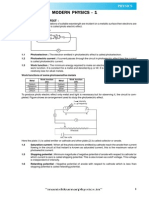
Plane mirror: A flat reflective surface. Creates an image that is virtual, upright, the same size and that appears to be as far behind the mirror as original is in front. Law of reflection: The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Angles are measured relative to a line normal to the surface. Normal line: A line drawn perpendicular to the surface. Virtual image: The rays of light do not actually pass through the image; they just seem to originate from that location. Cannot be projected onto a screen. Diffuse reflection: Reflection from a rough surface where variations in the direction of the surface cause light to reflect in different directions. Concave mirror: A curved surface that focuses parallel rays of light to a single point, the focal point. Image type, size, and orientation depend on objects position. Also called a converging mirror. Convex mirror: A curved surface that diverges light as if it originates from a point behind the mirror, the focal point. Forms a virtual image. Also called a diverging mirror. Focal length: Distance from the lens or mirror to the focal point. Center of curvature: Twice the focal length of a lens or mirror. This represents the center of the spherical surface if it was extended. Real image: An image where the rays of light actually pass through the image. It can be projected onto a screen. Ray diagram: A tool for tracing the path of light incident on a lens or mirror, assumes light is a straight line. Refraction: The bending of light due to a change in its velocity in various media. Index of refraction: The ratio between the speed of light in a vacuum and speed of light in a particular medium. Dispersion: The separation of light into colors by refraction. Used in prism and cause of rainbows. Total internal reflection: The complete reflection of light when it strikes the boundary between two media at greater than a critical angle. Used in fiber optics. Convex lens: A converging lens that gathers incoming parallel light rays to a single focal point. Image may be real or virtual depending on objects position. Concave lens: A diverging lens that diverges light as if it originates from a point in front of the lens, the focal point. Forms a virtual image, smaller, upright image. Spherical aberration: A lens defect where light is imperfectly focused near the focal point. Chromatic aberration: A lens defect where various color focus at different locations.
Geometric Optics Problem Solving Tips
These tips will make it easier to solve any physics problems. Thoroughly read the entire problem. Draw a ray diagram carefully. Identify all given information. Identify the quantity to be found. Select appropriate formula(s) that incorporate what you know and what you want to find. Pay extra attention of sign conventions. Convert units if needed. Do any mathematical calculations carefully.
Ray Diagrams
object
2f
Focal point
Focal point
Image Rays meet to give an inverted, real, larger image.
With this convex lens notice how the rays travel and meet when the image is formed. In this case, a real, magnified, inverted image is formed. With this convex mirror, notice how the rays dont actually meet. You must trace the rays backwards into the mirror to see where they seem to originate.
Orientation/ Size Inverted, smaller Inverted, same Inverted, larger None Upright, larger Upright, smaller
image Focal point
In this case, a virtual, smaller, and upright image is formed.
Mirror/Lens Type Concave Mirror Or Convex Lens Convex Mirror Or Concave Lens
Object Position Beyond C At C Between F & C At F In front of F Anywhere
Type of Image Real Real Real None Virtual Virtual
Sign Conventions
Virtual images are di Real images are +di Converging optics have +f Diverging optics have f Objects distance is always +do
Variables Used and Key Metric Units
f= focal length of mirror or lens. Units, m do=objects distance from the mirror or lens. Units, m di= images distance from the mirror or lens. Units, m n= index of refraction hi= height of image. Units, m ho= height of object. Units, m m = magnification v= velocity of light in a particular medium. Units, m/s = angle between given ray and normal line. Units, degrees
Example Refraction Diagram
air Air, n=1.00 Glass, n=1.52 glass
Key Formulas and Constants
Air, n=1.00 1/f=1/do+1/di air m=hi/ho=-di/do n=c/v n1sin1=n2sin2 speed of light in a vacuum, c = 3.0 x 108m/s refractive index of air = 1.00 How to Use This Cheat Sheet: These are the keys related this topic. Try to read through it carefully twice then rewrite it on a blank sheet of paper. Review it again before the exams.
Note how the beam bends to the normal when entering the more dense glass medium. Then it bends away from the normal when re entering air.
RapidLearningCenter.com
Rapid Learning Inc. All Rights Reserved
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Geometric Optics Cheat Sheet for Curved Mirrors and LensesDocumento5 pagineGeometric Optics Cheat Sheet for Curved Mirrors and LensesWillTurnerNessuna valutazione finora
- Optics Cheat SheetDocumento1 paginaOptics Cheat SheetAlex MuresanNessuna valutazione finora
- Optics Cheat Sheet: MirrorsDocumento1 paginaOptics Cheat Sheet: MirrorsWillTurnerNessuna valutazione finora
- Ray Optics NotesDocumento74 pagineRay Optics Notessatyam07r100% (5)
- Topic 4.5 Formative Answer KeyDocumento1 paginaTopic 4.5 Formative Answer Key이수연Nessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Physics (Optics Notes)Documento30 pagineBasics of Physics (Optics Notes)omkardashetwar100% (1)
- OpticsDocumento89 pagineOpticsKarunya nidhi100% (1)
- Classical Optics Reflection and Image FormationDocumento11 pagineClassical Optics Reflection and Image FormationMa-anJaneDiamos100% (1)
- Set C: CouplingDocumento7 pagineSet C: CouplingLuke Matthew MondaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics 71 Cheat SheetsDocumento3 paginePhysics 71 Cheat Sheetsdanielle3225100% (1)
- Formula Booklet Physics XIDocumento35 pagineFormula Booklet Physics XIsreenatpppp84% (147)
- AP Physics 2 - Waves & Sound Full NotesDocumento19 pagineAP Physics 2 - Waves & Sound Full Notes孙铭阳Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum Chemistry Notes Brief ReviewDocumento61 pagineQuantum Chemistry Notes Brief ReviewLina Silaban100% (1)
- Introduction and Review Differential CalculusbDocumento32 pagineIntroduction and Review Differential CalculusbRalph Piolo BuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Self Evalution Test-OpticsDocumento5 pagineSelf Evalution Test-OpticsBHAAJI0001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics 1121 A Cheat SheetDocumento8 paginePhysics 1121 A Cheat SheetAmmar Tirmzey100% (1)
- All Physics Formula and Glossary - GCE Study Buddy - The Best O Level Revision ResourceDocumento13 pagineAll Physics Formula and Glossary - GCE Study Buddy - The Best O Level Revision ResourceVei Adoptante100% (2)
- Geometrical OpticsDocumento35 pagineGeometrical Opticsthinkiit90% (10)
- Ch25 Giancoli7e TestBankDocumento37 pagineCh25 Giancoli7e TestBankLopez Shian ErvinNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 10 Physics Chapter 3 Revision Problems - Answer Key: Multiple Choice Questions. Q1Documento6 pagineGrade 10 Physics Chapter 3 Revision Problems - Answer Key: Multiple Choice Questions. Q1NONO0% (1)
- Geometric Optics Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento14 pagineGeometric Optics Multiple Choice QuestionsqvrlenarasegtNessuna valutazione finora
- Light Wave Particle Dual NatureDocumento4 pagineLight Wave Particle Dual NatureSyed Mairaj Ul Haq100% (1)
- Organic Nomenclature HTTPDocumento19 pagineOrganic Nomenclature HTTPmyiitchemistry91% (11)
- Physics Chapter 26 AnswersDocumento7 paginePhysics Chapter 26 AnswersKarissaNessuna valutazione finora
- OpticsDocumento487 pagineOpticsZeen Majid100% (8)
- Del OperatorDocumento6 pagineDel OperatorSupriya Aggarwal100% (1)
- Sph4u KinematicsDocumento7 pagineSph4u KinematicsVoormila NithianandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometric Optics Exam QuestionsDocumento10 pagineGeometric Optics Exam QuestionsMahendra Chouhan100% (3)
- RefractionDocumento15 pagineRefractionSudharsan Gupta Sudhir100% (1)
- Lab Report #1 Photoelectric EffectDocumento8 pagineLab Report #1 Photoelectric EffectJohn FiveNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern PhysicsDocumento34 pagineModern PhysicsAditya BansalNessuna valutazione finora
- Snells Law, Refraction of LightDocumento7 pagineSnells Law, Refraction of LightMichael Simba100% (1)
- OpticsDocumento285 pagineOpticsqwerty100% (3)
- Physics Chapter 2Documento13 paginePhysics Chapter 2RaheEl Mukhtar0% (1)
- 15 Induction RL CircuitsDocumento23 pagine15 Induction RL CircuitsHermawan AngghaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 10 Science SNC2D Review Unit 4 PhysicsDocumento6 pagineGrade 10 Science SNC2D Review Unit 4 PhysicsRiazNessuna valutazione finora
- SpectrosDocumento21 pagineSpectrosAman Rathore100% (1)
- Wave Optics Theory and ExercisesDocumento26 pagineWave Optics Theory and ExercisesBalajiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Schrödinger Equation in One DimensionDocumento23 pagineThe Schrödinger Equation in One DimensionjunaidNessuna valutazione finora
- Optics-Hecht - 04-Chap5-Geometrical Optics - OKDocumento58 pagineOptics-Hecht - 04-Chap5-Geometrical Optics - OKfara latifa100% (1)
- Homework Problems on Forces, Motion and EnergyDocumento7 pagineHomework Problems on Forces, Motion and EnergyQuinnNgo100% (1)
- Focal Length of Thin LensesDocumento10 pagineFocal Length of Thin LensesAlixandrea Kassandra Jurial100% (1)
- Sample Calculus AOPSDocumento7 pagineSample Calculus AOPS45698722Nessuna valutazione finora
- New Modern PhysicsDocumento3 pagineNew Modern PhysicsshabbirtechnicalNessuna valutazione finora
- Derivatives Cheat SheetDocumento3 pagineDerivatives Cheat SheetalexNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear Physics A Level RevisionDocumento32 pagineNuclear Physics A Level Revisionsupniggas80% (5)
- Optics Cheat SheetDocumento1 paginaOptics Cheat SheetadamhamelehNessuna valutazione finora
- Reflection and Refraction of Light: By: Fajri Mohammed Ophthalmology Resident (R1) JUDO Oct.2021Documento61 pagineReflection and Refraction of Light: By: Fajri Mohammed Ophthalmology Resident (R1) JUDO Oct.2021abo kooNessuna valutazione finora
- HPH103 - Waves and Optics 1 - Lecture # 10-1Documento45 pagineHPH103 - Waves and Optics 1 - Lecture # 10-1Praise NehumambiNessuna valutazione finora
- Light Chapter'sDocumento24 pagineLight Chapter'sPratik ChavanNessuna valutazione finora
- G10 Science Q2-Week 8 - Properties of MirrorDocumento29 pagineG10 Science Q2-Week 8 - Properties of MirrorKarina GentonNessuna valutazione finora
- Image Formation and Ray Diagrams Involving MirrorsDocumento75 pagineImage Formation and Ray Diagrams Involving Mirrorsjohn charles garalde100% (1)
- Chapter 19 - Physical Science RevDocumento33 pagineChapter 19 - Physical Science Revapi-30718309Nessuna valutazione finora
- MIRRORDocumento62 pagineMIRRORHoneyNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 TH Class NotesDocumento27 pagine10 TH Class NotesPavana Kumar KallakuriNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 7 5Documento29 pagineLecture 7 5mysaustine1Nessuna valutazione finora
- P102LN2324Documento35 pagineP102LN2324Ayush BirlaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesDocumento78 pagineThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesWarren Dela CernaNessuna valutazione finora
- Formation of ImagesDocumento32 pagineFormation of ImagesBlueaux roseNessuna valutazione finora
- Photographic Composition: Principles of Image DesignDa EverandPhotographic Composition: Principles of Image DesignValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (10)
- Ec III Year Ieo Paper IDocumento9 pagineEc III Year Ieo Paper IAakash AkronosNessuna valutazione finora
- Visual Basic NetDocumento2 pagineVisual Basic NetAakash AkronosNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Reg ExDocumento26 pagine4 Reg ExasinawahabNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabi GATE2017 PDFDocumento73 pagineSyllabi GATE2017 PDFAnkit Kumar AJNessuna valutazione finora
- Form NESTDocumento1 paginaForm NESTAakash AkronosNessuna valutazione finora
- Handout35 PDFDocumento12 pagineHandout35 PDFAakash AkronosNessuna valutazione finora
- MARVELS Instrument PrimerDocumento24 pagineMARVELS Instrument PrimerAakash AkronosNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Wiring Estimation and Installation GuideDocumento90 pagineElectrical Wiring Estimation and Installation GuideAakash AkronosNessuna valutazione finora
- P An Integer Number, R Radius of Curvature of The Curved Face of The Plano Convex LensDocumento3 pagineP An Integer Number, R Radius of Curvature of The Curved Face of The Plano Convex LensAakash AkronosNessuna valutazione finora
- Probability For Dummies Cheat Sheet - For DummiesDocumento3 pagineProbability For Dummies Cheat Sheet - For DummiesBrian O'ConnellNessuna valutazione finora
- MARVELS Instrument PrimerDocumento24 pagineMARVELS Instrument PrimerAakash AkronosNessuna valutazione finora
- Emo Spark Press KitDocumento5 pagineEmo Spark Press KitAakash AkronosNessuna valutazione finora
- Penetration TestingAdditional Insights GeorgiaDocumento27 paginePenetration TestingAdditional Insights GeorgiaconqueroroNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Chemistry Numerical Question BankDocumento4 pagineEngineering Chemistry Numerical Question BankAakash AkronosNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 English Core Impq ReadingDocumento21 pagine12 English Core Impq ReadingHarsh VardhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics 12th PracticalDocumento8 paginePhysics 12th PracticalAakash AkronosNessuna valutazione finora
- Jee Advanced 2014 PDFDocumento39 pagineJee Advanced 2014 PDFAnonymous BnbPSoovbNNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Salt Analysis CheatsheetDocumento4 pagineChemistry Salt Analysis CheatsheetSumit Dhall74% (50)
- Soi-14 Viettel Vtu-Bha 25kmDocumento1 paginaSoi-14 Viettel Vtu-Bha 25kmhabuon060687Nessuna valutazione finora
- SEMINAR Silicon Photonics PresentationDocumento25 pagineSEMINAR Silicon Photonics PresentationARAVIND100% (5)
- Radiation Detection Instrumentation Fundamentals Rev0Documento203 pagineRadiation Detection Instrumentation Fundamentals Rev0Siti HannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Standard: IPS-E-IN-120Documento49 pagineEngineering Standard: IPS-E-IN-120charleselitb92Nessuna valutazione finora
- HFSSintro PDFDocumento45 pagineHFSSintro PDFuserdceNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 7 Components of Optical Instruments - IIIDocumento12 pagineChap 7 Components of Optical Instruments - IIISkriikkNessuna valutazione finora
- Heliotherapy 121003100409 Phpapp02Documento26 pagineHeliotherapy 121003100409 Phpapp02Ajay DherwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 Week - Q2 - Physical ScienceDocumento2 pagine11 Week - Q2 - Physical ScienceAngel Guillermo Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 External DosimetryDocumento129 pagineUnit 4 External DosimetryHashir SaeedNessuna valutazione finora
- PYL560 Applied Optics: Anurag SharmaDocumento74 paginePYL560 Applied Optics: Anurag SharmaValma GestNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Space EnvironmentDocumento250 pagineIntroduction To Space EnvironmentIKOROMILOS100% (1)
- Modern Physics PDFDocumento46 pagineModern Physics PDFMarcos ShepardNessuna valutazione finora
- Visible Light Is One Way Energy Moves AroundDocumento2 pagineVisible Light Is One Way Energy Moves AroundNash Gemar Braga EvangelistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Optical Signal DegradationDocumento53 pagineChapter 4 Optical Signal DegradationAhmed AmrNessuna valutazione finora
- Development OfpointkernelDocumento13 pagineDevelopment Ofpointkernelbilguun_byambadorjNessuna valutazione finora
- X-Ray Production and Interactions GuideDocumento111 pagineX-Ray Production and Interactions GuidexhibaxNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiber Optic Training - 09-24-2009Documento3 pagineFiber Optic Training - 09-24-2009Everthing ON REQUESTNessuna valutazione finora
- Uses of Electromagnetic WavesDocumento4 pagineUses of Electromagnetic WavesMarlou PrincesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Physics RegulationDocumento2 pagineMedical Physics RegulationnNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit VDocumento2 pagineUnit VSivakumar KNessuna valutazione finora
- Saudi Aramco radiation protection requirements for analytical x-ray equipmentDocumento4 pagineSaudi Aramco radiation protection requirements for analytical x-ray equipmentzapNessuna valutazione finora
- (166 Marks) : (1 Mark)Documento32 pagine(166 Marks) : (1 Mark)Divit RayNessuna valutazione finora
- Oxidative Mechanisms of Biological Activity of Low-Intensity Radiofrequency RadiationDocumento16 pagineOxidative Mechanisms of Biological Activity of Low-Intensity Radiofrequency RadiationNikko Giovanni Sagredo MorenoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Simultaneous Determination of Caffeine and Acetylsalicylic Acid in An Analgesic by Ultraviolet SpectrophotometryDocumento8 pagineThe Simultaneous Determination of Caffeine and Acetylsalicylic Acid in An Analgesic by Ultraviolet SpectrophotometryAthirah RaZi40% (5)
- Modern Physics Target QuestionDocumento2 pagineModern Physics Target QuestionAnkur GoyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluoroscopy imaging technique overviewDocumento5 pagineFluoroscopy imaging technique overviewDidimo Antonio Paez ClavijoNessuna valutazione finora
- Density & Neutron LogDocumento54 pagineDensity & Neutron LogHamdan Hamzah100% (1)
- 7th LightDocumento29 pagine7th Lightsmi_santhoshNessuna valutazione finora
- RAPHEX Diagnostic Physics 2014 - QuestionsDocumento30 pagineRAPHEX Diagnostic Physics 2014 - QuestionsElvis Sammartino100% (5)
- Light Prism Pandathe Test2 Question PaperDocumento4 pagineLight Prism Pandathe Test2 Question Paperboltu100% (1)