Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Caricato da
Paul CubacubTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Caricato da
Paul CubacubCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Cubacub, Paul John A.
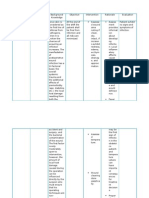
BSN402 / Group 8A Patient: FND Age: 62 Diagnosis: T/C UTI/ DM2 poorly controlled/ hypercholesterolemia/ hypertriglyceridemia/ pulmonary Tb/ Anime 2nd degree to renal disease DOA: Jan. 17, 2014
Nursing Care Plan
Nursing Diagnosis
Risk for infection related to Preexisting respiratory infection and UTI secondary to Diabetes Mellitus II Cues/Data Paresthesia on lower extremities Anemia related to renal disease
Analysis
Respiratory tract infections are responsible for a significant number of medical appointments by persons with DM compared to those without DM. Streptococcus pneumoniae and influenza virus The most frequent respiratory infections associated with DM are caused by Streptococcus pneumoniaeand influenza virus. Persons with DM six times more likely need
Goal and Objectives
Goal: After 8 hours of nursing intervention the patient will be able to identify interventions to prevent/reduce the risk of infection
Nursing Interventions
Rationale
Evaluation
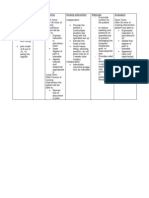
Independent Establish rapport
to obtain patients trust and cooperation To obtain baseline data facilitates grieving the loss
Take and record vital signs Encourage expression of feelings and anxieties Promote good hand washing by staff and patient. Encourage to
Goal: After 8 hours of nursing intervention the patient was able to identify interventions to prevent/reduce the risk of infection Yes_ No_ Why? Objective: After 4 hours of nursing intervention the patient will be able to: Establish good working relationship with health
Objective: After 4 hours of nursing intervention the patient will be able to: Establish good working relationship
Reduces risk of crosscontaminatio n. to prevent
V/S as follows: T: 36.2 C PR:73 RR:25 BP:160/80
hospitalization duringinfluenza epidemics than non-diabetic patients. Diabetes is also a common coexisting condition and a risk factor for complications in patients with H1N1 (pandemic influenza virus) infection. Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are more prevalent in individuals with DM and may evolve to complications and/or serious manifestations. The main risk factors for UTI in DM are: inadequate glycemic control, duration of DM, diabetic microangiopathy, impaired leukocyte function, recurrent vaginitis, and anatomical and functional abnormalities of the urinary tract. Reference: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov /pmc/articles/PMC3354930/
with health care providers
Have knowledge and awareness about his condition and the disease process
increase fluid intake-increase Vit. C in the dietincrease CHON intake if not contraindicated
dehydration to boost immune system and promote collagen formation-for tissue repair Peripheral circulation maybe impaired placing patient at increased risk for skin irritation or breakdown and infection. Facilitates lung expansion and reduces risk of aspiration. These measures reduce stasis of secretions in the lungs and bronchial tree. When stasis occurs,
care providers Yes_ No_ Why? Have knowledge and awareness about his condition and the disease process Yes_ No_ Why? Practice proper hand washing Yes_ No_ Why? Know interventions to facilitate early recognition of infection Yes_ No_ Why?
Provide conscientious skin care, gently massage bony areas. Keep the skin dry, linens dry and wrinkle free.
Practice proper hand washing Place in semi fowlers position. Know intervention s to facilitate early recognition of infection
Encourage coughing and deep breathing; consider use of incentive spirometer.
pathogens can cause upper respiratory infections, including pneumonia. Provide a safe and quiet environment Take Due meds on time Collaborative Obtain specimen for culture and sensitivities as indicated To promote pts comfort To meet the bodys requirements Identifies organisms so that most appropriate drug therapy can be instituted. Early treatment may help prevent sepsis.
Administer antibiotics as appropriate.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Delayed Surgical Recovery Nursing Care PlanDocumento3 pagineDelayed Surgical Recovery Nursing Care PlanMichala100% (3)
- Care Plan Risk For Infection 2Documento3 pagineCare Plan Risk For Infection 2Brian Bracher93% (43)
- Risk For InfectionDocumento18 pagineRisk For InfectionValiant Baybay0% (1)
- NCP-Risk For InfectionDocumento4 pagineNCP-Risk For InfectionMarianne May Loquias100% (4)
- NCP Ineffective CopingDocumento3 pagineNCP Ineffective CopingAqua RentoNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessme NT Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective CuesDocumento3 pagineAssessme NT Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective CuesTricia100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: WWW - Unp.edu - PHDocumento4 pagineNursing Care Plan: WWW - Unp.edu - PHKrizha Angela Nicolas0% (1)
- NCP For Infection !Documento1 paginaNCP For Infection !Clariss AlotaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocumento2 pagineNCP Risk For InfectionI Am SmilingNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Impaired SkinDocumento2 pagineNCP Impaired Skinarjay2306_obcq100% (1)
- Acute Pain NCPDocumento1 paginaAcute Pain NCPJed AvesNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocumento6 pagineNCP Risk For InfectionKeoni Ruggiero VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For InfectionDocumento1 paginaNCP For InfectionNathaniel EllanoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion R/T Space Occupying Lesion (Neuroblastoma On Frontal Lobe)Documento4 pagineNCP - Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion R/T Space Occupying Lesion (Neuroblastoma On Frontal Lobe)Carl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (4)
- Risk For Infection NCP Ortho JadDocumento1 paginaRisk For Infection NCP Ortho JadjadpauloNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Diagnosis Background Study Inference Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocumento5 pagineNursing Diagnosis Background Study Inference Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationAubrey SungaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nature of TechnopreneurshipDocumento4 pagineNature of Technopreneurshiprichard nuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Key Issues Desired Outcomes Interventions Actual OutcomesDocumento4 pagineKey Issues Desired Outcomes Interventions Actual OutcomesAngel FiloteoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP UtiDocumento2 pagineNCP UtiyasiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk For InfectionDocumento3 pagineRisk For InfectioncamziiiNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For PCAPCDocumento6 pagineNCP For PCAPCEnrique Lu100% (1)
- Flank Pain, Anxiety...Documento7 pagineFlank Pain, Anxiety...reneighdNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Impaired Skin IntegrityDocumento4 pagineNCP - Impaired Skin IntegrityColette Marie PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP MCMC Post OperativeDocumento3 pagineNCP MCMC Post OperativeKristiyanong KabataanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento4 pagineCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjomsportg0% (1)
- Discharge Plan For Dengue Fever 1Documento4 pagineDischarge Plan For Dengue Fever 1Cecille Ursua0% (1)
- NCP Impaired Skin IntegrityDocumento2 pagineNCP Impaired Skin IntegrityAshley Kate SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- CHN NCPDocumento2 pagineCHN NCPIna Marie Calungcaguin Castro100% (1)
- NCP HemoDocumento2 pagineNCP HemoJigs HechNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Risk For Bleeding 3Documento2 pagineNCP Risk For Bleeding 3Jayson Olile100% (1)
- Cancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For InfectionDocumento2 pagineCancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For InfectionAngie MandeoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Risk For InfectionDocumento2 pagineNCP - Risk For InfectionJet Bautista100% (1)
- NCP-Risk For InfectionDocumento2 pagineNCP-Risk For InfectionJea Joel Mendoza100% (1)
- NCP Loss of AppetiteDocumento5 pagineNCP Loss of AppetiteStenneli Gumban Trojillo50% (2)
- Risk For InfectionDocumento3 pagineRisk For Infectionprickybiik100% (1)
- Risk For InfectionDocumento2 pagineRisk For InfectionSuzette Rae Tate0% (1)
- NCP For Post Op Wound and FractureDocumento6 pagineNCP For Post Op Wound and FractureAlyssa Marie0% (1)
- Assessment Objectives: "Masakit Lagi Yung Lalamunan NyaDocumento3 pagineAssessment Objectives: "Masakit Lagi Yung Lalamunan Nyaangel_pearl413100% (2)
- NCP: Patient With A Pressure UlcerDocumento2 pagineNCP: Patient With A Pressure UlcerICa MarlinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Infection NCPDocumento1 paginaInfection NCPMsOrangeNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP UtiDocumento1 paginaNCP UtiElaisa Mae Delos SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP ImmobilityDocumento2 pagineNCP Immobilityxxxcamzxxx67% (6)
- Acute Pain Related To Inflammation of Tissues Secondary To AppendicitisDocumento2 pagineAcute Pain Related To Inflammation of Tissues Secondary To AppendicitisRachel SaavedraNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Acute Pain Stomach CancerDocumento2 pagineNCP - Acute Pain Stomach CancerJohn Michael TaylanNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Pain NCPDocumento2 pagineAcute Pain NCPCaren AntonioNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Risk For Infection Related To Post Surgical IncisionDocumento2 pagineNCP Risk For Infection Related To Post Surgical IncisionJyedenn Ponce100% (2)
- Update in Managing Cough Cold and Flu - Knowledge-Based ActivityDocumento11 pagineUpdate in Managing Cough Cold and Flu - Knowledge-Based ActivityMohamed OmerNessuna valutazione finora
- I and I Module Infectious DisordersDocumento23 pagineI and I Module Infectious DisordersCaitlynNessuna valutazione finora
- I and I MODULE INFECTIOUS DISORDERSDocumento23 pagineI and I MODULE INFECTIOUS DISORDERSJeffrey GazmenNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Process Lab FinalDocumento8 pagineNursing Process Lab FinalGary Mikha SitohangNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Care Organization To Face Dengue EpidemicsDocumento15 pagineMedical Care Organization To Face Dengue EpidemicsepadmoralNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Care Organization To Face Dengue EpidemicsDocumento12 pagineMedical Care Organization To Face Dengue EpidemicsDAVIDSERGIO39946Nessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Elective (Risk For Infection)Documento1 paginaNCP Elective (Risk For Infection)student_019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Five Summary of Findings, Conclusion and RecommendationsDocumento5 pagineChapter Five Summary of Findings, Conclusion and RecommendationsKojo AduNessuna valutazione finora
- Pulmonary TBDocumento13 paginePulmonary TBAmanda ScarletNessuna valutazione finora
- Infections in ICUDocumento7 pagineInfections in ICUNikolay ToméNessuna valutazione finora
- TB Dots: Public Health Nursing Responsibilities (Adult TB)Documento7 pagineTB Dots: Public Health Nursing Responsibilities (Adult TB)Roevanie Corpuz CagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Prevention and Control of DiseaseDocumento48 paginePrevention and Control of Diseasemanoti swamiNessuna valutazione finora
- TB Nursing CareplanDocumento14 pagineTB Nursing CareplanEstherThompson100% (1)
- Tbhiv Infectioncontrol AddendumDocumento43 pagineTbhiv Infectioncontrol AddendumBich Le Thi NgocNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento3 pagineNCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionPaul Cubacub0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues and Data Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plan: Cues and Data Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationPaul Cubacub100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues and Data Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plan: Cues and Data Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationPaul Cubacub100% (1)
- Definition of PyelonephritisDocumento3 pagineDefinition of PyelonephritisPaul CubacubNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Assessment: Physiological Psychological Sociological SpiritualDocumento5 pagineNursing Assessment: Physiological Psychological Sociological SpiritualFay DalanonNessuna valutazione finora
- Elitrol I Elitrol Ii: Français - FR English - EN Español - ES Português - PTDocumento2 pagineElitrol I Elitrol Ii: Français - FR English - EN Español - ES Português - PTYousra ZeidanNessuna valutazione finora
- Microbiology and Parasitology LectureDocumento5 pagineMicrobiology and Parasitology LectureMark TindoyNessuna valutazione finora
- 69-Article Text-283-2-10-2022Documento8 pagine69-Article Text-283-2-10-2022EfanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pub Personality TypeDocumento16 paginePub Personality TypeYessika Adelwin NataliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Constipation NCPDocumento2 pagineConstipation NCPjudaperlNessuna valutazione finora
- Histrionic Personality DisorderDocumento2 pagineHistrionic Personality DisorderRodeneNessuna valutazione finora
- (Pharma-TRANS) 2.09 Geriatric Pharmacology: D. Protein BindingDocumento2 pagine(Pharma-TRANS) 2.09 Geriatric Pharmacology: D. Protein BindingStudy ReviewersNessuna valutazione finora
- NNNJKDocumento7 pagineNNNJKFelix EquinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anxiety Disorder Teaching PlanDocumento21 pagineAnxiety Disorder Teaching PlanEcaroh Hew Smailliw0% (1)
- MRI Vs CT ScanDocumento10 pagineMRI Vs CT ScanMunazzah IjazNessuna valutazione finora
- Rule 15Documento2 pagineRule 15begenyolNessuna valutazione finora
- Host Parasite InteractionDocumento20 pagineHost Parasite InteractionRhomizal MazaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Hospital Design: Flow Chart of DepartmentsDocumento15 pagineHospital Design: Flow Chart of DepartmentsAbirami80% (5)
- Hepatitis C in PregDocumento4 pagineHepatitis C in PregYwagar YwagarNessuna valutazione finora
- A 55-Year-Old Woman With Shock and Labile Blood PressureDocumento11 pagineA 55-Year-Old Woman With Shock and Labile Blood PressureMr. LNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function: Page 1. Introduction Page 2. GoalsDocumento6 pagineAnatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function: Page 1. Introduction Page 2. GoalsUta Provinsiana SukmaraNessuna valutazione finora
- NycoCard Brochure 01Documento2 pagineNycoCard Brochure 01TimNessuna valutazione finora
- Karakteristik Penderita Nonarteritic Anterior DENPASAR TAHUN 2014 - 2015Documento6 pagineKarakteristik Penderita Nonarteritic Anterior DENPASAR TAHUN 2014 - 2015antrrtna anthraxNessuna valutazione finora
- Conns Current Therapy 2021 Rick D Kellerman Full ChapterDocumento67 pagineConns Current Therapy 2021 Rick D Kellerman Full Chapterkelly.caughlin506100% (2)
- Patient CounsellingDocumento46 paginePatient CounsellingKeith OmwoyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Life Support in Infants and ChildrenDocumento9 pagineBasic Life Support in Infants and ChildrenMelissa Espinoza PeñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Band Keratopathy ArticleDocumento9 pagineBand Keratopathy ArticleDecha Pradea MaulinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetic Foot InfectionDocumento26 pagineDiabetic Foot InfectionAmanda Abdat100% (1)
- Biomentors (MCDB 1B) - Immunology Quiz (ANSWERS)Documento2 pagineBiomentors (MCDB 1B) - Immunology Quiz (ANSWERS)Tiff VoNessuna valutazione finora
- ActinobacillosisDocumento17 pagineActinobacillosisKhalid Gul100% (1)
- Lplpo Agustus 2017Documento66 pagineLplpo Agustus 2017Selly Wijaya BermawiNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Birth DefectsDocumento40 pagine6 Birth DefectsjulieNessuna valutazione finora
- FHTMonitoringDocumento21 pagineFHTMonitoringlaarnie100% (1)
- Parameters of Automated Cell Counter Automation in Hematology Laboratory and CBC Via Automated Blood AnalyzerDocumento40 pagineParameters of Automated Cell Counter Automation in Hematology Laboratory and CBC Via Automated Blood AnalyzerArslan Arshad100% (1)