Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
AP Micro Formula Packet
Caricato da
lhv48Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
AP Micro Formula Packet
Caricato da
lhv48Copyright:
Formati disponibili
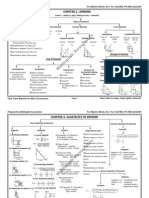
Formula Chart AP Microeconomics Unit 2 Supply and Demand Total Revenue = price x quantity Total revenue test P P P P and
nd TR and TR and TR and TR then demand elastic then demand inelastic then demand elastic then demand inelastic Unit 3 Production Markets Revenue: Total Revenue = price x quantity TR Q output
Average Revenue =
Marginal Revenue = Coefficient of price elasticity of demand:
TR Q output
TR @ maximum when MR goes negative % quantity demanded % price Coefficient > 1 = elastic demand Coefficient < 1 = inelastic demand Coefficient = 1 = unit elastic demand Coefficient = = perfectly elastic demand Coefficient = 0 = perfectly inelastic demand Cross elasticity of demand: comparing 2 items: % quantity of 1st item % price of 2nd item Cross elasticity coefficient positive = items substitute for each other Cross elasticity coefficient negative = items complement each other Income elasticity of demand: % quantity % income In perfect competition, MR = price (demand) for individual sellers In perfect competition, individual seller price = market price (price taker) In imperfect competition, MR < price (Demand) In imperfect competition, individual seller IS THE MARKET (price maker) Cost: Total Cost = Total fixed cost + Total average cost Total Cost = unit cost x quantity output Average fixed cost = TFC Q output TVC Q output
Average variable cost =
Income elasticity coefficient positive = normal good Income elasticity coefficient negative = inferior good Supply elasticity: % quantity supplied % price Tax Revenue = (Price w/tax price seller receives) x Quantity
Average total cost =
TC Q output
Average total cost = AFC + AVC Marginal cost = TC Q output
Product (aka output): Average product = Total product Q input TP Q input
Utility maximization rule Marginal Utility of Good A Unit cost of A
Marginal product =
Marginal Utility of Good B Unit cost of B
TP @ maximum when MP goes negative In perfect competition market supply = individual seller cost curves or S = mcs
Unit 3 Production Markets continued Profit: Profit maximization rule for all markets: Marginal Revenue = Marginal Cost or MR = MC Total cost + total profit = total revenue also TR = Price x quantity Total cost = unit cost x quantity Total profit = unit profit x quantity Unit 4 Resource Markets Marginal revenue product = TR Q of resource
Unit 5 - Government Externalities: MSB = MSC Market Equilibrium MPC = MPB Marginal Private Cost = Marginal Private Benefit
Negative production externality (overallocation): Social cost > private cost Example: pollution Fix: taxes, regulations Positive production externality (underallocation): Social cost < private cost Example: technology Fix: subsidies, regulations Negative consumption externality (overallocation): Social benefit < private benefit Examples: cigarettes, alcohol, gambling Fix: taxes, regulations Positive consumption externality (underallocation): Social benefit > private benefit Examples: education, vaccines, smoke alarms Fix: taxes, subsidies or regulations
Marginal resource cost aka Marginal factor cost
T resource C Q of resource
Profit maximization rule when purchasing a single resource:
Marginal Revenue Product = Marginal Resource Cost
or MRP = MRC In perfect competition market demand for labor = demand of all individual purchasers of labor or D = mrps In perfect competition, MRP = product price x marginal product In imperfect competition, MRP = product price x marginal product MINUS price change on previous units sold In perfect competition, market wage = individual firms MRC (wage taker) In imperfect competition (monopsony), wage is MRP = MRC @ labor supply curve (wage maker) /MRC lies above S curve
Least Cost Rule Marginal product of labor = Unit price of labor Marginal product of capital Unit price of capital
Profit maximization rule for purchasing multiple resources Marginal product of labor Unit price of labor = Marginal product of capital = 1 Unit price of capital
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 2000 AP Microeconomics Released ExamDocumento17 pagine2000 AP Microeconomics Released ExamJoseph Weng100% (3)
- AP® Macroeconomics Crash Course, For the 2021 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeDa EverandAP® Macroeconomics Crash Course, For the 2021 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeNessuna valutazione finora
- Essential Graphs For AP MicroeconomicsDocumento5 pagineEssential Graphs For AP Microeconomicsjlvmrbd777100% (7)
- AP Macroeconomics Review Sheet 2013Documento7 pagineAP Macroeconomics Review Sheet 2013Crystal Farmer100% (4)
- Microeconomics Class NotesDocumento79 pagineMicroeconomics Class Notesdec100% (2)
- Microeconomics Cue CardDocumento4 pagineMicroeconomics Cue CardPaul FareseNessuna valutazione finora
- Microeconomics Test Bank and Solutions ManualDocumento7 pagineMicroeconomics Test Bank and Solutions ManualTestBank0% (13)
- AP Macroeconomics Study GuideDocumento39 pagineAP Macroeconomics Study GuideAustin Chungsta100% (1)
- Microeconomics HomeworkDocumento16 pagineMicroeconomics HomeworkTaylor Townsend100% (1)
- AP Microecon GraphsDocumento12 pagineAP Microecon GraphsQizhen Su100% (1)
- MicroeconomicsDocumento10 pagineMicroeconomicsVishal Gattani100% (5)
- Microeconomics - ECO402 Final Term QuizDocumento28 pagineMicroeconomics - ECO402 Final Term QuizSuleyman KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Microeconomics Course NotesDocumento37 pagineAP Microeconomics Course Notescandy_am05100% (4)
- Essential Graphs For MicroeconomicsDocumento12 pagineEssential Graphs For MicroeconomicsSayed Tehmeed AbbasNessuna valutazione finora
- Microeconomics FormulasDocumento1 paginaMicroeconomics FormulasmarghebroganNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank for Introductory Economics: And Introductory Macroeconomics and Introductory MicroeconomicsDa EverandTest Bank for Introductory Economics: And Introductory Macroeconomics and Introductory MicroeconomicsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- MicroEconomics Practice TestDocumento7 pagineMicroEconomics Practice TestDavid BurfordNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Macroeconomics TestDocumento10 pagineAP Macroeconomics TestTomMusic100% (1)
- Midterm Exam Code - 01Documento7 pagineMidterm Exam Code - 01Phương MaiNessuna valutazione finora
- 2000 AP Micro Test 1Documento13 pagine2000 AP Micro Test 1newtonokewoye75% (4)
- Intermediate Microeconomics Exam 1Documento6 pagineIntermediate Microeconomics Exam 1Chet GemaehlichNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Macroeconomic Models and Graphs Study GuideDocumento23 pagineAP Macroeconomic Models and Graphs Study GuideAznAlexT90% (20)
- Microeconomics Study Sheet Microeconomics Study Sheet: More Free Study Sheet and Practice Tests atDocumento3 pagineMicroeconomics Study Sheet Microeconomics Study Sheet: More Free Study Sheet and Practice Tests atanandsemails6968100% (1)
- AP Economics FRQ ReviewDocumento6 pagineAP Economics FRQ ReviewBilal QureshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Microeconomics NotesDocumento26 pagineIntroduction To Microeconomics NotesChristine Keh100% (2)
- Eco201 Exam1Documento8 pagineEco201 Exam1sonhai0901100% (1)
- Macroeconomics Key GraphsDocumento5 pagineMacroeconomics Key Graphsapi-243723152Nessuna valutazione finora
- AP Macro Economics 2005 MCDocumento14 pagineAP Macro Economics 2005 MCJames LiNessuna valutazione finora
- Sp15 Micro Study Questions-6Documento33 pagineSp15 Micro Study Questions-6Ahmed MahmoudNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Microeconomics Lecture NotesDocumento57 pagineAdvanced Microeconomics Lecture NotesAnders Munk-NielsenNessuna valutazione finora
- Microeconomics: Sample Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocumento6 pagineMicroeconomics: Sample Multiple-Choice Questionskunalshah81Nessuna valutazione finora
- Microeconomics Summary NotesDocumento14 pagineMicroeconomics Summary NotesNg Chai SheanNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Macroeconomics Study SheetDocumento3 pagineAP Macroeconomics Study SheetepiphanyyNessuna valutazione finora
- Microecon Cheat Sheet - FinalDocumento3 pagineMicroecon Cheat Sheet - FinalDananana100100% (3)
- Economics Edexcel AS Level Microeconomics GlossaryDocumento7 pagineEconomics Edexcel AS Level Microeconomics Glossarymarcodl18Nessuna valutazione finora
- AP Microeconomics Multiple-ChoiceDocumento13 pagineAP Microeconomics Multiple-Choicethemadhatter10667% (3)
- Microeconomics SummaryDocumento22 pagineMicroeconomics SummaryChristie Osarenren100% (1)
- Economics - Markets With Asymmetric InformationDocumento21 pagineEconomics - Markets With Asymmetric Informationragneshr100% (1)
- Macroeconomics Class NotesDocumento83 pagineMacroeconomics Class NotesGreta Schneider100% (1)
- Principles of Microeconomics - SyllabusDocumento10 paginePrinciples of Microeconomics - SyllabusKatherine Sauer0% (1)
- Micro Review PacketDocumento18 pagineMicro Review Packetlhv48100% (1)
- Worksheet 3-Indifference CurveDocumento1 paginaWorksheet 3-Indifference CurvearushiNessuna valutazione finora
- 90,95,2000 Macro Multiple ChoiceDocumento37 pagine90,95,2000 Macro Multiple ChoiceAaron TagueNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Notes On Intermediate MicroeconomicsDocumento69 pagineLecture Notes On Intermediate MicroeconomicsSayemin Naheen100% (2)
- Econ Cheat SheetDocumento3 pagineEcon Cheat SheetadviceviceNessuna valutazione finora
- Mock Test Questions Micro e ConsDocumento10 pagineMock Test Questions Micro e Conscalz..100% (1)
- Econ 301 Past Final Exams With SolutionsDocumento18 pagineEcon 301 Past Final Exams With SolutionsmauveskiersNessuna valutazione finora
- ECO401 Economics 10 Midterm Solved Papers Subjective and Objective in For Exam Preparation Spring 2013Documento0 pagineECO401 Economics 10 Midterm Solved Papers Subjective and Objective in For Exam Preparation Spring 2013Muhammad Ayub100% (1)
- Lecturer Economics MCQs 1 PDFDocumento36 pagineLecturer Economics MCQs 1 PDFJaleel RounaqNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Micro 4-4 OligopoliesDocumento36 pagineAP Micro 4-4 OligopoliesXauen ZirpoloNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz 5 - Microeconomics Pindyck and Rubinfeld MCQ QuestionsDocumento4 pagineQuiz 5 - Microeconomics Pindyck and Rubinfeld MCQ Questionsanusha500Nessuna valutazione finora
- Intermediate Microeconomics SyllabusDocumento6 pagineIntermediate Microeconomics SyllabusAlbert RofiNessuna valutazione finora
- Extended Response Questions From IB Test Bank Responses MICRO MACRO Nkv2zcDocumento28 pagineExtended Response Questions From IB Test Bank Responses MICRO MACRO Nkv2zcAlexander Betz100% (1)
- Intermediate Microeconomics Quiz 2Documento5 pagineIntermediate Microeconomics Quiz 2paterneNessuna valutazione finora
- Macro Study GuideDocumento21 pagineMacro Study GuideJohn WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework MicroeconomicsDocumento4 pagineHomework MicroeconomicsNguyễn Bảo Ngọc100% (1)
- Chapters 5-8 Microeconomics Test Review QuestionsDocumento157 pagineChapters 5-8 Microeconomics Test Review Questionscfesel4557% (7)
- Snazzlefrags Microeconomics Clep Study NotesDocumento4 pagineSnazzlefrags Microeconomics Clep Study NotesEllenNessuna valutazione finora