Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Footing MCN
Caricato da
nsutharCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Footing MCN
Caricato da
nsutharCopyright:
Formati disponibili
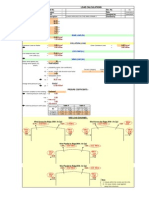
DETAILING OF STEEL IN FOOTINGS
(For class held on 13th March 07) Dr. M. C. Nataraja, Professor, Civil Engineering Department, Sri Jayachamarajendra Collge of Engineering, Mysore-5a70 006 Phone: 0821-2343521, 9880447742 e-mail: nataraja96@yahoo.com Footing: The function of a footing or a foundation is to transmit the load form the structure to the underlying soil. The choice of suitable type of footing depends on the depth at which the bearing strata lies, the soil condition and the type of superstructure. Types of footing Following are the different types of footing used for concrete structure. Refer figure 1. 1. Isolated footing 2. Combined footings 3. Strap footing 4. Mat or raft foundation 5. Pile foundation Isolated footings are provided under each column and may be square, rectangular, or circular in plan. Footing may be flat or tapered. Combined footings are provided to support two or more column loads. These may be continuous with rectangular or trapezoidal in plan as shown. Combined footings become necessary under the following circumstances: when the isolated footings overlap. when the exterior column is close to the property line with the result symmetrical isolated footing can not be provided.
Strap footing is one of the types of combined types of combined. It consists of an isolated footing of two columns connected by a beam called strap beam. The strap beam does not remain in contact with the soil and thus does not transfer any load to the soil. This is provided when one of the columns is on the property line.
The mat foundation is provided when the soil is having very low bearing capacity and or when columns loads are heavy, the required footing area becomes very large and uneconomical.
ISOLATED FOOTINGS PROPERTY LINE
COMBINED FOOTING
COMBINED FOOTING
STRAP BEAM
STRAP FOOTING
MAT FOUNDATION
FIGURE 1. TYPES OF FOOTINGS
Detailing: Following points are to be kept in mind in detailing. Size of footing Depth at footing Depth of footing edge Nominal and effective cover Development length Depth of foundation
Minimum and maximum steel Spacing of bars and stirrups
Detailing of steel in rectangular footing as per IS:456-2000 In rectangular footing the reinforcement parallel to the long direction shall be distributed uniformly across the width of the footing. In short direction, since the support provided to the footing by the column is concentrated near the middle, the moment per unit length is largest i.e., the curvature of the footing is sharpest immediately under the column and decreases in the long direction with the increasing distance from the column. For this reason larger steel area is needed in the central portion and is determined in accordance with the equation given below.
Ast , central band Ast ,total , short direaction
2 ( L / B) + 1
Reminder of the steel is distributed uniformly in the outer portions of the footing (end bands)
Development length= Ldt=
f s . s 4 bd
Ldt = 47s for M20 concrete and Fe 415 steel Problems: 1. An isolated footing is to be provided for a column of section 400 mm x 400 mm. The following details re given: Height of the column =3m Main reinforcement in column = 4 Nos. 16 mm diameter. Transverse reinforcement = 6 mm at 220 mm c/c Plan size of footing = 2.7 m x 2.7 m Depth of footing at column face = 500 mm Depth of footing at edge = 150 mm Depth of foundation = 1000 mm Footing reinforcement = a mesh of 20 mm diameter steel at 250 mm c/c. Grade of concrete= M20 Grade of steel = Fe415
Draw to a suitable scale the following: a. Plan b. Sectional Elevation c. Prepare bar bending schedule Solution: Development length in tension = 47 = 47 x 16= 752 mm Depth at junction = 500 mm Leg length available for column bars = Ldt 500 = 252 mm < 300 mm. Provide 300 mm minimum. Development length of 20 mm bars in footing = 47 x 20 = 940 mm This is provided by the horizontal projection of bars. Bars need not be bent at ends in to the depth of footing. Number of bars in footing = 11 Numbers at 200 mm c/c with a side cover of 100 mm. Width of footing= 10 x 250 + 100 x 2 =2700 mm Follow all specification of SP 34 and prepare the drawing. Exercise problems 2. Exam: December/January 2007 An isolated footing is to be provided for a column of section 400 mm x 400 mm. The following details re given: Height of the column =3m Main reinforcement in column = 4 Nos. 16 mm diameter. Transverse reinforcement = 6 mm at 220 mm c/c Plan size of footing = 3.2 m x 3.2 m Depth of footing at column face = 500 mm Depth of footing at edge = 300 mm Footing reinforcement = a mesh of 16 mm diameter steel at 180 mm c/c. Grade of concrete= M20 Grade of steel = Fe415 20 Marks
Draw to a suitable scale the following: d. Plan e. Sectional Elevation f. Prepare bar bending schedule Rectangular footing: An isolated rectangular footing is to be provided for a column of section 450 mm x 300 mm. The following details re given: Height of the column =3m Main reinforcement in column = 6 Nos. 20 mm diameter. Transverse reinforcement = 8 mm at 200 mm c/c Plan size of footing = 3.2 m x 2.2 m Depth of footing at column face = 500 mm Depth of footing at edge = 500 mm Footing reinforcement = a mesh of 16 mm diameter steel at 200 mm c/c. Grade of concrete= M20 Grade of steel = Fe415 Draw to a suitable scale the following: g. Plan h. Sectional Elevation i. Prepare bar bending schedule 20 Marks 20 Marks
Solution: Similar to square footing. Footing steel is a mesh of 16 mm bars at 200 mm c/c both ways. For detailing as per IS: 456-2000, footing steel should be distributed by creating central band and end bands. Steel should be distributed as per IS:456-2000.
CROSS SECTION
400
4- #16
3000 mm
GROUND LEVEL 4- #16 #6@220 #20@200 Ldt L dc 150 min.
DEPTH OF FOUNDATION 500 mm
75 Ldt 75
300 min. LEVELLING COURSE SECTIONAL ELEVATION 2700
2700
PLAN
450 300
CROSS SECTION
GROUND LEVEL DEPTH OF FOUNDATION 500 mm 6- #20 #8@200 #16@200 Ldt 75 75 Ldt 75 SECTIONAL ELEVATION 300 min. LEVELLING COURSE L dc
PLAN
450 300
CROSS SECTION
GROUND LEVEL DEPTH OF FOUNDATION 500 mm 6- #20 #8@200 #16@200 Ldt 75 75 Ldt 75 SECTIONAL ELEVATION 3200 300 min. LEVELLING COURSE L dc
2200
EB
CB= 2200 PLAN
EB
Arrangement of steel in column cross section The type of stirrups and its arrangement depends of the type of cross section and the arrangement of longitudinal bars in the column cross section. The specifications of SP-34 and IS:456-2000 should be satisfied. Some of the details can be seen in the following figures.
48tr
75 > 48tr 48tr
> 75 > 48tr > 75
> 75
> 75
> 75
tr
48 tr
75
TYPICAL ARRANGEMENT OF COLUMN TIES
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Retaining WallDocumento29 pagineRetaining WallnsutharNessuna valutazione finora
- Andi 5 LiDocumento43 pagineAndi 5 LiSuhail N R PuraNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals: ObjectivesDocumento9 pagineFundamentals: ObjectivesnsutharNessuna valutazione finora
- Vb.netDocumento293 pagineVb.netnsutharNessuna valutazione finora
- GDIDocumento16 pagineGDIamsundaram06Nessuna valutazione finora
- Database SystemDocumento24 pagineDatabase SystemnsutharNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Wing WallDocumento3 pagineDesign of Wing WallGoanengineerNessuna valutazione finora
- Staad Auto Load CombinationDocumento1 paginaStaad Auto Load CombinationAnonymous 48jYxR1CNessuna valutazione finora
- Retaining WallDocumento12 pagineRetaining WallnsutharNessuna valutazione finora
- TankDocumento2 pagineTanknsutharNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Concrete Ring Beam For Storage TankDocumento5 pagineDesign of Concrete Ring Beam For Storage TanknsutharNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison of Desing Results Etabs - StaadDocumento7 pagineComparison of Desing Results Etabs - StaadCIVIL100Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vb.netDocumento293 pagineVb.netnsutharNessuna valutazione finora
- Bridge Design (Shear Force and Bending Moment Calculation) : Irc Class Aa Tracked VehicleDocumento16 pagineBridge Design (Shear Force and Bending Moment Calculation) : Irc Class Aa Tracked VehiclensutharNessuna valutazione finora
- Building Drifts in EtabsDocumento9 pagineBuilding Drifts in EtabsnsutharNessuna valutazione finora
- Co RaftDocumento1 paginaCo RaftnsutharNessuna valutazione finora
- Vessal FoundationDocumento21 pagineVessal FoundationnsutharNessuna valutazione finora
- HorticularDocumento2 pagineHorticularnsutharNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil MechanicsDocumento42 pagineSoil MechanicsbentapadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Layout DrawingDocumento18 pagineLayout DrawingSandesh Kumar100% (1)
- Mult Istorie RCC BuildingDocumento21 pagineMult Istorie RCC BuildingnsutharNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison of Desing Results Etabs - StaadDocumento7 pagineComparison of Desing Results Etabs - StaadCIVIL100Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To The Finite Element Method: G.P.NikishkovDocumento32 pagineIntroduction To The Finite Element Method: G.P.NikishkovsanoizuNessuna valutazione finora
- 07 Matrix FrameDocumento72 pagine07 Matrix FrameAminatul Fadillah MarpaungNessuna valutazione finora
- Wind ExampleDocumento8 pagineWind ExampleKyle ForemanNessuna valutazione finora
- Rsa BMDDocumento2 pagineRsa BMDnsutharNessuna valutazione finora
- Wind Load CalculationsDocumento1 paginaWind Load CalculationsnsutharNessuna valutazione finora
- Yang and Liu (2007)Documento11 pagineYang and Liu (2007)nsutharNessuna valutazione finora
- Bridge DesignDocumento3 pagineBridge DesignnsutharNessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Duplex 1500 8000 Mutli-N Rooftop en 2014 06Documento8 pagineDuplex 1500 8000 Mutli-N Rooftop en 2014 06chaesar1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Grayloc CatalogDocumento32 pagineGrayloc CatalogRamonNessuna valutazione finora
- RCC54 Circular Column ChartingDocumento13 pagineRCC54 Circular Column ChartingvaideehNessuna valutazione finora
- ASME IX QW (Welding General Requirements)Documento12 pagineASME IX QW (Welding General Requirements)Ariq Fauzan100% (1)
- Roofing Application Standard No 111Documento14 pagineRoofing Application Standard No 111nmblobNessuna valutazione finora
- Ultra Clean OT PDFDocumento4 pagineUltra Clean OT PDFaysh2383Nessuna valutazione finora
- Boq1 SKTT 150 KV JGC - Kandang SapiDocumento4 pagineBoq1 SKTT 150 KV JGC - Kandang SapiDimas Rio100% (1)
- A Seminar Report OnDocumento20 pagineA Seminar Report Onadarsh_m00675% (4)
- Tenmat Feroform t14 DatasheetDocumento1 paginaTenmat Feroform t14 DatasheettungNessuna valutazione finora
- Cec 110p PDFDocumento20 pagineCec 110p PDFJoifry DonnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 11 Flow in PipesDocumento34 pagineChapter 11 Flow in PipesTombiruoNessuna valutazione finora
- LG MultiV III - CatalogueDocumento13 pagineLG MultiV III - CatalogueMuhidin KozicaNessuna valutazione finora
- High Speed Bi-Directional Circuit Breaker For DC ApplicationsDocumento2 pagineHigh Speed Bi-Directional Circuit Breaker For DC ApplicationsagarwaalaaaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Denso Tape: Composition ApplicationDocumento1 paginaDenso Tape: Composition ApplicationDito NarendraNessuna valutazione finora
- Tesy LB 2509 E04 TRV UputstvoDocumento12 pagineTesy LB 2509 E04 TRV Uputstvozix013Nessuna valutazione finora
- Accomplishment Report # 4Documento2 pagineAccomplishment Report # 4Arnel FreoNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 EXPT Blu1718,1719Documento1 pagina2016 EXPT Blu1718,1719Toto MidgleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Design - Sheet - For Self Supported Stack-2Documento4 pagineDesign - Sheet - For Self Supported Stack-2Sabir NasimNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio FiberDocumento2 pagineBio FiberGelina HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Conbextra EP: T T T T T TDocumento4 pagineConbextra EP: T T T T T TFeri Oktara IrawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Buy Affordable Residential Flats in Zirakpur at Escon ArenaDocumento26 pagineBuy Affordable Residential Flats in Zirakpur at Escon ArenaEscon ArenaNessuna valutazione finora
- YW Daytripper ChairDocumento8 pagineYW Daytripper ChairEric HubbardNessuna valutazione finora
- Persta Industrie e PDFDocumento140 paginePersta Industrie e PDFZoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiantec Radiant Heat Design and Construction Manual PDFDocumento16 pagineRadiantec Radiant Heat Design and Construction Manual PDFPhil KrahnNessuna valutazione finora
- Essential Points For Bridge Inspector During Inspection of BridgeDocumento26 pagineEssential Points For Bridge Inspector During Inspection of BridgeSeptinurriandianiNessuna valutazione finora
- Pile Bearing Capacity Prediction by Means of Static Penetrometer CPTDocumento8 paginePile Bearing Capacity Prediction by Means of Static Penetrometer CPTJohn STCNessuna valutazione finora
- CFJV00198BDocumento360 pagineCFJV00198BCheongNessuna valutazione finora
- CSSBI 59 05 Chapter1Documento16 pagineCSSBI 59 05 Chapter1tiagomecanicaNessuna valutazione finora
- DLP-8 Base Metal Preparation in Welding.Documento6 pagineDLP-8 Base Metal Preparation in Welding.Chinelle Joseph Sollano TinoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Maz 10 Ym - Mip Ea 151 - 02 - RNCCDocumento62 pagineMaz 10 Ym - Mip Ea 151 - 02 - RNCCFilipe Areas100% (1)