Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
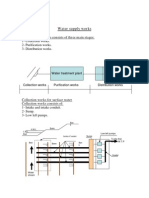
Activated Sludge Process Suspended Growth Reactor
Caricato da
api-247600939Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Activated Sludge Process Suspended Growth Reactor
Caricato da
api-247600939Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Activated Sludge Process
Suspended growth reactor
In this type of reactor , reaction between organic matter and bacteria takes
place in suspension on the surface of the suspended solids ( suspended
returned sludge particles).
Purpose:
Stabilize organic matter and make it satiable.
A microscopic photo of the reaction between organic matter and bacteria
which takes place in suspension solids on the surface of the suspended
Types of activated sludge process:
1- Conventional aeration.
2- Contact stabilization.
3- Step aeration.
4- Extended aeration.
5- Oxidation ditch (orbital aeration).
Conventional aeration
Advantages of aeration tanks :
1- It does not need large land areas.
2- It is more efficient than trickling filters.
3- No fly and odor problems occurs around the trickling filter.
Disadvantages of aeration tanks:
1- It can not take shock loads and sudden increase in discharge.
2- Needs a supervisor since it is the most complicated systems.
3- High cost of construction , operation and maintenance.
P.S.T A.T
X
F.S.T Q Q+QR.S
QR.S , Xr
Excess sludge
Qw
Xr
Effluent
Se
Xe
Set
Q - Qw
pump
Q
So
Xo
Flow line diagram of activated sludge process
Diffused air system of aeration tank
sedimentation tank
From primary
compression
(94.18)
air compressed pipes
To FINAL SETTELING TANK
( 94.00 )
Air diffiusers
To F.S.T
7
.
7
COMPRESSED AIR
( 93.42 )
x
section x-x
5
m
Aeration tank
Factors affecting design of aeration tank:
1- Temperature: the biological reaction increase with the increase of
temperature.
2- MLSS: ( mixed liqueur suspended solids ) 2000 - 4000 mg/L
MLVSS: ( mixed liqueur volatile suspended solids )
MLVSS = 0.8 MLSS
3- Sludge retention time = T = 4 - 8 hrs
4- Sludge return rate (R) = 0.2 0.3
R = QR / Qd
Return sludge QR.s = 0.2 - 0.3 Qd
Surface aerators of aeration tank
Types of aeration :
1- Diffused air system
2- Surface aerators
X: total number of microorganisms responsible for the stabilization of
organic matter.
X = MLVSS
MLVSS = 0.8 MLSS
c = sludge age =5 - 15 days
y: cell yield coefficient
y = gm MLVSS/gm BOD5
Y observed = y / ( 1+ kd c ) = 0.31
Kd = decay coefficient = 0.05 day-1
A = V / d
Depth = 3 - 5 m
n 2
b = 1.5 2 d
L 50 m
Checks :
Design criteria :
Q = discharge influent to the aeration tank (A.T).
= 1.5 x Q
ave sewage
(Q = 0.8 x 1.5 x pop x q
ave
)
S
o
= dissolved BOD
5
influent to the A.T.
S
e
= dissolved effluent BOD
5
Set = effluent total BOD
5
Xe = suspended solids concentration (S.S)
BOD
5
suspended = S.S x 0.7
BOD
5
dissolved = total BOD
5
- BOD
5
suspended
S
e
= Set Xe x 0.7
) 1 (
) (
0
c d
e c
K X
S S Q y
V
u
u
+
=
suspended
dissolved
organic 70%
inorganic 30%
4 . 0 2 . 0 /
) (
/ =
= M F
V MLVSS
S S Q
M F
e o
hrs T
Q
V
T 8 4 = =
1000
. .
=
=
V
Q S
L
L
L O T
V
o
Allowable organic load (L) = 0.3 - 2 kg BOD5 /m/ day
Qw = sludge withdrawal rate
Xr =MLVSS in return sludge
Xe = effluent S.S
Example:
Determine the volume and dimensions of aeration tank and the required
air flow for an activated sludge process treatment plant. Which is
designed to treat the flow Q = 12000 m3/d and fined overall efficiency,
F/M ratio, allowable organic load and the diffused air system. Given the
following data:
- BOD5 of primary effluent (So) = 200 mg/l
- Required effluent BOD5 = 30 mg/l (Set)
- Required effluent suspended solids (Xe) = 20 mg/l
- MLVSS in aeration tank (X) = 2500 mg/l
- MLSS in return sludge = 10000 mg/l
- Cell residence time (uc) = 6 days
- Coefficient of decay (kd) = 0.06 day-1
- Cell yield coefficient (y) = 0.65 gm MLVSS/gm BOD5
- Efficiency of aeration = 8%
) (
.
.
w e r w
c
r w
C
S R
Q Q X X Q
V X
X Q
V X
MLSS S TSSinR
MLSS
Q
Q
R
+
= =
u
u
BOD5 dissolved = BOD5 eff. S.Seff x 0.7
Se =Set Xe x 0.7
= 30 -20 x 0.7 = 17.45 ~ 17.5 mg/l
Assume d = 4m d= 3 5 m
Number of tanks n =2
Area of one tank =
b = 1.5 2 d take b = 8m
P.S.T A.T
X=2500
F.S.
T
Q+QR.
S
QR.S , Xr
Excess
sludge
Qw
Xr
Effluent
Se
Xe=20mg/l
Set=
30mg/l
Q
pump
Q
So=200mg/l
Xo
Solution:
100 %
=
o
et o
S
S S
iciencyE Overalleff
% 85 100
200
30 200
=
=
) 1 (
) (
0
c d
e c
K X
S S Q y
V
u
u
+
=
Set
Dissolved suspended
Xe
70% organic 30% inorganic
Q=12000
3
2512
) 6 06 . 0 1 ( 2500
) 5 . 17 200 ( 12000 6 65 . 0
m V =
+
=
2
015 . 638
4
5 . 2512
m area
d
V
area
= =
=
2
314
2
015 . 628
m =
m m
b
A
L 50 25 . 39
8
314
s = = =
Checks :
Allowable organic load (L) = 0.3 - 2 kg BOD
5
/m/ day
day gmMLVSS
gmBOD
M F
.
346 . 0
06 . 2512 2500
) 5 . 17 200 ( 12000
/
5
=
=
Q
V
T =
T = 4 - 8 hrs
V MLVSS
S S Q
M F
e o
=
) (
/
F/M = 0.2 - 0.4
hrs T 03 . 5 24
12000
06 . 2512
= =
day m
kgBOD
L
V
Q S
L
o
.
955 . 0
1000 5 . 2512
12000 200
1000
3
5
=
=
The design of the return sludge pipe:
m
v
Q
d m Q
Q
Q
MLSS S TSSinR
MLSS
Q
Q
R
S R
S R
S R
S R
3 . 0 28 . 0
1
4 60 60 24
5 . 5454
4 60 60 24
/ 5 . 5454 12000 45 . 0
45 . 0
)
8 . 0
2500
( 10000
)
8 . 0
2500
(
.
2
2
.
3
.
.
.
~ =
=
=
= =
=
= =
|
t|
t|
MLVSS = 0.8 MLSS
Determination of excess sludge:
d m Q
Q Q
Q Q X X Q
V X
d m Q
Q
X Q
V X
w
w w
w e r w
c
w
w
r w
C
/ 6 . 126
) 12000 ( 20 ) 8 . 0 10000 (
06 . 2512 2500
6
) (
/ 83 . 130
) 8 . 0 10000 (
06 . 2512 2500
6
3
3
=
+
=
+
=
=
=
=
u
u
Design of air pipe in aeration tank:
Design of surface aerators:
blower each of cpacity design
capacity blowers
blowers of No
m blowers of Head
T waterinA of depth blowers of Head
d m capacity Blowers
air actual capacity Blowers
d m required air Actual
oxygen of effeciency
demand air l theoritica
required air Actual
=
= =
=
= =
=
= =
=
.
2 . 5 4 3 . 1
. 3 . 1
/ 3 . 233810 54 . 155873 5 . 1
5 . 1
/ 54 . 155873
08 . 0
88 . 12469
3
3
s m v v capacity Blower / 15
4
2
= =
t|
Design of diffused air system:
3
2
2
2
2
3
2
5
3
2
/ 88 . 12469
232 . 0 2 . 1
61 . 3471
) ( 232 . 0 2 . 1
/ 61 . 3471
65 . 0
55 . 2256
) ( tan
65 . 0
) (
) ( tan
/ 55 . 2256 9 . 678 42 . 1
) 68 . 0 (
10 12000 ) 5 . 17 200 (
) (
42 . 1
) (
10 ) (
) (
/ 9 . 678
1000
) 5 . 17 200 ( 12000 31 . 0
1000
) (
m kg demand air l Theoritica
ratio O
SOR
demand air l Theoritica
d kgO SOR required oxygen dard S
O oygen pure l Theoritica
SOR required oxygen dard S
d kgO O oygen pure l Theoritica
P
BOD
BOD
Q S S
O oygen pure l Theoritica
d kg P
S S Q y
P
x
U
e o
x
e o obs
x
=
=
= =
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
aerator O
SOR
aerators of NO
d O kg capacity aerators Total
SOR capacity aerators Total
d O kg SOR required oxygen dard S
O oygen pure l Theoritica
SOR required oxygen dard S
d kgO O oygen pure l Theoritica
P
BOD
BOD
Q S S
O oygen pure l Theoritica
d kg P
S S Q y
P
x
U
e o
x
e o obs
x
/
2
.
/ 22 . 6943 61 . 3471 2
2
/ 61 . 3471
65 . 0
55 . 2256
) ( tan
65 . 0
) (
) ( tan
/ 55 . 2256 9 . 678 42 . 1
) 68 . 0 (
10 12000 ) 5 . 17 200 (
) (
42 . 1
) (
10 ) (
) (
/ 9 . 678
1000
) 5 . 17 200 ( 12000 31 . 0
1000
) (
2
2
2
2
2
3
2
5
3
2
=
= =
=
= =
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
3
2
2
2
2
3
2
5
3
2
/ 88 . 12469
232 . 0 2 . 1
61 . 3471
) ( 232 . 0 2 . 1
/ 61 . 3471
65 . 0
55 . 2256
) ( tan
65 . 0
) (
) ( tan
/ 55 . 2256 9 . 678 42 . 1
) 68 . 0 (
10 12000 ) 5 . 17 200 (
) (
42 . 1
) (
10 ) (
) (
/ 9 . 678
1000
) 5 . 17 200 ( 12000 31 . 0
1000
) (
m kg demand air l Theoritica
ratio O
SOR
demand air l Theoritica
d kgO SOR required oxygen dard S
O oygen pure l Theoritica
SOR required oxygen dard S
d kgO O oygen pure l Theoritica
P
BOD
BOD
Q S S
O oygen pure l Theoritica
d kg P
S S Q y
P
x
U
e o
x
e o obs
x
=
=
= =
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
Des
ig
n
of
di
ff
u
s
e
d
ai
r
s
y
st
e
m
:
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- DryingbedsDocumento1 paginaDryingbedsapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Biologicalwastewatertreatmentlecture2 4Documento3 pagineBiologicalwastewatertreatmentlecture2 4api-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- SludgetreatmentDocumento13 pagineSludgetreatmentapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Finalsettlingtanklecture2 7Documento6 pagineFinalsettlingtanklecture2 7api-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Sewagepumpstationlecture2 3Documento9 pagineSewagepumpstationlecture2 3api-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Tricklingfilterslecture2 6Documento7 pagineTricklingfilterslecture2 6api-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Lecture 11 PrimarysedimentationtankDocumento8 pagineLecture 11 Primarysedimentationtankapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Lecture 10 GritremovalchamberDocumento4 pagineLecture 10 Gritremovalchamberapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Lecture 8 WastewaterDocumento3 pagineLecture 8 Wastewaterapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- Lecture 9 WastewatertreatmentDocumento7 pagineLecture 9 Wastewatertreatmentapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 7 DistributionworksDocumento6 pagineLecture 7 Distributionworksapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Lecture 8 Water Supply Network LectureDocumento15 pagineLecture 8 Water Supply Network Lectureapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Lecture 6 DisinfectionDocumento4 pagineLecture 6 Disinfectionapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Lecture 5 FiltrationDocumento7 pagineLecture 5 Filtrationapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3 PurificationworksDocumento10 pagineLecture 3 Purificationworksapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Lecture 2 Water Supply WorksDocumento10 pagineLecture 2 Water Supply Worksahmedabeer12000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4 SedimentationDocumento6 pagineLecture 4 Sedimentationapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1 SanitaryengineeringDocumento8 pagineLecture 1 Sanitaryengineeringapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- Hexweb CR Iii: Corrosion Resistant Specification Grade Aluminum HoneycombDocumento6 pagineHexweb CR Iii: Corrosion Resistant Specification Grade Aluminum Honeycombsahiljain_146Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Drew Marine - Bulk Carrier Guide For Cargo Hold CleaningDocumento2 pagineDrew Marine - Bulk Carrier Guide For Cargo Hold CleaningGauravNessuna valutazione finora
- Check Valve (Swagelok) MS-01-176 PDFDocumento16 pagineCheck Valve (Swagelok) MS-01-176 PDFIsmailIbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Chemical Food SafetyDocumento297 pagineChemical Food SafetyqtrystNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Conduction Heat TransferDocumento52 pagine2 Conduction Heat Transferbirhanu kefieNessuna valutazione finora
- Assigment of NDTDocumento3 pagineAssigment of NDTHamid AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Yara Fertilizer Industry Handbook: February 2014Documento90 pagineYara Fertilizer Industry Handbook: February 2014douglasminasNessuna valutazione finora
- Zeon Productguide 20150717Documento16 pagineZeon Productguide 20150717khushboo.mamtani2932Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lattice Enthalpy, Ionisation Energy, Born-Haber Cycles, Hydration EnthalpyDocumento8 pagineLattice Enthalpy, Ionisation Energy, Born-Haber Cycles, Hydration Enthalpyzubair0% (1)
- ConcentrationExpresion QM Chp6Documento38 pagineConcentrationExpresion QM Chp6theking12ion25% (4)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- DLL SCIENCE 9 Dec 9-13Documento49 pagineDLL SCIENCE 9 Dec 9-13Raiza Lainah MianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Can Man Alter MarsDocumento1 paginaCan Man Alter MarsJan Gabriel Gimao100% (2)
- TPXData SheetDocumento4 pagineTPXData Sheetrameshkarthik810Nessuna valutazione finora
- Amali 3Documento9 pagineAmali 3Aiman FarhanNessuna valutazione finora
- AS 1358-2004 - Bursting Discs and Devices PDFDocumento45 pagineAS 1358-2004 - Bursting Discs and Devices PDFThaiminh VoNessuna valutazione finora
- Philippine National StandardsDocumento30 paginePhilippine National StandardsJonathan Pascua CamachoNessuna valutazione finora
- HoneywellDocumento2 pagineHoneywellzenerdiodeNessuna valutazione finora
- Section F S-6001 (2008) Bearing Temperature PerformanceDocumento2 pagineSection F S-6001 (2008) Bearing Temperature Performanceslowrie151Nessuna valutazione finora
- Antibacterial Activity of Thuja OrientalisDocumento9 pagineAntibacterial Activity of Thuja OrientalisMădălina FrunzeteNessuna valutazione finora
- Airy ExampleDocumento3 pagineAiry Examplevennila-puviNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood TestDocumento6 pagineBlood TestMaharani Indri100% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Zeeman EffectDocumento11 pagineThe Zeeman EffectAlex TarrNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzyme Virtual LabDocumento4 pagineEnzyme Virtual LabSamuel Morales NavarroNessuna valutazione finora
- 00300E04Documento30 pagine00300E04halim_kaNessuna valutazione finora
- Zhang Et Al. 2010Documento6 pagineZhang Et Al. 2010Aizat HawariNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbon Carbon CompositeDocumento22 pagineCarbon Carbon Compositeyogeshkmr01100% (1)
- Thumb RuleDocumento13 pagineThumb RuleAtiqur RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Xie Rehren 2009 Lead Silver Slag China BUMA VIDocumento9 pagineXie Rehren 2009 Lead Silver Slag China BUMA VIth_rehrenNessuna valutazione finora
- Scaling of MosfetDocumento40 pagineScaling of MosfetSaumitra TripathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Bank of ESTDocumento5 pagineQuestion Bank of ESTKishor PatilNessuna valutazione finora