Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Lecture 11 Primarysedimentationtank
Caricato da
api-247600939Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Lecture 11 Primarysedimentationtank
Caricato da
api-247600939Copyright:
Formati disponibili
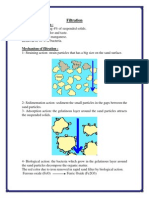
Primary Sedimentation tank
Purpose:
1- Removal of 40 - 60 % of suspended solids
2- Removal of 25 - 35 % of B.O.D.
3- Sediment the organic and inorganic matters to improve the properties of
the sewage and prepare it for the biological treatment.
Types of primary sedimentation tanks:
1- Rectangular tank.
2- Circular tank.
Factors affecting sedimentation efficiency:
1- Viscosity
2- Concentration of suspended solids
3- Retention period
4- Horizontal velocity
5- Temperature
6- Surface loading rate = 24 - 48 m/m/day
Primary sedimentation tank
(horizontal flow)
Effluent weir of rectangular sedimentation tank
Rectangular primary sedimentation tank
Primary sedimentation tank
(Radial flow)
Circular primary sedimentation tank
7- Dimension of tank
8- Dead zones.
Design criteria:
1- Retention period = T = 2 - 3 hrs
2- Surface loading rate (S.L.R.) = 24 - 48 m/m/day
3- Horizontal velocity 0.3 m/min
4- Effluent weir loading (E.W.L.) 600 m/m/day ( 25 m/m/hr)
5- L = 3 5 B
L 40 m
6- d = 3 - 5 m
7- B = 2 3 d
8- 40 m
9- Bottom slope for circular tank = 4 - 10 %
for rectangular tank = 1 - 2 %
V = Qd x T
S.L.R = Qd / S.A
Example:
For a sewage treatment plant, the following data are given:
- Qave summer = 18000 m3/d
- S.L.R = 30 m3/m2/d
It is required to design primary sedimentation tanks.
Solution:
Qd = 1.5 x 18000 = 27000 m3/d
For rectangular tank:
Assume T = 2.5 hr
2
3
900
30
27000
.
.
. .
5 . 2812
24
5 . 2
27000
m A S
A S
Q
R L S
m
T Q V
d
d
= =
=
= =
=
m
loading weir
Q
weir of Length
d m m loading weir take
unsafe d m m
b n
Q
L W E
safe m
d b n
Q
area tional cross
Q
V
Check
m
L
A S
b
m length Assume
m k one of A S
n Take
m
A S
V
d
d
d
d d
h
5 . 22
600 2
27000
/ / 600
600 / / 1200
25 . 11 2
27000
. . 2
min / 3 . 0 269 . 0
60 24 ) 1 . 3 25 . 11 2 (
27000
sec
1
:
25 . 11
40
450 .
40
450
2
900
tan .
2
1 . 3
900
5 . 2812
.
3
3
2
=
= =
=
=
=
=
=
= =
= = =
=
= =
=
= =
=
L/7
L/7
Circular primary sedimentation tank:
Example:
Estimate the volume of sludge produced per 27000 m3/d if the influent S.S
300 mg/l. The removal efficiency is 60%.
2
3
900
30
2700
.
.
. .
5 . 2812
24
5 . 2
27000
m A S
A S
Q
R L S
m
T Q V
d
d
= =
=
= =
=
m
m k one of A S
n Take
m
A S
V
d
24
4
450
2
900
tan .
2
1 . 3
900
2700
.
2
2
=
=
= =
=
= =
=
|
t|
safe d m m
n
n
Q
L W E
safe m m
d n
Q
v
Chick
d
d
h
600 / / 179
24
27000
. . 2
min / 3 . 0 min / 04 . 0
) 60 24 ( 1 . 3 24 2
27000
1
:
3
=
=
=
=
=
=
t
| t
t
| t
Solution:
For circular tank:
d m
G S
weight
solids dry of Volume
m t sludge of gravity Specific
d t solids dry of Weight
/ 718 . 4
03 . 1
86 . 4
.
/ 03 . 1
/ 86 . 4 10 27000 300
100
60
3
3
6
= = =
=
= =
) 2 1 ( 925 . 0
265 . 38
3 796 . 11
) 64 . 31 1 64 . 31 1 (
3
796 . 11
64 . 31
2
25 . 11
2
25 . 11
2 2
1 1
) (
3
/ 796 . 11
2
59 . 23
12 min
/ 59 . 23
2
18 . 47
/ 18 . 47
2
37 . 94
tan
:
/ 37 . 94
05 . 0
718 . 4
) % 5 ( % 95
2
2
1
2 1 2 1
3
3
3
3
= =
=
+ + + =
= =
=
=
+ + + =
= =
= =
= =
= =
=
h m h
h
m
B B
a
m m a
a a a a
h
V
d m hopper per sludge of Volume
hours every withdrawal sludge g Assu
d m hopper per sludge of Volume
d m k per sludge of Volume
hopper of Design
d m sludge of Volume
solids sludge of content Moisture
o o
u
|
| | t
60 45
2 1
1
)
2
(
4
2 2
=
=
>
+
=
m h
m
h V
s
s b
safe s m v
mm mm m
s m pipe sludge in v v A Q
s m Q
utes utes withdrawal of time Assume
pipe withdrawal sludge of Design
act
sludge
sludge
/ 24 . 1
) 150 ( 200 22 . 0
1
4
039 . 0
/ 5 . 1 1
/ 039 . 0
60 5
796 . 11
) min 20 5 ( min 5
:
2
3
=
> ~ =
=
= =
=
| |
t|
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Silt Trap - 19.10.25Documento14 pagineSilt Trap - 19.10.25azwanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Lecture 5 FiltrationDocumento7 pagineLecture 5 Filtrationapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Elemental Geosystems 9th EditionDocumento39 pagineTest Bank For Elemental Geosystems 9th Editionstephenhallpoanmyxgwi100% (23)
- 03 Rainwater Harvesting System DesignDocumento20 pagine03 Rainwater Harvesting System DesignMohd Muzani MustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Spill Report Form: SpillsDocumento2 pagineSpill Report Form: SpillsNoor Muddassir Khan100% (1)
- Silt Trap Design Calculation: GaasbDocumento8 pagineSilt Trap Design Calculation: GaasbAnonymous EXPXRz100% (1)
- Tricklingfilterslecture2 6Documento7 pagineTricklingfilterslecture2 6api-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- DryingbedsDocumento1 paginaDryingbedsapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Finalsettlingtanklecture2 7Documento6 pagineFinalsettlingtanklecture2 7api-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- SludgetreatmentDocumento13 pagineSludgetreatmentapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biologicalwastewatertreatmentlecture2 4Documento3 pagineBiologicalwastewatertreatmentlecture2 4api-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Activated Sludge Process Suspended Growth ReactorDocumento9 pagineActivated Sludge Process Suspended Growth Reactorapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 8 Water Supply Network LectureDocumento15 pagineLecture 8 Water Supply Network Lectureapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 10 GritremovalchamberDocumento4 pagineLecture 10 Gritremovalchamberapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sewagepumpstationlecture2 3Documento9 pagineSewagepumpstationlecture2 3api-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 8 WastewaterDocumento3 pagineLecture 8 Wastewaterapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 9 WastewatertreatmentDocumento7 pagineLecture 9 Wastewatertreatmentapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1 SanitaryengineeringDocumento8 pagineLecture 1 Sanitaryengineeringapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 6 DisinfectionDocumento4 pagineLecture 6 Disinfectionapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 7 DistributionworksDocumento6 pagineLecture 7 Distributionworksapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2 Water Supply WorksDocumento10 pagineLecture 2 Water Supply Worksahmedabeer12000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4 SedimentationDocumento6 pagineLecture 4 Sedimentationapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3 PurificationworksDocumento10 pagineLecture 3 Purificationworksapi-247600939Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrographs: Base-Flow SeparationDocumento19 pagineHydrographs: Base-Flow SeparationMuhammad Farooq ZiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Visual Inspection Test ReportDocumento2 pagineVisual Inspection Test Reportم.ذكى فضل ذكىNessuna valutazione finora
- Iit Dharwad PDFDocumento37 pagineIit Dharwad PDFRakesh RNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Hydrology: Puan Saedatulfirdaus BT Sa'AraniDocumento26 pagineEngineering Hydrology: Puan Saedatulfirdaus BT Sa'AraniHasmittha100% (1)
- Army TM 5-813-1 Navy Air Force Afm 88 10, Vol. 1Documento53 pagineArmy TM 5-813-1 Navy Air Force Afm 88 10, Vol. 1mojeebmashalNessuna valutazione finora
- A Guide To Flooding in PhiladelphiaDocumento36 pagineA Guide To Flooding in PhiladelphiaPhiladelphia Water DeparmentNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1 WRE PDFDocumento81 pagineLecture 1 WRE PDFAiko FeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles and Practices of Water ManagementDocumento3 paginePrinciples and Practices of Water ManagementMahendra paudel PaudelNessuna valutazione finora
- CE-402: Irrigation Engineering: 8 Semester (4 Year) Civil Engineering Spring 2021Documento23 pagineCE-402: Irrigation Engineering: 8 Semester (4 Year) Civil Engineering Spring 2021SajadNessuna valutazione finora
- Jaef 2010: Water Sector of Saudi ArabiaDocumento23 pagineJaef 2010: Water Sector of Saudi ArabiaintequabNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. I S N Raju RWH in Urban AreasDocumento94 pagineDr. I S N Raju RWH in Urban Areaskethan2212Nessuna valutazione finora
- Executive Summary of KJA Recommendation On Karnataka State Water Policy 2019Documento55 pagineExecutive Summary of KJA Recommendation On Karnataka State Water Policy 2019junkchanduNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.bu Sedra Mosque Drainage System-0001-Layout13 PDFDocumento1 pagina1.bu Sedra Mosque Drainage System-0001-Layout13 PDFMohammed Javid HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Orissa Flood News Alert - Jul - 17&18 - 09Documento20 pagineOrissa Flood News Alert - Jul - 17&18 - 09Pranab Ranjan Choudhury100% (2)
- 03 - Stormwater MSMA 2nd 2012 - Quality Design FundamentalsDocumento19 pagine03 - Stormwater MSMA 2nd 2012 - Quality Design Fundamentalsang.xicongNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Waste WaterDocumento1 paginaTypes of Waste WaterNwachukwu UmehNessuna valutazione finora
- Faecal Sludge Treatment Plant (FSTP), Leh, Ladakh: School of Planning and Architecture, BhopalDocumento7 pagineFaecal Sludge Treatment Plant (FSTP), Leh, Ladakh: School of Planning and Architecture, BhopalShaun George100% (1)
- Case StudyDocumento11 pagineCase StudyHumairah ShabriNessuna valutazione finora
- ExplanationDocumento40 pagineExplanationShimeka Kho Suk YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Sewage Management For Boat OwnersDocumento2 pagineSewage Management For Boat OwnersBernewsAdminNessuna valutazione finora
- Reed Bed Treatment PlantDocumento9 pagineReed Bed Treatment PlantUmesh AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Marksheet CIV3113 2021 Preliminary GradesDocumento1 paginaMarksheet CIV3113 2021 Preliminary GradesFrank SterileNessuna valutazione finora
- Rain Water HarvestingDocumento16 pagineRain Water HarvestingSamir ShekharNessuna valutazione finora
- Anantnag VerinagDocumento18 pagineAnantnag VerinagstoicNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Wil - Eastern Nile Water Simulation Model Based On RIBASIM V9 (Wil)Documento51 pagineDr. Wil - Eastern Nile Water Simulation Model Based On RIBASIM V9 (Wil)Ahmed El AdawyNessuna valutazione finora