Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Changing Iron to Steel
Caricato da
retno pideksoDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Changing Iron to Steel
Caricato da
retno pideksoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Passage 1
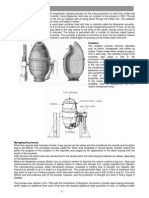
The railroad industry could not have grown as large as it did without steel. The first rails were made of iron. But iron rails were not strong enough to support heavy trains running at high speeds. Railroad executives wanted to replace them with steel rails because steel was ten or fifteen times stronger and lasted twenty times longer. Before the 1870's, however, steel was too expensive to be widely used. It was made by a slow and expensive process of heating. Stirring, and reheating iron ore. Then the inventor Henry Bessemer discovered that directing a blast of air at melted iron in a furnace would burn out the impurities that made the iron brittle. As the air shot, through the furnace, the bubbling metal would erupt in showers of sparks. When the fire cooled, the metal had been changed, or converted, to steel. The Bessemer converter made possible the mass production of steel. Now three to five tons of iron could be changed into steel in a matter of minutes. Just when the demand for more and more steel developed, prospectors discovered huge new deposits of iron ore in the Mesabi Range, a 120-mile-long region in Minnesota near Lake Superior. The Mesabi deposits were so near the surface that they could be mined with steam' shovels. Barges and steamers carried the iron ore through Lake Superior to depots or the southern shores of Lake Michigan and Lake Erie. With dizzying speed Gary, Indiana, and Toledo, Youngstown, and Cleveland, Chic, became major steel-manufacturing centers Pittsburgh was the greatest steel city of all. Steel was the basic building material of the industrial age. Production sky-rocketed from seventy-seven thousand tons in 1870 to over eleven million tons in 1900.
1. Which of the following is the best title for the passage (A) The Railroad industry (B) Famous Inventors (C) Changing Iron into Steel (D) Steel Manufacturing Centers 2. According to the passage, the railroad industry try preferred steel to iron because steel was (A) cheaper and more plentiful (B) lighter, and easier to mold (C) cleaner. And easier to mine (D) stronger and more durable 3. According to the passage, how did the Bessemer method make the mass production of steel possible? (A) It directed air at melted iron in a furnace. removing all impurities. (B) It slowly heated iron ore.. then stirred it and heated it again. (C) It changed iron ore into iron, which was a substitute for steel. (D) It could quickly find deposits of iron ore under the ground. 4. The furnace that Bessemer used to process iron into steel was called a (A) heater (B) steamer (C) converter (D) shower 5. According to the passage where were large deposits of iron one uncovered? (A) In Pittsburgh (B) In the Mesabi Range (C) Near Lake Michigan (D) Near Lake Erie 6. In line 17 the words Barges and steamers could best be replaced by which of the following? (A) Trains (B) Planes (C) Boats (D) Trucks 7. It can be inferred from the passage that the mass production of steel caused (A) a decline in the railroad industry (B) a revolution in the industrial world (C) an increase in the price of steel (D) a feeling of discontent among steel work
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Bessemer ProcessDocumento22 pagineBessemer ProcessJosua Aditya PratamaNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Steel MakingDocumento3 pagineHistory of Steel MakingAb Wajid FarukiNessuna valutazione finora
- VISLDocumento78 pagineVISLKshama Asha SunderNessuna valutazione finora
- History of SteelDocumento79 pagineHistory of SteelChrissa100% (2)
- Iron Processing: Iron Processing, Use of A Smelting Process To Turn The Ore Into A Form From Which ProductsDocumento9 pagineIron Processing: Iron Processing, Use of A Smelting Process To Turn The Ore Into A Form From Which ProductsDevina DianmahendraNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Process Steel Pig Iron Henry Bessemer William Kelly Removal of Impurities Iron OxidationDocumento12 pagineIndustrial Process Steel Pig Iron Henry Bessemer William Kelly Removal of Impurities Iron OxidationjayaprabhalNessuna valutazione finora
- The Bessemer Process Revolutionized Steel ManufacturingDocumento3 pagineThe Bessemer Process Revolutionized Steel ManufacturingSaurabh PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Layout: 4.1 Steel's GenesisDocumento3 pagineLayout: 4.1 Steel's GenesisDroffy GuyNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel History: Mild Steels Are The Steels With The Lowest Carbon Ratio, Less Than 0,02%. They Are HighlyDocumento2 pagineSteel History: Mild Steels Are The Steels With The Lowest Carbon Ratio, Less Than 0,02%. They Are HighlyMarius MariusNessuna valutazione finora
- Aerocom Metals: A History of SteelDocumento16 pagineAerocom Metals: A History of SteelDrGanesh KameNessuna valutazione finora
- Barrow Steelworks: An Illustrated History of the Haematite Steel CompanyDa EverandBarrow Steelworks: An Illustrated History of the Haematite Steel CompanyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento12 pagineChapter 1Oscar Espinosa BonillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Origins and evolution of extraction metallurgyDocumento1 paginaOrigins and evolution of extraction metallurgyLuis OliveiraNessuna valutazione finora
- CIVDES2 Lecture Notes - 1Documento18 pagineCIVDES2 Lecture Notes - 1Anthony TangNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel Age: By: Kuo Garol SarongDocumento14 pagineSteel Age: By: Kuo Garol SarongKuo SarongNessuna valutazione finora
- Historical DevelopmentDocumento3 pagineHistorical DevelopmentShakil AkhterNessuna valutazione finora
- Layout: 4.1 Steel's GenesisDocumento2 pagineLayout: 4.1 Steel's GenesisDroffy GuyNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Historical Development and Characteristics of Structural SteelsDocumento30 pagine1 Historical Development and Characteristics of Structural Steelsron_dany100% (1)
- On The Role of Ferroalloys in SteelmakingDocumento8 pagineOn The Role of Ferroalloys in SteelmakingJavo GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction of Steel Columns in US Buil PDFDocumento9 pagineIntroduction of Steel Columns in US Buil PDFMariana AlvesNessuna valutazione finora
- Abraham Darby IIIDocumento31 pagineAbraham Darby IIISabah GazgeNessuna valutazione finora
- History of SteelmakingDocumento1 paginaHistory of SteelmakingMark Anthony Asañez BrianNessuna valutazione finora
- 1E7 Rehabilitation AD 2Documento111 pagine1E7 Rehabilitation AD 2alexrodriguezabcNessuna valutazione finora
- History of WeldingDocumento10 pagineHistory of WeldingGracie O. ChingNessuna valutazione finora
- SteelDocumento79 pagineSteelWardah وردہNessuna valutazione finora
- đề thi chứng chỉ B2 và C1 đề 25Documento6 pagineđề thi chứng chỉ B2 và C1 đề 25Ngân HồNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Iron and Steel BridgesDocumento2 pagineHistory of Iron and Steel BridgesKAii Magno Guia0% (1)
- Technology of Iron and SteelDocumento29 pagineTechnology of Iron and SteelTanya SirohiNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel MillDocumento6 pagineSteel MillRenato Gigliotti MPhNessuna valutazione finora
- The History of Welding - MillerWeldsDocumento7 pagineThe History of Welding - MillerWeldsJayakrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Oxygen Steel MakingDocumento3 pagineBasic Oxygen Steel Making06me395Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit - 1 - Introduction, Advent of Steel, Glass, Ferro Concrete PDFDocumento119 pagineUnit - 1 - Introduction, Advent of Steel, Glass, Ferro Concrete PDFnawin1234100% (1)
- MinhDocumento2 pagineMinhKhanh Minh LuuNessuna valutazione finora
- 2409 Steel and The Skyscraper City A Study On The Influence of Steel On The Design of Tall BuildingsDocumento11 pagine2409 Steel and The Skyscraper City A Study On The Influence of Steel On The Design of Tall BuildingsAndrea Perez PellegrinoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Working of Steel Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelDa EverandThe Working of Steel Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (4)
- Incremental Bulk Metal FormingDocumento22 pagineIncremental Bulk Metal FormingYonjon SubhaNessuna valutazione finora
- THE Working of Steel: Page V Preface To Second EditionDocumento207 pagineTHE Working of Steel: Page V Preface To Second EditionGutenberg.org100% (2)
- Module 5 SteelDocumento21 pagineModule 5 SteelRoseMarieDagonNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Steel MakingDocumento44 pagineIntroduction To Steel MakingDrTrinath TalapaneniNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel AsiaDocumento19 pagineSteel AsiamalynNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering in HistoryDocumento259 pagineEngineering in HistoryjosedevianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Background: MeteoritesDocumento16 pagineBackground: MeteoritesAwadhesh SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Eads Bridge:: A Revolution in Bridge BuildingDocumento4 pagineThe Eads Bridge:: A Revolution in Bridge BuildingGolam Mostofa100% (1)
- All About Welding Book1Documento51 pagineAll About Welding Book1Arnel MoralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Timeline CastingDocumento5 pagineTimeline CastingCam Miller100% (1)
- The Process of Steel HistoryDocumento22 pagineThe Process of Steel HistorydaveNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Metal in ConstructionDocumento2 pagineHistory of Metal in ConstructionAsh Denem0% (1)
- A Tale of Wootz SteelDocumento11 pagineA Tale of Wootz SteelBijay Prasad UpadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- Ventajas Del Acero Como Material EstructuralDocumento3 pagineVentajas Del Acero Como Material EstructuralJohan OrdoñezNessuna valutazione finora
- The Steel StoryDocumento48 pagineThe Steel StoryChen Hsiang-ChunNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 4 Metals 1Documento15 pagineGroup 4 Metals 1Rosario BonNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel Making - Open-Hearth TehniqueDocumento5 pagineSteel Making - Open-Hearth TehniqueMarcelo Rodriguez FujimotoNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrosion of Copper and Copper Alloys in Potable Water SystemsDocumento122 pagineCorrosion of Copper and Copper Alloys in Potable Water SystemsEduardo Villacrés100% (1)
- Unit 2: Begining of A New Era Industrial RevolutionDocumento27 pagineUnit 2: Begining of A New Era Industrial RevolutionManoj KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Stainless SteelDocumento65 pagineHistory of Stainless SteelMayank100% (1)
- Sheet Metal and TinsmithryDocumento22 pagineSheet Metal and TinsmithryVictor EvangelioNessuna valutazione finora
- The Maintenance and Repair of Architectural Cast IronDocumento17 pagineThe Maintenance and Repair of Architectural Cast IronDan Octavian PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- ASSUMPTIONDocumento1 paginaASSUMPTIONretno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Reading Skills in Foreign LanguagesDocumento1 paginaTeaching Reading Skills in Foreign Languagesretno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Summarizing Paraphrasing and QuotingDocumento6 pagineSummarizing Paraphrasing and Quotingretno pidekso100% (1)
- MatrixDocumento2 pagineMatrixretno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Company To Company Teachers Book9Documento6 pagineCompany To Company Teachers Book9retno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- LESSON PLAN Retno PDFDocumento1 paginaLESSON PLAN Retno PDFretno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Exer 1Documento1 paginaExer 1retno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- EV0599Documento1 paginaEV0599retno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- All Sorts of CarsDocumento27 pagineAll Sorts of Carstammygirl772784Nessuna valutazione finora
- TOEFL practice exercises dialoguesDocumento1 paginaTOEFL practice exercises dialoguesretno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Readability and Academic Communication: A Comparative Study of Undergraduate Students' and Handbook of Three Ghanaian UniversitiesDocumento10 pagineReadability and Academic Communication: A Comparative Study of Undergraduate Students' and Handbook of Three Ghanaian UniversitiesInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Company To Company Teachers Book5Documento6 pagineCompany To Company Teachers Book5retno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Company To Company Teachers Book3Documento7 pagineCompany To Company Teachers Book3retno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Company To Company Teachers BookDocumento6 pagineCompany To Company Teachers Bookretno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Company To Company Teachers Book8Documento5 pagineCompany To Company Teachers Book8retno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap05 3Documento2 pagineChap05 3retno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Company To Company Teachers Book PART 10Documento7 pagineCompany To Company Teachers Book PART 10retno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Company To Company Teachers Book6Documento6 pagineCompany To Company Teachers Book6retno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap14 2Documento2 pagineChap14 2retno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Company To Company Teachers, Part 4Documento7 pagineCompany To Company Teachers, Part 4retno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Company To Company Teachers Book. Part 2Documento9 pagineCompany To Company Teachers Book. Part 2retno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Company To Company Teachers Book5Documento6 pagineCompany To Company Teachers Book5retno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Company To Company Teachers Book. Part 2Documento9 pagineCompany To Company Teachers Book. Part 2retno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap12 2Documento2 pagineChap12 2retno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Company To Company Teachers Book. Part 2Documento9 pagineCompany To Company Teachers Book. Part 2retno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 15Documento20 pagineChap 15retno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge Professional English Correspondence GuideDocumento4 pagineCambridge Professional English Correspondence Guideretno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 09Documento30 pagineChap 09retno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 17Documento24 pagineChap 17retno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 07Documento28 pagineChap 07retno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel PropertiesDocumento22 pagineSteel PropertiesMOHD SALMANNessuna valutazione finora
- For Product Analysis of Steel Castings (: IS:6601 - 1987 I Permissible Deviations in Chemical CompositionDocumento3 pagineFor Product Analysis of Steel Castings (: IS:6601 - 1987 I Permissible Deviations in Chemical Compositionrohan sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tec Metaric Materials Xref En-UsDocumento4 pagineTec Metaric Materials Xref En-UsSalvadorNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Elements On SteelDocumento18 pagineEffect of Elements On SteelMohamed Ahmed MaherNessuna valutazione finora
- Changing Iron to SteelDocumento1 paginaChanging Iron to Steelretno pideksoNessuna valutazione finora
- ASTM A1008/A1008M - (2018) : Stándard Specification For Steel Sheet: COLD ROLLEDDocumento1 paginaASTM A1008/A1008M - (2018) : Stándard Specification For Steel Sheet: COLD ROLLEDSilverio AcuñaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6th Sem Group Diploma Front Pkiet BargarhDocumento10 pagine6th Sem Group Diploma Front Pkiet BargarhPrabir Kumar PatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Traditional RailingDocumento21 pagineTraditional RailingSiddesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Mass Balance Modeling For Electric Arc Furnace PDFDocumento7 pagineMass Balance Modeling For Electric Arc Furnace PDFmshahNessuna valutazione finora
- STAINLESS STEEL GRADES AND PROPERTIESDocumento2 pagineSTAINLESS STEEL GRADES AND PROPERTIESHammer StormNessuna valutazione finora
- KOP PERUSAHAAN LAMPIRAN PENAWARAN JASA PT KARYA INSANI JAYADocumento10 pagineKOP PERUSAHAAN LAMPIRAN PENAWARAN JASA PT KARYA INSANI JAYAtomy ramaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ksp-Instrument Impulse Piping & TubingDocumento18 pagineKsp-Instrument Impulse Piping & TubingZulfequar R. Ali KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic part numbers and codesDocumento37 pagineBasic part numbers and codesMani Rathinam RajamaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Ferro Alloys - AR - 2017 Plant & CapacityDocumento28 pagineFerro Alloys - AR - 2017 Plant & CapacitysmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Update Jis Norms 2007 PDFDocumento3 pagineUpdate Jis Norms 2007 PDFarjun prajapatiNessuna valutazione finora
- On MetalDocumento57 pagineOn Metalkatyayani tiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- A Woodworker's Guide To Tool Steel and Heat TreatingDocumento7 pagineA Woodworker's Guide To Tool Steel and Heat TreatingCorneliu CarabellaNessuna valutazione finora
- b205g - MS Plus - 201601Documento32 pagineb205g - MS Plus - 201601Alexandre SouzaNessuna valutazione finora
- VALUES OF CRM UpdatedDocumento137 pagineVALUES OF CRM UpdatedArijit DasGuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Balanced EquationDocumento13 pagineBalanced EquationMiha FlorentinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Stainless Steel: Weldability and Joining of MaterialsDocumento3 pagineStainless Steel: Weldability and Joining of MaterialsMehmet SoysalNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Knowledge MaterialDocumento75 pagineDesign Knowledge MaterialAkin ErsozNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 - 09 Ref - Table For Type JDocumento3 pagine3 - 09 Ref - Table For Type JCharu ChhabraNessuna valutazione finora
- WPS and Welding IndexDocumento32 pagineWPS and Welding Indexantony_7100% (1)
- S1 TITAN 500 Alloy CalibrationDocumento3 pagineS1 TITAN 500 Alloy CalibrationfrankieNessuna valutazione finora
- Band Saw Blade Reference Guide: Bulletin 1037Documento8 pagineBand Saw Blade Reference Guide: Bulletin 1037Palaniappan SolaiyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermanit Nicro 82: TIG Rods, Nickel-AlloyDocumento2 pagineThermanit Nicro 82: TIG Rods, Nickel-AlloyMaximiliano Ezequiel LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrochloric Acid PDFDocumento2 pagineHydrochloric Acid PDFMai NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch. 5 - Metals and Alloys - Slides PDFDocumento134 pagineCh. 5 - Metals and Alloys - Slides PDFTamara GhroufNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacture of SteelDocumento10 pagineManufacture of SteelBGSSAP 2017Nessuna valutazione finora