Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
A Mucocele Skenario in Eng Blok 14
Caricato da
SinarinTyasDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
A Mucocele Skenario in Eng Blok 14
Caricato da
SinarinTyasCopyright:
Formati disponibili
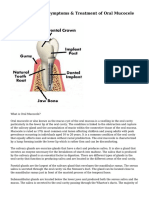
A mucocele (MYOO-koh-seal) is a swelling in your mouth. It can happen when a salivary gland is injured or blocked.
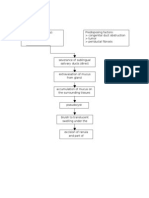
It occurs in about 1 out of 500 adults. You have many salivary glands in your mouth. They produce saliva. Saliva is made of water, mucus and enzymes. Saliva moves from a gland into your mouth through tiny tubes called ducts. Sometimes, one of these tubes is cut. The saliva pools at the cut spot and causes a swelling, or mucocele. These swellings commonly occur inside the lower lip. They also can be found in other places inside the mouth, including the roof of the mouth (palate) and the floor of the mouth. Swelling also can occur if one of these tubes is blocked and saliva backs up in the tube. If swelling occurs because the submandibular duct is blocked, the mucocele is called a ranula. A ranula is quite large and appears under the tongue. Mucocele is a common lesion of the oral mucosa that results from an alteration of minor salivary glands due to a mucous accumulation. Mucocele involves mucin accumulation causing limited swelling. Two types of mucocele can appear - extravasation and retention. Extravasation mucocele results from a broken salivary glands duct and the consequent spillage into the soft tissues around this gland. Extravasation mucoceles are caused by a leaking of fluid from surrounding tissue ducts or acini. This type of mucocele is commonly found on the minor salivary glands. Physical trauma can cause a leakage of salivary secretion into surrounding submucosal tissue. Inflammation becomes obvious due to stagnant mucous resulting from extravasation. Extravasation mucoceles appear frequently on the lower lip whereas retention mucoceles appear at any other location of the oral cavity. Occasionally mucoceles can involve the glands of Blandin-Nuhn. These glands are located on the muscle of the ventral side of the tongue; the histological diagnosis is always extravasation type, and normally affecting young patients
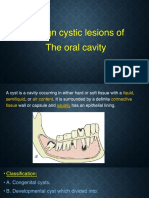
Retention mucocele appears due to a decrease or absence of glandular secretion produced by blockage of the salivary gland ducts . Retention mucoceles are formed by dilation of the duct secondary to its obstruction or caused by a sialolith or dense mucosa. The majority of retention cysts develop in the ducts of the major salivary glands.
There is no clinical difference between extravasation and retention mucoceles. Mucoceles present a bluish, soft and transparent cystic swelling which frequently resolves spontaneously. The blue colour is caused by vascular congestion, and tissular cyanosis of the tissue above and the accumulation of fluid below. Coloration can also vary depending on the size of the lesion, proximity to the surface and upper tissue elasticity
When located on the floor of the mouth these lesions are called ranulas because the inflammation resembles the cheeks of a frog. Diagnosis : Palpation can be helpful for a correct differential diagnosis. Mucoceles are mobile lesions with soft and elastic consistency depending on how much tissue is present over the lesion Despite this fluctuation, a drained mucocele would not fluctuate and a chronic mucocele with a developed fibrosis would have less fluctuation. A simple technique known as fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) is very helpful, especially when differential diagnosis of angiomatous lesions is involved. Abundant mucosa without epithelial components is found within mucoceles as well as many inflammatory cells, especially histiocytes. A histopathologic study is crucial to confirm the diagnosis and to ensure that glandular tissue is completely removed. Two types of mucoceles exist: retention mucoceles and extravasation mucoceles. In the case of retention mucoceles a cyst cavity can be found, this is generally well defined with an epithelial wall covered with a row of cuboidal or flat cells produced from the excretory duct of the salivary glands (3). Compared to extravasation mucoceles, retention mucoceles show no inflammatory reaction and are true cysts with an epithelial covering (5). Extravasation mucoceles are pseudocysts without defined walls. The extravasated mucous is surrounded by a layer of inflammatory cells and then by a reactive granulation tissue made up of fibroblasts caused by an immune reaction. Even though there is no epithelial covering around the mucosa, this is well encapsulated by the granulation tissue A mucocele can be described as a painless cyst, which is usually seen on the inner side of a persons lip. Also known as a mucous retention cyst, mucoceles are quite common, and fortunately, harmless. These cysts usually occur because of the accumulation of clear fluid on the surface of the inner lip. In several people, these cysts heal on their own, but a person may face the problem of recurrent mucoceles. If these cysts are recurrent, they have the ability to leave permanent scars on the area that they form on. Mucoceles are common in both men, as well as women, of all ages. Studies reveal that it is mostly the younger people, who are below the age group of 20, that are affected the most by this affliction. In people who are above the age of 30, the formation of the mucoceles is mainly superficial. In general, a mucocele looks like a clear, bluish bubble, which has been filled with a liquid. Some of them may also seem to have a rubbery appearance. While they do not really hurt, they could cause a bit of discomfort, if any pressure is applied on them. Although these cysts are mainly harmless, they could interfere with usual mastication process, depending on their size and location. Though this is rare, in certain instances a few types of mucocele formations could lead to complications, which require medical assistance. Hence, in such instances,mucocele treatment may be required. However, in order to use the appropriatetreatment for mucocele problems, it is important to identify the exact factors that could be causing them.
There could be several factors that lead to the formation of mucoceles in the body. One of the most common causes of this problem is a blocked or a damaged salivary gland. A rupture or even a ductal
obstruction of the salivary glands could lead to oral mucoceles. Another common cause of mucoceles in most people is the habitual and the excessive sucking of the lower lip area. This increases the pressure placed on the membranes on the inner lip, which increases the collection of clear liquid in the area, leading to a mucous cyst. It is also possible to get a mucocele on the upper lip due to the same reason. Some of the other common health conditions and occurrences that lead to mucoceles include: Biting an area on the inner lip repeatedly Trauma, in the form of a burn, inflammation, mouth infection or an injury A disease or a disorder known as oral lichen planus Taking drugs that could cause the saliva to thicken A piercing in the tongue or the lower lip
Most mucoceles, which are shallow, rupture on their own, without leading to any pain, bleeding, pus or anything else like that. Hence, in most people, the treatment of mucoceleis not required. However, though it is not very common, in some cases the mucocele may go on for a longer period of time, without bursting or getting drained. In such instances, a person may need to seek mucoceles treatment or even go through a mucocele removal surgery, to prevent the cyst from turning into a permanent nodular scar.
Mucocele treatment Before suggesting any form of treatment, mucocele home remedy or a mucocele removalprocedure, a medical health care giver needs to confirm the diagnosis of the mucocele, by examining the area visually. At times, it could be continued trauma that is causing a delay in the healing of the mucocele. Hence after identifying the main cause of the problem, a doctor may suggest various options, right from home remedies for mucocele to mucocele treatment with laser. For longer lasting cysts, some of the common procedures that are usually suggested by doctors are drainage, aspiration, cryotherapy, surgical removal and laser treatment. Mucocele home treatment Several people swear by the home treatment options for oral mucous retention cysts. Many health experts too, recommend mucocele treatment with alum, since it causes the cyst to grow rapidly and then pop on its own. Moreover, alum reduces the possibilities of any infections or inflammations in the area. For best results, it is suggested that a small amount of alum should be applied on the mucocele for around 10 to 15 minutes and then, rinsed off using a good mouthwash. Another common home remedy in mucocele treatment is salt therapy. Around a teaspoon of sea salt should be added to a glass of warm water and used as a mouth rinse, twice or three times each day. After about four or five days, the size of the cyst should have reduced considerably. However, it is important to regulate the size of the mucocele on a daily basis and continue with this remedy, only if the size seems to have reduced within a day or two.
Primrose oil can also be applied directly on to the cyst, in order to help it heal faster. This home remedy also reduces the chances of an infection. Some people use castor oil combined with honey too, in place of primrose oil. In case the home remedies for mucocele mentioned above are not very effective in treating the condition, it is best to check with a doctor, for other medical treatment options. The doctor should also be consulted about mucocele treatment cost, effectiveness, side effects as well as the chances of the cysts recurring, before taking any decision. Mucocele removal surgery In case the home remedies or other treatment options for getting rid of mucoceles do not yield the desired result, it may be best to consider mucocele removal options. However, there is no guarantee that a mucocele will not return even after a surgical or a laser procedure. This is just a chance that several people decide to take and hope that they will not be bothered with mucoceles in the future. Since most of the procedures are as good as non invasive, mucocele removal care is minimal. However, mucocele removal recovery time could take up to a week, where a person may need to eat soft foods for about two days. Mucocele removal cost could range from a few dollars, to a few hundreds, depending on the doctor and the medical facility. It is important to discuss these aspects with a doctor carefully.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Sebaceous Cyst, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandSebaceous Cyst, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- What Are Mucous CystsDocumento10 pagineWhat Are Mucous CystsNena TamaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Date-58954846779f70 45433502 PDFDocumento3 pagineDate-58954846779f70 45433502 PDFernestohiggins02Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A MucoceleDocumento2 pagineWhat Is A MucoceleGieh SyafitriNessuna valutazione finora
- Mucocele Ranula Sialolithiasis SialoadenitisDocumento4 pagineMucocele Ranula Sialolithiasis SialoadenitisNegin HekmatjooNessuna valutazione finora
- Mucocele On The Lower Lip Treated by Scalpel Excision Method-A CaseDocumento5 pagineMucocele On The Lower Lip Treated by Scalpel Excision Method-A CaseGea Akalili SabrinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sjogren Syndrome Xerostomia Traumatic ApaliDocumento4 pagineSjogren Syndrome Xerostomia Traumatic ApaliNegin HekmatjooNessuna valutazione finora
- Saint Louis University School of Medicine Department of OphthalmologyDocumento6 pagineSaint Louis University School of Medicine Department of OphthalmologyDjan Kurvie ValencerinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Article 1452106206 PDFDocumento5 pagineArticle 1452106206 PDFYosu Obok HermanlieNessuna valutazione finora
- Extravasation Mucocele - A Case ReportDocumento3 pagineExtravasation Mucocele - A Case ReportSSR-IIJLS JournalNessuna valutazione finora
- Non Neoplastic Ds of Salivary GlandDocumento30 pagineNon Neoplastic Ds of Salivary Glandgud4nothingNessuna valutazione finora
- A Case Report of Mucocele: International Journal of Clinical Preventive DentistryDocumento4 pagineA Case Report of Mucocele: International Journal of Clinical Preventive DentistryDhiya Salma AzminidaNessuna valutazione finora
- ميدسنDocumento43 pagineميدسنjuren.zafat.05Nessuna valutazione finora
- Salivary MI Ucoceles Jul16Documento1 paginaSalivary MI Ucoceles Jul16PoopooNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Report MukokelDocumento4 pagineCase Report MukokelWidychii GadiestchhetyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Goo Jurnal MukokelDocumento4 pagineGoo Jurnal MukokelRhea Zarna IrsataniNessuna valutazione finora
- Mukokel OralDocumento4 pagineMukokel OralIlma Kurnia SariNessuna valutazione finora
- Cara Perawatan Gigi Tiruan LepasanDocumento3 pagineCara Perawatan Gigi Tiruan LepasanBayyin Bunayya CholidNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral Mucocele: Report of Two CasesDocumento4 pagineOral Mucocele: Report of Two CasesSukma Ayu RossaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anal FissureDocumento9 pagineAnal FissureKnight StingrayNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 19 DISEASES OF THE SALIVARY GLANDDocumento17 pagineLec 19 DISEASES OF THE SALIVARY GLANDpxb8dhqgs9Nessuna valutazione finora
- HYDROCELEDocumento3 pagineHYDROCELESean Patrick Acoba100% (2)
- Inflammation (Sialadenitis) Report in PathologyDocumento7 pagineInflammation (Sialadenitis) Report in PathologyHerlene Lyneth ZalamedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral Mucocele: Review of The Literature: Key WordsDocumento4 pagineOral Mucocele: Review of The Literature: Key WordsEndah Dwi AriyaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Jihvaagat RogDocumento13 pagine1 Jihvaagat RogKnr GannuNessuna valutazione finora
- Functions of Parotid GlandDocumento32 pagineFunctions of Parotid GlandAsline JesicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Oralmucocele AcasereportDocumento5 pagineOralmucocele AcasereportxxxNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral Pathology: Non-Epithelialized Primary Bone CystDocumento4 pagineOral Pathology: Non-Epithelialized Primary Bone Cystعلي صادق جعفرNessuna valutazione finora
- A StyeDocumento12 pagineA StyeNaomi Cyden YapNessuna valutazione finora
- Nasal Lacrimal Duct ObstructionDocumento2 pagineNasal Lacrimal Duct ObstructionAgitha Melita PutriNessuna valutazione finora
- Disease of Salivary Gland Single Choice QuestionsDocumento3 pagineDisease of Salivary Gland Single Choice Questions龙龙Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrocele: CausesDocumento7 pagineHydrocele: CauseslanaNessuna valutazione finora
- IV - Morganti@libero - It M.morganti@libero - It: Pilonidal Sinus (Pilonidal Cysts and Fistulas)Documento3 pagineIV - Morganti@libero - It M.morganti@libero - It: Pilonidal Sinus (Pilonidal Cysts and Fistulas)Madhan Mohan Reddy KatikareddyNessuna valutazione finora
- MNJJDocumento12 pagineMNJJFadhli AzhimiNessuna valutazione finora
- HYDROCELEDocumento3 pagineHYDROCELEnayr77100% (1)
- Odontogenic CystsDocumento5 pagineOdontogenic CystsBH ASMRNessuna valutazione finora
- Meconium Plug SyndromeDocumento3 pagineMeconium Plug SyndromeGlen Jacobs SumadihardjaNessuna valutazione finora
- Benign Vulvar Lesions: DR Sally Sayed El-Tawab Lecturer of Gyne-Oncology Alexandria UniversityDocumento34 pagineBenign Vulvar Lesions: DR Sally Sayed El-Tawab Lecturer of Gyne-Oncology Alexandria Universitysalah subbahNessuna valutazione finora
- د.نجاة Cyst-7 (Muhadharaty) 1Documento28 pagineد.نجاة Cyst-7 (Muhadharaty) 1بكر الدوريNessuna valutazione finora
- Ahmed Hussain Al-Ghdban 200910244 Saif Haider Al - Kaisi 200911232Documento19 pagineAhmed Hussain Al-Ghdban 200910244 Saif Haider Al - Kaisi 200911232alsakar26Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Clinical Approach White LesionDocumento5 pagineA Clinical Approach White LesionTirta KusumaNessuna valutazione finora
- Epidermolysis Bullosa: Dr. Prasant National Burns CentreDocumento15 pagineEpidermolysis Bullosa: Dr. Prasant National Burns CentresandhyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Salivary Duct CystDocumento11 pagineSalivary Duct Cystrnad foudahNessuna valutazione finora
- Odontogenic Keratocyst: - Jayalakshmi Preetha Meyyanathan CRIDocumento48 pagineOdontogenic Keratocyst: - Jayalakshmi Preetha Meyyanathan CRIJayalakshmi PreethaNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral CystDocumento47 pagineOral CystmelNessuna valutazione finora
- PulpitisDocumento23 paginePulpitisvinnu kalyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study PresentationDocumento28 pagineCase Study PresentationRyka GalvanNessuna valutazione finora
- Phatology The Eyelids, Lacrimal GlandsDocumento62 paginePhatology The Eyelids, Lacrimal GlandsGermanyNessuna valutazione finora
- Rangkuman Penyakit MataDocumento11 pagineRangkuman Penyakit MataliorahelgaNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Ranula Formation PathophysiologyDocumento2 pagineSimple Ranula Formation PathophysiologyDolly BenitezNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.epulis Fissuratum: ClassificationDocumento3 pagine1.epulis Fissuratum: ClassificationArafat Masud NiloyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lip Mucocele: A Case Report: DR - Rushi Kumar Patel, DR - Nishant Singh, DR - Aniket Singh Chauhan, DR - Vinay KumarDocumento3 pagineLip Mucocele: A Case Report: DR - Rushi Kumar Patel, DR - Nishant Singh, DR - Aniket Singh Chauhan, DR - Vinay Kumaryuliatinnurhasanah100% (1)
- Oral Complications of Cancer TreatmentDocumento68 pagineOral Complications of Cancer TreatmentFarisha RasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- Molluscum ContagiosumDocumento1 paginaMolluscum Contagiosumshailesh284Nessuna valutazione finora
- Odontogenic CystsDocumento54 pagineOdontogenic CystssamsoomaustNessuna valutazione finora
- Odontogenic CystsDocumento106 pagineOdontogenic Cystsريام الموسويNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of PulpitisDocumento18 pagineClassification of PulpitisEkrar Okto ViarNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Patients With Oral and Esophageal DisordersDocumento81 pagineManagement of Patients With Oral and Esophageal DisordersEdmond ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ranula Cyst, (Salivary Cyst) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandRanula Cyst, (Salivary Cyst) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3.3Documento21 pagineLesson 3.3Claude Nathan AlidoNessuna valutazione finora
- Rhopalocera (Butterfly) : FunctionsDocumento18 pagineRhopalocera (Butterfly) : FunctionsChris Anthony EdulanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - Part IIDocumento183 pagine2.ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - Part IIBharat ThapaNessuna valutazione finora
- USMLE Step 1 - ReproductionDocumento65 pagineUSMLE Step 1 - ReproductionMatt McGlothlin100% (1)
- Bio1301 Lecture Note - Plant Section PDFDocumento32 pagineBio1301 Lecture Note - Plant Section PDFAjomNessuna valutazione finora
- June 2023 (v1) (9-1) QP - Paper 4 CAIE Biology IGCSEDocumento20 pagineJune 2023 (v1) (9-1) QP - Paper 4 CAIE Biology IGCSEismgilovamunisa150Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alborz B7: Pooyandegan Rah SaadatDocumento203 pagineAlborz B7: Pooyandegan Rah SaadatjuanmaraviNessuna valutazione finora
- Characterization of CarbohydratesDocumento3 pagineCharacterization of CarbohydratesHyvieNessuna valutazione finora
- Tumor Immunology BMS 3.1Documento38 pagineTumor Immunology BMS 3.1Kato CalebNessuna valutazione finora
- IADVL Color Atlas of Dermatopathology - BookDocumento41 pagineIADVL Color Atlas of Dermatopathology - Book65gkenNessuna valutazione finora
- Resume CurrentDocumento2 pagineResume Currentapi-462451258Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ubah HpaDocumento1 paginaUbah HpaChidiebereNessuna valutazione finora
- Penile US and Doppler USDocumento2 paginePenile US and Doppler UShardrocker_2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- CellBiologyLec3Spring2020DrMIKotbEl SayedDocumento35 pagineCellBiologyLec3Spring2020DrMIKotbEl SayeddeyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Struct and FunctionDocumento4 pagineCell Struct and Functionamitdeo99Nessuna valutazione finora
- Supervised Classification Techniques and Deep Learning For Mortality Prediction in Sepsis PatientsDocumento6 pagineSupervised Classification Techniques and Deep Learning For Mortality Prediction in Sepsis PatientsFabian Alberto Jaimes BarraganNessuna valutazione finora
- AutopsyDocumento24 pagineAutopsyRoberto Giorgio N. Pacheco100% (1)
- AnaemiaDocumento7 pagineAnaemiaYousef El3alameyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 20: ApoptosisDocumento56 pagineLecture 20: ApoptosisTran Nhat ThangNessuna valutazione finora
- 23 Anatomy Physiology TermsDocumento30 pagine23 Anatomy Physiology TermsAlyssa Gwyneth GalubaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ice TherapyDocumento5 pagineIce TherapyDiane CastillonNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Sicu!Documento6 pagineNCP Sicu!joanne190Nessuna valutazione finora
- Proliferasi in Vitro Dan Aklimatisasi Pisang Kepok Unti Sayang (ABB) Dengan Penambahan Bahan OrganikDocumento10 pagineProliferasi in Vitro Dan Aklimatisasi Pisang Kepok Unti Sayang (ABB) Dengan Penambahan Bahan Organiksarah khoerun nisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar PustakaDocumento2 pagineDaftar PustakaRakanita Tiara PuspitasariNessuna valutazione finora
- HTTPS://WWW - Scribd.com/presentation/332117871/mga Uri NG Tekstong ImpormatiboDocumento2 pagineHTTPS://WWW - Scribd.com/presentation/332117871/mga Uri NG Tekstong ImpormatiboRegine AbilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Kemu A & P 2Documento6 pagineKemu A & P 2malenya1Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 PBDocumento8 pagine1 PBVelani ElendiaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Heart AnatomyDocumento21 pagineThe Heart AnatomyLidia Dwi PutriNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics - CMIDocumento177 pagineGenetics - CMI7ett_100% (1)
- Science Discovers The Physiological Value of Continence 2Documento20 pagineScience Discovers The Physiological Value of Continence 2shaswata_panjaNessuna valutazione finora