Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Albin Countergambit, Lasker Trap - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Caricato da
andhityaputraDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Albin Countergambit, Lasker Trap - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Caricato da
andhityaputraCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Albin Countergambit, Lasker Trap - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lasker_Trap
Albin Countergambit, Lasker Trap
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
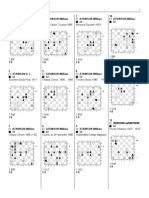
(Redirected from Lasker Trap) The Lasker Trap is a chess opening trap in the Albin Countergambit, named after Emanuel Lasker, although it was first noted by Serafino Dubois (Hooper & Whyld 1996, p. 219).[1] It is unusual in that it features an underpromotion as early as the seventh move.
a 8 7 6 5 4 b c d e f g h 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 a b c d e f g h
Contents
1 Analysis 2 See also 3 References
3 2 1
Position after 5...dxe3, setting the trap
Analysis
1. d4 d5 2. c4 e5 The Albin Countergambit. 3. dxe5 d4 The black pawn on d4 is stronger than it appears. 4. e3? Careless. Usual and better is 4.Nf3. 4... Bb4+ 5. Bd2 dxe3! (see diagram) Now White's best option is to accept doubled pawns with 6.fxe3. 6. Bxb4?? Blundering into the Lasker Trap. In an 1899 consultation game in Moscow, Blumenfeld, Boyarkow, and Falk playing White against Lasker tried 6.Qa4+?, but Black wins after this move also. The game continued 6...Nc6 7.Bxb4 Qh4 8.Ne2 Qxf2+ 9.Kd1 Bg4 10.Nc3 0-0-0+ 11.Bd6 cxd6 12.e6 fxe6 13.Kc1 Nf6 14.b4 d5 15.b5 Ne5 16.cxd5 Nxd5 17.Qc2 Nb4 18.Nd1+ Nxc2 19.Nxf2 Rd2 White resigned. The Encyclopedia of Chess Openings (volume D) gives 6.fxe3 as the best move. Black gets a slight advantage, but White has avoided the worst and can defend. 6... exf2+ Now 7.Kxf2 would lose the queen to 7...Qxd1, so White must play 7.Ke2.
1 dari 2
19/01/2014 13:05
Albin Countergambit, Lasker Trap - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lasker_Trap
7. Ke2 fxg1=N+! (see diagram) Underpromotion is the key to the trap. (If instead 7...fxg1=Q, then 8.Qxd8+ Kxd8 9.Rxg1 is okay for White.) Now 8.Rxg1 Bg4+ skewers White's queen, so the king must move again. 8. Ke1 Qh4+ 9. Kd2 The alternative, 9.g3, loses the h1-rook to the fork 9...Qe4+. 9... Nc6 White is hopelessly lost. After 10.Bc3, 10...Bg4 followed by 11...0-0-0+ is crushing.
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
h 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Position after 7...fxg1=N+!
See also
List of chess traps
References
Notes
1. ^ Hooper & Whyld 1996 say that Dubois pointed out the trap in 1872 (p. 219). Although they don't specify where Dubois published the trap, it could refer to the three-volume work on the openings that Dubois published from 1868 to 1873 (p.116). Elsewhere they state that the Albin Countergambit was not introduced until 1881 (p. 6), which seems to be a contradiction. It isn't clear if the trap discovery date 1872 should perhaps instead be 1882, or if 1881 was the tournament introduction of an opening that had been published in 1872 or earlier.
Bibliography
Burgess, Graham (2000), The Mammoth Book of Chess, Carroll & Graf, ISBN 0-7867-0725-9 Hooper, David; Whyld, Kenneth (1996), The Oxford Companion to Chess (2 ed.), Oxford University, ISBN 0-19-280049-3 Blumenfeld/Boyarkow/Falk vs Emanuel Lasker, Moscow 1899 (http://www.chessgames.com /perl/chessgame?gid=1380336), retrieved 2008-01-24 (game score at chessgames.com)
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Albin_Countergambit,_Lasker_Trap& oldid=569198847" Categories: Chess traps 1899 in chess This page was last modified on 19 August 2013 at 09:59. Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License; additional terms may apply. By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-profit organization.
2 dari 2
19/01/2014 13:05
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Interntional Cat PDFDocumento2 pagineInterntional Cat PDFandhityaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- Bill of Materials and Engineering DrawingsDocumento1 paginaBill of Materials and Engineering DrawingsFaull JackmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Layout Titik Uji SondirDocumento1 paginaLayout Titik Uji SondirandhityaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- 204.a Vendor Data CCTV - Layout of Panel Arrangement (Attach)Documento3 pagine204.a Vendor Data CCTV - Layout of Panel Arrangement (Attach)andhityaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- NDTDocumento11 pagineNDTandhityaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- Royal SinkDocumento1 paginaRoyal SinkandhityaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- Cara Pasang STP Biofive 5m3Documento1 paginaCara Pasang STP Biofive 5m3andhityaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- Vertical CompressDocumento47 pagineVertical CompressAskar InanNessuna valutazione finora
- U Dict BelokDocumento1 paginaU Dict BelokandhityaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- 012.water Pond Garawangi-WATER PONDDocumento1 pagina012.water Pond Garawangi-WATER PONDandhityaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- Sika WaterProofing MortarDocumento3 pagineSika WaterProofing MortarandhityaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- 016.foudation Lightning Protection Sunyaragi.b-deTAILSDocumento1 pagina016.foudation Lightning Protection Sunyaragi.b-deTAILSandhityaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- HTTP Www7.Ncdc - Noaa.gov CDO GSOD DESCDocumento6 pagineHTTP Www7.Ncdc - Noaa.gov CDO GSOD DESCandhityaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- Anchore MeteringDocumento1 paginaAnchore MeteringandhityaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- App Ground SoilResistivityDocumento7 pagineApp Ground SoilResistivityPrashanth Reddy GouniNessuna valutazione finora
- DL1Documento1 paginaDL1andhityaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Expansive SoilDocumento12 pagine7 Expansive Soilईशान्त शर्माNessuna valutazione finora
- Laws of FootballDocumento144 pagineLaws of FootballBeljun FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Plane StressDocumento15 paginePlane Stressచిమ్ముల సందీప్ రెడ్డిNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 98Documento30 pagineChapter 7 98andhityaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- Gpanjang PDFDocumento24 pagineGpanjang PDFandhityaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- TabelberatbesiDocumento12 pagineTabelberatbesiandhityaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- Tabel Konversi SatuanDocumento1 paginaTabel Konversi SatuanSutopo AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Struktur Beton BertulangDocumento271 pagineStruktur Beton BertulangHarly Bigbang100% (1)
- D4546 SwellDocumento7 pagineD4546 SwellAlysson SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Gambar Desain - 3 ModelDocumento1 paginaGambar Desain - 3 ModelandhityaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- 115603-3939 Ijcee-Ijens PDFDocumento7 pagine115603-3939 Ijcee-Ijens PDFandhityaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Modern Chess MagazineDocumento96 pagineModern Chess MagazineMauricio Abril Guiza100% (3)
- Sicilian Defence - E4c5Documento21 pagineSicilian Defence - E4c5starpenchal2014Nessuna valutazione finora
- MDF304 Cory Pattern Letter A4Documento45 pagineMDF304 Cory Pattern Letter A4BeaNessuna valutazione finora
- GM2 ExcerptDocumento7 pagineGM2 ExcerptmjhermanNessuna valutazione finora
- Fide Survey March 2013 - MarinDocumento5 pagineFide Survey March 2013 - MarinRenukha PannalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tim Harding - Chess Cafe - The Kibitzer (Columns With FENs)Documento925 pagineTim Harding - Chess Cafe - The Kibitzer (Columns With FENs)Carlos Pastor García100% (3)
- Mate in 2 Part 1Documento1.355 pagineMate in 2 Part 1James NeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Experts On The Anti Sicilian PDFDocumento2 pagineExperts On The Anti Sicilian PDFMonique0% (1)
- French Defence Chess OpeningDocumento9 pagineFrench Defence Chess OpeningheneryNessuna valutazione finora
- Advance French 5... Qb6 6.a3 As WhiteDocumento160 pagineAdvance French 5... Qb6 6.a3 As WhiteKim Kenneth SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- CHESS Grandmaster - Queens Indian Defense - Understanding The Chess Openings - by Soltis A Et Al - PDF RoomDocumento96 pagineCHESS Grandmaster - Queens Indian Defense - Understanding The Chess Openings - by Soltis A Et Al - PDF Roomvandanapu rameshNessuna valutazione finora
- 101 Chess Opening TrapsDocumento3 pagine101 Chess Opening Trapsradovanb33% (3)
- Keres-Furman, 17th USSR-ch, Moscow 1949Documento5 pagineKeres-Furman, 17th USSR-ch, Moscow 1949Douglas GriffinNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Sheet 1-50Documento1 paginaAnswer Sheet 1-50Rio OrpianoNessuna valutazione finora
- DownloadDocumento29 pagineDownloadAndrei K.Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2014 N-Max 155.psDocumento448 pagine2014 N-Max 155.psC sNessuna valutazione finora
- Palkovi Joszef - Hedgehog System Against The English Opening 1997 PDFDocumento132 paginePalkovi Joszef - Hedgehog System Against The English Opening 1997 PDFMayara JulianNessuna valutazione finora
- ScandinavianDocumento11 pagineScandinavianJess0% (3)
- Prodigy Program Written Lecture Opening Principles 1 PDFDocumento2 pagineProdigy Program Written Lecture Opening Principles 1 PDFMelwyn CardozaNessuna valutazione finora
- entrenador-ARM-esquema-nuevo ModeloDocumento1 paginaentrenador-ARM-esquema-nuevo ModeloLeevan BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Canada'S Chess Magazine For Kids: September 2019 Number 145Documento27 pagineCanada'S Chess Magazine For Kids: September 2019 Number 145Bolo BTNessuna valutazione finora
- Kindermann Stefan - Leningrader System, 2002Documento208 pagineKindermann Stefan - Leningrader System, 2002sycil100% (1)
- Chess Tactics 5000+ VOL. 1 RAWDocumento33 pagineChess Tactics 5000+ VOL. 1 RAWTj Ronz Saguid100% (4)
- Solo Chet Baker - Dancing On The CeilingDocumento1 paginaSolo Chet Baker - Dancing On The CeilingPaola FrancioniNessuna valutazione finora
- Masterclass on Legendary Chess Grandmaster Akiba RubinsteinDocumento8 pagineMasterclass on Legendary Chess Grandmaster Akiba RubinsteinSagnik RayNessuna valutazione finora
- Mating PatternsDocumento13 pagineMating PatternsRenukha PannalaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1... B6 Move by Move Cyrus Lakdawala Everyman Chess PDFDocumento380 pagine1... B6 Move by Move Cyrus Lakdawala Everyman Chess PDFshreyas anand100% (4)
- Frequencies of Musical Notes, A4 440 HZDocumento5 pagineFrequencies of Musical Notes, A4 440 HZbrentfolsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Danish Gambit 01Documento4 pagineDanish Gambit 01Ahmad RiyantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tips To Improve Middlegame Play: Lesson-1: Chess Strategy: Weak SquaresDocumento3 pagineTips To Improve Middlegame Play: Lesson-1: Chess Strategy: Weak SquaresDavid FrancoNessuna valutazione finora