Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Angle of Minimum Deviation
Caricato da
ajithfanDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Angle of Minimum Deviation
Caricato da
ajithfanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1
ANGLE OF MINIMUM DEVIATION OF PRISM
Objective: Study of the variation of angle of deviation with the angle of incidence by plotting I~ D curve
and hence determine the angle of minimum deviation for a given wavelength using a spectrometer.
APPARATUS:
Spectrometer, Prism, Sodium Lamp and Spirit level.
Overview:
A light ray is said to be deviated when there is a
change in the path of light ray suffering reflection or
refraction. When a light ray suffers from refraction, the angle
between the incident ray and emergent ray is called the angle
of deviation. In Fig. 1 i is the angle of incidence, r is the
angle of emergence and is the angle of deviation. When
refraction takes place, through a prism in such a manner that
the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of emergence, the
refracted ray will be parallel to the base of the prism. The ray is symmetrical under these
conditions. It can be mathematically proved that when the above conditions are satisfied for a
particular value of i, the deviation suffered by the light ray is minimum and the angle of
deviation is known as the angle of minimum deviation
m
. For any other value of i, the value of
increases.
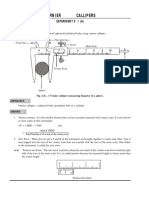
Fig. 2: Experimental set up
Fig. 1
2
Procedure:
1. Become familiar with the spectrometer
Identify each component: the circular scale, the prism table, the collimator, and the telescope.
Note the clamping screws and the fine adjustment screws for the telescope. Note the
clamping screw for the prism table.
Note how to adjust focusing of the slit in the collimator tube and also the telescope focus and
the eyepiece.
Note how the slit width can be adjusted.
2. Determine the vernier constant (VC) of the spectrometer by filling up Table-1.
3. Practice reading the angle from the circular scale. Use the vernier scale with the little
magnifying glass to read the angle to the nearest arc minute. (1 arcmin = 1' = 1/ 60 degree.)
The following is an example: In the figure below, the zero point on the vernier scale is
between the 155 and 15530' (or 155.5) marks on
the degree plate. So the main scale reading (M) is
155. Now note the vernier reading (V) by finding the
line on the vernier scale that aligns most closely with
any line on the main scale. From figure, V=15.
Assuming the vernier constant (VC) = 1', the total
reading (T) is T = 155 + (1'15) = 155 15' or
155.4. For convenience convert all the readings to
degrees.
4. Complete all the preliminary adjustments and focusing of the spectrometer as instructed
in the supporting manual.
5. Clamp the prism table
6. Illuminate the slit of the collimator with the given source, i.e. sodium lamp. Note that the
lamp takes some time to warm up before getting fully illuminated. Adjust the telescope
position in line with the collimator so that the direct image of the slit is centered on the
vertical crosswire. Note the reading for this position of telescope on any one of the
verniers (say V
1
). (No need to tabulate it.)
7. Setting the angle of incidence (i): (Refer
Fig. 2)
DO NOT PLACE THE PRISM ON THE
SPECTROMETER YET.
Let us start with an angle of incidence, i (say 45).
To set this angle the telescope should be rotated in
clockwise or anticlockwise direction from the direct
image position exactly by an angle = 180-2i, i.e.
(180 90) = 90, looking at the same vernier V
1
.
Clamp the telescope in this position. The angle
between the axes of the collimator and telescope is
2i (i.e.90
0
).
Telescope position
for angle of incidence
Telescope position
for angle of deviation
Collimator
Fig. 2
3
Keep the prism on the prism table oriented as shown in Fig. 2.
Release the prism table and turn it slowly, till the reflected image of the slit from the
refracting surface AB is visible in the field of view of the telescope.
Clamp the prism table. Using the fine adjustment screw allow the image of the slit to
coincide with the vertical cross-wire. The prism is now adjusted for an angle of incidence
i = 45.
8. Angle of deviation (): (Refer Figs. 2 and 3)
Keeping the prism table clamped, slowly turn the
telescope towards the second refracting surface AC (away
from the collimator till the image of the slit is visible in
the field of view of the telescope.
Clamp the telescope. Using the fine adjustment screw
allow the image of the slit coincide with the vertical
cross-wire. Note down the readings. Let the readings be
1
and
2
on the two verniers V
1
and V
2
respectively.
Remove the prism and rotate the telescope as shown by
arrow in Fig. 3 to get the direct image of the slit
coinciding with the vertical cross-wire. Let the readings
be D
1
and D
2
on the two verniers V
1
and V
2
respectively.
The angle of deviation can then be calculated as
1
= (
1
~B
1
) for V
1
2
= (
2
~B
2
) for V
2
Thus the mean angle of deviation for an angle of
incidence i = 45 is determined as o =
1
2
(o
1
+o
2
).
9. Repeat the above procedure (7 & 8) to find the angle of deviation o, for various values of
i starting from 45 to 80 in steps of 5 and fill up tables 2 & 3 simultaneously.
10. Plot a graph between angle of incidence i (X-axis) and the angle of deviation 6 (Y-axis)
and determine the angle of minimum deviation o
m.
11. Knowing the angle of prism and refracting index of the material of the prism, calculate
the value of o
m
and compare with the value determine from graph.
Observations:
Table 1: Determination of vernier constant (VC) of the spectrometer
Value of 1 small main scale division (MSD) =
. vernier scale divisions = .. main scale divisions
Hence, 1 vernier scale division = main scale division (VSD)
Vernier Constant (VC) = (1 VSD) x MSD =
Fig. 3
4
Table 2: For Vernier I
i (
0
) Deviated ray (
1
) (
0
) Direct ray ( D
1
) (
0
) Angle of deviation
1
= (
1
~B
1
)
(
0
)
M.S.R V.C V.S.R Total M.S.R V.C V.S.R Total
45
50
Table 3: For Vernier II
i (
0
) Deviated ray (
2
) (
0
) Direct ray ( D
2
) (
0
) Angle of deviation
2
= (
2
~B
2
)
(
0
)
M.S.R V.C V.S.R Total M.S.R V.C V.S.R Total
45
50
Table 4: data for i ~ 6 plot
Calculations:
From graph, angle of minimum deviation, 6
m
=
From calculation: Given, angle of prism A= 60
0
,
refractive index of the material of prism = 1.52 (for crown glass) and 1.62 (for flint glass)
i (
0
) 45 50
=
1
2
(o
1
+o
2
)
Mean 6
(
0
)
5
Using the equation, p =
sn[
A+6
m
2
sIn [
A
2
, calculate 6
m
=
Discussions:
Precautions:
1. Leveling of both the spectrometer and the prism table has to be done accurately and Prism
table should be fixed to its axis.
2. The slit should be as narrow as possible.
3. Gently turn the fine adjustment screws and avoid backlash errors.
4. Carefully handle the prism. Do not touch the refracting surfaces by hand. Place the prism on
the prism table or remove it from the prism table by holding it with fingers at the top and
bottom faces.
Reference:
1. Practical Physics, R.K. Shukla and A. Srivastava.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 5 Reflection High Energy Electron Diffraction (RHEED)Documento19 pagine5 Reflection High Energy Electron Diffraction (RHEED)Lương Hữu BắcNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Mechanics Vectors and ScalarsDocumento42 pagineEngineering Mechanics Vectors and ScalarssatwantNessuna valutazione finora
- QuesDocumento2 pagineQuesGmind0% (5)
- ASTM D5361 Sampling of Compacted PavementDocumento3 pagineASTM D5361 Sampling of Compacted Pavementrajeshji_000100% (5)
- Prism SpectrometerDocumento8 paginePrism SpectrometerAnuruddha Dilshan RathnayakeNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Lab Report For Phy 112 and 110Documento28 pagineFinal Lab Report For Phy 112 and 110fireballhunter646Nessuna valutazione finora
- Refractive Index of PrismDocumento3 pagineRefractive Index of PrismPaul GeorgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Material Physics Lab Report #2Documento6 pagineMaterial Physics Lab Report #2Justas Petrauskas100% (1)
- 11 Refractive Index - Using Concave MirrorDocumento3 pagine11 Refractive Index - Using Concave MirrorAbhiram ChaturvediNessuna valutazione finora
- CE 6306 / Strength of Materials Mechanical Engineering 2016-17Documento6 pagineCE 6306 / Strength of Materials Mechanical Engineering 2016-17amdevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Manual Phy1Lab Expt. 1Documento7 pagineLab Manual Phy1Lab Expt. 1Riyad NahinNessuna valutazione finora
- EXP 9 AC MainsDocumento5 pagineEXP 9 AC MainsRude BøyNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Concepts of A CircleDocumento11 pagineBasic Concepts of A CircleSudharani Sudha100% (1)
- Practical Physics For XI and XIIDocumento36 paginePractical Physics For XI and XIIRameshkumar Ramanathan100% (1)
- Physics Instruction Manual 2015 16 SRM UniversityDocumento65 paginePhysics Instruction Manual 2015 16 SRM UniversityDEVVARUNNessuna valutazione finora
- N P Fermi-Gas ModelDocumento8 pagineN P Fermi-Gas ModelabdulbaseerNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry ProjectDocumento9 pagineChemistry ProjectShivam Kumar100% (1)
- Practical BookDocumento70 paginePractical Bookbyekwaso umaruNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Physics (Part-I)Documento84 paginePractical Physics (Part-I)Raju SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrochemical-Cells Kec PDFDocumento10 pagineElectrochemical-Cells Kec PDFsachinNessuna valutazione finora
- Module-01 Oscillations & Shock WavesDocumento23 pagineModule-01 Oscillations & Shock WavesSoundarya T j100% (1)
- Some Applications of Differential Equations in RL-RC Electrical CircuitDocumento12 pagineSome Applications of Differential Equations in RL-RC Electrical CircuitArindam MondalNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment (1) Refraction of The Light and Snell's Law: ObjectiveDocumento5 pagineExperiment (1) Refraction of The Light and Snell's Law: Objectivealvin talaveraNessuna valutazione finora
- 05.huygen's PrincipleDocumento17 pagine05.huygen's PrincipleSergio Saldano YudaNessuna valutazione finora
- Study of Magnetic Field Along The Axis of A Circular Coil Stewart and Gees ExperimentDocumento5 pagineStudy of Magnetic Field Along The Axis of A Circular Coil Stewart and Gees Experimentraoram76995940% (5)
- Screw Gauge (Micrometer) : Determination of Thickness/dameter of Thin Sheet/wire. Important FormulaeDocumento2 pagineScrew Gauge (Micrometer) : Determination of Thickness/dameter of Thin Sheet/wire. Important Formulaevishal_kalraNessuna valutazione finora
- Carey Foster BridgeDocumento9 pagineCarey Foster BridgeAstronaut Kennedy100% (4)
- Newton's Ring ExperimentDocumento10 pagineNewton's Ring ExperimentOm JaiswalNessuna valutazione finora
- Relationship Between Critical Angle and Refractive IndexDocumento23 pagineRelationship Between Critical Angle and Refractive IndexNurul Syafiqah RoslanNessuna valutazione finora
- Maxwell NeedleDocumento2 pagineMaxwell NeedleKashifChaudhary50% (2)
- Power Source.Documento12 paginePower Source.SaritechNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Practice Lab Manual Electrical and ElectronicsDocumento55 pagineEngineering Practice Lab Manual Electrical and ElectronicsThanix SubramanianNessuna valutazione finora
- Plane and Solid Geom Problem Set PDFDocumento1 paginaPlane and Solid Geom Problem Set PDFRenz FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- IO.5 Elliptically Polarized Light: 1. PurposeDocumento5 pagineIO.5 Elliptically Polarized Light: 1. PurposeAaloka GautamaNessuna valutazione finora
- To Convert A Weston Type Galvanometer Into An Ammeter of Range 0Documento4 pagineTo Convert A Weston Type Galvanometer Into An Ammeter of Range 0Sulman Abbasi0% (2)
- B.tech Applied Physics Lab ManualDocumento87 pagineB.tech Applied Physics Lab ManualSwastika sainNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 3 - Prism SpectrometerDocumento6 pagineExperiment 3 - Prism SpectrometerTATENDA GOTONessuna valutazione finora
- Radio Inverse Square Law 2021may10v1Documento6 pagineRadio Inverse Square Law 2021may10v1shruti sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 19eng111 Semester I Technical Communication Workbook: Compiled by Amrita School of Engineering Department of EnglishDocumento13 pagine19eng111 Semester I Technical Communication Workbook: Compiled by Amrita School of Engineering Department of EnglishAntonetteNessuna valutazione finora
- AC and DC CircuitsDocumento87 pagineAC and DC Circuitsjan paul OmandapNessuna valutazione finora
- Study of CRODocumento7 pagineStudy of CROGarima Saraf100% (1)
- Conduction by Free ElectronsDocumento30 pagineConduction by Free Electronstejas chikhlikar100% (1)
- Helium Neon LaserDocumento10 pagineHelium Neon LaserSai SridharNessuna valutazione finora
- Phasor DiagramDocumento10 paginePhasor Diagram10rodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY2 GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit - 4 15032021082835AMDocumento19 paginePHY2 GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit - 4 15032021082835AMPiyush ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 4 Deflection Magneto Meter PDFDocumento11 pagine04 4 Deflection Magneto Meter PDFReddyvari VenugopalNessuna valutazione finora
- PHYSICS - 1 (PH 191 & PH 291) - Practical Manual-2Documento54 paginePHYSICS - 1 (PH 191 & PH 291) - Practical Manual-2Soumodip ChakrabortyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 17Documento9 pagineChapter 17michaelanunag26Nessuna valutazione finora
- Structure Analysis Lab Subject Code:-Rce-453Documento25 pagineStructure Analysis Lab Subject Code:-Rce-453Anubhav KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 5 Title: Acceleration of Free Fall by Means of The Simple Pendulum. ObjectiveDocumento2 pagineExperiment 5 Title: Acceleration of Free Fall by Means of The Simple Pendulum. ObjectiveReam MairNessuna valutazione finora
- Experimental Verification of Network Theorems, UGC Practical - Physics - S - PaulDocumento8 pagineExperimental Verification of Network Theorems, UGC Practical - Physics - S - PaulspNessuna valutazione finora
- POLARISATION (Part-1) : Dyal Singh College, University of Delhi (E-Resource Material / Study Material)Documento14 paginePOLARISATION (Part-1) : Dyal Singh College, University of Delhi (E-Resource Material / Study Material)Gayatree Tripathy100% (1)
- ME 174: Mechanical Engineering Drawing and CadDocumento24 pagineME 174: Mechanical Engineering Drawing and CadMohammad Asif KabirNessuna valutazione finora
- A Project Report On Wavelength of Sodium Light Using Newton's RingsDocumento27 pagineA Project Report On Wavelength of Sodium Light Using Newton's RingsAnirudh Mittal100% (1)
- Refraction Through PrismDocumento8 pagineRefraction Through PrismKabeer Golechha100% (2)
- EP13 Measurement of Angle of Prism - Use of SpectrometerDocumento5 pagineEP13 Measurement of Angle of Prism - Use of SpectrometerKw ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Dispersive Power of PrismDocumento6 pagineDispersive Power of PrismGanesh AdhikaryNessuna valutazione finora
- DiffractionDocumento3 pagineDiffractionKannupriya KalraNessuna valutazione finora
- The Prism Spectrometer: Experiment 5Documento4 pagineThe Prism Spectrometer: Experiment 5Mridu Poban BoraNessuna valutazione finora
- To Determine The Angle of A Prism 000000Documento3 pagineTo Determine The Angle of A Prism 000000TasnimProttoy HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- To DetermineDocumento4 pagineTo DetermineTasnimProttoy HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantum ComputingDocumento15 pagineQuantum ComputingSriharanNessuna valutazione finora
- ĐỀ HSG ANH LỚP 9 năm 2021 - 802Documento2 pagineĐỀ HSG ANH LỚP 9 năm 2021 - 802Hồ Ngọc TrAnhNessuna valutazione finora
- Magneto-Hydro Dynamic Generator: Hannes AlfvénDocumento34 pagineMagneto-Hydro Dynamic Generator: Hannes AlfvénHuzaifa WasimNessuna valutazione finora
- MECH3423 Building Services Engineering II Experiment 1: Basic Water Cooling TowerDocumento6 pagineMECH3423 Building Services Engineering II Experiment 1: Basic Water Cooling TowerMahleh Thabe'khuluNessuna valutazione finora
- JP 32 91 260Documento5 pagineJP 32 91 260MonikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dam Deformation-2Documento20 pagineDam Deformation-2Fajar A KurniawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Saturated and Unsaturated FlowDocumento48 pagineSaturated and Unsaturated FlowJulio César ChávezNessuna valutazione finora
- Fast Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy As A Statistical Condition Monitoring ToolDocumento90 pagineFast Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy As A Statistical Condition Monitoring ToolrenatojrNessuna valutazione finora
- Molina-Garip 2019 SocarxivDocumento27 pagineMolina-Garip 2019 Socarxiv3nuzulNessuna valutazione finora
- 21 Casting Defects and How To Prevent Them in Your ProductsDocumento1 pagina21 Casting Defects and How To Prevent Them in Your ProductsmkmkhairiNessuna valutazione finora
- Pump Basics Presentation (Grundfoss)Documento45 paginePump Basics Presentation (Grundfoss)Roudy J. MhawasNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 12 MathematicsDocumento9 pagineGrade 12 MathematicsMPS QUESTION PAPER SUBMISSIONNessuna valutazione finora
- Corning Gorilla Glass 5 - PI SheetDocumento2 pagineCorning Gorilla Glass 5 - PI SheetJ. RagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Agacita John PaulDocumento10 pagineAgacita John PaulCarlo Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- PHD Thesis Structures and Publications - Rasyid (2022!11!18)Documento4 paginePHD Thesis Structures and Publications - Rasyid (2022!11!18)m_abdur_rasyidNessuna valutazione finora
- Euclid CDM 1254748659 PDFDocumento108 pagineEuclid CDM 1254748659 PDFSangat BaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Mechanics - KL - Ramachandran SDocumento744 pagineEngineering Mechanics - KL - Ramachandran SFe Fernandez100% (1)
- (Engineering Materials) Murat Bengisu (Auth.) - Engineering Ceramics-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (2001)Documento629 pagine(Engineering Materials) Murat Bengisu (Auth.) - Engineering Ceramics-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (2001)Prosenjit DuttaNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal of Food Engineering: Matteo Cordioli, Massimiliano Rinaldi, Gabriele Copelli, Paolo Casoli, Davide BarbantiDocumento8 pagineJournal of Food Engineering: Matteo Cordioli, Massimiliano Rinaldi, Gabriele Copelli, Paolo Casoli, Davide Barbantimohammad9906426240Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fluke Infrared Thermometer 59 MiniDocumento1 paginaFluke Infrared Thermometer 59 MiniRashidNessuna valutazione finora
- DRD Rescue: Double Rope Descender With Two Jamming PositionsDocumento3 pagineDRD Rescue: Double Rope Descender With Two Jamming PositionsferreiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Torque Wrench Calibration and UncertaintDocumento7 pagineTorque Wrench Calibration and UncertaintWin AsharNessuna valutazione finora
- Drawing:: SG01 (20KAF) - 3P001-000 SPG30-20KDocumento1 paginaDrawing:: SG01 (20KAF) - 3P001-000 SPG30-20KAkhilesh Kumar MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- @face X 0, Ux 0 @face X Width, " Linear Constraint Equation" @face Y 0, Uy 0 @face Y Width, Uy Is Specified @face Z 0, Uz 0 @face Z Width, " Linear Constraint Equation"Documento3 pagine@face X 0, Ux 0 @face X Width, " Linear Constraint Equation" @face Y 0, Uy 0 @face Y Width, Uy Is Specified @face Z 0, Uz 0 @face Z Width, " Linear Constraint Equation"VijaybalajiNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment n1Documento1 paginaAssignment n1Afzaal FiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Vacuum: 2 6 R. Luna, C. Mill An, M. Domingo, C. Santonja, M.A. SatorreDocumento7 pagineVacuum: 2 6 R. Luna, C. Mill An, M. Domingo, C. Santonja, M.A. SatorreTobias De SomerNessuna valutazione finora
- Reaction Kinetice and Reactor DESIGN (CH-322) : by H. Scott Fogler Fourth EditionDocumento140 pagineReaction Kinetice and Reactor DESIGN (CH-322) : by H. Scott Fogler Fourth EditionTEZ ANALYSIS AND STORIESNessuna valutazione finora
- PTM 7001a PDFDocumento3 paginePTM 7001a PDFKeyur ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Laws NotesDocumento3 paginePhysics Laws NotesYEO MING HUI Moe100% (1)