Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Weld Profiles - AWS D1.1 D1.1M-2010
Caricato da
gigiphiCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Weld Profiles - AWS D1.1 D1.1M-2010
Caricato da
gigiphiCopyright:
Formati disponibili
AWS D1.1/D1.
1M:2010
CLAUSE 5. FABRICATION
[ 1.8 m] deep, with due regard for members which frame into them.
5.23.11.3 Straightness and Location of Bearing Stiffeners. The out-of-straightness variation of bearing stiffeners shall not exceed I /4 in [6 mm J up to 6 ft [1.8 m] deep or 1/2 in [ 12 mm] over 6 ft [1.8 m] deep. The actual centerline of the stiffener shall lie within the thickness of the stiffener as measured from the theoretical centerline location. 5.23.12 Other Dimensional Tolerances. Twist of box members and other dimensional tolerances of members not covered by 5.23 shall be individually determined and mutually agreed upon by the Contractor and the Owner with proper regard for erection requirements.
5.24.4 Shelf Bars. Shelf bars shall conform to the requirements of 5.10.1 through 5.10.5. Shelf bars may be left in place only for statically loaded members.
5.25 Technique for Plug and Slot Welds
5.25.1 Plug Welds. The technique used to make plug welds when using SMAW, GMAW (except GMAW-S), and FCAW processes shall be as follows: 5.25.1.1 Flat Position. For welds to be made in the tlat position, each pass shall be deposited around the root of the joint and then deposited along a spiral path to the center of the hole, fusing and depositing a layer of weld metal in the root and bottom of the joint. The arc shall then be moved to the periphery of the hole and the procedure repeated, fusing and depositing successive layers to fill the hole to the required depth. The slag covering the weld metal should be kept molten until the weld is finished. If the arc is broken or the slag is allowed to cool, the slag must be completely removed before restarting the weld. 5.25.1.2 Vertical Position. For welds to be made in the vertical position, the arc is started at the root of the joint at the lower side of the hole and is carried upward, fusing into the face of the inner plate and to the side of the hole. The arc is stopped at the top of the hole, the slag is cleaned off, and the process is repeated on the opposite side of the hole. After cleaning slag from the weld, other layers should be similarly deposited to fill the hole to the required depth. 5.25.1.3 Overhead Position. For welds to be made in the overhead position, the procedure is the same as for the flat position, except that the slag should be allowed to cool and should be completely removed after depositing each successive bead until the hole is filled to the required depth. 5.25.2 Slot Welds. Slot welds shall be made using techniques similar to those specified in 5.25.1 for plug welds, except that if the length of the slot exceeds three times the width, or if the slot extends to the edge of the part, the technique requirements of 5.25.1.3 shall apply.
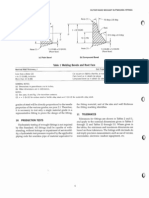
5.24 Weld Profiles
All welds shall meet the visual acceptance criteria of Table 6.1 and shall be free from cracks, overlaps, and the unacceptable profile discontinuities exhibited in Figure 5.4, Table 5.9, and Table 5.10, except as otherwise allowed in 5.24.1, 5.24.2, and 5.24.3.
5.24.1 Fillet Welds. The faces of fillet welds may be slightly convex, flat, or slightly concave as shown in Figure 5.4 and as allowed by Table 6.1. 5.24.2 Exception for Intermittent Fillet Welds. Except for undercut, as allowed by the code, the profile requirements of Figure 5.4 shall not apply to the ends of intermittent fillet welds outside their effective length. 5.24.3 Groove Welds. Groove weld reinforcement shall comply with Table 5.9, Table 5.1 0, and with the provisions below. Welds shall have a gradual transition to the plane of the base-metal surfaces. 5.24.J.1 Flush Surfaces. Welds required to be flush shall be finished so as to not reduce the thicknesses of the thinner base metal or weld metal by more than 1/32 in [I mm]. Remaining reinforcement shall not exceed 1/32 in [I mm] in height and shall blend smoothly into the base metal surfaces with transition areas free from undercut. However, all reinforcement shall be removed where the weld forms part of a faying or contact surface. 5.24.3.2 Finish Methods and Values. Where surface finishing is required, roughness values (see ASME B46.1) shall not exceed 250 microinches [6.3 micrometers]. Chipping and gouging may be used provided these are followed by grinding or machining. For cyclically loaded structures, finishing shall be parallel to the direction of primary stress, except final roughness of 125 microinches [3.2 micrometers] or less may be finished in any direction.
5.26 Repairs
The removal of weld metal or portions of the base metal may be done by machining, grinding, chipping, or gouging. It shall be done in such a manner that the adjacent weld metal or base metal is not nicked or gouged. Oxygen gouging shall not be used in quenched and tempered steel. Unacceptable portions of the weld shall be removed without substantial removal of the base metal.
205
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- NS-1-60. Disposition of DefectsDocumento4 pagineNS-1-60. Disposition of DefectsWHWENNessuna valutazione finora
- Weld Joint Detail PDFDocumento9 pagineWeld Joint Detail PDFKosit WongpinkaewNessuna valutazione finora
- Specification No: LMB-COI-TRG-001 Rev No. R0 Page ofDocumento16 pagineSpecification No: LMB-COI-TRG-001 Rev No. R0 Page ofApoorv MathurNessuna valutazione finora
- Norma CWB Cambios en W47.1-2009Documento6 pagineNorma CWB Cambios en W47.1-2009Jose ManuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamic and Static Balancing of Rolls - How, Why and WhenDocumento2 pagineDynamic and Static Balancing of Rolls - How, Why and WhenAbolfazl KhakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Tack WeldDocumento1 paginaTack Weldbhatti19Nessuna valutazione finora
- 350xt Data Sheet EnglishDocumento1 pagina350xt Data Sheet Englishanon_726020506Nessuna valutazione finora
- Weld DefectsDocumento23 pagineWeld DefectsSridhar CnNessuna valutazione finora
- GB-T 232-2010 Metallic Materials-Bend TestDocumento14 pagineGB-T 232-2010 Metallic Materials-Bend TestH. Camer E.Nessuna valutazione finora
- British Universal Columns and Beams Weight ChartDocumento6 pagineBritish Universal Columns and Beams Weight ChartSameer SawantNessuna valutazione finora
- SSPC QP 3Documento6 pagineSSPC QP 3anoopkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Paint Systems For Steel StructuresDocumento7 paginePaint Systems For Steel StructuresHermann Lowe100% (1)
- CWB Weld Specialist Branding GuideDocumento5 pagineCWB Weld Specialist Branding GuideBala SingamNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3B. Welded Connections: CE4: Design of Steel Structures - Prof. Dr. A. VarmaDocumento14 pagineChapter 3B. Welded Connections: CE4: Design of Steel Structures - Prof. Dr. A. VarmaGNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Testing 01B: Part 2 Charpy Impact TestingDocumento25 pagineMechanical Testing 01B: Part 2 Charpy Impact Testingsamurai7_77100% (1)
- Welding TypesDocumento6 pagineWelding TypestNessuna valutazione finora
- Defects Lack of Side Wall FusionDocumento4 pagineDefects Lack of Side Wall Fusionguru_terexNessuna valutazione finora
- En10204 Certification For Steel PlatesDocumento6 pagineEn10204 Certification For Steel PlatesTree Tawee100% (1)
- 2062Documento17 pagine2062hswed91100% (1)
- For For: 9pecificationDocumento21 pagineFor For: 9pecificationmrNessuna valutazione finora
- Welding TWIDocumento16 pagineWelding TWIEngr Arfan Ali DhamrahoNessuna valutazione finora
- Catalog Fabricante TechnipDocumento9 pagineCatalog Fabricante Technipjimy GutiérrezNessuna valutazione finora
- AISC - Engineering FAQsDocumento3 pagineAISC - Engineering FAQsAshish SadaNessuna valutazione finora
- HDG Datasheet 4a - Specifying Hot Dip Galvanized SteelDocumento1 paginaHDG Datasheet 4a - Specifying Hot Dip Galvanized SteelCheah Hon KeongNessuna valutazione finora
- Cover BlockDocumento6 pagineCover BlockRandhvir KharatmolNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Prevent Control Welding DistortionDocumento2 pagineHow To Prevent Control Welding DistortionNilesh DalviNessuna valutazione finora
- Welding PositionDocumento6 pagineWelding Positionenels77Nessuna valutazione finora
- AA0850126 Rev 02Documento10 pagineAA0850126 Rev 02Manish KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Projects Assessments For Welding ProcessDocumento8 pagineProjects Assessments For Welding ProcessKamarul NizamNessuna valutazione finora
- Projection WeldDocumento20 pagineProjection WeldCebrac ItatibaNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel Sections: Submitted By-Ankit Gupta Aniruddh Babbar Dipanshu GuptaDocumento13 pagineSteel Sections: Submitted By-Ankit Gupta Aniruddh Babbar Dipanshu GuptaAnirudh BabbarNessuna valutazione finora
- Best Welding Practices (Pernis) : Doel / ScopeDocumento91 pagineBest Welding Practices (Pernis) : Doel / Scopechompink6900100% (1)
- Welding Inspector: Weld Repairs Section 16Documento20 pagineWelding Inspector: Weld Repairs Section 16manojballaNessuna valutazione finora
- MODULE 9 - Weld and Base Metal Discontinuities Discontinuity: Discontinuity IsDocumento7 pagineMODULE 9 - Weld and Base Metal Discontinuities Discontinuity: Discontinuity IsNsidibe Michael EtimNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.0 Destructive TestingDocumento81 pagine4.0 Destructive TestingfinhayNessuna valutazione finora
- The Importance of Visual Welding InspectionDocumento4 pagineThe Importance of Visual Welding Inspectionhekayat71Nessuna valutazione finora
- Weld SysmbolDocumento17 pagineWeld SysmbolBashu PoudelNessuna valutazione finora
- Dye Penetrant Inspection - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento5 pagineDye Penetrant Inspection - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaviswamanoj100% (1)
- Weld Weave WidthDocumento4 pagineWeld Weave Widthapply19842371Nessuna valutazione finora
- 0301e - Guidebook For Inspectors - 2018-3Documento6 pagine0301e - Guidebook For Inspectors - 2018-3FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- AISE Anchor Bolt Details PDFDocumento1 paginaAISE Anchor Bolt Details PDFYash PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 - Exhibit C Sp-Welding of Pipelines &facilitiesDocumento13 pagine12 - Exhibit C Sp-Welding of Pipelines &facilitiesMoaatazz Nouisri100% (1)
- Hot Chamber Die Casting ProcessDocumento1 paginaHot Chamber Die Casting ProcessNordiana IdrisNessuna valutazione finora
- VT Acceptance Criteria WeldsDocumento14 pagineVT Acceptance Criteria WeldsCharwin Xiao100% (1)
- Weld Over WeldDocumento1 paginaWeld Over Weldmoha23Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pulleys - Sole Plates - Standard Sole Plate DataDocumento3 paginePulleys - Sole Plates - Standard Sole Plate DataWaris La Joi Wakatobi0% (1)
- Rolltec Coupler BrochureDocumento4 pagineRolltec Coupler BrochureMohammad Aasimuddin100% (1)
- ARTICLE - Destructive Testing Basics (2012)Documento4 pagineARTICLE - Destructive Testing Basics (2012)Sangameswaran RamarajNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.23 Weld Profiles: AWS D1.1/D1.1M:2015 Clause 5. FabricationDocumento1 pagina5.23 Weld Profiles: AWS D1.1/D1.1M:2015 Clause 5. FabricationRohit KambleNessuna valutazione finora
- Visual Inspection - AWS & BS PDFDocumento22 pagineVisual Inspection - AWS & BS PDFSelvakpm06Nessuna valutazione finora
- Acceptable Weld ProfilesDocumento9 pagineAcceptable Weld ProfilesDominic Apollo Robles100% (1)
- Tank Erection Method Statement For Mot Oil Storage TanksDocumento13 pagineTank Erection Method Statement For Mot Oil Storage Tanksmeshahan78% (9)
- Bifurcation Methodology: Basic Welding ProcedureDocumento7 pagineBifurcation Methodology: Basic Welding ProcedureNischal PokharelNessuna valutazione finora
- Tank Erection Method Statement For Mot Oil Storage TanksDocumento13 pagineTank Erection Method Statement For Mot Oil Storage TanksErmal RulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Method Statement - Pipe WorksDocumento14 pagineMethod Statement - Pipe WorksDarl Anthony Veloso100% (4)
- Nozzle Welding DesignDocumento12 pagineNozzle Welding DesignAlvin Smith100% (2)
- Welding DesignDocumento28 pagineWelding DesignSitaram JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Specification For Visula Welding InspectionsDocumento5 pagineSpecification For Visula Welding InspectionsAhmed Shaban KotbNessuna valutazione finora
- SheetDocumento1 paginaSheetgigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- VGL 65Documento1 paginaVGL 65gigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- HRD Process Platform Project MC Inspection & Test Record: P03-A Sheet 1 of 1Documento2 pagineHRD Process Platform Project MC Inspection & Test Record: P03-A Sheet 1 of 1gigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- Piston Check Bolted SW - Red B. 800Documento1 paginaPiston Check Bolted SW - Red B. 800gigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- f3213-6500r0 - General Notes For Piping Support FabricationDocumento11 paginef3213-6500r0 - General Notes For Piping Support FabricationgigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- HRD Process Platform Project MC Inspection & Test Record: Pressure Test Certificate P05-A Sheet 1 of 1Documento1 paginaHRD Process Platform Project MC Inspection & Test Record: Pressure Test Certificate P05-A Sheet 1 of 1gigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- Piping Specialties Rev 4Documento25 paginePiping Specialties Rev 4gigiphi100% (1)
- F3213-6108.01a - r0 - Piping Ga (Train-A) Top Deck Plan View12 NorthDocumento1 paginaF3213-6108.01a - r0 - Piping Ga (Train-A) Top Deck Plan View12 NorthgigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- F3213-6115a - r0 - Piping Ga (Train-A) Top Deck Elevation View5Documento1 paginaF3213-6115a - r0 - Piping Ga (Train-A) Top Deck Elevation View5gigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- F3213-6107.01a - r0 - Piping Ga (Train-A) Main Deck Plan View11 NorthDocumento1 paginaF3213-6107.01a - r0 - Piping Ga (Train-A) Main Deck Plan View11 NorthgigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- f3213-6751 - r1 Piping Specialty Item ListDocumento4 paginef3213-6751 - r1 Piping Specialty Item ListgigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- WeldingDocumento41 pagineWeldinggigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- Extract Pages From ASME B16.9 - 2003 - TEE (Factory-Made Wrought Buttwelding Fittings)Documento4 pagineExtract Pages From ASME B16.9 - 2003 - TEE (Factory-Made Wrought Buttwelding Fittings)gigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- f3213-61m1.02r1 - Linewise Pipe Mto (4-Inch and Below)Documento13 paginef3213-61m1.02r1 - Linewise Pipe Mto (4-Inch and Below)gigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- PMC - POS Split Scope of WorkDocumento10 paginePMC - POS Split Scope of Workgigiphi100% (1)
- Welder List For Structure 2Documento4 pagineWelder List For Structure 2gigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- Table 6.1 AWS D1.1 D1.1M-2010Documento1 paginaTable 6.1 AWS D1.1 D1.1M-2010gigiphi75% (8)
- SmokingDocumento2 pagineSmokinggigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- s1 Sorter BrochureDocumento8 pagines1 Sorter BrochuregigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- Welder List For Structure 1Documento7 pagineWelder List For Structure 1gigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- App T8-Tech Excep - 21 Nov - Huc (Pos) - PMC 23nov11Documento2 pagineApp T8-Tech Excep - 21 Nov - Huc (Pos) - PMC 23nov11gigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- App T8-Tech Excep - 21 Nov - Huc (Pos) - PMC 23nov11Documento2 pagineApp T8-Tech Excep - 21 Nov - Huc (Pos) - PMC 23nov11gigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- STT PTSC NISCONI L 0xxx Electrical Cable ScheduleDocumento1 paginaSTT PTSC NISCONI L 0xxx Electrical Cable SchedulegigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- HUC Technical Exception (POS Response - 19 Oct 2011) - Rev 1Documento37 pagineHUC Technical Exception (POS Response - 19 Oct 2011) - Rev 1gigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- Welding InspectionDocumento137 pagineWelding InspectiongigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- Welding InspectionDocumento137 pagineWelding InspectiongigiphiNessuna valutazione finora
- CRM47885 Lrac9768Documento5 pagineCRM47885 Lrac9768Sergio mauricio sergioNessuna valutazione finora
- DA35 (B) Pipeline Risk Management Plan PDFDocumento33 pagineDA35 (B) Pipeline Risk Management Plan PDFmalik jahanNessuna valutazione finora
- CND 4.medication & Dispensing ErrorDocumento32 pagineCND 4.medication & Dispensing Errorlisnawati farmasicbthNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial - Cord Chemicals IncDocumento1 paginaIndustrial - Cord Chemicals IncEddie Resurreccion Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Yeast Cell BiologyDocumento3 pagineYeast Cell BiologyeupheemaNessuna valutazione finora
- Osram QuartzDocumento29 pagineOsram QuartzVarun KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2012 Catalogo GraceDocumento84 pagine2012 Catalogo GraceValery FujitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid SaturationDocumento14 pagineFluid SaturationHarry JakeNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing Method For CompositesDocumento41 pagineManufacturing Method For CompositestpmendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fuel Specification Guide: Shell Marine ProductsDocumento6 pagineFuel Specification Guide: Shell Marine ProductsVilius BukysNessuna valutazione finora
- 1397 2011Documento7 pagine1397 2011khurshedlakhoNessuna valutazione finora
- 0610 w07 QP 1Documento20 pagine0610 w07 QP 1farsxdchgNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper+Cutting+Knives+englDocumento23 paginePaper+Cutting+Knives+englbelan_80Nessuna valutazione finora
- Loss of Nitrogen Compounds During CompostingDocumento9 pagineLoss of Nitrogen Compounds During CompostingRonaldo SaludesNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Cooled Condensers Selection GuideDocumento16 pagineAir Cooled Condensers Selection GuideelmerbayhonNessuna valutazione finora
- Evidence of Acceptability of Oral Paediatric Medicines: A ReviewDocumento16 pagineEvidence of Acceptability of Oral Paediatric Medicines: A ReviewDenise Yanci DemiarNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 - Titration Curves LBBBIANDocumento81 pagine6 - Titration Curves LBBBIANroyalNessuna valutazione finora
- SD7000 InstructionsDocumento8 pagineSD7000 InstructionsMarcelo CheloNessuna valutazione finora
- Case StudyDocumento2 pagineCase StudyArtee Aggrawal100% (1)
- Precipitated Silica-Surface Area by Multipoint BET Nitrogen AdsorptionDocumento3 paginePrecipitated Silica-Surface Area by Multipoint BET Nitrogen Adsorptiondavid dawoudNessuna valutazione finora
- BS 5950-1 1990Documento126 pagineBS 5950-1 1990Anoy100% (4)
- Handbook On Chlorine HandlingDocumento106 pagineHandbook On Chlorine Handlingkirandevi1981100% (1)
- Npt14 MaintenanceDocumento26 pagineNpt14 Maintenanceluis100% (2)
- Whiteboard Activity-Intermolecular ForcesDocumento4 pagineWhiteboard Activity-Intermolecular ForcesadityathegreatkarthiNessuna valutazione finora
- 660 MW Warm Startup Procedures Warm Start Up After 36 Hrs Shutdown and HPC Temperature 340 C and Ipc 320 C With Boiler PR 1 To 30 KSCDocumento6 pagine660 MW Warm Startup Procedures Warm Start Up After 36 Hrs Shutdown and HPC Temperature 340 C and Ipc 320 C With Boiler PR 1 To 30 KSCdjfffNessuna valutazione finora
- SdarticleDocumento25 pagineSdarticleCees van ApeldoornNessuna valutazione finora
- Scientific Validation of Standardization of Narayana Chendrooram (Kannusamy Paramparai Vaithiyam) Through The Siddha and Modern TechniquesDocumento12 pagineScientific Validation of Standardization of Narayana Chendrooram (Kannusamy Paramparai Vaithiyam) Through The Siddha and Modern TechniquesBala Kiran GaddamNessuna valutazione finora
- 2008 Failure of Refurbished Turbine Blades in A Power Station by Improper Heat TreatmentDocumento6 pagine2008 Failure of Refurbished Turbine Blades in A Power Station by Improper Heat TreatmentArun KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Fossil Fuels - BioNinjaDocumento2 pagineFossil Fuels - BioNinjaDaniel WalshNessuna valutazione finora
- Summarized Research PresentationDocumento4 pagineSummarized Research PresentationDaryl A. Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cyanide Canary: A True Story of InjusticeDa EverandThe Cyanide Canary: A True Story of InjusticeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (52)
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelDa EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Waste: One Woman’s Fight Against America’s Dirty SecretDa EverandWaste: One Woman’s Fight Against America’s Dirty SecretValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Analog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceDa EverandAnalog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceNessuna valutazione finora
- Art of Commenting: How to Influence Environmental Decisionmaking With Effective Comments, The, 2d EditionDa EverandArt of Commenting: How to Influence Environmental Decisionmaking With Effective Comments, The, 2d EditionValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- The Art of Welding: Featuring Ryan Friedlinghaus of West Coast CustomsDa EverandThe Art of Welding: Featuring Ryan Friedlinghaus of West Coast CustomsNessuna valutazione finora
- The Design Thinking Playbook: Mindful Digital Transformation of Teams, Products, Services, Businesses and EcosystemsDa EverandThe Design Thinking Playbook: Mindful Digital Transformation of Teams, Products, Services, Businesses and EcosystemsNessuna valutazione finora
- Articulating Design Decisions: Communicate with Stakeholders, Keep Your Sanity, and Deliver the Best User ExperienceDa EverandArticulating Design Decisions: Communicate with Stakeholders, Keep Your Sanity, and Deliver the Best User ExperienceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (19)
- Laws of UX: Using Psychology to Design Better Products & ServicesDa EverandLaws of UX: Using Psychology to Design Better Products & ServicesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (9)
- The Maker's Field Guide: The Art & Science of Making Anything ImaginableDa EverandThe Maker's Field Guide: The Art & Science of Making Anything ImaginableNessuna valutazione finora
- Lean vs Agile vs Design Thinking: What You Really Need to Know to Build High-Performing Digital Product TeamsDa EverandLean vs Agile vs Design Thinking: What You Really Need to Know to Build High-Performing Digital Product TeamsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- Understanding Automotive Electronics: An Engineering PerspectiveDa EverandUnderstanding Automotive Electronics: An Engineering PerspectiveValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (16)
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsDa EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- The Jobs To Be Done Playbook: Align Your Markets, Organization, and Strategy Around Customer NeedsDa EverandThe Jobs To Be Done Playbook: Align Your Markets, Organization, and Strategy Around Customer NeedsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureDa EverandArtificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Heat Exchanger Design Guide: A Practical Guide for Planning, Selecting and Designing of Shell and Tube ExchangersDa EverandHeat Exchanger Design Guide: A Practical Guide for Planning, Selecting and Designing of Shell and Tube ExchangersValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (13)
- CATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part I : Getting Started and Sketcher WorkbenchDa EverandCATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part I : Getting Started and Sketcher WorkbenchValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (10)
- Basic Electric Circuits: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesDa EverandBasic Electric Circuits: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- 507 Mechanical Movements: Mechanisms and DevicesDa Everand507 Mechanical Movements: Mechanisms and DevicesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (28)