Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
FORM 1 SCIENCE NOTES: Understanding Nature Through Systematic Study
Caricato da
Khadijah YusopDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
FORM 1 SCIENCE NOTES: Understanding Nature Through Systematic Study
Caricato da
Khadijah YusopCopyright:
Formati disponibili
FORM 1 SCIENCE NOTES What is Science? 1. 2. 3.
Science is a systematic study of nature and how it affects our lives and the environment. Natural phenomena are events that happen around us. Example of natural phenomena : 4. Growth of a baby into an adult An object falling to the ground Melting of ice Volcano eruptions, earthquakes and tsunami Thunderstorm, snow and lightning
Science is important to us because it Enables us to understand ourselves and our surrounding environment Solves mysteries of science through the systematic investigation Contributes to new discoveries inventions and knowledge gained Improve our standard of living and quality of our environment Creates science-based job opportunities
Hazard Warning Symbols 1. Flammable substances 2. May become hot and finally ignite in contact with air White phosphorus, yellow phosphorus, petrol, kerosene, ethanol, methylated spirit
Explosive substances May explode under the effect of a flame or if subjected to shocks or friction Sodium, potassium, mixture of hydrogen and air, hydrazoic acid, hydrazine, diazo
3.
Corrosive substances May destroy or burn living tissues on contact with them Hydrogen peroxide, concentrated hydrochloric acid, concentrated sodium hydroxide
4.
Poisonous or toxic substances May cause immediate or long term health risks and even death if inhaled, ingested or absorbed into the skin
5.
Mercury, bromine, lead, sodium cyanide, chlorine, hydrogen sulphide, benzene
Irritating or harmful substances May cause discomfort or inflammation to the body Ammonia, chloroform, bromine vapour, chlorine
6.
Radioactive substances May cause cell mutation
X-ray, uranium, plutonium, thorium, radium
The steps in a scientific investigation
Identifying the problem Forming a hypothesis Planning the experiment Identifying variables Determining apparatus and materials Determining the procedure to carry out the experiment Determining method to collect and analyses data Controlling the variables Collecting data Analyzing and interpreting data Drawing a conclusion Writing a report
Physical quantities and their units 1. Five physical quantities which can be measured 2. Length Mass Time Temperature Electric current
Physical quantities can be measured in systeme international dunites (SI) units. SI Unit Metre Kilogram Second Kelvin Ampere Symbol M K C M Symbol m Kg s K A Numerical value 1000000 1000 0.01 0.001 0.000001
Physical quantity Length Mass Time Temperature Electric current Prefix Mega Kilo Centi Milli Micro
Weight and Mass Mass 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Mass is the amount of matter in an object. The more the matter in an object, the bigger is its mass. SI Unit kilogram (kg) Mass can measured in gram (g) and milligram (mg). Mass can be measured by beam balance and lever balance. I kg = 1000 g 1g 1000 mg
Weight 1. 2. 3. 4. Weight is the gravitational force acting on an object. The greater the force pulling the object towards centres of Earth, the heavier the object. Weight is measured in Newton (N). Compression balance and spring balance is used to measure weight. 1 N = 0.1 kg 1 kg = 10 N Cell as a unit of life 1. 2. A cell is the basic unit of living things which can function on its own. Cells are microscopic and cannot be seen with naked eye.
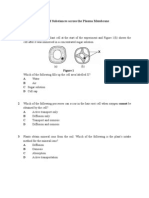
General structures and functions of animal cells and plant cells Most cells consist of protoplasm which is surrounded by cell membrane. Structures Nucleus Characteristics Is dense and spherical structure. Is surrounded by a nuclear membrane. Contain chromosomes which carry genetic materials that determine the characteristics of organisms. Is a flexible, colorless, jellylike substance. Is surrounded by a cell membrane. Contains water and chemical substances such as proteins, stored food and minerals. Is a thin, elastic layer on the outer surface or animal cells. Contains fats and proteins. Is partially permeable. This means that it allows certain substances to pass through. Is a thick and rigid layer on the outer surface of plant cells. Is mainly composed of tough substance called cellulose. Are tiny, oval structures found inside the cytoplasm of most plant cells. Contain a green pigment called chlorophyll. Absorbs light energy and uses it to make food. This process is Function It is the control centre of the cell because it controls all chemical reactions in the cell.
Cytoplasm
Acts as the medium for chemical reactions of the cell.
Cell membrane
Controls the movement of substance in and out the cell.
Cell wall
It gives the cell a definite shape. They enable green plants to manufacture their won food.
Chloroplasts
Vacuoles
called photosynthesis. Is a fluid-filled sac found in the cytoplasm. Is surrounded by a membrane and is filled with cell sap. Contains of a solution of sugars, proteins, minerals.
The vacuole acts as a store of various substances such as water, food, pigments, enzymes, and waste products.
Unicellular organisms Are simple organisms that are made up of only one cell In animal kingdom: Amoeba and Paramecium In plant kingdom: Pleurococcus, Euglena, Chlamydomonas and yeast.
Multicellular organisms Are organisms which have more than one cell In animal kingdom: mammals, amphibians, reptiles, birds, dish, and Hydra In plant kingdom: mosses, algae (Chondrus, Spirogyra), ferns.
Life processes of unicellular and multicellular organisms 1. 2. Unicellular organism Can grow Sensitive to light, chemical substances, and sharp objects Main food is bacteria Its excretory organ is the vacuole Moves by extending pseudopodium Breathes through cell membrane Reproduces asexually Multicellular organism Main food is zooplankton Excretes through its excretory pores Moves by means of its tail and fins Can grow Sensitive to light and vibrations in water Reproduces sexually Breathes through gills
Cell organization in the human body 1. Types of cells found in human body : a.) Nerve cells conducts nerve impulses b.) Red blood cells transport oxygen from lungs to all cells c.) White blood cells- protect body from microorganisms. d.) Skeletal muscle cells controls movement of bones and organs of body e.) Reproduction cells-produce off spring f.) Epithelial cells controls exchange of substances g.) Bone cells functions in the support system of the body 2. Types of tissue a.) Epithelial tissue protects the tissues beneath it b.) Connective tissue connects one tissue to another tissue , supports organs in the body c.) Muscle tissue enables the movement of body parts d.) Nerve tissue enables body to respond to stimuli e.) Carries nerve impulses from one part of the body to another 3. Types of systems a.) Excretory system discards toxic waste products produced by the body cells b.) Reproductive system produces offspring c.) Respiratory system inhales oxygen and exhales carbon dioxide d.) Lymphatic system defends the body against disease e.) Skeletal system provides support and protection to soft internal organs f.) Blood circulatory system transport food substances, oxygen, hormones, and others to the entire body g.) Endocrine system produces hormones that control the bodys responses toward stimuli h.) Nervous system coordinates and controls all bodily activities related to impulses and reactions i.) Muscular system helps in movement of the body
j.) Digestive system breaks down complex food into simple substances for easy absorption by body cells
4.
Cells, tissues, organs and systems can be interconnected by the following chart :
Cells Tissue Organ System Organism
5.
The importance of organization of cells : a.) Enables body to perform life processes simultaneously b.) Ensure life processes function efficiently and smoothly
What is matter? Everything that has mass and occupies space is called matter. The states of matter 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Matter is made up of tiny particles which are separate. These particles can be composed of atoms or molecules An atom is the smallest particle of matter and cannot be further divided. A molecule is made up of two or more atoms Proofs that matter is made up of tiny and discrete particles Dissolving copper (II) sulphate crystals in water Diffusion of gas
Arrangement of particles in matter Matter exists as solids, liquids and gases. 1. Arrangement of particles in solids : a.) Are arranged close together and in a regular pattern b.) Are very small spaces between particles of a solid c.) Cannot be compressed d.) Volume of a solid is definite 2. Arrangement of particles in liquids : a.) Are arranged closer but not in a regular pattern b.) Spaces between the particles of a liquid are bigger c.) Cannot be compressed d.) Shape is not definite
e.) Known as fluids because of its flowing property 3. Arrangement of particles in a gas : a.) The particles of a gas are far apart and are not arranged in a regular pattern b.) Does not have define shape or volume c.) Large spaces d.) Volumes of a gas increases when the particles move apart e.) Can be compressed f.) Known as fluids because of their flowing property
4.
Free motion or Brownian motion is the movement of particles in all directions at high speeds.
The concept of density Density and buoyancy 1. Density of a substance is the mass per unit volume Formula:
2. 3.
The SI Unit for density is kg/m or kg m-. The density of a substance depends on two factors : a.) Mass The bigger its mass, the bigger is its density.
b.) Volume 4. 5. The bigger its volume, the smaller is its density. Buoyancy of a matter refers to whether the matter floats on or sinks in another matter. A solid that has a lower density than the density of a liquid will float on the surface of the liquid A solid that has a higher density than the density of a liquid will sink in the liquid
6.
The variety of resources on earth Water, air, soil, mineral, fossil fuels and living things are the most important things. Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Elements 1. 2. 3. An element is the simplest substance. All elements made up of only one type of atom. Examples of elements : a.) Gold b.) Zinc c.) Iron d.) Oxygen e.) Carbon f.) Nitrogen g.) Hydrogen h.) Aluminium 4. Metals 1. Examples of metals : a.) Potassium b.) Calcium c.) Magnesium d.) Mercury e.) Lead f.) Sodium g.) Silver h.) Copper i.) Platinum Elements can be grouped into metals and non-metals.
j.) Gold
2.
The properties of metals : Surface appearance metals have shiny surfaces and can be polished Heat conductivity metals are good conductors Electrical conductivity metals are good conductors of electricity Density metals have high densities Malleability metals are elastic Melting point metal have high melting points State of matter metal is solid at room temperature except mercury
Non-metals 1. Example of non-metals : a.) Hydrogen b.) Fluorine c.) Carbon d.) Bromine e.) Nitrogen f.) Oxygen g.) Chlorine h.) Phosphorus i.) Iodine
j.) Sulphur Condition at room temperature Solid Liquid Gas Examples of non-metals Carbon, sulphur, iodine, selenium, phosphorus Bromine, mercury Hydrogen, helium, oxygen, fluorine, neon, chlorine, argon, krypton, xenon, radon
2.
The properties of non-metals : Surface appearance non metals have dull surfaces Heat conductivity non metals are poor heat conductors Electrical conductivity non metals are poor electrical conductors Density non metals have low densities
Malleability non metals cannot be beaten into other shapes and are brittle Melting point non metals have low melting points State of matter non metals can exist as solids, liquids or gases at room temperature Compounds 1. 2. 3. A compound is formed when two or more types of elements combine chemically. The smallest particle in a compound is the molecule. Several types of compounds and their components: a.) Carbon dioxide one carbon atom, two oxygen atoms b.) Sodium chloride one sodium atom, one chlorine atom c.) Benzene six carbon atoms, six hydrogen atoms d.) Methane one carbon atom, four hydrogen atoms e.) Ammonia one nitrogen atoms, three hydrogen atoms f.) Water one oxygen atom, two hydrogen atoms 4. 5. The components of a compound cannot be separated physically The components of a compound can only be separated chemically. Example by using high heat or using electrolysis. Mixture 1. 2. 3. A mixture is made up of two or more substances combined physically for example, by stirring. Mixtures are divided into two types of homogeneous mixture and heterogeneous mixture. A homogeneous mixture is formed when its substances are mixed evenly and the identity of each substance cannot be identified so easily. Example: common salt solution and soft drinks. A heterogeneous mixture is formed when its substances can be identified easily. Example: air. Substances in a mixture can be separated physically as follows: a.) Mixture of sand and water Filtration b.) Mixture of flour and sand Sifting c.) Mixture of common salt and water Evaporation d.) Mixture of alcohol and water Distillation e.) Mixture of chlorophyll pigments Chromatography f.) Mixture of water and oil Extraction
4. 5.
g.) Mixture of iron fillings and sulphur Using a magnet h.) Mixture of soil and water Precipitation 6. A mixture can be converted to a compound by heating. For example, iron filings and sulphur form a compound called iron (II) sulphide or ferrum (II) sulphide when they are heated. Iron + Sulphur heat Iron (II) sulphide The composition of air 1. 2. Air is a mixture of various substances that is odourless, colourless, or tasteless. Water vapour in the air depends on the humidity in the air. The more humid the air, the more the water vapour in the air.
Nitrogen 78%
Carbon dioxide 0.03% Inert gas and others 0.97% Oxygen 21%
3.
Examples of inert gases are: a.) Dust b.) Water vapour c.) Microorganisms
The properties of oxygen and carbon dioxide 1. 2. 3. Air is made up of three main gases: oxygen, carbon dioxide and nitrogen. Each gas has its own chemical properties. The properties of the gases can be observed by : a.) Solubility in the water b.) Reaction with sodium hydroxide
c.) Effects on 4. Properties Colour Smell Solubility in water Reaction with sodium hydroxide The effect on glowing wooden splinter The effect on burning wooden splinter The effect on moist litmus paper The effect on lime water The effect on hydrogen carbonate indicator Glowing wooden splinter Burning wooden splinter Litmus paper Lime water Hydrogen carbonate indicator Nitrogen is a gas that does not react chemically. Observation and conclusion Carbon dioxide None None None None The level of water in the test tube The level of water in the test tube rise rises slightly. Oxygen is slightly a lot. Carbon dioxide is soluble in soluble in water. water. The level of water does not rise. The level of water in the test tube rises Oxygen is not soluble in sodium a lot. Carbon dioxide is very soluble hydroxide. sodium hydroxide. The glowing wooden splinter bursts The glowing wooden splinter into flame. Oxygen supports extinguishes. Carbon dioxide does not combustion. support combustion. The burning wooden splinter burns The burning wooden splinter even brighter. The gas is nonextinguishes. The gas is non-flammable. flammable. Oxygen supports Carbon dioxide does not support combustion but is not selfcombustion and is not self combustible. combustible. The litmus papers do not change The blue litmus paper turns red. colour. Oxygen is neutral. Carbon dioxide is slightly acidic. Oxygen The lime water does not change colour. The red indicator does not change colour. Oxygen is neutral. Carbon dioxide turns the lime water cloudy. The red indicator turns yellow. Carbon dioxide is slightly acidic.
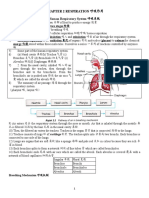
Oxygen is needed for respiration 1. 2. 3. Air that is breathed into the body is called inhaled air. Air that is breathed out of the body is called exhaled air. Oxygen is needed for respiration: Inhaled oxygen will be dissolved at the surface of the moist alveolus. Oxygen will be absorbed into the blood capillary through the thin alveolus wall. Oxygen is then transported by red blood cells to the other blood cells for the process of respiration.
At the same time, carbon dioxide and water from blood capillaries will be absorbed alveolus. Carbon dioxide and water will be expelled body when air is exhaled.
Oxygen is needed for combustion 1. Combustion is a process that takes place when a substance unites with oxygen chemically and this produces energy and light. Without oxygen. Combustion cannot occur because chemical process does not take place. Carbon is a chemical compound that is made up of the carbon element only. Combustion of carbon releases carbon dioxide, heat energy and light energy. Examples of carbon are wood, cloth, charcoal, and paper. Carbon + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + Heat energy + Light energy 6. 7. 8. Hydrocarbon is a chemical compound which is formed from only hydrogen and carbon. Combustion of hydrocarbon produces carbon dioxide, water, heat energy and light energy. Water is formed when hydrogen from hydrocarbon combines with oxygen during combustion. Hydrocarbon + Carbon Carbon Dioxide + Water + Heat energy + Light energy 9. Combustion produces light energy and heat energy.
2. 3. 4. 5.
10. Carbon dioxide produced is absorbed by green plants to conduct photosynthesis. Source of energy 1. 2. 3. Energy is defined as the ability to do work. Energy is measured in joules (J). Energy can be found in many forms: a.) Kinetic energy b.) Potential energy c.) Light energy d.) Electrical energy e.) Sound energy f.) Nuclear energy g.) Heat energy h.) Chemical energy 4. Kinetic energy
Is the energy possessed by a moving object Depends on mass and velocity Will increase if a.) The mass of the object increases b.) The velocity of the object increases
5.
Potential energy Is the energy stored in a body due to its position or its physical condition Depends on a.) The mass of the object b.) The distance of the object from the Earths surface c.) The power of the gravitational pull on the object Will increases a.) The mass of the object increases b.) The higher the object is raised from the ground c.) The gravitational pull on the object increases. A falling object can gain kinetic energy but loses potential energy Elastic potential energy can only elastic substances such as a spring or a rubber.
6.
Heat energy Is the energy that is stored in a hot object Depends on its temperature and volume Flows from a hot area to a cold area by conduction, convection and radiation.
7.
Light energy Is the energy produced by an object that emits light Can be detected by the eye Can travel in a vacuum and in a straight line in the form of waves A luminous object is an object that gives out its own light energy. For example, sun and stars.
A non luminous object is an object that does not give out its own light energy but can only reflect light. For example, mirror and metal.
8.
Sound energy Is the energy produced by a vibrating object An object which vibrates produces a recurring movement. The vibrating air forms sound waves. Can be transferred through a medium but cannot travel in a vacuum.
9.
Chemical energy Is the energy stored in a chemical substance Is found in fuels
10. Electrical energy Is the energy produced by the flow of electric charges.
11. Nuclear energy Is the energy stored in the nucleus of an atom. Known as atomic energy.
12. Mechanical energy Is produced when a machine or object changes its position. Known as energy of motion Is composed of kinetic energy and potential energy
13. Solar energy Is produced during the process of nuclear fusion in the suns core
Source of energy Types of energy sources on Earth a.) Fossil fuels b.) Biomass fuels c.) Radioactive substances d.) Mechanical sources e.) Geothermal sources f.) Solar energy
Energy sources Fossil fuel
Formation of petroleum and natural gas
Biomass fuels
Radioactive substances
Mechanical sources
Geothermal sources Sun (solar energy)
Details Formed from remains of plant and animals buried in the ground and which had decomposed million of years ago Examples: Coals Petroleum Natural gas Formed from remains of animals and plants that had sank to the bottom of the sea and was buried there for millions of years. The decomposed animals and plants combine with sand and earth in the sea bed form shale while the remains turn into petroleum and natural gas. Normally petroleum is found below the layer of natural gas because petroleum is denser than natural gas. Are obtained from decomposed organisms such as plants and animals. Decomposed plants and animals produce methane gas and alcohol which then become fuel sources. Uranium is a common energy source used in nuclear power stations. Uranium is split into two lighter elements in the process of nuclear fission. Are natural sources of energy such as wind, water, and wave. Are renewable energy source Comes from heat in the inside of the Earth Is the primary source of energy on Earth Can be harnessed and used to generate electrical energy
Heat 1. Heat is a form of energy which flows from a region of high temperature to another region of lower temperature. Heat can travel through solids, liquids, gas, and even vacuum. SI Unit for heat is joule (J) Temperature is a physical quantity which refers to the degree of hotness or coldness of a matter. SI Unit for temperature is Kelvin (K) The hotter a body, the higher is its temperature. The colder a body, the lower is its temperature. The more the energy contained in an object, the higher the temperature of the object. Heat capacity is the quantity of heat energy contained in a matter. Is properties are:
2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.
Dependent on the type of volume, mass of volume, and the temperature of matter At the same temperature, a larger matter has more heat content With the same volume, a hotter matter has higher heat content
Expansion and contraction of matter 1. 2. Matter absorbs heat when heated and expels heat when cooled. When heated: a.) Particles of matter absorb heat energy and change it into kinetic energy. Kinetic energy causes particles to vibrate faster b.) This vibration causes the particles to move further apart. Therefore, the size and volume of matter will increase. 3. When cooled: a.) Particles of matter vibrate less and their speed also decreases b.) Distance between the particles reduces. This means that the size and volume of matter also decreases. Heat flow and conduction 1. 2. Heat is a form of energy possessed by a matter Heat flow in three ways : a.) Conduction Is the flow of heat through a solid due to a difference in temperature throughout the solid
b.) Convection Is the process of flow of heat in a fluid
c.) Radiation Is known as radiant heatIs a process of energy flow through infrared waves which move in straight line
Effect of heat on matter Melting 1. 2. 3. Melting is a process by which a solid changes into a liquid A solid melts into a liquid when heated When a solid is heated, the particles absorb heat energy
4.
At the melting point, particles vibrate most forcefully until they break away from their fixed positions.
Freezing 1. 2. Boiling 1. 2. Boiling is a process of a liquid changes into a gas At the boiling point, the liquid move speedily and freely. Freezing is a process by which a liquid changes into a solid At freezing point, the particles no longer move freely
Condensation 1. 2. Condensation is the process of a gas changing into a liquid As gas particles move slower and closer together, the liquid will be formed.
Evaporation 1. 2. Evaporation is a process of changes of a liquid into gas at any temperature. Factors which influence the rate of evaporation: a.) Temperature of liquid : The higher the temperature of the liquid, the faster the liquid evaporates
b.) Air moisture in the surrounding of the liquid: The lower the humidity, the faster the liquid evaporates
c.) Exposed area of the liquid surface: Sublimation 1. 2. Sublimation is the conversion process of a solid directly to gas without melting. In this process, the particles of a solid absorb heat energy. When enough energy is absorbed, the particles separate to form gas. The wider the liquid surface area, the faster the liquid evaporates
Absorbing and giving out heat 1. The ability of an object to absorb or radiate heat depends on the surface nature and the surrounding temperature of the object. Objects with opaque (black) and rough surface are good heat absorbers and radiators. Objects with burnished (shiny) and smooth surfaces are poor heat absorbers and radiators. Hotter objects are better heat radiators than cold objects.
2. 3. 4.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Exercise Introduction To ScienceDocumento17 pagineExercise Introduction To ScienceShu85Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sains Form1 Final ExamDocumento10 pagineSains Form1 Final ExamNOR SUAKMA BT JAAFARNessuna valutazione finora
- Sains Form3 Final ChapterDocumento14 pagineSains Form3 Final ChapterNik Dhaniel100% (1)
- PBL (Mathematics) - Income Tax Assessment-Poah Zhi XianDocumento14 paginePBL (Mathematics) - Income Tax Assessment-Poah Zhi XianZhi Xian PoahNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Form 4 Nuclear Energy NotesDocumento4 pagineScience Form 4 Nuclear Energy Noteslaukhaisiang89% (9)
- Form 2 Science Air Pressure NotesDocumento15 pagineForm 2 Science Air Pressure NotesAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 2 Science Chapter 7Documento32 pagineForm 2 Science Chapter 7qq23582% (11)
- Science F3 RespirationDocumento3 pagineScience F3 RespirationSuntharan MuniandyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 TeacherDocumento46 pagineChapter 8 TeachercsteeeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Section A (20 Marks)Documento8 pagineSection A (20 Marks)Elen UningNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneDocumento45 pagineChapter 3 Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneNurul Husna100% (1)
- Ayu Shahirah Binti Salem: ObjectiveDocumento2 pagineAyu Shahirah Binti Salem: ObjectiveNoor NaxihahNessuna valutazione finora
- Sci F1 T1 (E)Documento7 pagineSci F1 T1 (E)Sylvia ChinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 Force and Motion: Learning OutcomesDocumento11 pagineChapter 8 Force and Motion: Learning OutcomesannabellNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 2 Chapter 9 HeatDocumento46 pagineForm 2 Chapter 9 HeatAmer MalekNessuna valutazione finora
- BIO F4 Paper 1Documento28 pagineBIO F4 Paper 1Zalina RoslanNessuna valutazione finora
- PMR 2012 Science 108 MantraDocumento16 paginePMR 2012 Science 108 MantraJun MingNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding the Process of Cell Division and GeneticsDocumento12 pagineUnderstanding the Process of Cell Division and GeneticsAnonymous klhru5ENessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3Documento7 pagineChapter 3api-3841154Nessuna valutazione finora
- Form 2 Chapter 4 Human HealthDocumento29 pagineForm 2 Chapter 4 Human HealthbadrulNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 7 Light, Sight and ColourDocumento43 pagineCHAPTER 7 Light, Sight and ColourAkmar MataliNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Form 3 Chapter 4 ReproductionDocumento18 pagineScience Form 3 Chapter 4 ReproductionAutumn JJ100% (3)
- Determine EMF and internal resistance of a dry cellDocumento3 pagineDetermine EMF and internal resistance of a dry cellmalaomarNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 1 - Chapter 8Documento6 pagineForm 1 - Chapter 8Anonymous fhlpbtbXzx67% (3)
- Sains - Tahun 6 (English)Documento46 pagineSains - Tahun 6 (English)Sekolah Portal96% (24)
- Science Form 1 Chapter 2: Cell Is The Unit of LifeDocumento25 pagineScience Form 1 Chapter 2: Cell Is The Unit of LifeMuhammad Shazni Daud100% (1)
- Theme: Heat Chapter 4: Heat: of WaterDocumento11 pagineTheme: Heat Chapter 4: Heat: of WaterJasbir SidhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 1 Science Pendulum ExperimentDocumento2 pagineForm 1 Science Pendulum ExperimentAngie Kong Su Mei0% (1)
- Obj Home WorkDocumento9 pagineObj Home WorkYuman WongNessuna valutazione finora
- Transport System in OrganismsDocumento19 pagineTransport System in OrganismsJue Hazea GoldshopNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Form 3 Chapter 2Documento31 pagineScience Form 3 Chapter 2rosya100% (5)
- Chapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuideDocumento39 pagineChapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuideMuhd Rifaie RodzilNessuna valutazione finora
- Instructions: Each Question Is Followed by Four Alternative Answers, A, B, C and D. Circle The Correct AnswerDocumento11 pagineInstructions: Each Question Is Followed by Four Alternative Answers, A, B, C and D. Circle The Correct AnswerrosyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiration Form 3Documento21 pagineRespiration Form 3Chin Kok SoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Form 5 Chapter 3 PDFDocumento18 pagineRevision Form 5 Chapter 3 PDFYz PohNessuna valutazione finora
- Nor Diana Binti HassanDocumento2 pagineNor Diana Binti HassanFazwadi Haliah100% (1)
- Revision Pack Science Form 1 + Form 2Documento21 pagineRevision Pack Science Form 1 + Form 2Shureen Baskaran100% (1)
- Human Respiratory SystemDocumento13 pagineHuman Respiratory SystemJue Hazea GoldshopNessuna valutazione finora
- M012-Consumer Mathematics (Taxation)Documento5 pagineM012-Consumer Mathematics (Taxation)Tan Jun YouNessuna valutazione finora
- Determining The Energy Value of Food SamplesDocumento2 pagineDetermining The Energy Value of Food SamplesShirmei Wang100% (1)
- Speed & Velocity IGCSEDocumento6 pagineSpeed & Velocity IGCSEsapiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 1.1 - Simple PendulumDocumento2 pagineExperiment 1.1 - Simple PendulumPauling Chia100% (1)
- Understanding Sexual and Asexual ReproductionDocumento95 pagineUnderstanding Sexual and Asexual ReproductionEric Chew100% (1)
- FORM 1 SCIENCE NOTES: Understanding the Basics of ScienceDocumento19 pagineFORM 1 SCIENCE NOTES: Understanding the Basics of ScienceQQLove92% (13)
- Form 1 Science NotesDocumento19 pagineForm 1 Science NotesTanYeeTingNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 1-Science NotesDocumento19 pagineForm 1-Science Notescikguanuar72% (18)
- Form 1 Science NotesDocumento21 pagineForm 1 Science NotesVanaja Mani SelvanNessuna valutazione finora
- General Biology for the Beginner: In Association with Afif Elnagger, Phd, Professor of BiologyDa EverandGeneral Biology for the Beginner: In Association with Afif Elnagger, Phd, Professor of BiologyNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER ONE: A View of Life: 1.1 How To Define LifeDocumento60 pagineCHAPTER ONE: A View of Life: 1.1 How To Define LifeIngrid Dominique P. SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- General Science Notes - Class 6Documento17 pagineGeneral Science Notes - Class 6FariNessuna valutazione finora
- Sciencia Du Gaia - Introduccion Du Sciencia BioDocumento56 pagineSciencia Du Gaia - Introduccion Du Sciencia BioRETLAWNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 101 Study Guide Test 1Documento8 pagineBio 101 Study Guide Test 1mattyg35Nessuna valutazione finora
- ScienceDocumento177 pagineSciencefoongNessuna valutazione finora
- SCIENCE PMR Notes and ExperimentsDocumento221 pagineSCIENCE PMR Notes and ExperimentsAzlina Ahmad100% (1)
- PMR Science Form 1 Chapter 2 Cell As A Unit of LifeDocumento8 paginePMR Science Form 1 Chapter 2 Cell As A Unit of LifeDavid AntonitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology PDFDocumento78 pagineBiology PDFRagini khargNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology NotesDocumento154 pagineBiology NotesMarwan YasserNessuna valutazione finora
- Elsq2 W1&2 - Fabrigas-11abmcharityDocumento4 pagineElsq2 W1&2 - Fabrigas-11abmcharityFabrigasBennetNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Science 7 NotesDocumento22 pagineFull Science 7 Notesnoelcaimoy45Nessuna valutazione finora
- IdeologyDocumento29 pagineIdeologyKhadijah YusopNessuna valutazione finora
- Sri Utama's 2012 Teachers Day CelebrationDocumento2 pagineSri Utama's 2012 Teachers Day CelebrationKhadijah Yusop0% (1)
- Are You Still Playing Your FluteDocumento10 pagineAre You Still Playing Your FluteKhadijah YusopNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 1 Science NotesDocumento20 pagineForm 1 Science NotesMyName Tiff68% (25)
- EIGA Doc 04 09 EDocumento34 pagineEIGA Doc 04 09 EFernando VenceslauNessuna valutazione finora
- Sekine Et Al 2011 EPSLDocumento10 pagineSekine Et Al 2011 EPSLpleasure masangoNessuna valutazione finora
- (Loga.vn) Đề thi chọn HSGDocumento7 pagine(Loga.vn) Đề thi chọn HSGKết MaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic concepts for explosion protectionDocumento41 pagineBasic concepts for explosion protectionRadu Babau100% (1)
- Limiting Oxygen Index LOI With HMIDocumento3 pagineLimiting Oxygen Index LOI With HMISanjeevNessuna valutazione finora
- Dissolved oxygen estimation by redox titrationDocumento2 pagineDissolved oxygen estimation by redox titrationSuet Wan GohNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam3 SolutionsDocumento7 pagineExam3 SolutionsVu Anh KienNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st PU Chemistry March 2014 PDFDocumento2 pagine1st PU Chemistry March 2014 PDFPrasad C M67% (15)
- SSA SpektroskopiDocumento2 pagineSSA SpektroskopianggunNessuna valutazione finora
- Questions&AnswersDocumento25 pagineQuestions&AnswersSenthiaathavan90% (10)
- Chapter 9Documento6 pagineChapter 9rickyNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.1 Classifying Matter NotesDocumento5 pagine3.1 Classifying Matter NotesJam Uly GastyNessuna valutazione finora
- Exploring Liquids Unit Planning GuideDocumento25 pagineExploring Liquids Unit Planning Guideapi-26590893067% (6)
- Biology Exam 4 Study GuideDocumento12 pagineBiology Exam 4 Study GuideKhusbu PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- A History of Light and LightingDocumento99 pagineA History of Light and LightingSiddharth BasuNessuna valutazione finora
- Sodium Borohydride Fuel Cell AVRCDocumento25 pagineSodium Borohydride Fuel Cell AVRCSriharsha GaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 16 Sample Problems 1Documento1 paginaChem 16 Sample Problems 1HeyowJeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cpe 420 Tutorial 2Documento3 pagineCpe 420 Tutorial 2Muhamad Baihakhi ShamsudinNessuna valutazione finora
- WP - Measuring Nitration, Oxidation and Sulfation - 2017 - 10 - 24 PDFDocumento3 pagineWP - Measuring Nitration, Oxidation and Sulfation - 2017 - 10 - 24 PDFOkey OkoliNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 3a ChemistryOnEarth Booklet Mar21Documento50 pagine8 3a ChemistryOnEarth Booklet Mar21Bee Bee TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nitrogen MSDS: Simple Asphyxiant GasDocumento4 pagineNitrogen MSDS: Simple Asphyxiant GasardipangulihiNessuna valutazione finora
- OHMEDA Gas Outlet AmcareMed 1Documento2 pagineOHMEDA Gas Outlet AmcareMed 1aditarian .pNessuna valutazione finora
- Pengantar Teknologi Desain Obat: H. Muhammad Nur Abdillah, M. Si., AptDocumento89 paginePengantar Teknologi Desain Obat: H. Muhammad Nur Abdillah, M. Si., AptDipperNessuna valutazione finora
- FHSC1114 Physical Chemistry Lab ManualDocumento36 pagineFHSC1114 Physical Chemistry Lab ManualTing TC100% (1)
- 9 1 WKSTDocumento3 pagine9 1 WKSTapi-262378640Nessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution and BiodiversityDocumento4 pagineEvolution and BiodiversityTrần ĐăngNessuna valutazione finora
- Asthma Nursing Care Plans - LippincottDocumento45 pagineAsthma Nursing Care Plans - LippincottDyllanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Oxygen Concentrator SpecsDocumento7 pagineOxygen Concentrator SpecsPike WinchurkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Oxygen Generator FlyerDocumento2 pagineMedical Oxygen Generator FlyertahatekriNessuna valutazione finora
- Laws of Chemical Combination Class 9Documento4 pagineLaws of Chemical Combination Class 9Pushpa Kumari0% (1)