Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
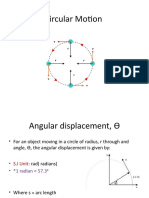
Conservation of Angular Momentum
Caricato da
idraumrCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Conservation of Angular Momentum
Caricato da
idraumrCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Examples of conservation of angular momentum
1. The circus acrobat leaves the swing with his arms and legs extended, with a certain angular velocity about a horizontal axis passing through his centre of mass to enable him to spin around the axis. When he brings his arms and legs closer to his body, moment of inertia (I decreases. To !eep his angular momentum constant (angular momentum " # I $ his angular velocity increase and he starts spinning faster.
2. % s!ater starts turning with her arms extended and then pulls them in closer (decreasing moment of inertia to her sides due to which she spins faster ( ma!ing her angular velocity increase
%long with this her rotational !inetic energy also increases, thereby increasing her energy and hence ability to do wor!. &. %s diver pushes himself slightly forward he ac'uires a small angular velocity. (nce in air, no external tor'ue acts on the body to change her angular momentum.
When he pulls in her body, moment of inertia decreases to increase his angular velocity which enables him to complete his summersault. While entering into the water again he stretches his body to reduce the angular velocity. ). % man standing on a platform which can rotate about the z * axis. +e holds a rotating wheel in his hand where axis of wheel is along ,-axis. .omponent about the z- axis is zero. If the wheel is turned so that its axis is parallel to the z * axis, the man must rotate in a direction opposite to wheel/s rotation in order that the angular momentum about the z-axis remains zero.
0. % spinning rugby ball is thrown in such a way that it gains spin about its long axis. 1ince external forces during its 2ourney in air are constant, angular moment is constant. Tor'ue is also zero and hence its direction does not very and can not travel end over end.
3. +elicopter with single propeller rotates in the opposite direction of the rotor to conserve the angular momentum. +owever if it has two propellers then one is at its tail. %s the helicopter starts, its body has tendency to rotate. To counter balanced it, the propeller rotates in the opposite direction.
4. The angular velocity of air in a tornado goes on increasing as we move towards its centre. It is on account of the fact that as the air moves towards the centre, its moment of inertia decreases and hence to maintain its angular momentum, its angular velocity increases.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------555 6'uilibrium (of force, energy, potential, angular momentum, moment of inertia of a body at a point means the sum of all (vectors (i.e force, energy, potential, angular momentum, moment of inertia is ZERO. If a body has three forces acting on a point then summation of all three forces is e'ual to zero. -----------------------------------------------------------------------If 7% 8 1 then distance over which effort is applied becomes greater than the distance over which the load is moved. 555 7echanical advantage is the factor by which a machine multiplies the force put into it. The mechanical advantage can be calculated for the simple machines by using the following formulas9 1imple machine - "ever9 MA = length of effort arm length of resistance arm.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Mechanics of Rigid BodyDocumento21 pagineMechanics of Rigid Bodyhenzel espinaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Method To Calculate Functions of The Product of G and F Used in Wilson's GF Matrix MethodDocumento4 pagineA Method To Calculate Functions of The Product of G and F Used in Wilson's GF Matrix MethodEditor IJTSRDNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution, Solubility & Gas LawsDocumento4 pagineSolution, Solubility & Gas LawsLover BoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Angular MomentumDocumento10 pagineAngular MomentumKlarence Medel PacerNessuna valutazione finora
- Cicero Prevod IDocumento1 paginaCicero Prevod IPathashalaNessuna valutazione finora
- EssayDocumento12 pagineEssayzaimNessuna valutazione finora
- Bohr Vector ModelDocumento24 pagineBohr Vector ModelJohn BeveridgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 10 Rotational MotionDocumento32 pagineChapter 10 Rotational MotionAna Dela Fuente100% (1)
- Torque, Angular MomentumDocumento17 pagineTorque, Angular Momentumkaushik247100% (1)
- Rotational DynamicsDocumento49 pagineRotational DynamicsMylene Jay PasosNessuna valutazione finora
- Photoelasticity Diffused Light Polariscope - 2019 - SOMDocumento7 paginePhotoelasticity Diffused Light Polariscope - 2019 - SOMKamini GoyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Moment of InertiaDocumento13 pagineMoment of InertiaRahmatullah RahmatNessuna valutazione finora
- Circular Motion TuteDocumento15 pagineCircular Motion TuteGayan Sanka PereraNessuna valutazione finora
- CATIA V5 R16 Sketcher Models ManualDocumento16 pagineCATIA V5 R16 Sketcher Models ManualyeswanthNessuna valutazione finora
- JK Flip FlopDocumento11 pagineJK Flip FlopprakashpacetNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 (Friction) PDFDocumento72 pagineChapter 4 (Friction) PDFRa Note A/l Som TebNessuna valutazione finora
- Born Oppenheimer ApproximationDocumento38 pagineBorn Oppenheimer Approximationmarce33236591Nessuna valutazione finora
- 11 Physics - Gravitation - NotesDocumento5 pagine11 Physics - Gravitation - Notesrahul pingaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Force Analysis of Machinery: 9.1. Inertia Force and Inertia TorqueDocumento16 pagineForce Analysis of Machinery: 9.1. Inertia Force and Inertia TorqueaddisudagneNessuna valutazione finora
- Random VibrationsDocumento20 pagineRandom VibrationsVivek PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Review Problems Semester 57Documento184 pagineReview Problems Semester 57Unkabogable AkoNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinetics of Rigid BodiesDocumento195 pagineKinetics of Rigid BodiesDexter F. RamagozaNessuna valutazione finora
- ch12 3Documento92 paginech12 3Julius Anthony MagallonNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 11 Solution MazurDocumento17 pagineChapter 11 Solution MazurKate KlopfensteinNessuna valutazione finora
- Emojis in Our Daily LifeDocumento12 pagineEmojis in Our Daily LifeLUYONessuna valutazione finora
- Conservation Laws and Energy TransformationsDocumento7 pagineConservation Laws and Energy TransformationsNikos KechagiasNessuna valutazione finora
- Friction AutoDocumento24 pagineFriction AutoSayyadh Rahamath BabaNessuna valutazione finora
- VARIGNON Theorem PDFDocumento1 paginaVARIGNON Theorem PDFNitinNessuna valutazione finora
- Macromechanics - 1: Generalized Hooke's Law For Anisotropic LaminaDocumento32 pagineMacromechanics - 1: Generalized Hooke's Law For Anisotropic LaminaIntan Khalida LukmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Linkages: 2.1. FOUR - Bar LinkageDocumento29 pagineLinkages: 2.1. FOUR - Bar LinkageaddisudagneNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Statics: Quaid-e-Azam College of Engineering & TechnologyDocumento19 pagineEngineering Statics: Quaid-e-Azam College of Engineering & TechnologywaseemjuttNessuna valutazione finora
- 6B Circular Motion & Gravitation 2020-2021Documento46 pagine6B Circular Motion & Gravitation 2020-2021RandominicNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 14Documento104 pagineChap 14noscribdyoucantNessuna valutazione finora
- Angular Momentum PDFDocumento14 pagineAngular Momentum PDFManuel ChacónNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Week 8 9 Rotational Motion and The Law of GravityDocumento44 paginePhysics Week 8 9 Rotational Motion and The Law of GravityMark Lorens Staana100% (1)
- Vibration: (BDA31103) Multi-Degree of FreedomDocumento65 pagineVibration: (BDA31103) Multi-Degree of FreedomhildaNessuna valutazione finora
- Moment of InertiaDocumento27 pagineMoment of InertiaTemoor AbbasNessuna valutazione finora
- Diffraction Physics 1Documento109 pagineDiffraction Physics 1Sudarshan GopalNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Center of Gravity, Stability and Equilibrium PDFDocumento3 pagine2 Center of Gravity, Stability and Equilibrium PDFPhilip Moore100% (1)
- ET202A B-1 (Unit 3)Documento21 pagineET202A B-1 (Unit 3)Darrell Carl Rizo JoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Group Phase VelocityDocumento7 pagineGroup Phase VelocityhassscribedNessuna valutazione finora
- 003 - Option B Chapter 14 Engineering Physics PDFDocumento62 pagine003 - Option B Chapter 14 Engineering Physics PDFyuke kristinaNessuna valutazione finora
- ULO2a - Basic Concepts of Crystal StructureDocumento14 pagineULO2a - Basic Concepts of Crystal StructureCHARLIE AMOGUIS JRNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Basic Concepts v2Documento29 pagine01 Basic Concepts v2Shashank SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Mechanics DistributedForcesDocumento47 pagineEngineering Mechanics DistributedForcesChamith KarunadharaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 With SolutionsDocumento31 pagineModule 3 With SolutionsGovind GauravNessuna valutazione finora
- Moment of Inertia PDFDocumento35 pagineMoment of Inertia PDFSwarnalatha SwarnalathaNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied Mechanics PDFDocumento18 pagineApplied Mechanics PDFSrinivas KandukuriNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 - Two Mark Questions With Answers Oct 23Documento4 pagineUnit 1 - Two Mark Questions With Answers Oct 23mk24inNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction - Forces, Equilibrium: Chapter HighlightsDocumento87 pagineIntroduction - Forces, Equilibrium: Chapter HighlightsJagannath MandalNessuna valutazione finora
- Photoelasticity تقريرDocumento8 paginePhotoelasticity تقريرحسين كاظم ياسينNessuna valutazione finora
- The Physics of Suspensions Using Computer SimulationDocumento7 pagineThe Physics of Suspensions Using Computer SimulationEric TendianNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Frictin Rough Inclined PlaneDocumento7 pagine2 Frictin Rough Inclined PlaneRAMAKANT RANANessuna valutazione finora
- Inertial Mass and Moment of InertiaDocumento1 paginaInertial Mass and Moment of InertiaKarlish WhiteNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics - Module 1 - Moving AboutDocumento19 paginePhysics - Module 1 - Moving AboutGeoffNessuna valutazione finora
- Torque and Rotation PhysicsDocumento20 pagineTorque and Rotation PhysicsSaf Tanggo DiampuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 11 BendingDocumento27 pagineChapter 11 BendingSofwan JuewekNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers 3Rd Edition Fishbane Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocumento38 paginePhysics For Scientists and Engineers 3Rd Edition Fishbane Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFwadeperlid9d98k100% (7)
- Gyroscope: Definition: A Gyroscope May Be Defined As ADocumento11 pagineGyroscope: Definition: A Gyroscope May Be Defined As AtewodrosNessuna valutazione finora
- 09 Rotational MotionDocumento10 pagine09 Rotational MotionBalaram MullapudiNessuna valutazione finora
- Equivalence PrincipleDocumento13 pagineEquivalence Principlerr1819100% (1)
- Active Correction of Dynamic Mass Imbalance For A Precise RotorDocumento6 pagineActive Correction of Dynamic Mass Imbalance For A Precise RotorJessica SandersNessuna valutazione finora
- Edexcel International GCSE Physics Student BookDocumento624 pagineEdexcel International GCSE Physics Student BookWai Lin Myint100% (2)
- N700 CatalogDocumento40 pagineN700 CatalogtranskingNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Mechanics Chapter2 Homework Set SolnsDocumento10 pagineFluid Mechanics Chapter2 Homework Set SolnsMilania DewiNessuna valutazione finora
- ENDocumento2 pagineENBenmark JabayNessuna valutazione finora
- RM6E1 Series Simple Version Operation ManualDocumento16 pagineRM6E1 Series Simple Version Operation ManualmvlNessuna valutazione finora
- General Physics1: Quarter 1 - Module 3: Title: Kinematics: Motion Along A Straight LineDocumento23 pagineGeneral Physics1: Quarter 1 - Module 3: Title: Kinematics: Motion Along A Straight LineJAMILAH JAVIER ORTIZ50% (4)
- PMDC MDCAT Curriculum 2023Documento30 paginePMDC MDCAT Curriculum 2023Muhammad Haris AzharNessuna valutazione finora
- UPCAT 2015 - SIMULATED EXAM - SET B - SECTION 2 - SCIENCE PROFICIENCY v.8.1.2015Documento12 pagineUPCAT 2015 - SIMULATED EXAM - SET B - SECTION 2 - SCIENCE PROFICIENCY v.8.1.2015windelyn butraNessuna valutazione finora
- Natreviewgrade6 160306045816 MergedDocumento22 pagineNatreviewgrade6 160306045816 MergedYamSiriOdarnohNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam1a Phys1110 Fa11Documento10 pagineExam1a Phys1110 Fa11TOPKEKNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Physics 1st YearDocumento173 pagineEngineering Physics 1st YearKishan Kewat100% (1)
- UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION - Notes PDFDocumento5 pagineUNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION - Notes PDFJohnston ThevarajahNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam 1 Study Guide - PHYS 121 - Spring 2019 - Dr. Goolsby-ColeDocumento4 pagineExam 1 Study Guide - PHYS 121 - Spring 2019 - Dr. Goolsby-ColeC G-CNessuna valutazione finora
- Suspension Acoustics - Temkin S PDFDocumento418 pagineSuspension Acoustics - Temkin S PDFDaniela VillegasNessuna valutazione finora
- The Use of Dry Lubricated Bearings in Reaction WheelsDocumento9 pagineThe Use of Dry Lubricated Bearings in Reaction WheelsankitsarvaiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Nature of Dark Energy and Dark Matter-LibreDocumento4 pagineThe Nature of Dark Energy and Dark Matter-Libreivansendacross5221Nessuna valutazione finora
- PHYSICS Newtons-1st-LawDocumento52 paginePHYSICS Newtons-1st-LawLago, Azel Chin L.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3-Vectors and Two Dimensional MotionDocumento42 pagineChapter 3-Vectors and Two Dimensional MotionShinosuke ExtendezNessuna valutazione finora
- Work, Energy & Power: Honors PhysicsDocumento20 pagineWork, Energy & Power: Honors PhysicsFebry ArdiansyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 2.1 Formative Answer KeyDocumento2 pagineTopic 2.1 Formative Answer KeyŁØNessuna valutazione finora
- B15三轴汽缸多刀头运动控制系统 英文使用手册Documento82 pagineB15三轴汽缸多刀头运动控制系统 英文使用手册Rabah RebouhNessuna valutazione finora
- GRFP01 CRU Gr12 Ch01 ALLDocumento20 pagineGRFP01 CRU Gr12 Ch01 ALLNyiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3 - Motion in A Straight LineDocumento36 pagineLecture 3 - Motion in A Straight LineMaitha AlhosaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Weekly Lesson Plan 2019 - 20 Grade: LX Subject:Physics Term:1stDocumento6 pagineWeekly Lesson Plan 2019 - 20 Grade: LX Subject:Physics Term:1starif asgarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2017 Mock Iit Advanced 1.Documento22 pagine2017 Mock Iit Advanced 1.gaurav gargNessuna valutazione finora
- MaxMotion ManualDocumento252 pagineMaxMotion ManualBarry WittNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics NotesDocumento91 paginePhysics NotesRachel Adams100% (2)
- The Yogi Code: Seven Universal Laws of Infinite SuccessDa EverandThe Yogi Code: Seven Universal Laws of Infinite SuccessValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (104)
- Boundless: Upgrade Your Brain, Optimize Your Body & Defy AgingDa EverandBoundless: Upgrade Your Brain, Optimize Your Body & Defy AgingValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (67)
- Peak: The New Science of Athletic Performance That is Revolutionizing SportsDa EverandPeak: The New Science of Athletic Performance That is Revolutionizing SportsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (97)
- Chair Yoga: Sit, Stretch, and Strengthen Your Way to a Happier, Healthier YouDa EverandChair Yoga: Sit, Stretch, and Strengthen Your Way to a Happier, Healthier YouValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (5)
- Power of 10: The Once-A-Week Slow Motion Fitness RevolutionDa EverandPower of 10: The Once-A-Week Slow Motion Fitness RevolutionValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (11)
- Aging Backwards: Reverse the Aging Process and Look 10 Years Younger in 30 Minutes a DayDa EverandAging Backwards: Reverse the Aging Process and Look 10 Years Younger in 30 Minutes a DayNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional Training and Beyond: Building the Ultimate Superfunctional Body and MindDa EverandFunctional Training and Beyond: Building the Ultimate Superfunctional Body and MindValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (1)
- Strong Is the New Beautiful: Embrace Your Natural Beauty, Eat Clean, and Harness Your PowerDa EverandStrong Is the New Beautiful: Embrace Your Natural Beauty, Eat Clean, and Harness Your PowerValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- Relentless: From Good to Great to UnstoppableDa EverandRelentless: From Good to Great to UnstoppableValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (787)
- Muscle for Life: Get Lean, Strong, and Healthy at Any Age!Da EverandMuscle for Life: Get Lean, Strong, and Healthy at Any Age!Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (22)
- 80/20 Running: Run Stronger and Race Faster by Training SlowerDa Everand80/20 Running: Run Stronger and Race Faster by Training SlowerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (97)
- The Total Kettlebell Workout: Trade Secrets of a Personal TrainerDa EverandThe Total Kettlebell Workout: Trade Secrets of a Personal TrainerValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Mind Your Body: 4 Weeks to a Leaner, Healthier LifeDa EverandMind Your Body: 4 Weeks to a Leaner, Healthier LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (5)
- Pranayama: The Yoga Science of BreathingDa EverandPranayama: The Yoga Science of BreathingValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (8)
- Strength Training Over 40: The Only Weight Training Workout Book You Will Need to Maintain or Build Your Strength, Muscle Mass, Energy, Overall Fitness and Stay Healthy Without Living in the GymDa EverandStrength Training Over 40: The Only Weight Training Workout Book You Will Need to Maintain or Build Your Strength, Muscle Mass, Energy, Overall Fitness and Stay Healthy Without Living in the GymValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (6)
- Enter The Kettlebell!: Strength Secret of the Soviet SupermenDa EverandEnter The Kettlebell!: Strength Secret of the Soviet SupermenValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (29)
- Easy Strength: How to Get a Lot Stronger Than Your Competition-And Dominate in Your SportDa EverandEasy Strength: How to Get a Lot Stronger Than Your Competition-And Dominate in Your SportValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (17)
- Not a Diet Book: Take Control. Gain Confidence. Change Your Life.Da EverandNot a Diet Book: Take Control. Gain Confidence. Change Your Life.Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (124)
- The Power of Fastercise: Using the New Science of Signaling Exercise to Get Surprisingly Fit in Just a Few Minutes a DayDa EverandThe Power of Fastercise: Using the New Science of Signaling Exercise to Get Surprisingly Fit in Just a Few Minutes a DayValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (4)
- The Yoga Sutras of Patanjali: The Final Guide for the Study and Practice of Patanjali's Yoga SutrasDa EverandThe Yoga Sutras of Patanjali: The Final Guide for the Study and Practice of Patanjali's Yoga SutrasNessuna valutazione finora
- Endure: Mind, Body, and the Curiously Elastic Limits of Human PerformanceDa EverandEndure: Mind, Body, and the Curiously Elastic Limits of Human PerformanceValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (237)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: Built for This: The Quiet Strength of PowerliftingDa EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: Built for This: The Quiet Strength of PowerliftingValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (133)
- Music For Healing: With Nature Sounds For Natural Healing Powers: Sounds Of Nature, Deep Sleep Music, Meditation, Relaxation, Healing MusicDa EverandMusic For Healing: With Nature Sounds For Natural Healing Powers: Sounds Of Nature, Deep Sleep Music, Meditation, Relaxation, Healing MusicValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- 8 Weeks to 30 Consecutive Pull-Ups: Build Your Upper Body Working Your Upper Back, Shoulders, and Biceps | at Home Workouts | No Gym Required |Da Everand8 Weeks to 30 Consecutive Pull-Ups: Build Your Upper Body Working Your Upper Back, Shoulders, and Biceps | at Home Workouts | No Gym Required |Nessuna valutazione finora
- Somatic Exercises for Beginners: Transform Your Life in 30 Days with Personalized Exercises for Body and MindDa EverandSomatic Exercises for Beginners: Transform Your Life in 30 Days with Personalized Exercises for Body and MindNessuna valutazione finora
- Yamas & Niyamas: Exploring Yoga's Ethical PracticeDa EverandYamas & Niyamas: Exploring Yoga's Ethical PracticeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (111)