Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Sharon Hampton 100 Word Vocabulary List Geometry
Caricato da
hodgeheg9991234Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Sharon Hampton 100 Word Vocabulary List Geometry
Caricato da
hodgeheg9991234Copyright:
Formati disponibili
100 Word Vocabulary List
1. 2. 2. !. #. $. %. &. '. (. 1). 11. 12. 1!. 1#. 1$. 1%. 1&. 1'. 1(. 2). 21. 22. 2!. 2#. 2$. 2%. 2&. 2'. 2(. !). !1. !2. !!. !#. !$. !%. !&. !'. !(. #). #1. #2. #!.
Geometry
Geometry - branch of mathematics that deals with points, lines, planes and solids and examines their properties. Point has no size; length, width, or height. It is represented by a dot and named by a capital letter. Line set of points which has infinite length but no width or height. line is named by a lower case letter or by any two points on the line. Plane set of points that has infinite length and width but no height. "e name a plane with a capital letter. Space set of all points. Collinear points points that lie on the same line. Noncollinear points points that do not lie on the same line. Coplanar points points that lie on the same plane. Noncoplanar points points that do not lie on the same plane. Segment part of a line that consists of two points called endpoints and all points between them. Ray- is the part of a line that contains an endpoint and all points extending in the other direction. Congruent segments segments that ha*e the same length. Bisector of a segment line, ray segment, or plane that di*ides a segment into two congruent segments. idpoint of a segment a point that di*ides the segment into two congruent segments. !cute angle angle whose measure is between ) degrees and () degrees. Rig"t angle angle whose measure is () degrees. #btuse angle angle whose measure is greater than () degrees but less than 1') degrees. Straig"t angle angle whose measure is 1') degrees. Congruent angles angles that ha*e the same measure. !ngle bisector ray that di*ides an angle into two congruent ad+acent angles. $riangle the figure formed by three segments +oining three noncollinear points. ,ach of the three points is a *ertex of the triangle and the segments are the sides. !cute triangle- triangle that has all acute angles. Rig"t triangle triangle with a right angle. #btuse triangle triangle with an obtuse angle. %&uiangular triangle triangle with all angles congruent. Scalene triangle triangle with no sides congruent. 'sosceles triangle triangle with at least two sides congruent. %&uilateral triangle triangle with all sides congruent. !d(acent angles two coplanar angles with a common *ertex and a common side between them Vertical angles the non-ad+acent angles formed by two intersecting lines. Complementary angles two angles whose sum is () degrees. Supplementary angles two angles whose sum is 1') degrees. Perpendicular lines two lines that intersect to form right angles. Parallel lines two lines are parallel if they are coplanar and do not intersect. S)e* lines are noncoplanar lines they will not intersect. Polygon union of ! or more coplanar segments that meet only at endpoints such that at most two segments meet at one endpoint and each segment meets exactly two other segments. Regular polygon polygon which is e-uilateral and e-uiangular. Congruent triangles two triangles are congruent if corresponding sides are congruent and corresponding angles are congruent. edian of a triangle segment from the *ertex of a triangle to the midpoint of the opposite side. !ltitude of a triangle segment from the *ertex of a triangle perpendicular to the line containing the opposite side. Parallelogram -uadrilateral with both pairs of opposite sides parallel. Rectangle parallelogram with a right angle. R"ombus parallelogram with consecuti*e sides congruent. S&uare all sides congruent and all four right angles.
##. #$. #%. #&. #'. #(. $). $1. $2. $!. $#. $$. $%. $&. $'. $(. %). %1. %2. %!. %#. %$. %%. %&. %'. %(. &). &1. &2. &!. &#. &$. &%. &&. &'. &(. '). '1. '2. '!. '#. '$. '%. '&. ''. '(. (). (1.
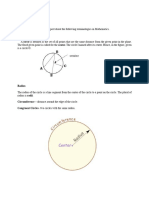
$rape+oid -uadrilateral with exactly one pair of opposite sides parallel. Ratio comparison of two numbers by di*ision. Proportion e-uation that states two ratios are e-ual. Pyt"agorean $"eorem in a right triangle, the sum of the s-uares of the legs is e-ual to the s-uare of the hypotenuse Circle the set of points in a plane that are e-uidistant from a fixed point called the center. Radius segment whose endpoints are the center of the circle and a point on the circle. C"ord segment that connects two points on the circle. ,iameter chord that passes through the center of the circle. Secant line that intersects a circle in two points. $angent line in the plane of the circle that intersects the circle in one point. Concentric circles two or more circles in the same plane with the same center. Congruent circles circles that ha*e congruent radii. Sp"ere set of points in space a gi*en distance from a gi*en point called the center. !rc consists of two points and the continuous part of a circle between them. Semi-circle arc whose endpoints are the endpoints of a diameter. inor arc arc whose measure is less than a semi-circle or 1') degree. a(or arc arc whose measure is greater than a semi-circle or 1') degrees. Central angle of a circle angle whose *ertex is the center of the circle and whose rays are radii of the circle. Congruent arcs arcs with e-ual measure in the same circle or in congruent circles. 'nscribed angles angle whose *ertex is on the circle and whose sides are chords of the circle. Bases congruent polygons lying in parallel planes. !ltitude segment +oining the two base planes and perpendicular to both. Lateral faces faces of a prism that are not its bases. Lateral edges intersection of ad+acent lateral faces form lateral edges. Lateral area sum of the area of its lateral faces. Surface area sum of the area of all its faces. Volume number of cubic units contained in a solid. .ight /rism is a prism whose lateral faces are rectangles. 0bli-ue prism is a prism whose lateral faces are parallelograms. 1ube is a prism where all sides are s-uares. 2riangular prism is a prism whose parallel faces 3the bases4 are congruent triangles. 1ylinder has two congruent circular bases in parallel planes. 1one has a *ertex and a circular base. 5ine of symmetry di*ides a figure into two congruent hal*es that reflect each other. /erimeter of a polygon is the distance around the polygon. rea of any surface is the number of s-uare units re-uired to co*er the surface. 6olume of a !-dimensional figure is the number of cubic units contained in the solid. 1ircumference the distance around a circle. 1onditional statement a statement that can be written in an if-then form. 7ypothesis in a conditional statement the statement that immediately follows the word if. 1onclusion in a conditional statement the statement that immediately follows the word then. 1on*erse the statement formed by exchanging the hypothesis and the conclusion of a conditional statement. In*erse the statement formed by negating both the hypothesis and the conclusion of a conditional statement. 1ontrapositi*e the statement formed by negating both the hypothesis and conclusion of the con*erse of a conditional statement. 8iconditional the con+unction of a conditional statement and its con*erse. 9educti*e reasoning a system of reasoning that uses facts, rules,definitions, or properties to reach logical conclusions. Inducti*e reasoning reasoning that uses a number of specific examples to arri*e at a plausible prediction. /roof a logical argument in which each statement you ma:e is supported by a statement that is accepted as true.
(2. /ostulate- a statement that describes a fundamental relationship between basic terms of geometry. /ostulates are accepted as true without proof. (!. 2heorems a statement or con+ecture that can be pro*en true by gi*en, definitions, postulates, or already pro*en theorems. (#. 2wo-column proof a formal proof that contains statements and reasons organized in two columns. ($. /aragraph proof an informal proof written in the form of a paragraph that explains why a con+ecture for a gi*en situation is true. (%. ;low proof a proof that organizes statements in logical order, starting with gi*en statements. ,ach statement is written in a box with the reason *erifying the statement written below the box. (&. 1on+ecture an educated guess based on :nown information. ('. <ine for an acute angle of a right triangle, the ratio of the measure of the leg opposite the acute angle to the measure of the hypotenuse. ((. 1osine for an acute angle of a right triangle, the ratio of the measure of the leg ad+acent to the acute angle to the measure of the hypotenuse. 1)). 2angent for an acute angle of a right triangle, the ratio of the measure of the leg opposite the acute angle to the measure of the leg ad+acent to the acute angle.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 100 Word Vocabulary List For GeometryDocumento3 pagine100 Word Vocabulary List For GeometryGezalla Joenjine Gunday100% (1)
- Lesson 5 Undefined Terms Postulates and TheoremsDocumento46 pagineLesson 5 Undefined Terms Postulates and TheoremsSpencer Phay Villaluna100% (2)
- Theorem 7Documento11 pagineTheorem 7terezkiNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry Postulates TheoremsDocumento4 pagineGeometry Postulates TheoremsCresencio Genobiagon JrNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry Glossary: M ABCDocumento19 pagineGeometry Glossary: M ABCfree_progNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Drawing 8 (Q1-Week 1)Documento4 pagineTechnical Drawing 8 (Q1-Week 1)chaNessuna valutazione finora
- AltitudeDocumento18 pagineAltitudeMichael AlvarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry Terms and DefinitionsDocumento4 pagineGeometry Terms and DefinitionsGezalla Joenjine GundayNessuna valutazione finora
- Dictionary PDFDocumento95 pagineDictionary PDFFaiza Faizan100% (1)
- Geometry Reference: Points, Lines and Planes CirclesDocumento2 pagineGeometry Reference: Points, Lines and Planes Circlesmarko1234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Plane Geometry: The Building Blocks of GeometryDocumento22 paginePlane Geometry: The Building Blocks of GeometryMarian Kaye100% (1)
- Theorems of Secant and Tangent of A CircleDocumento4 pagineTheorems of Secant and Tangent of A CircleMelgeri Aubrey E. UngosNessuna valutazione finora
- Vikash Residential School: Math-Ix, Key PointsDocumento2 pagineVikash Residential School: Math-Ix, Key Pointsaswin1947Nessuna valutazione finora
- Defined TermsDocumento11 pagineDefined TermsSantanah Daxene Daylo100% (1)
- Plane Geometry: The Building Blocks of GeometryDocumento22 paginePlane Geometry: The Building Blocks of GeometrySouphia MatteousNessuna valutazione finora
- ODB - Math (Geometry)Documento4 pagineODB - Math (Geometry)Jerric CristobalNessuna valutazione finora
- Dorothy Claire Parungao III-Remedies Postulates TheoremsDocumento4 pagineDorothy Claire Parungao III-Remedies Postulates TheoremsacciofabNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre-Algebra Ch. 8 Quiz 2Documento2 paginePre-Algebra Ch. 8 Quiz 2KaitlynNessuna valutazione finora
- g7 Math q3w1-8Documento8 pagineg7 Math q3w1-8Audree JeanNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review of Basic Concepts in Geometry and AlgebraDocumento20 pagineA Review of Basic Concepts in Geometry and AlgebraJoy Cabato Bayno100% (2)
- SOLID MENSURATION Chapter 1Documento27 pagineSOLID MENSURATION Chapter 1Kate ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Solid Geometry: Clarita R. GuevaraDocumento157 pagineSolid Geometry: Clarita R. GuevaraJoshua Saldaña100% (1)
- Geometry Reviewed: This Page May Need To Be For QualityDocumento4 pagineGeometry Reviewed: This Page May Need To Be For QualityAngelicaP.OrdoniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry RodriguezDocumento3 pagineGeometry RodriguezVI DALAGAN RODRIGUEZNessuna valutazione finora
- Sophomore Honors Geometry Study GuideDocumento9 pagineSophomore Honors Geometry Study Guidelily2lilyNessuna valutazione finora
- Module For Hyperbolic GeometryDocumento41 pagineModule For Hyperbolic Geometryjohndoe21718Nessuna valutazione finora
- Concepts MMWDocumento7 pagineConcepts MMWJoshua CuarterosNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer in MathDocumento2 pagineReviewer in MathJosh Deinille ManarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematical TermsDocumento8 pagineMathematical TermsMohan LalNessuna valutazione finora
- Plane & Solid Geometry HandoutDocumento14 paginePlane & Solid Geometry HandoutAngelo Luigi Yasay100% (1)
- German V. Canibas Jr. 8 - Rizal 1. Reflexive Property of EqualityDocumento45 pagineGerman V. Canibas Jr. 8 - Rizal 1. Reflexive Property of EqualityDanilo Fronda Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Math OverviewDocumento5 pagineMath OverviewJerdyn Marrianne GludaNessuna valutazione finora
- Circle GeometryDocumento65 pagineCircle GeometrygideonmknNessuna valutazione finora
- Q3W5 - Math 4Documento43 pagineQ3W5 - Math 4Daren TolentinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Geometric Construction-TermsDocumento21 pagineBasic Geometric Construction-TermsCarinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Euclid Geometry 9thDocumento5 pagineEuclid Geometry 9thGaurav Kumar SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- MathDocumento5 pagineMathRosemeinn Jaden PinedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry Undefined TermsDocumento26 pagineGeometry Undefined TermsShe Quintos67% (3)
- Lines, Planes and AnglesDocumento55 pagineLines, Planes and AnglesYen Aduana100% (1)
- Geometry - Part 1Documento8 pagineGeometry - Part 1Jeffrey RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- ಮೈಸೂರು ವಿಶ್ವವಿದ್ಯಾಲಯDocumento39 pagineಮೈಸೂರು ವಿಶ್ವವಿದ್ಯಾಲಯWebcomCyberCafeNessuna valutazione finora
- Deriving the Metric of Euclidean Space without AnglesDocumento3 pagineDeriving the Metric of Euclidean Space without Anglesjohndoe21718Nessuna valutazione finora
- Eureka Page: By: Alexis Canyon Unit 2 - TrianglesDocumento14 pagineEureka Page: By: Alexis Canyon Unit 2 - Trianglesapi-319393167Nessuna valutazione finora
- Math Q9 Gr9Documento11 pagineMath Q9 Gr9Ops, huli kaNessuna valutazione finora
- High School Math NotesDocumento24 pagineHigh School Math NotesaoeusnthidNessuna valutazione finora
- Plane Geometry Let Review PowerpointDocumento59 paginePlane Geometry Let Review PowerpointjaywarvenNessuna valutazione finora
- Arithmetic and geometric sequencesDocumento7 pagineArithmetic and geometric sequencesKierr KawasakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Schoolisfun's Math Level 2 Subject Test Guide and FormulasDocumento40 pagineSchoolisfun's Math Level 2 Subject Test Guide and Formulassudhakaralla1100% (2)
- 3 Dimenstional Geometry - Planes - 1: What Is A Plane?Documento5 pagine3 Dimenstional Geometry - Planes - 1: What Is A Plane?manisha choudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- ImprotantPropertiesConceptsofGeometry ModifiedDocumento11 pagineImprotantPropertiesConceptsofGeometry ModifiedVamshikrishna PuppalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Reviewer v2Documento6 pagineMath Reviewer v2helmaparisanNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Dictionary PDF FreeDocumento18 pagineMath Dictionary PDF FreeRoss AlteaNessuna valutazione finora
- MG21 List of PropertiesDocumento9 pagineMG21 List of PropertiesJorge ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Solid Mensuration REVIEWERDocumento5 pagineSolid Mensuration REVIEWER21-07543Nessuna valutazione finora
- Class IXLines and AnglesDocumento40 pagineClass IXLines and AnglesManoj Pandey100% (1)
- Quantitative Aptitude - Geometry - Formulas E - BookDocumento50 pagineQuantitative Aptitude - Geometry - Formulas E - BookOminilife SantiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Alg 2010 BDocumento1 paginaAlg 2010 Bhodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Triple Letter Score Triple Letter ScoreDocumento1 paginaTriple Letter Score Triple Letter Scorehodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Abacus 1415 Grades 3-4 ResultsDocumento1 paginaAbacus 1415 Grades 3-4 Resultshodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematical Reflections Answer SheetDocumento1 paginaMathematical Reflections Answer Sheethodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kingdom Animalia Phyla ReviewerDocumento1 paginaKingdom Animalia Phyla Reviewerhodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Adulthood and Aging Quiz Answer KeyDocumento2 pagineAdulthood and Aging Quiz Answer Keyhodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Carolus Linnaeus Father of TaxonomyDocumento2 pagineCarolus Linnaeus Father of Taxonomyhodgeheg9991234100% (1)
- 1 Test 1 Study GuideDocumento6 pagine1 Test 1 Study Guidehodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Farrellwu Pem-Tuklas November 15, 2014Documento3 pagineFarrellwu Pem-Tuklas November 15, 2014hodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4 TH IndividualDocumento5 pagine4 TH Individualhodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Famous PeopleDocumento4 pagineFamous Peoplehodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- 07 Jun ExercisesDocumento1 pagina07 Jun Exerciseshodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Procedures and Regulations For The Asian Pacific Mathematics Olympiad, 2014Documento6 pagineProcedures and Regulations For The Asian Pacific Mathematics Olympiad, 2014hodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2014 Imc SG Primary Level - Participants - Confirmed, Passport & Initial Paid As of 1635h 23june14Documento8 pagine2014 Imc SG Primary Level - Participants - Confirmed, Passport & Initial Paid As of 1635h 23june14hodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rain AnimationDocumento1 paginaRain Animationhodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Letter in Cases of Suspected Cheating On A Test or ExamDocumento2 pagineSample Letter in Cases of Suspected Cheating On A Test or Examhodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Business English Spelling List 4Documento1 paginaBusiness English Spelling List 4hodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- TeaserDocumento18 pagineTeaserhodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- G9 33sketch Effect InstructionsDocumento1 paginaG9 33sketch Effect Instructionshodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tylers College Application EssayDocumento4 pagineTylers College Application Essayhodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- AP Calc MC Index 97-98-03Documento1 paginaAP Calc MC Index 97-98-03hodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Blog Owner Entries Views Last EntryDocumento5 pagineBlog Owner Entries Views Last Entryhodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2 - 2 - Lecture 1 - Introductory Material (2923)Documento13 pagine2 - 2 - Lecture 1 - Introductory Material (2923)hodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- PMO20072008 Questions& SolutionsDocumento38 paginePMO20072008 Questions& SolutionsSheila Marie Navarro88% (8)
- 2009 Waseda UniversityDocumento10 pagine2009 Waseda Universityhodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- BrainstormingDocumento3 pagineBrainstorminghodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- DrumLine Film Reaction Paper GuideDocumento1 paginaDrumLine Film Reaction Paper Guidehodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- 11 - 1 MineralsDocumento22 pagine11 - 1 Mineralshodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Test 1 Study GuideDocumento6 pagine1 Test 1 Study Guidehodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- IMSO 2009: Short Answer ProblemsDocumento7 pagineIMSO 2009: Short Answer Problemshodgeheg9991234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Eng Math Lesson 12Documento5 pagineEng Math Lesson 12Kyla Jynell SaquitonNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths (041) Set 30 3 1,2,3 Class X Marking Scheme 2020Documento33 pagineMaths (041) Set 30 3 1,2,3 Class X Marking Scheme 2020KishiNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytic GeometryDocumento14 pagineAnalytic GeometrySherwinNessuna valutazione finora
- Micro Project MathsDocumento15 pagineMicro Project Mathsharshawardhan deshmukhNessuna valutazione finora
- Jee Adv JR Maths Vol IIDocumento337 pagineJee Adv JR Maths Vol IIdaksh282006Nessuna valutazione finora
- CATDocumento36 pagineCATSapna KanwasiNessuna valutazione finora
- Table of IntegralsDocumento2 pagineTable of IntegralsJeanGallegoNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry and Trigonometry Concepts ExplainedDocumento2 pagineGeometry and Trigonometry Concepts ExplainedPam SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- IMO Shortlist 2009 OriginalDocumento90 pagineIMO Shortlist 2009 OriginalMark Jason CelizNessuna valutazione finora
- C2 Trigonometry - QuestionsDocumento17 pagineC2 Trigonometry - QuestionsahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Vermont High School Prize Examination in MathematicsDocumento251 pagineVermont High School Prize Examination in MathematicsRodver ArlosNessuna valutazione finora
- Lagrisola EXAMDocumento93 pagineLagrisola EXAM3 stacks100% (2)
- Affine Transformations PDFDocumento5 pagineAffine Transformations PDFVermo FouqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Barycentric Coordinates - Zachary AbelDocumento10 pagineBarycentric Coordinates - Zachary AbelAltananyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ncert Solutions Class 7 Math Chapter 6 The Triangle and Its PropertiesDocumento29 pagineNcert Solutions Class 7 Math Chapter 6 The Triangle and Its PropertiesBali ManNessuna valutazione finora
- Notice on fair use of IMAS assessment materialsDocumento9 pagineNotice on fair use of IMAS assessment materialsMark Kevin AguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 3 - Chapter 15-TrigonometryDocumento15 pagineForm 3 - Chapter 15-TrigonometryIlyana Ghazali0% (1)
- Moi3D 4 DocumentationDocumento99 pagineMoi3D 4 DocumentationkoxaNessuna valutazione finora
- Summative Test No. 4 Objectives Code Percenta Ge No. of Items Item PlacementDocumento4 pagineSummative Test No. 4 Objectives Code Percenta Ge No. of Items Item PlacementCorazon GingoyonNessuna valutazione finora
- T5 SolvingTrigEquations BP 9 22 14Documento7 pagineT5 SolvingTrigEquations BP 9 22 14Yee MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12 Assignment AnswersDocumento16 pagineChapter 12 Assignment Answersapi-262088658Nessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Tricks For Engineering Drawing For ConesDocumento6 pagineEngineering Tricks For Engineering Drawing For ConestalhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Areas and Perimeters WSDocumento7 pagineAreas and Perimeters WSDiego RamírezNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 - Simple CurveDocumento66 pagineLesson 1 - Simple CurveFrancis Philippe Cruzana CariñoNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 Test Review UpdatedDocumento6 pagineUnit 4 Test Review Updatedapi-210608556Nessuna valutazione finora
- Disha Class 10 Mathematics Basic Sample Paper For Term 1Documento160 pagineDisha Class 10 Mathematics Basic Sample Paper For Term 1karthiksaro100% (4)
- Math4 q3 Module6 Week6Documento4 pagineMath4 q3 Module6 Week6ALLYSSA MAE PELONIANessuna valutazione finora
- 50 Counting Figures Practice Questions: For Bank, SSC, Railway & Government ExamsDocumento26 pagine50 Counting Figures Practice Questions: For Bank, SSC, Railway & Government ExamsDoddy FeryantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 Multiple Choice - NotesDocumento3 pagineChapter 5 Multiple Choice - Notesalex montemayoresNessuna valutazione finora
- Master Special Right TrianglesDocumento6 pagineMaster Special Right TrianglesJhuna Sasan Ajesta - BartolomeNessuna valutazione finora