Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Heart and Neck Vessels
Caricato da
Mark ElbenDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Heart and Neck Vessels
Caricato da
Mark ElbenCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Heart and neck vessels Structure and function Cardiovascular syste o Is a highly complex system that includes the
e heart and a closed system o f blood vesselsHeart is a hollow, muscular, four chambered organ located in the middle of the thoracic cavity between the lungs in the space called the mediastinum 2 type of circulation o Pulmonary circulation o Systemic circulation Great vessels large veins annd arteries leading directly to and away from the heart. Superior and inferior vena cava return blood to the right atrium. Pulmonary artery exist the right ventricle, bifurcates and carries blood to the lungs Pulmonary veins return oxygenated blood to the left atrium Aorta trasport oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the body 4 chamber or cavities o 2 upper chambers, the right and left atria o 2lower chamber, the right and left ventricles Interventricular septum separates the right and left sides of the heart. Atrioventricular(AV) valve located at the entrance into the ventricles o 2 AV Valve Tricuspid valve composed of three cups or flaps and is loceted between the right atrium and right ventricle Bicusbid (mitral) valve composed of two cups or flaps and is located between the atrium and left ventricle. Semilunar valve located at the exit of each ventricles at the beginning of the great vessels o 2 semilunar valve Pulmonic valve located at the entrance of the pulmonary artery as it exits the right ventricle Aortic valve located at the beginning of the ascending aorta as it exits the left ventricle.
Heart covering and walls Pericardium tough inextensible, loose-fitting, fibroserous sack that attaches to the great vessels and these by sorround the heart. Epicardium serous membranes covers the outer surface of the heart Myocardium thickest layer of the heart and is made up of contractable cardiac muscles cells Endocardium thin layer of endothilial tissues that forms the innermost layer of the heart.
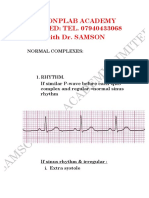
The cardiac cycle Cardiac cycle refers to the filling and emptying of the heart chambers 2phases of cardiac cycle o Diastole relaxation of the ventricles, known as filling. o Systole contracting of the ventricles, known as emtying. Cardiac output Cardiac output (CO) amout of blood pumped by the ventricles during a given period of time (usually in 1 minuet) Stroke Volume Stroke volume amount of blood pumped from the heart with each contraction. Neck vessels Assessment of the cardiovascular system includes evaluation of the neck; the carotid artery and the jugular veins. Carotid atery pulse Right and left common carotid arteries extended from the branhiocephalic trunk and the aortic arch are located in the groove between the trachea and the roght and left sternocleidomastoid muscles Carotid artery pulse centrally located arterial pulse Jugular venous pulse and pressure 2 sets of jugular veins o Internal jugular veins lie deep and medial to the sternocleidomastoid muscle o External jugular veins superficial: they lie lateral to the sternocleidomastoid muscle and above the clavicle.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessing The SkinDocumento22 pagineAssessing The Skinjasnate84Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Breasts & The AxillaeDocumento26 pagineThe Breasts & The AxillaeMark Villarmea AlforqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To The Musculoskeletal SystemDocumento39 pagineIntroduction To The Musculoskeletal SystemdesyNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Volume Deficit and Excess: Types, Causes, Signs and Nursing ManagementDocumento32 pagineFluid Volume Deficit and Excess: Types, Causes, Signs and Nursing ManagementAcohCChaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Focus Charting in Pedia WardDocumento32 pagineFocus Charting in Pedia Ward2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNessuna valutazione finora
- Providing Steam InhalationDocumento3 pagineProviding Steam InhalationMyrvic Ortiz La OrdenNessuna valutazione finora
- Postpartum Physical and Emotional Assessment GuideDocumento39 paginePostpartum Physical and Emotional Assessment GuidePerrilyn PereyNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review On Otitis Media (Karnapaka) : Ayurvedic Aspects and TreatmentDocumento4 pagineA Review On Otitis Media (Karnapaka) : Ayurvedic Aspects and TreatmentEditor_IAIMNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Old ClientDocumento33 pagineHistory of Old ClientMuhammad Aamir100% (1)
- Case Study 7Documento29 pagineCase Study 7Hanniel MontecalboNessuna valutazione finora
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocumento10 pagineRheumatic Heart DiseaseSuhas IngaleNessuna valutazione finora
- CMCA LEC 12-IntrapartumDocumento189 pagineCMCA LEC 12-IntrapartumCarl Josef C. GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 Tips On How To Make A Good SOAPIEDocumento7 pagine9 Tips On How To Make A Good SOAPIEMagbanua Airene MarielNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocumento30 pagineAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentOya Zuraini KamalNessuna valutazione finora
- CHNDocumento12 pagineCHNJhara100% (1)
- Unit 6 Hot and Cold ApplicationDocumento9 pagineUnit 6 Hot and Cold ApplicationElaine Frances IlloNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Skills ChecklistDocumento6 pagineNursing Skills Checklistapi-433883631Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tonsillitis and AdenoiditisDocumento12 pagineTonsillitis and AdenoiditisHannah Angelu CabadingNessuna valutazione finora
- MARCOS - Legal Issues of ElderlyDocumento2 pagineMARCOS - Legal Issues of ElderlyArian May MarcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Atenolol TenorminDocumento3 pagineAtenolol TenorminLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Physical AssessmentDocumento5 pagineNursing Physical AssessmentApril Louise PaluganNessuna valutazione finora
- Eming Report Precipitous LaborDocumento11 pagineEming Report Precipitous LaborJudeLaxNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Lymphoid Tissue & Immune System & Histology of Lymph Node & Thymus PDFDocumento12 pagineIntroduction To Lymphoid Tissue & Immune System & Histology of Lymph Node & Thymus PDFhassam qaziNessuna valutazione finora
- Leopold'S Maneuver: DefinitionDocumento3 pagineLeopold'S Maneuver: DefinitionJyra Mae TaganasNessuna valutazione finora
- PRINTED Cardiovascular System (Heart) HandoutsDocumento7 paginePRINTED Cardiovascular System (Heart) HandoutsKate GutierrezNessuna valutazione finora
- Health History and Interview GuidelinesDocumento2 pagineHealth History and Interview GuidelinesGeraldine GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- ElectrocardiogramDocumento3 pagineElectrocardiogramladydreamer_92Nessuna valutazione finora
- Process of ConceptionDocumento42 pagineProcess of ConceptionimnasNessuna valutazione finora
- A Drug Study On FansidarDocumento7 pagineA Drug Study On FansidarCasey EmellanoNessuna valutazione finora
- PNS Pain Management Guideline For Nursing CompetencyDocumento10 paginePNS Pain Management Guideline For Nursing Competencyvhon100% (1)
- Patient Positioning: Complete Guide For MidwivesDocumento12 paginePatient Positioning: Complete Guide For MidwivesRohlen BaguioNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Data Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plan Assessment Data Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation IndependentWyeth Earl Padar EndrianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Kawasaki DiseaseDocumento7 pagineKawasaki DiseaseRitamariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessing The IntegumentaryDocumento73 pagineAssessing The IntegumentaryHelena Meurial HilkiahNessuna valutazione finora
- Skill 12-5 Applying An External Condom CatheterDocumento6 pagineSkill 12-5 Applying An External Condom CatheterFitrio Citizen AntonyNessuna valutazione finora
- NCM 107-A Nursing Leadership & Management ConceptsDocumento241 pagineNCM 107-A Nursing Leadership & Management ConceptsMichael Anthony Ermita50% (2)
- Atrial Septal DefectDocumento4 pagineAtrial Septal DefectDimpal ChoudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Sexually Transmitted InfectionsDocumento34 pagineSexually Transmitted InfectionsMariana Creciun100% (1)
- HANDOUT Chapter 11 Promoting Fetal and Maternal HealthDocumento7 pagineHANDOUT Chapter 11 Promoting Fetal and Maternal HealthClouiseNessuna valutazione finora
- Alterations in Oxygenation 1Documento15 pagineAlterations in Oxygenation 1alejandrino_leoaugustoNessuna valutazione finora
- Determine Gestational Age Using LMP and UltrasoundDocumento18 pagineDetermine Gestational Age Using LMP and UltrasoundMomshie Felaih Binasoy Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)Documento7 pagineIdiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)Rizqka PertiwiNessuna valutazione finora
- Standardized Toolbox for Pediac Surgery: Abdominal Masses of ChildhoodDocumento30 pagineStandardized Toolbox for Pediac Surgery: Abdominal Masses of ChildhoodririlibertiNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary SystemDocumento10 pagineUrinary SystemElyka Alivan Valdez PolonioNessuna valutazione finora
- DOH Programs EEINC Newborn Screening BEmONC CEmONC NutritionDocumento46 pagineDOH Programs EEINC Newborn Screening BEmONC CEmONC NutritionKRISTINE ANGELIE PANESNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Acute PainDocumento3 pagineNCP Acute PainSian Grace AsadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Applying Pharmacology Concepts to Beta Blocker TherapyDocumento269 pagineApplying Pharmacology Concepts to Beta Blocker TherapyTrishaNessuna valutazione finora
- What is an NCPDocumento38 pagineWhat is an NCPSARAH DIANA ROSE S. MANALILI100% (1)
- Complication of PregnancyDocumento44 pagineComplication of PregnancyJharaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiovascular HealthDocumento20 pagineCardiovascular HealthChrrieNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento8 pagineDrug StudyJay-ar Batara SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Vaccination or ImmunizationDocumento4 pagineVaccination or ImmunizationPrincessNessuna valutazione finora
- Handout # 10Documento22 pagineHandout # 10Ram August100% (1)
- Compre Ho PsychDocumento114 pagineCompre Ho PsychRyan Mae Tutor GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Meal Planning For ChildrenDocumento2 pagineMeal Planning For ChildrenSheryl Anne GonzagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy Needs and Insulin's Role in Cellular Glucose UptakeDocumento4 pagineEnergy Needs and Insulin's Role in Cellular Glucose UptakeBeRnAlieNessuna valutazione finora
- AtherosclerosisDocumento9 pagineAtherosclerosisBixuan ChiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Reflective Journal 1Documento4 pagineReflective Journal 1api-365605511Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tally SheetDocumento2 pagineTally SheetMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- Future DirectionsDocumento5 pagineFuture DirectionsMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- BibliographyDocumento22 pagineBibliographyMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- Statement of The ProblemDocumento3 pagineStatement of The ProblemMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Growth & Development: Morphology, Physiology, FactorsDocumento3 paginePlant Growth & Development: Morphology, Physiology, FactorsMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- Educ 4Documento2 pagineEduc 4Mark Elben0% (1)
- Professional Education: Pre - Board ExamDocumento12 pagineProfessional Education: Pre - Board ExamMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- Tally SheetDocumento4 pagineTally SheetMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- Janille Ashlee G. Ballener: Personal InformationDocumento2 pagineJanille Ashlee G. Ballener: Personal InformationMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- Ed TechDocumento6 pagineEd TechMark Elben0% (1)
- Plant Growth & Development: Morphology, Physiology, FactorsDocumento3 paginePlant Growth & Development: Morphology, Physiology, FactorsMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Students Motivation Toward Their StudiesDocumento7 pagineNursing Students Motivation Toward Their StudiesJacqueline MarcosNessuna valutazione finora
- Cover Letter For The ParticipantDocumento2 pagineCover Letter For The ParticipantMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapters 1 and 2Documento59 pagineChapters 1 and 2Mark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- Questionnaire on Breastfeeding and Cognitive Development (38 charactersDocumento4 pagineQuestionnaire on Breastfeeding and Cognitive Development (38 charactersMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- Questionnaire on Breastfeeding and Cognitive Development (38 charactersDocumento4 pagineQuestionnaire on Breastfeeding and Cognitive Development (38 charactersMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- Home visitation form Philippines schoolDocumento1 paginaHome visitation form Philippines schoolMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- Research ParadigmDocumento1 paginaResearch ParadigmMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- HIEDocumento25 pagineHIEMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- AccountingDocumento2 pagineAccountingMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- ResearchDocumento11 pagineResearchMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- PRINCIPLES AND STRATEGIES OF TEACHINGDocumento5 paginePRINCIPLES AND STRATEGIES OF TEACHINGMark Elben100% (2)
- MATI DOCTORS SOCIOLOGY EXAMDocumento1 paginaMATI DOCTORS SOCIOLOGY EXAMMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- How Educational Technology Reinforces LearningDocumento6 pagineHow Educational Technology Reinforces LearningMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- Singing CompetitionDocumento1 paginaSinging CompetitionMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- Ca 2Documento5 pagineCa 2Mark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2 - Quantitative ResearchDocumento9 pagineLesson 2 - Quantitative ResearchMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- How Educational Technology Reinforces LearningDocumento6 pagineHow Educational Technology Reinforces LearningMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- Educ 1 - Final ExamDocumento6 pagineEduc 1 - Final ExamMark Elben100% (1)
- AccountingDocumento2 pagineAccountingMark ElbenNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Pressure and SoundDocumento45 pagineBlood Pressure and SoundRamanathan SunderNessuna valutazione finora
- Charting GuidelinesDocumento4 pagineCharting Guidelinesgrad_nurse_2015Nessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal Pakai 5 (Patofisiologi, Gejala)Documento7 pagineJurnal Pakai 5 (Patofisiologi, Gejala)Satrya DitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Housestaff Manual 2023-2024 - MeadeDocumento267 pagineHousestaff Manual 2023-2024 - MeadeMelchor Alcántara Barrera100% (2)
- AgeingDocumento14 pagineAgeingLoma Waghmare (Jadhav)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quit Smoking BrochureDocumento21 pagineQuit Smoking BrochureDumitrita NegoitaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cardiovascular System ReviewDocumento18 pagineThe Cardiovascular System ReviewDanisha Reeves100% (1)
- 12 Lead EKG Interpretation PDFDocumento251 pagine12 Lead EKG Interpretation PDFRobert So JrNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Body SIMDocumento37 pagineHuman Body SIMRhea Mae S. Sode100% (13)
- The Ultimate Krok2 Companion Comprehensive Explanations and InsiDocumento263 pagineThe Ultimate Krok2 Companion Comprehensive Explanations and InsiRamy Aso ZainalNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical AssessmentDocumento19 paginePhysical AssessmentMamerto Q. Flores IIINessuna valutazione finora
- ECG With DR Samson-1.Documento10 pagineECG With DR Samson-1.Ebuwa AmadasunNessuna valutazione finora
- TCI Regiment - Candidate Medical FormDocumento2 pagineTCI Regiment - Candidate Medical FormRichard Inoa JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- 5fcdf83bcd182 PDFDocumento258 pagine5fcdf83bcd182 PDFAnamikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 9 Worktext, Sketchnote, Face Mask Activity and Assessment L1 PRINTEDDocumento7 pagineScience 9 Worktext, Sketchnote, Face Mask Activity and Assessment L1 PRINTEDClarice Jenn MaltoNessuna valutazione finora
- Bahir Dar University College of Medicine and Other Health ScienceDocumento61 pagineBahir Dar University College of Medicine and Other Health ScienceGizachew AsimareNessuna valutazione finora
- L3 A&p#3 With AnswersDocumento7 pagineL3 A&p#3 With AnswersFergus DaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocumento30 pagineCoronary Artery Diseasesarguss14100% (1)
- Bhandas - Swami Niranjanananda SaraswatiDocumento8 pagineBhandas - Swami Niranjanananda SaraswatiagustinNessuna valutazione finora
- CH4:Biological molecules overviewDocumento34 pagineCH4:Biological molecules overviewToXicNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Paper 1Documento32 pagineBiology Paper 1Cameron DaviesNessuna valutazione finora
- ACLS Test Sinus BradycardiaDocumento1 paginaACLS Test Sinus BradycardiaFiya Sahrul0% (1)
- Heart Failure Part 1Documento3 pagineHeart Failure Part 1SaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Manual Asc 301 (O+1) - DR A S PatilDocumento122 paginePractical Manual Asc 301 (O+1) - DR A S Patil4JN20CS084 Rohit.DNessuna valutazione finora
- ACLS ECG Rhythm Strips Pretest Question Answers (Quiz) PDFDocumento11 pagineACLS ECG Rhythm Strips Pretest Question Answers (Quiz) PDF김민길100% (1)
- Blood: Anna Garcia Evidence BoardDocumento10 pagineBlood: Anna Garcia Evidence Boardapi-286516531Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dominga A. Salmone vs. Employees' Compensation Commission and Social Security SystemDocumento3 pagineDominga A. Salmone vs. Employees' Compensation Commission and Social Security SystemmarielNessuna valutazione finora
- Contemporary Diagnosis and Management of Patients With MINOCADocumento10 pagineContemporary Diagnosis and Management of Patients With MINOCAAlirio Angulo QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- Agricultural ErgonomicsDocumento7 pagineAgricultural ErgonomicsIan Jay TumulakNessuna valutazione finora