Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Organelles in Cells
Caricato da
Suntharan MuniandyDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Organelles in Cells
Caricato da
Suntharan MuniandyCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Organelles in cells
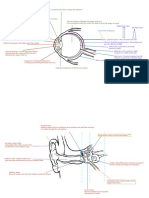
Animal Cell: 1: Nucleus: It is composed of nucleus plasma and nucleolus; It stores the genetic materials such as the Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and Ribonucleic Acid (RNA). The main function of nucleus is to store the genetic materials and to produce proteins using the genes that are present in the DNA molecules. The nucleolus structure is condensed with RNA molecules. These content are stored within the nuclear membrane. The nuclear membrane has two layers, the inner membrane and outer membrane. The nuclear membrane also contains nuclear pores that allow the Nucleotides such as DNA and RNA or other protein structures to move in and out of the nucleus.
2. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum: It is known to be rough because it contains the Ribosome on the Endoplasmic Reticulum. The main function is to produce extracellular proteins. The proteins synthesised will be stored in vesicles and sent further to the Golgi Apparatus for further modification until it is sent out of the cell by the help of the vesicles that will be produced by the Golgi Apparatus. The extra cellular proteins are synthesised in Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum with the help of Messenger RNA (mRNA) that brings the information to produce the proteins from the DNA molecule in the nucleus. 3. Golgi Apparatus: It receives proteins in vesicles from Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum and modifies the protein. It will pack the extra cellular proteins in vesicles to be sent out of the cell. 4. Ribosome: Ribosome is two kinds. One is the one attached on the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum and the other ribosomes are floating free in the cytoplasm of the cell. The main function is to produce protein in association with other RNA molecules. The free ribosomes in the cytoplasm produce intracellular proteins. These are the proteins that will be used for the use of the cell alone, for example it produces enzymes and other globular proteins for metabolic activities of the cell. It will not be sent out of the cell. 5. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum: The main function is to produce fat based molecules. Mainly it produces, fatty acids and glycerols and other sterols such as cholesterols. Adipose tissue are densed with this organelle. 6. Centrioles: It is only present in Animal cell and not in Plant cell. The main function is to produce fibres that will be spread in the cytoplasm for the movement of the vesicles and other organelles to suspend on it. During the mitosis or meiosis stage the Spindle fibres will form the spindle fibres that will be used in pulling the chromosomes/homologous chromosomes to the opposite poles of the cell. 7. Mitochondria: It is a unique organelle that contains its own genetic material to reproduce in the cell. It is composed of two layers of membrane, the inner membrane and the outer membrane. The inner membrane contains any enzymes that conducts cellular respiration. This organelle oxidises glucose using Oxygen molecule to produce energy in the form of Adenosine Tri Phosphate (ATP) and also other products such as water and carbon dioxide. It is also well known as the power house of
the cell. Muscle cells and other cells that requires energy to function will have high density of mitochondria. The neck of a Sperm cell also contains allot of this organelle so it can supply enough energy to the tail to whip and swim until it reaches fallopian tube. 8. Lysosomes: It is a small vesicles in cells that contain lytic enzymes. This organelle is responsible to protect the cells from harmful foreign bodies. The cells engulf an unwanted substance by phagocytises process, the lysosome will merge with the vesicle containing the foreign boy and digest the molecules and makes it inactive. 9. Cytoplasm: It is a gel like material that allows metabolic process to occur in the cell. All the organelles are stored here. The content within the nucleus and plasma membrane are known as protoplasm. It suspends all the organelles. 10. Cell membrane: Composed of phospholipids bilayer and severl pore proteins and carrier proteins. This structure appear like fluid because the substances moves randomly in lateral positions. The various proteins structures makes it to look like a mosaic structure. Hence, this structure is known as fluid and mosaic model structure. 11. Carbohydrate storage: Animal cell stores carbohydrate in the form of glycogen.
Plant cell: Plant cell contains all the organelles listed in the animal cell however, plant cells does not contain centrioles. 1. Cell Wall: Plant cell has this structure composed of cellulose (a type of carbohydrate storage). This structure is mainly to protect from physical injuries and fungal infections and give a distinct shape to the cell. 2. Chloroplast: An independent organelle that contains its own genetic material. It is composed of two membranes. It has a structure called grana and thylokoids. Thylakoids are stacks of chloroplasts structure. It absorbs sunlight and conducts photolysis process. Grana conducts the second part of photosynthesis process that is the dark reaction. 3. Vacuole: Is the largest organelle in a plant cell. It stores the cell sap ( Water and mineral salts). If the water moves in to the cell via osmosis, the vacuole will become bigger and this will cause the cytoplasm and other organelles pushed towards the cell membrane and cell wall. This action will cause the cells pressure to increase. This pressure is called the turger pressure. 4. Carbohydrate storage: Plant cell stores carbohydrate in the form of cellulose or starch.
Difference Between plant cell and an animal cell
Plant cell has cell walls that are composed of cellulose and lignin structure. It is a structure that is made of carbohydrate. This structure protects the cell and gives the cell a distinct shape. The animal cell has no cell wall and it does not have a fixed shaped like plant cells.
Plant cell has a Chloroplast that contains chlorophyll molecule that conducts photosynthesis process. This process is also known as photoautotroph that makes its own food. Animal cell does not have this structure and animal cells are holozoic organism whereby they ingest food in solid or liquid form. Animal cell has an organelle called the Centriole. It exists in pair and are perpendicular to one another. Centriole makes the spindle fibres during the cell division process to pull the chromosomes/ chromatids to opposite poles of the cell. Plant cell does not have centrioles. It produces spindle fibres by itself without centrioles. Plant cells stores carbohydrates in the form of starch and cellulose. Animal cell stores carbohydrate in the form of glycogen. Plant cell has a large vacuole that contains sap cell. Under hypotonic solution, the water moves in to the cell via osmosis and causes the vacuole to swell. This will push the cytoplasm and other organelles towards the cell wall. Causing the cell to create a pressure known as the turgor pressure. Animal cell has small vacuoles that are used to transport substances or protein molecules.
Multicellular and unicellular
Cell is the basic unit of life. Few cell joins together to make a type of tissue. The combination of few types of tissue will produce and organ that conducts a specific function. A few types of organs combines together to conduct a complex function is called a system. This is how a multicellular organism is composed. There are many kinds of cell that produces different kinds of tissue, organs and system. Take an example of Blood circulatory system. It is composed of few organs such as the heart, vessels, lungs and etc. The tissues are many kinds for instance, the blood tissue, epithelial tissue, cardiac muscle tissue and etc. The cells involved in blood tissue are Platelets, Red Blood Cells and White Blood Cells. Unicellular organisms are made up of only one cell. There are many kinds of unicellular cells such as the amoeba
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Animal Cell DefinitionDocumento7 pagineAnimal Cell DefinitionJoanne AlindayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell and TissueDocumento10 pagineCell and TissueCarl SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5 Cells: 1. Unicellular: Organisms Made Up of Only One Cell Are Known As UnicellularDocumento6 pagineUnit 5 Cells: 1. Unicellular: Organisms Made Up of Only One Cell Are Known As Unicellularpraneeth satishNessuna valutazione finora
- CellDocumento7 pagineCellnik29569Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Cell StructureDocumento2 pagineBiology Cell StructureCut Rizka RahmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Life Processes and Cells: Chapter 1:-Longman GCSE BiologyDocumento16 pagineLife Processes and Cells: Chapter 1:-Longman GCSE BiologynkllaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksDa EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Earth and Life Science 11Documento23 pagineEarth and Life Science 11Red LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Physiology-1Documento32 pagineCell Physiology-1yoga karsendaNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth Life Science Module 5Documento15 pagineEarth Life Science Module 5Rosalyn Pagatpatan BarolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Cell Diagram and Sickle CellDocumento11 pagineHuman Cell Diagram and Sickle Cellaryaa2020Nessuna valutazione finora
- CellsDocumento2 pagineCellsJohn TacordaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cells - The Building Blocks of LifeDocumento2 pagineCells - The Building Blocks of LifeMuhammad QasimNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal CellDocumento7 pagineAnimal CellLezircYojDapmalNessuna valutazione finora
- Sir Syed University of Engineering and Technology: Assignment No 1Documento10 pagineSir Syed University of Engineering and Technology: Assignment No 1Ali InamNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio - UNIT 1 - Organisms and Life ProcessesDocumento18 pagineBio - UNIT 1 - Organisms and Life ProcessesMuhammad Mahi Nurul IslamNessuna valutazione finora
- THE CELL I: Cytoplasm and Cytoplasmic Components: by Dr. Taiwo-OlaDocumento16 pagineTHE CELL I: Cytoplasm and Cytoplasmic Components: by Dr. Taiwo-OlaJoshua DorisNessuna valutazione finora
- Functions of A CellDocumento4 pagineFunctions of A CellyayayanizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatDocumento7 pagineCell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatSpongie BobNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Function and The ComponentsDocumento5 pagineCell Function and The ComponentssalisongloNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Notes: Plant and Animal CellDocumento4 pagineScience Notes: Plant and Animal CellRosalinda LappayNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 1Documento5 pagineBiology 1Zeynep AkıNessuna valutazione finora
- NotesDocumento37 pagineNotesDaideepya SaxenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes Science CellsDocumento12 pagineNotes Science CellsHina SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.1 Cell As A Unit of LifeDocumento9 pagine4.1 Cell As A Unit of Lifehola adiosNessuna valutazione finora
- Nucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticDocumento5 pagineNucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticHustler ZaydeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Biology PresentationDocumento14 pagineCell Biology Presentationahmadihamed1459Nessuna valutazione finora
- Plant CellDocumento4 paginePlant CellKenneth FungoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 BotanyDocumento6 pagineChapter 2 BotanyLebanan Aprille MarieNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiDocumento8 pagineAnimal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiKolade YousuffNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cell: Types of CellsDocumento4 pagineThe Cell: Types of CellsAllen MurilloNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cell: Types of CellsDocumento8 pagineThe Cell: Types of CellsushapvermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagram of Plant CellDocumento4 pagineDiagram of Plant CellekongNessuna valutazione finora
- Sci.-7 Lesson 5Documento13 pagineSci.-7 Lesson 5ROTER M. RABINONessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 8 Chapter 2 Cells The Building Block of LifeDocumento21 pagineGrade 8 Chapter 2 Cells The Building Block of LifeMunmun AfnanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Fundamental Unit of Life - CW Copy Notes Class 9 PDFDocumento5 pagineThe Fundamental Unit of Life - CW Copy Notes Class 9 PDFmanoharrish3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life: What Are Living Organisms Made Up Of?Documento5 pagineChapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life: What Are Living Organisms Made Up Of?HeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2 CytoplasmmDocumento46 pagineLecture 2 Cytoplasmmdiyarberwari15Nessuna valutazione finora
- Intro To Cells 2017Documento38 pagineIntro To Cells 2017YHTAK1792Nessuna valutazione finora
- Week 7. Reading Materials - Cell Structure and Function 2021Documento4 pagineWeek 7. Reading Materials - Cell Structure and Function 2021yui kirigayayuukiNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal and Plant CellsDocumento3 pagineAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocumento6 pagineCell Structure and FunctionYeshua Dan BigasaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gen Zoology ReviewerDocumento19 pagineGen Zoology ReviewerDarey ApostolNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 - Cell Structure and Function - NotesDocumento8 pagineUnit 2 - Cell Structure and Function - Notesronel.jnmsNessuna valutazione finora
- CellDocumento7 pagineCellPrashant PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life: Cell Life Cell Division Multicellular Organisms Egg Energy Flow Metabolism DNADocumento8 pagineCell: The Fundamental Unit of Life: Cell Life Cell Division Multicellular Organisms Egg Energy Flow Metabolism DNAQadirNessuna valutazione finora
- Acad Fall08 ThecellDocumento13 pagineAcad Fall08 Thecellhassanmusahassan81Nessuna valutazione finora
- Handouts For Lesson 1-3 General BiologyDocumento9 pagineHandouts For Lesson 1-3 General BiologyGenesse MarasiganNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell (Biology) : Structures Outside The Cell WallDocumento5 pagineCell (Biology) : Structures Outside The Cell WallAsad MasoodNessuna valutazione finora
- CELLSDocumento6 pagineCELLSFenny May SebonNessuna valutazione finora
- Cells - Structure and Function: Important Events in The Discovery of CellsDocumento24 pagineCells - Structure and Function: Important Events in The Discovery of CellsJaspher Joshua CallangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 1st DiscussionDocumento52 pagineBiology 1st DiscussionBea BulasaNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal and Plant CellsDocumento14 pagineAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoNessuna valutazione finora
- CellsDocumento26 pagineCellsNairita LetipoNessuna valutazione finora
- BIO ReviewerDocumento14 pagineBIO ReviewerRenjyl Gay DeguinionNessuna valutazione finora
- NucleusDocumento10 pagineNucleusjhariesargente05Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Structures and Their Functions SLADocumento19 pagineCell Structures and Their Functions SLAMaricar Baria100% (2)
- Cells and Organelles - 1Documento6 pagineCells and Organelles - 1Izabayo philippeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell OrganellesDocumento6 pagineCell OrganellesMark Kenneth CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Body Coordination Part 2Documento22 pagineBody Coordination Part 2Suntharan MuniandyNessuna valutazione finora
- Coordination and Response. PT3 2022Documento3 pagineCoordination and Response. PT3 2022Suntharan MuniandyNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Upsr Sebenar 2002Documento12 pagineMaths Upsr Sebenar 2002Anonymous xGCiF6oNessuna valutazione finora
- 2019 Sains PT3Documento25 pagine2019 Sains PT3Suntharan MuniandyNessuna valutazione finora
- Pt3 Science Seminar ModuleDocumento28 paginePt3 Science Seminar ModuleSuntharan Muniandy100% (5)
- Science Chapter 7 PMRDocumento10 pagineScience Chapter 7 PMRSuntharan MuniandyNessuna valutazione finora
- ArtistDocumento4 pagineArtistSuntharan MuniandyNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Math Question Paper 4 October/November 2007Documento12 pagineIGCSE Math Question Paper 4 October/November 2007Mariam A.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Favourite 3rd Party Transfer: SuccessfulDocumento1 paginaFavourite 3rd Party Transfer: SuccessfulSuntharan MuniandyNessuna valutazione finora
- Examiner Tips For IGCSE BiologyDocumento12 pagineExaminer Tips For IGCSE BiologySunSun Hemnilrat42% (12)
- Science F3 RespirationDocumento3 pagineScience F3 RespirationSuntharan MuniandyNessuna valutazione finora
- Carrier Guidance BrochureDocumento1 paginaCarrier Guidance BrochureSuntharan MuniandyNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 7 Respiration StudentDocumento25 pagineCH 7 Respiration StudentSuntharan MuniandyNessuna valutazione finora
- PMR Science Form 3 TipsDocumento41 paginePMR Science Form 3 TipsSuntharan MuniandyNessuna valutazione finora
- Biotips 2013Documento3 pagineBiotips 2013Suntharan MuniandyNessuna valutazione finora
- Science F3 RespirationDocumento3 pagineScience F3 RespirationSuntharan MuniandyNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar Pendidkan SPM Science: by MR Suntharan MuniandyDocumento17 pagineSeminar Pendidkan SPM Science: by MR Suntharan MuniandySuntharan MuniandyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - ExcretionDocumento3 pagineChapter 3 - ExcretionSuntharan MuniandyNessuna valutazione finora
- 07 Bibliography FormatDocumento14 pagine07 Bibliography FormatArjun KafleNessuna valutazione finora
- CRT Exam Review Guide Chapter 8Documento10 pagineCRT Exam Review Guide Chapter 8Dharlyn MungcalNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Health Care 4th Edition Mitchell Solutions Manual DownloadDocumento5 pagineIntroduction To Health Care 4th Edition Mitchell Solutions Manual DownloadMark Prindle100% (20)
- Gout CPG Manuscript - PJIM 072808Documento16 pagineGout CPG Manuscript - PJIM 072808Francis CastellNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Assessment Feu NRMFDocumento16 paginePhysical Assessment Feu NRMFJhen Bitco FidelNessuna valutazione finora
- The Real TabataDocumento11 pagineThe Real TabataJason TiongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- U.S. Army Survival Manual FM 21-76 (June 1992)Documento572 pagineU.S. Army Survival Manual FM 21-76 (June 1992)explorer_ebook100% (1)
- Actifluor Adamts13 Activity: Product No. 812RUODocumento4 pagineActifluor Adamts13 Activity: Product No. 812RUOSukma EffendyNessuna valutazione finora
- The Peripheral Nervous System Branches Throughout The Body Worksheet1Documento2 pagineThe Peripheral Nervous System Branches Throughout The Body Worksheet1Shekeyva SmalleyNessuna valutazione finora
- CAD in Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento22 pagineCAD in Nephrotic SyndromeSudhesna MohapatraNessuna valutazione finora
- Erin Lommen - Adrenal Fatigue or Sagging SeratoninDocumento18 pagineErin Lommen - Adrenal Fatigue or Sagging Seratoningreencrystal81Nessuna valutazione finora
- Manual Therapy For The Thorax - A Biomechanical Approach - D. Lee (DOPC, 1994) WW PDFDocumento156 pagineManual Therapy For The Thorax - A Biomechanical Approach - D. Lee (DOPC, 1994) WW PDFEliMihaela100% (2)
- DISACCHARIDES Lecture For 1st Year MBBS Delivered by Dr. Waseem On 01 March 2010Documento29 pagineDISACCHARIDES Lecture For 1st Year MBBS Delivered by Dr. Waseem On 01 March 2010IMDCBiochemNessuna valutazione finora
- ADR Common Drug - Induced Organ DisordersDocumento45 pagineADR Common Drug - Induced Organ Disorders0009439Nessuna valutazione finora
- Neurexan Patient Flyer ANG May 2010 7311Documento2 pagineNeurexan Patient Flyer ANG May 2010 7311Waqar GhoryNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac CatheterizationDocumento7 pagineCardiac CatheterizationkereklovagNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Biology Notes Ch06 Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocumento6 pagine12 Biology Notes Ch06 Molecular Basis of InheritanceInderpal SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Dijabetička KetoacidozaDocumento19 pagineDijabetička KetoacidozaToNijeToniNessuna valutazione finora
- NCLEX QuestionsDocumento5 pagineNCLEX QuestionsMeganNessuna valutazione finora
- Anemia and AnesthesiaDocumento11 pagineAnemia and AnesthesialhalamNessuna valutazione finora
- Patho OTDocumento23 paginePatho OTBea Y. Bas-ongNessuna valutazione finora
- Women's Health MagazineDocumento140 pagineWomen's Health MagazineAgiimaa0% (1)
- Drug Study NubainDocumento2 pagineDrug Study NubainampalNessuna valutazione finora
- Melatonin Disturbances in Anorexia Nervosa and Bulimia NervosaDocumento9 pagineMelatonin Disturbances in Anorexia Nervosa and Bulimia NervosaImelia AnggraeniNessuna valutazione finora
- Xi - Bio Zoo Question PaperDocumento9 pagineXi - Bio Zoo Question PaperVeeramaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Cerebrovascular Disease (Emphasis On CVA)Documento29 pagineCerebrovascular Disease (Emphasis On CVA)OlynsieMorrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Best HST WorkoutDocumento29 pagineBest HST WorkoutVova ShushNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Ways To Wake Up Early - WikihowDocumento8 pagine4 Ways To Wake Up Early - WikihowkbkkrNessuna valutazione finora
- Endothelial Dysfunction and Vascular Disease - A 30th Anniversary UpdateDocumento75 pagineEndothelial Dysfunction and Vascular Disease - A 30th Anniversary UpdateAna Clara RodriguesNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller 8Documento2 pagineTaller 8monchito83hotmailesNessuna valutazione finora