Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Interpretation of Cardiac Enzymes:: Test: SGOT
Caricato da
Mohammed AbdouDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Interpretation of Cardiac Enzymes:: Test: SGOT
Caricato da
Mohammed AbdouCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Interpretation of Cardiac Enzymes:
Certain enzymes (CPK, LDH, and SGOT) are released from the heart muscle cells hen it is in!ured ("heart attac#")$ These enzymes are normally found in the %lood at lo le&els$ The a%normal ele&ation of these enzymes in the %lood stream can occasionally %e the only indicator that a heart attac# (myocardial infarction) has occurred$ 'or heart attac#s, measurin( the le&els of cardiac enzymes in the %lood is a common test for the dia(nosis of a heart attac# and the amount the dama(e done to the heart) the medical field considers the measurement of cardiac enzyme le&els in the %lood to %e a relia%le test for a heart attac#$ Ho e&er, it is im*ortant to #no that cardiac enzymes lea# slo ly into the %lood, and unusually hi(h le&els of cardiac enzymes in the %lood may not a**ear until si+ or more hours after the onset of a heart attac#$ Thus, if a *erson has chest *ain %ut has normal le&els of cardiac enzymes in the %lood, a heart attac# cannot %e ruled out$ ,n that instance, re*eated cardiac enzymes tests are normally conducted to confirm dia(nosis of a heart attac#$ 'ollo in( are the main cardiac enzymes.$ SGOT /$ LDH (also called LD) 0$ CPK (also called CK) 1$ Tro*onin
Test: SGOT
Serum Glutamic O+aloacetic Transaminase, called- 2ST, (2s*artate 2minotransferase) 2 %lood chemistry test for the le&el of SGOT in %lood (is released ith tissue necrosis)$ 3ormal 4alues- 5617 89ml ('ran#el) 160: ,89L) or .:6:7 (Karmen) 89ml 89L at 07 de(rees C) or ;600 (S, units) at 0< de(rees C$
Clinical Implications:
This enzyme sho s an ele&ation ;6./ hours after infarction$ Pea# le&els are reached /16 1; hours after the =,$ This enzyme is not *articularly indicati&e of an =,$ Other conditions can also cause a rise in the le&els$ Hi(h le&els of SGOT may %e o%tained ith
trauma to the s#eletal muscles, in li&er disease, *ancreatitis and others$ SGOT is found inheart muscle, li&er, some also in s#eletal muscle, #idneys and the *ancreas$ Demerol and mor*hine may ele&ate the le&els tem*orarily$ This enzyme then is used ith other enzyme results to more definitely dia(nose the =,$ 2ST le&els ele&ate in :6.7 hours follo in( acute =,$ They *ea# in /1 to 1; hours$
Test: LDH, Lactic Dehydrogenase:
2n intracellular enzyme *resent in nearly all meta%olizin( cells in the %ody$ The hi(hest concentration of enzyme is located in the heart, s#eletal muscle, li&er, #idney, %rain, and erythrocytes$ There are 5 isoenzymes of LDH$ This is a %lood chemistry test to measure the amount of enzyme in the %lood$ LDH catalyzes the re&ersi%le con&ersion of muscle lactic acid into *yru&ic acid, an essential ste* in the meta%olic *rocess that ultimately *roduces cellular ener(y$ >ecause LDH is *resent in almost all %ody tissues, cellular dama(e increases total serum LDH, limitin( the dia(nostic usefulness of this test$ ,soenzymes LD. and LD/ a**ear *rimarily in the heart, red %lood cells and #idneys$ LD0 is *rimarily in the lun(s$ LD1 and LD5 are located in the li&er, s#in, and the s#eletal muscles$
Normal Values:
Total LDH- .576157 89ml (?ro%le s#i6LaDue method), :76./7 89ml (?ac#er method) <76/77 ,89L66results are different accordin( to method used$ 3e %orn- 0776.577,89L Child- 576.57 ,89L
LD.666.<$5@ to /;$0@ of total LD/66607$1@ to 0:$1@ of total LD0666.A$/@ to /1$;@ of total LD16666A$:@ to .5$:@ of total
>ecause many common diseases increase total LDH (LD) le&els, isoenzyme electro*horesis is usually necessary for dia(nosis$ ,n some disorders, total LDH may %e ithin normal limits, %ut a%normal *ro*ortions of each enzyme indicate s*ecific or(an tissue dama(e$ 'or e+am*le, in acute =,, the LD. and LD/ isoenzyme ratio is ty*ically (reater than . ithin ./ to 1; hours after onset of sym*toms (#no n as fli**ed LD)$ =idzone fractions (LD/, LD0, and LD1) can %e increased in (ranulocytic leu#emia, lym*homas, and *latelet disorders$
Clinical Implications:
The total LDH may %e influenced %y other %ody tissues, other than the heart$ Therefore, the LDH is s*lit into its fractions, isoenzymes, in order to isolate the *articular one hich is located almost solely in the myocardium$ This isoenzyme is the num%er . isoenzyme$ 2lthou(h not fool*roof, if this isoenzyme is ele&ated, it is stron(ly indicati&e of an =,$ LDH ele&ates in /161; hours and *ea#s in 1;6</ hours after the e*isode$ 3arcotic dru(s and ,= in!ections can ele&ate serum LDH le&els$ Hemolysis of the %lood can cause an ele&ated LDH %ecause LDH is *lentiful in the erythrocytes$ 2(ain, ith this enzyme, it is im*ortant to (ather a detailed *atient history$ 'ind out if there has %een in!ury to any systems hich mi(ht ele&ate the LDH le&els$ These includetrauma, cancers, leu#emia, he*atitis, shoc#, heat stro#e, sic#le cell disease$ Test: C !, Creatine hospho"inase #C!$ Creatine !inase This is a %lood chemistry test to measure the amount of enzyme in the %lood$ The CPK enzyme is found in hi(h concentration in heart and s#eletal muscle) lo concentration is %rain tissue$ CPK is an enzyme that catalyzes the creatine6creatinine meta%olic *ath ay in muscle cells and %rain tissue$ >ecause of its intimate role in ener(y *roduction, CPK reflects normal tissue cata%olism) increased serum le&els indicate trauma to cells$
Normal Values:
male- 5605 B(9ml (mc(9ml)) female- 56/5 B(9ml ne %orn- .76077 ,89L
Clinical Implications:
Serum CPK9CK ill %e ele&ated in s#eletal muscle disease, in acute =,, in cere%ral &ascular disease, &i(orous e+ercise, ,= in!ections, electrolyte im%alance, and hy*o#alemia$ CPK has three isoenzymes as *resented earlier$ 'ractionation and measurement of these three distinct CPK isoenzymes ha&e re*laced the use of total CK (or CPK) le&els to accurately localize the site of increased tissue destruction$ CK6>> is most often found in %rain tissue$ CK6== and CK6=> are found *rimarily in s#eletal and heart muscle$ ,n addition, su%units of CK6=> and CK6==, called isoforms or isoenzymes, can %e assayed to increase the testCs sensiti&ity$ These isoenzymes are.$ CK6>> (CK.) ,soenzyme D. /$ CK6=> (CK/) ,soenzyme D/ 0$ CK6== (CK0) ,soenzyme D0
?hen the isoenzyme CPK6=> is ele&ated, (reater than 5@, it could stron(ly indicate dama(e to the myocardial cells$ The CPK6=> ele&ates ithin 16: hours after an acute =,) *ea#s in .;6/1 hours) it then returns to normal ithin 061 days$ ,t is %est to a&oid ,= in!ections, e&en thou(h the in!ections ill usually not cause ele&ation of the CPK6=>$ This is %ecause other enzymes can %e affected %y the in!ections, and other enzyme studies are *erformed in con!unction ith the CPK studies$ Trauma and sur(ery ill ele&ate the CPK le&els$
Test: Troponin: The Tro*onin test is considered the most accurate cardiac enzyme
test in the dia(nosis of a heart attac#$ ,t is the most sensiti&e and s*ecific test for myocardial dama(e$ >ecause it has increased s*ecificity com*ared ith CK6=>, tro*onin is a su*erior mar#er for myocardial in!ury$
Clinical implications:
Tro*onin is the first ele&ated su%stance than any other enzymes$ ,t is released durin( =, from the cytosolic *ool of the myocytes$ ,ts su%seEuent release is *rolon(ed ith de(radation of actin and myosin filaments$ Differential dia(nosis of tro*onin ele&ation includes acute infarction, se&ere *ulmonary em%olism causin( acute ri(ht heart o&erload, heart failure, and myocarditis$ Tro*onins can also calculate infarct size %ut the *ea# must %e measured in the 0rd day$ ,t released in /F1 hours and *ersists for u* to < days$ Ho e&er, one should note that cardiac enzymes lea# slo ly into the %lood, and unusually hi(h le&els of cardiac enzymes in the %lood may not a**ear until si+ or more hours after the onset of a heart attac#$ Thus, if a *erson has chest *ain %ut has normal le&els of cardiac enzymes in the %lood, a heart attac# cannot %e ruled out$ ,n that instance, re*eated cardiac enzymes tests are normally conducted to confirm dia(nosis of a heart attac#$
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Interpretation of Cardiac Enzymes:: Test: SGOTDocumento4 pagineInterpretation of Cardiac Enzymes:: Test: SGOTFrances FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzyme, LDH, Etc.Documento3 pagineEnzyme, LDH, Etc.Jessica MarianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzyme TestsDocumento12 pagineEnzyme TestsgireeshsachinNessuna valutazione finora
- Brief Notes On Laboratory Diagnosis PDFDocumento19 pagineBrief Notes On Laboratory Diagnosis PDFAngelica JanoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenal Function: Adrenocorticotropic HormoneDocumento11 pagineAdrenal Function: Adrenocorticotropic HormonehansenNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Enzyme StudiesDocumento4 pagineCardiac Enzyme StudiesDara VinsonNessuna valutazione finora
- The Endocrine SystemDocumento13 pagineThe Endocrine SystemThenmozhi SivajiNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenergics and AntiadrenergicsDocumento5 pagineAdrenergics and Antiadrenergicsabe8284Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 Systemic Response To InjeryDocumento46 pagineChapter 1 Systemic Response To Injerysabina_grapiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Reference Values Lab Tests Cardiac Profile Tests 3 PgsDocumento3 pagineReference Values Lab Tests Cardiac Profile Tests 3 PgsJim Varghese100% (1)
- Biochemistry For Medics WWW - Namrata.coDocumento48 pagineBiochemistry For Medics WWW - Namrata.coOsteo FerdianNessuna valutazione finora
- CFTsDocumento92 pagineCFTsSreya SanilNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Enzymes Practical Handout For 2nd Year MBBSDocumento7 pagineIntroduction To Enzymes Practical Handout For 2nd Year MBBSIMDCBiochemNessuna valutazione finora
- Penyakit Jantung Didapat: Idrus AlwiDocumento110 paginePenyakit Jantung Didapat: Idrus AlwiraannttiiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Enzymes Practical Handout For 2nd Year MBBSDocumento7 pagineCardiac Enzymes Practical Handout For 2nd Year MBBSIMDCBiochemNessuna valutazione finora
- The Adrenal GlandDocumento13 pagineThe Adrenal GlandardevanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenal Gland: Biochemistry by ZonesDocumento12 pagineAdrenal Gland: Biochemistry by ZonesWael AlkhatibNessuna valutazione finora
- FRCPath Mock 2014 Model AnswersDocumento29 pagineFRCPath Mock 2014 Model Answersmonday125Nessuna valutazione finora
- CUSHINGSDocumento205 pagineCUSHINGSDaroo D.TNessuna valutazione finora
- Class-14 - Plasma Lipoproteins - EnzymesDocumento39 pagineClass-14 - Plasma Lipoproteins - EnzymesAyi FurqonNessuna valutazione finora
- Serum Markers For The Diagnosis of Myocardial InfarctionDocumento4 pagineSerum Markers For The Diagnosis of Myocardial InfarctionEliza Paula BacudNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Test Result MeaningDocumento35 pagineLab Test Result MeaningSenthil SubramanianNessuna valutazione finora
- File NameDocumento7 pagineFile NameHabib AbdurhmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenal GlandsDocumento19 pagineAdrenal GlandsWinnie Salazar AriolaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Clinical Enzymology 2Documento48 pagine6 Clinical Enzymology 2sandyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 15 - Adrenal Gland BNS KUMDocumento17 pagineLecture 15 - Adrenal Gland BNS KUMabdulsaboor30Nessuna valutazione finora
- Enzim CardiovascularDocumento64 pagineEnzim Cardiovascularandre kesumaNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical EnzymologyDocumento23 pagineClinical EnzymologyOsei TonyNessuna valutazione finora
- AdrenalDocumento5 pagineAdrenalJC MolNessuna valutazione finora
- Decoding Blood Tests - GoodRx GuideDocumento7 pagineDecoding Blood Tests - GoodRx Guidegatsby.milesNessuna valutazione finora
- Welcome To The Clinical LaboratoryDocumento36 pagineWelcome To The Clinical LaboratoryAndi NamirahNessuna valutazione finora
- AddisonDocumento6 pagineAddisonsilent2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Endocrine SystemDocumento16 pagineThe Endocrine Systemanon_63895130Nessuna valutazione finora
- First Page PDFDocumento1 paginaFirst Page PDFWeverson LinharesNessuna valutazione finora
- Plasma EnzymesDocumento13 paginePlasma EnzymesBobskinnyNessuna valutazione finora
- Resubmission of My SD805 ECADocumento38 pagineResubmission of My SD805 ECAJanine NoVax GillespieNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical EnzymologyDocumento40 pagineClinical Enzymologyxyz uNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical EnzymologyDocumento38 pagineClinical EnzymologyLloyd Jay LinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9 Hospital Pharmacy Notes Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Documento5 pagineChapter 9 Hospital Pharmacy Notes Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Mobeen AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Chemistry EnzymeDocumento8 pagineClinical Chemistry EnzymeFrances del RosarioNessuna valutazione finora
- A Laboratory Diagnostic Approach To Hepatobiliary Disease in Small AnimalsDocumento17 pagineA Laboratory Diagnostic Approach To Hepatobiliary Disease in Small Animalsl.fernandagonzalez97Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac BiomarkersDocumento35 pagineCardiac BiomarkersArya Khan Arya KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 33 - Biomarkers: Learning ObjectivesDocumento37 pagineLecture 33 - Biomarkers: Learning ObjectivesAustin KellyNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinically Significant EnzymesDocumento4 pagineClinically Significant EnzymesMaam ShaNessuna valutazione finora
- Corticosteroid PDFDocumento21 pagineCorticosteroid PDFAida YuliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cortisol: Alternative Names For Cortisol What Is Cortisol?Documento7 pagineCortisol: Alternative Names For Cortisol What Is Cortisol?Ifeoluwa AdeniyiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mercy's Enzyme Markers of Diagnostic ImportanceDocumento20 pagineMercy's Enzyme Markers of Diagnostic ImportanceAnietieNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood TestDocumento6 pagineBlood TestMaharani Indri100% (1)
- Adrenal GlandDocumento9 pagineAdrenal GlandArzooGargNessuna valutazione finora
- BCH 202 NursingDocumento41 pagineBCH 202 NursingbeulaholuwabunkunfunmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Test: For The Novel by Jonathan Kellerman, SeeDocumento7 pagineBlood Test: For The Novel by Jonathan Kellerman, SeeMaharani IndriNessuna valutazione finora
- Assign NewDocumento9 pagineAssign Newsyedamasoomazahra9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Applications of EnzymesDocumento4 pagineApplications of Enzymesshekinah656Nessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Seminar On PheochromocytomaDocumento9 pagineClinical Seminar On PheochromocytomaParvathy JoshyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 40 Neuro-SurgeryDocumento43 pagineChapter 40 Neuro-SurgeryAnastasia FebriantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Enzyme Analysis: Anika Dahal Lecturer MmihsDocumento40 pagineCardiac Enzyme Analysis: Anika Dahal Lecturer Mmihsanika dahalNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal DispanDocumento19 pagineJurnal Dispanrahmani kadarningsihNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods For The Determination in Serum and Urine: Dr. Essam H. AljiffriDocumento20 pagineMethods For The Determination in Serum and Urine: Dr. Essam H. AljiffriWael AlkhiaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Advances in MVDocumento186 pagineAdvances in MVMohammed AbdouNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Bacillus Calmette-Guérin Lymphadenitis:, Yw K, CW LDocumento10 pagineManagement of Bacillus Calmette-Guérin Lymphadenitis:, Yw K, CW LMohammed AbdouNessuna valutazione finora
- Antimicrobial 2013Documento82 pagineAntimicrobial 2013Mohammed AbdouNessuna valutazione finora
- 2011 ACLS Pretest Annotated Answer KeyDocumento19 pagine2011 ACLS Pretest Annotated Answer KeyMohammed Abdou92% (13)
- Performance Task On Nucleic AcidsDocumento3 paginePerformance Task On Nucleic AcidsPrincess Mejia De VeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3 Eyesight Student WorksheetDocumento10 pagineLesson 3 Eyesight Student WorksheetcupcakekidNessuna valutazione finora
- Ornamental Breeding ConceptsDocumento83 pagineOrnamental Breeding ConceptsjoshigautaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocumento5 pagineSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsBobbyNessuna valutazione finora
- Online Test: Nurture X DLP-2012Documento15 pagineOnline Test: Nurture X DLP-2012sohan12345Nessuna valutazione finora
- Carbohydrate Digestion and AbsorptionDocumento31 pagineCarbohydrate Digestion and Absorptionlovelots1234100% (4)
- PPPVD Fecal Scoring Chart UPDATE EN FINALDocumento2 paginePPPVD Fecal Scoring Chart UPDATE EN FINALJon DoughballNessuna valutazione finora
- Top 50 Biotech CompaniesDocumento3 pagineTop 50 Biotech CompaniesVidya SagarNessuna valutazione finora
- PhetDocumento4 paginePhetCarlos Matute NeavesNessuna valutazione finora
- Westcotts Plant Disease HandbookDocumento185 pagineWestcotts Plant Disease Handbooktira flechasNessuna valutazione finora
- Extra 23-2-23 InsertDocumento12 pagineExtra 23-2-23 Insertfaridaahmed2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 57 Introduction To The Urinary SystemDocumento24 pagineChapter 57 Introduction To The Urinary SystemtikkimarshallNessuna valutazione finora
- Compendial Methods of Dissolution and Biopharmaceutic Considerations in Drug Product DesignDocumento31 pagineCompendial Methods of Dissolution and Biopharmaceutic Considerations in Drug Product DesignGiovanne BuendiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Harris Solutions OddDocumento228 pagineHarris Solutions OddAndrea AquinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Current Concepts On How To Optimise Skin Needling 2020 2Documento6 pagineCurrent Concepts On How To Optimise Skin Needling 2020 2maat1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Neuro Informo1Documento8 pagineNeuro Informo1Dr. Kaushal Kishor SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- GDR - Poc Update (01.07.21)Documento2 pagineGDR - Poc Update (01.07.21)Dr ThietNessuna valutazione finora
- Filaments in Bioprocesses: Rainer Krull Thomas Bley EditorsDocumento370 pagineFilaments in Bioprocesses: Rainer Krull Thomas Bley EditorsMel Esparza0% (1)
- Science Form 1 KSSM Chapter 2Documento3 pagineScience Form 1 KSSM Chapter 2Nisa MuhdNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 14 Lifespan PsychologyDocumento4 pagineModule 14 Lifespan PsychologybobNessuna valutazione finora
- H560 Haematology AnalyserDocumento200 pagineH560 Haematology Analyserfuwjigfuwjig_4935018Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mini FixatorsDocumento4 pagineMini FixatorsRajNessuna valutazione finora
- Read Up 2 - Word ListsDocumento43 pagineRead Up 2 - Word ListsHANANessuna valutazione finora
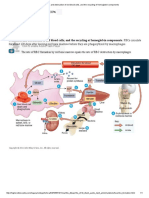
- Formation and Destruction of Red Blood Cells, and The Recycling of Hemoglobin ComponentsDocumento1 paginaFormation and Destruction of Red Blood Cells, and The Recycling of Hemoglobin ComponentsK-Alert R-Man100% (2)
- Anatomy For Beginners - Movement WorksheetDocumento4 pagineAnatomy For Beginners - Movement WorksheetJames DaurayNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes Blood Glucose Meter & Strip Product Reference - FOR INTERNAL USE ONLYDocumento2 pagineDiabetes Blood Glucose Meter & Strip Product Reference - FOR INTERNAL USE ONLYLorie FadolNessuna valutazione finora
- S. 3 Biology Paper 1Documento9 pagineS. 3 Biology Paper 1Nsaiga RonaldNessuna valutazione finora
- Spesifikasi Produk - Yumizen H500Documento1 paginaSpesifikasi Produk - Yumizen H500Dexa Arfindo PratamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Block Diagram: P552LJ Repair GuideDocumento5 pagineBlock Diagram: P552LJ Repair Guidepesce provaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anexo Norma HolandesaDocumento13 pagineAnexo Norma HolandesaThePomboNessuna valutazione finora
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceDa EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (517)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseDa EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (52)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDa EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerDa EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (393)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincDa EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (137)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesDa EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (397)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessDa Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (33)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeDa EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeNessuna valutazione finora
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsDa EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (6)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperDa EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (16)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorDa EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNessuna valutazione finora
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomDa EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (216)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceDa EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (18)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionDa EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (812)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainDa EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (65)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedDa EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (11)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldDa EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (597)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainDa EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (110)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveDa EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (66)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Da EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (411)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildDa EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (44)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueDa EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (38)
- Change Your Brain, Change Your Life (Before 25): Change Your Developing Mind for Real-World SuccessDa EverandChange Your Brain, Change Your Life (Before 25): Change Your Developing Mind for Real-World SuccessValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (18)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemDa EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (115)