Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Cheetsheet 6
Caricato da
Rick FreaDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Cheetsheet 6
Caricato da
Rick FreaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Respiratory Therapy Cave
Respiratorytherapycave.blogspot.com
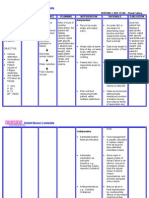
Critical Lab Values and Hemodynamics
Indicators for calling patient’s Dr: (Sepsis Screen = Temp>100.3 or < 96.8, HR>80, RR >20, SBP <90)
Respiratory Change in Change in LOC Change in Staff Worry Chest Pain Fluid status Temp Labs
Status Change HR (mental status) BP
8 or >28 >130 <40 <90 >170 Not look right I>O >100.4 or WBC > 12,000
or Lethargic or New < 96.8 or < 4,000
SOB changed by Confused Changed by Nausea/ Wet lungs
20% from Unresponsive 20% from vomiting Recurring Critical Critical >25,000
O2 Sat: decreased baseline Agitated baseline Diaphoretic UOP: >106 <2,500
from baseline <50cc/ <91
Rhythm Undetectable What’s wrong? 4hours
Respiratorytherapycave.blogspot.com 09/07/2009
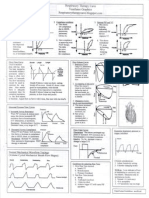
Lab tests & possible reasons for abnormal results: Hemodynamic Monitoring & Normal Values:
(Critical values in parenthesis.) 1. BP: Systolic = 90-140; Diastolic 60-90
1. CK: >200 (>351-2000 critical) = Muscle damage (nonspecific) a. As BP increases CO & CI usually decrease
2. CKMB: >2.5-3.0 (>5.5) = Heart muscle damage b. As BP decreases CO and CI usually increase
3. Troponin: >0.1 (>0.4) = Heart muscle damage (most specific) 2. Pulse Pressure = Systolic – Diastolic = 40 mmHg
4. ALK: >136 = Liver or bone damage >40 indicates decreased Stroke Volume (SV)
5. ALP: >150 = Liver or bone damage 3. SV = CO/HR = 60 – 130 ml/beat = volume ejected per beat
6. AST: >37 (>200 critical) = Liver tissue damage (nonspecific) 4. CO = HR(SV) = 4.8 LPM (More reliable than MAP)
7. ALT: >65 = Liver tissue damage (Specific for Hepatitis) 5. CI = CO/BSA = 2.5 LPMm2 or simply CO/2
8. Biliruben: >1.0 = Liver cell damage (best indicator of liver function) a. Decreased with shock, dehydration, cardiac fail, PE.
9. Albumin: >5.0 = Dehydration (best indicator of liver function) b. Increased with hypoxia, low BP.
<3.5 (<1.5) = Liver disease, shock, malnutrition c. More reliable measurement than CO.
10. Gamma-Gt: >51 = CHF, liver damage 6. Ejection Fraction (EF): % of blood volume pushed out of heart per beat.
11. BNP: >100 = CHF (300=mild, 600=mod, 900 severe) a. Normal = 65 – 75%
OK = 125-450, <75 YO = 125, >75 YO = 450 b. Reduced with ventricular damage
12. Glucose: >120 (>350) = Diabetes (>150 = insulin protocol) 7. MAP = systolic + (Diastolic*2)/3 = 70 – 105
<90 (<40)= Liver failure if not on Insulen (sepsis?) 8. Preload: Blood that returns to ventricles at end diastolic, & refers to
13. GFR: <60 (<29 critical) <15=Kidney failure stretch of myocardial fibers. Preload increases = heart function increase
14. BUN: >18 (>45 critical) = Kidney problems, CHF, shock, stress a. PCWP: Measures left heart function.
MI, dehydration, GI bleed 1. Normal = 5 – 12 mmHg (same as PAP diastolic)
<07 = Severe liver disease, malnutrition, over-hydrated 2. >18 = edema forming in lungs (if no signs CHF think ARDS)
15. Creatinin: >1.7 (3.0 critical) = Kidney probs, dehydration, CHF, shock 3. >25 = edema in lungs from left heart failure (CHF)
16. Sodium: >145 (>160 critical) = Dehydration 4. >5 – 12 + edema = noncardiogenic edema (ARDS)
<136 (<120) Kidney disease, over-hydrated (edema), not 5. > 12 may also indicate Mitral valve stenosis
eating well, CHF, effects of Lasix, diarrhea, vomiting b. CVP: Measures right heart function and used to monitor systemic
sweating. (<126=critical, confusion, lethargy, seizures) venous drainage (fluid levels).
17. Potassium: >5.1 (>6 critical) Kidney failure, massive tissue trauma, 1. Normal = 2 – 6 mmHg
(post op), metabolic acidosis (diabetes), dehydration. 2. <5 = hypovolemia, fluid restriction, diuretics shock, hemorrhage,
<3.5 (<2.8) = Not enough in diet, gastro-intestinal disorder, vasodilators (Nipride, Morphine) blood thinners, peep, ippb
vomiting. Due to Insulen, Lasix, dig, steroids? 3. >7 = hypervolemia, fluid challenge, increased SNS tone (fight or
18. Magnesium: >2.4(>2.7) = Kidney failure, dehydration, diabetic acidosis flight), shock, slow HR, decreased ejection fraction (CHF,
<1.3 (<1.0 critical) Malnourished (low intake), elderly, pump failure, Aortic valve failure, thick blood)
alcoholism, long-term diuretic use, diarrhea. 9. Afterload: Resistance heart must work against, or blood that returns
19. Chloride: >107 = Dehydration, met acidosis, hypoventilation (alkalosis) & fills the atria. All other values constant, has an inverse relationship
<98) = When Sodium low with CO, and is indirectly monitored by Blood Pressure.
20. Calcium: >10.1 (>13) = Bone breaks, prolonged bed rest, etc. a. SVR = (MAP – CVP)/CO
<8.5 (<6) = Bone disease, malnutrition, alcoholism 1. Normal = 900 – 1400 dynes or < 20 mmHg/L/min
21. PTT/ PT: >33/ >12.7(>60/>40) = transfusion, therapeutic, DIC. 2. Increased = HTN = vasoconstriction, increased SNS tone, cardiac
PTT is one of the best measures of liver function. stimulants (EPI, alpha action drugs), thick blood, narrow valves.
<24/<10 = Impaired clotting ability 3. Decreased by vasodilators, decreased WOH, adequate preload,
22. INR: >1.2 (>6) = Acute bleed, DIC or therapeutic. alpha blockers (Regitine, Dibenzylene), decreased SNS tone.
23. Fibrinogen: >450 = Risk for heart disease (checked often) b. PVR = (meanPAP – PCWP)/CO
<160 (<70) = Acute bleed, liver disease, malnutrition, DIC 1. Normal = 150 – 250 dynes or <2.5 mmHg/L/min
24. D-Dimer: >500 = DVT, PE, DIC, acute bleed, surgery, trauma 2. Increased with hypoxia, pulmonary hypertensin, PE
25. Platelets: <80,000 = bleeding problems, Heparin, DIC alcoholic, c. PAP: Monitors blood moving into lungs, afterload of right ventricle.
leukemia (Vitamin K increases clotting) 1. Normal is 25/8 (mean = 14)
26. Phosphorus: >4.1 (>8) = Liver disease, Kidney failure, bone mets. 2. PAP diastolic can be used to estimate PCWP.
<3.0 (<1.1) = Diabetic Keto-acidosis 10. Cardiac Electrolytes:
27. Uric Acid: >7.0 = Acidosis, alcoholism, diabetes, Kidney failure --Potassium:
28. Folic Acid: <2.0 = Malnutrition Increases and
29. Lactic Acid: >19.8 = Hypoxia, O2 deprivation, shock, CHF, tissue death decreases in this
Increases when organs failing/dying (sepsis?) result in majority
30. LDH: >136 (>350 critical) = Nonspecific Tissue damage or death of cardiac
31. Osmology >300 = Dehydration arrhythmias.
32. Hematocrit: >47 = Dehydration -- Magnesium:
33. Keytones: Positive test = Diabetes, starvation, vomiting, increased Low Mg
metabolism (fever, severe illness). associated with
34. Neutrophils: >48-73% = increased levels of bacterial infection (acute) low K. Results
a. Segs >60 if new infection in numbness,
b. Bands >2% = worsening infection tingling,
35. Eisinophils: >2% with allergic reaction (associated with asthma). contractions,
36. Lymphocytes: >18-48% = may indicate viral infection (mono, measles, pox) cramps, seizures,
37. Basophils: >2% = allergic reaction & cardiac
arrhythmias.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Lab Values Chart That Includes What Each Abnormal Might Indicate (Nursing)Documento9 pagineLab Values Chart That Includes What Each Abnormal Might Indicate (Nursing)Linsey Bowen75% (8)
- MAP, CO, and SV+HRDocumento11 pagineMAP, CO, and SV+HRjenwiley318096% (73)
- Role of Critical Care Nurses in Caring for Critically Ill PatientsDocumento10 pagineRole of Critical Care Nurses in Caring for Critically Ill PatientsHanis Rozib99% (69)
- Cardiac Medications and Treatments GuideDocumento10 pagineCardiac Medications and Treatments GuideNursePoor98% (47)
- 100 Essential Drugs1Documento8 pagine100 Essential Drugs1Matt McGlothlin85% (13)
- EKG Cheat SheetDocumento9 pagineEKG Cheat SheetAlert Twitter100% (5)
- Lab ValuesDocumento3 pagineLab Valuessurviving nursing schoolNessuna valutazione finora
- ArrhythmiaDocumento2 pagineArrhythmiaChris Pritchard93% (30)
- Acid-Base WorksheetDocumento2 pagineAcid-Base WorksheetMayer Rosenberg100% (17)
- Common Cardiac MedicationsDocumento1 paginaCommon Cardiac MedicationsPaige HardekopfNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Meds ChartDocumento1 paginaCardiac Meds ChartCharlotte Louise75% (4)
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis - making it easyDa EverandArterial Blood Gas Analysis - making it easyValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (4)
- EKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!Da EverandEKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!Nessuna valutazione finora
- The 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsDa EverandThe 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Arrhythmia RulesDocumento3 pagineBasic Arrhythmia Rulesgreenflames0997% (30)
- Risk For Diseases Cheat SheetDocumento1 paginaRisk For Diseases Cheat SheetRick Frea100% (5)
- Risk For Diseases Cheat SheetDocumento1 paginaRisk For Diseases Cheat SheetRick Frea100% (5)
- Nursing: Lab Values: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideDa EverandNursing: Lab Values: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- A Simplified ECG GuideDocumento4 pagineA Simplified ECG Guidejalan_z96% (25)
- ABG InterpretationDocumento1 paginaABG Interpretationnulall100% (18)
- Nursing School Drug ChartDocumento13 pagineNursing School Drug ChartEve Lester100% (3)
- Dysrhythmias ChartDocumento6 pagineDysrhythmias Chartjkrix100% (1)
- Haemodynamic Pocket GuideDocumento2 pagineHaemodynamic Pocket GuideDarryl Betts85% (13)
- Normal Pediatric RR and HRDocumento1 paginaNormal Pediatric RR and HRRick FreaNessuna valutazione finora
- CO2 Pocket GuideDocumento2 pagineCO2 Pocket GuideDarryl Betts100% (7)
- Lab CheatsheetDocumento1 paginaLab CheatsheetRick Frea86% (7)
- ACLS PharmacologyDocumento6 pagineACLS PharmacologyEunice Angela Fulgueras80% (5)
- ACLS Study Guide NewDocumento35 pagineACLS Study Guide NewNIRANJANA SHALININessuna valutazione finora
- Critical Care Survival GuideDocumento2 pagineCritical Care Survival Guidetringalama100% (4)
- Electrolyte CompleteDocumento6 pagineElectrolyte CompleteTofan Ana100% (2)
- Types of Assisted VentilationDocumento1 paginaTypes of Assisted VentilationJerry G100% (2)
- Respiratory PathophysDocumento1 paginaRespiratory PathophysTori IkeharaNessuna valutazione finora
- (SVR) Measures Systemic Resistance and Reflects Afterload of Left Ventricle Average Perfusion of A Cardiac CycleDocumento1 pagina(SVR) Measures Systemic Resistance and Reflects Afterload of Left Ventricle Average Perfusion of A Cardiac Cyclesarah_stover_1100% (4)
- ACLS Memory AidsDocumento2 pagineACLS Memory Aidsmaur_jmp78% (9)
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Recognition: an easy learning guideDa EverandCardiac Arrhythmia Recognition: an easy learning guideNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory Therapy Formulas and Values GuideDocumento1 paginaRespiratory Therapy Formulas and Values Guidelizzy59683% (6)
- Boot Camp Hemodynamic MonitoringDocumento37 pagineBoot Camp Hemodynamic MonitoringTinaHo100% (7)
- Neo-Peds Intubation Cheat SheetDocumento1 paginaNeo-Peds Intubation Cheat SheetRick FreaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cheatsheet 2Documento1 paginaCheatsheet 2Rick Frea86% (7)
- Cheatsheet 2Documento1 paginaCheatsheet 2Rick Frea86% (7)
- HF Case Analysis: Signs, Symptoms, and TypesDocumento14 pagineHF Case Analysis: Signs, Symptoms, and TypesBrix ValdrizNessuna valutazione finora
- Haemodynamic Monitoring & Manipulation: an easy learning guideDa EverandHaemodynamic Monitoring & Manipulation: an easy learning guideNessuna valutazione finora
- Ekg Strip NotesDocumento13 pagineEkg Strip NotesNick Loizzo100% (2)
- ACLS EKG Rhythms and InterpretationDocumento10 pagineACLS EKG Rhythms and Interpretationdonheyzz_02Nessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Card LasixDocumento2 pagineDrug Card LasixAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Cheatsheet 5Documento1 paginaCheatsheet 5Rick Frea80% (5)
- Cheat Sheet 1Documento1 paginaCheat Sheet 1Rick Frea100% (9)
- Cheat Sheet 1Documento1 paginaCheat Sheet 1Rick Frea100% (9)
- ECG Rhythm Interpretation GuideDocumento3 pagineECG Rhythm Interpretation Guideis_aradanas0% (1)
- ACLS PharmacologyDocumento5 pagineACLS PharmacologyKuruva MallikarjunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Know Common Disease ManagementDocumento14 pagineKnow Common Disease Managementcdx25Nessuna valutazione finora
- ABG Made EasyDocumento10 pagineABG Made EasyMayer Rosenberg100% (38)
- Mechanical Ventilator Management ProtocolDocumento3 pagineMechanical Ventilator Management ProtocolRick Frea100% (2)
- Mechanical Ventilator Management ProtocolDocumento3 pagineMechanical Ventilator Management ProtocolRick Frea100% (2)
- Cardiac Tamponade, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandCardiac Tamponade, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Rhythm Abnormalities GuideDocumento7 pagineCardiac Rhythm Abnormalities GuideAya KamajayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vent Modes ChartDocumento1 paginaVent Modes Chartladyhavocinc100% (1)
- Surviving the ICU: A Toolkit for the Critical Care NurseDa EverandSurviving the ICU: A Toolkit for the Critical Care NurseNessuna valutazione finora
- EKG Flash CardsDocumento5 pagineEKG Flash CardsRyann Sampino FreitasNessuna valutazione finora
- Food and Drug InteractionsDocumento16 pagineFood and Drug InteractionsSirijoti KanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cheatsheet 4Documento1 paginaCheatsheet 4Rick FreaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cheatsheet 4Documento1 paginaCheatsheet 4Rick FreaNessuna valutazione finora
- CRITICAL CARE NURSE: Passbooks Study GuideDa EverandCRITICAL CARE NURSE: Passbooks Study GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- Neonatal Ventilator Vent Set-Up CheatsheetDocumento1 paginaNeonatal Ventilator Vent Set-Up CheatsheetRick Frea50% (2)
- Neonatal Ventilator Vent Set-Up CheatsheetDocumento1 paginaNeonatal Ventilator Vent Set-Up CheatsheetRick Frea50% (2)
- Respiratory DysfunctionDocumento1 paginaRespiratory Dysfunctionoxidalaj100% (3)
- Pediatric Respiratory Distress GuidelinesDocumento1 paginaPediatric Respiratory Distress GuidelinesRick FreaNessuna valutazione finora
- Static Compliance & RSBI CheatsheetDocumento1 paginaStatic Compliance & RSBI CheatsheetRick FreaNessuna valutazione finora
- Static Compliance & RSBI CheatsheetDocumento1 paginaStatic Compliance & RSBI CheatsheetRick FreaNessuna valutazione finora
- RT Consult Form Side #1Documento2 pagineRT Consult Form Side #1Rick Frea100% (2)
- RT ConsultDocumento5 pagineRT ConsultRick Frea100% (2)
- Cheatsheet 3Documento1 paginaCheatsheet 3Rick Frea100% (1)
- Cheatsheet 3Documento1 paginaCheatsheet 3Rick Frea100% (1)
- Peek Flow FlowsheetDocumento3 paginePeek Flow FlowsheetRick FreaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tidal Volumes Cheat SheetDocumento1 paginaTidal Volumes Cheat SheetRick Frea100% (1)
- Tidal Volumes Cheat SheetDocumento1 paginaTidal Volumes Cheat SheetRick Frea100% (1)
- Pulmonary Function TestsDocumento9 paginePulmonary Function TestsRick Frea0% (1)
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocumento29 pagineAcute Respiratory Distress SyndromeRucelyn CampitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nclex PogiDocumento8 pagineNclex Pogijackyd5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Inhaler LexiconDocumento4 pagineInhaler LexiconRick Frea100% (2)
- Inhaler LexiconDocumento4 pagineInhaler LexiconRick Frea100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan - Renal FailureDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan - Renal Failurederic87% (31)
- Plabable-Gems-28. Pharmacology Plabable GemsDocumento60 paginePlabable-Gems-28. Pharmacology Plabable GemsHabo HaboNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP EsrdDocumento9 pagineNCP EsrdWilmar AngeloNessuna valutazione finora
- Neonatal Resuscitation ProgramDocumento6 pagineNeonatal Resuscitation ProgramRick Frea100% (5)
- Drug StudyDocumento18 pagineDrug StudyAntonethe DemdamNessuna valutazione finora
- RT Consult Form Side #2Documento1 paginaRT Consult Form Side #2Rick Frea100% (1)
- RT Consult Form Side #2Documento1 paginaRT Consult Form Side #2Rick Frea100% (1)
- Neonatal Special ConsiderationsDocumento1 paginaNeonatal Special ConsiderationsRick Frea100% (1)
- Nle Pentagon Reviewer For Nclex Answer QuestionsDocumento30 pagineNle Pentagon Reviewer For Nclex Answer QuestionsSpoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Emergency Room Aerosolized Medication ProtocolDocumento3 pagineEmergency Room Aerosolized Medication ProtocolRick Frea67% (3)
- RsbiDocumento1 paginaRsbiRick FreaNessuna valutazione finora
- Capnography Cheat SheetDocumento1 paginaCapnography Cheat SheetRick Frea100% (1)
- Ventilator Graphics Cheat Sheet (Part 1)Documento1 paginaVentilator Graphics Cheat Sheet (Part 1)Rick Frea100% (2)
- Indicators For Calling A DoctorDocumento1 paginaIndicators For Calling A DoctorRick Frea100% (1)
- Intracranial SurgeryDocumento12 pagineIntracranial SurgerysetanpikulanNessuna valutazione finora
- Managing ARDS and cardiac complications in a trauma patientDocumento3 pagineManaging ARDS and cardiac complications in a trauma patientKrisianne Mae Lorenzo Francisco0% (2)
- Drug Study FUROSEMIDE (Eugene San)Documento2 pagineDrug Study FUROSEMIDE (Eugene San)Ana LanticseNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Guideline For Fluid Overload Pulmonary OedemaDocumento3 pagineClinical Guideline For Fluid Overload Pulmonary OedemaEka HandreanNessuna valutazione finora
- Sar Loop DiureticsDocumento2 pagineSar Loop DiureticsTikendraNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs Affecting Renal SystemDocumento58 pagineDrugs Affecting Renal SystemDaniel OkakaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cirrhotic Ascites: A Review of Pathophysiology and ManagementDocumento10 pagineCirrhotic Ascites: A Review of Pathophysiology and ManagementromyNessuna valutazione finora
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocumento4 pagineFurosemide Drug StudyAngelou Joefred CongresoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyperkalemia Treatment - EmedicineDocumento16 pagineHyperkalemia Treatment - EmedicineRian Segal HidajatNessuna valutazione finora
- Diuretic Drugs PHMDocumento36 pagineDiuretic Drugs PHMshenae3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Furosemide (Lasix)Documento1 paginaFurosemide (Lasix)E100% (3)
- NRSG 2445 ARDS AssignmentDocumento4 pagineNRSG 2445 ARDS AssignmentregisterednurseNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiovascular Drugs and the Renin-Angiotensin SystemDocumento16 pagineCardiovascular Drugs and the Renin-Angiotensin SystemAngel DiangNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug of The Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Nursing Consideration Generic NameDocumento12 pagineDrug of The Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Nursing Consideration Generic NameJemina Rafanan RacadioNessuna valutazione finora
- Articulo Fono PDFDocumento11 pagineArticulo Fono PDFPaola MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines For The Use of Furosemide (Lasix) : Recommended Neonatal Dose, Route, and IntervalDocumento2 pagineGuidelines For The Use of Furosemide (Lasix) : Recommended Neonatal Dose, Route, and IntervalGenerix MarvindoNessuna valutazione finora
- CASE STUDY 2 With RETDRM VIDEO LINK (Operaña, Ellayza)Documento5 pagineCASE STUDY 2 With RETDRM VIDEO LINK (Operaña, Ellayza)OPERAñA ELLAYZA RB DECANONessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study HazDocumento7 pagineDrug Study HazRichard HazNessuna valutazione finora