Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Syllabus1stsem (Revised)
Caricato da
Akshit GuptaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Syllabus1stsem (Revised)
Caricato da
Akshit GuptaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
M.B.
S COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY JAMMU
COURSE SCHEME Common to All Branches st B.E 1 Semester
(Approved by University of Jammu) For the Session 2008 2010
BABLIANA, P.O. MIRAN SAHIB, JAMMU 181101 (J&K) INDIA Phone : 0191 2262896, 2262897 Fax: 0191 2262896
B.E CURRICULUM University of Jammu Semester 1st (Common)
Course No.
Course Name
Lecture
Tutorial
Practical Theory
Marks Sessional 25 Practical Total 125
MTH-101
Engg. Math-I Engg. Phy-I Engg. Chem-I Engg. Mech Comm. Skills Engg. Graphics Engg. Physics Lab.
100
PHY-102 CHM-102
3 3
1 1
100 100
25 25
125 125
M-104 HUM-105
3 3
1 1 -
100 100
25 25
125 125
M-106
100
50
150
PHY-107
50
50
CHM-108
Engg. Chemistry Lab.
50
50
M-109
Engg. Mech. Lab. WS Technology
50
50
M-110
75
75
Total
17
12
600
125
275
1000
Course Title : Engineering Mathematics I Course Code : MTH - 101 SECTION - A 1. Differential Calculus
L 3
T 2
P -
Tr 100
S 25
P 0
Successive differentiation, Leibnitz theorem (without proof), Partial differentiation with errors and approximations, Eulars theorem on homogeneous functions, Taylors and Maclaurins series of two variables, Maxima and Minima of functions of two variables, Asymptotes, Double points, Curvature, Curve tracing in Cartesian, polar and parametric forms.
2.
Integral Calculus Definite integral with important properties, differentiation under the integral sign, Gamma function, Beta and
error functions with simple problems, Application of definite integrals to find length , area, volume and surface area of revolution, transformation of coordinates, double and triple integrals with simple problems.
SECTION B 1. Complex Trigonometry Hyperbolic functions of complex variable, Inverse Hyperbolic functions, Logarithmic function of a complex variable, summation of series by c+ iS method
2. Ordinary differential Equations Differential equations of first order and first degree: Exact and non-exact differential equations, Linear and Bernoullis differential equations. H igher order linear differential equations: complementary solution, particular integral and general solution of these equations, variation of parameters technique to find particular integral of second order differential equations, Cauchys and Lagranges differential equations. Applications of ordinary differential equations to simple Electrical and Mechanical Engg. Problems.
3.
Solid Geometry Sphere, Intersection of sphere and plane, tangent plane property, cone and cylinder, related problems to
right circular cone and cylinder.
Books Recommended:1. Engineering Mathematics 2. Calculus and Analytic Geometry 3. Differential Calculus 5. Integral Calculus B. S. Grewal, Khanna Pub.., New Delhi Thomas and Finney, Addison Wesley, Narosa. Shanti Narayan, New Delhi Shanti Narayan, New Delhi
NOTE: There shall be total eight questions, four from each section. Each question carry 20 marks. Five questions will have to be attempted, selecting atleast two from each section. Use of calculator is allowed
Course Title : Engineering Physics I Course Code : PHY- 102 SECTION - A 1. Mathematical Physics
L 3
T 1
P 2
Tr 100
S 25
P 50
Review of Vector Algebra, Scalar and Vector fields, Gradient of a scalar field, Divergence and curl of a vector field and their physical significance, Gauss divergence theorem, Stokes theorem and their applications, Vector identities. 2. Electromagnetic Fields and Waves Guasss law invector notation ( differential and integral form), Applications of Guasss law to find electric fields due to a long straight charged wire, Cylindrical and Spherical charge distributions. Derivation of Amperes circuital law, applications of Amperes circuital law to find magnetic intensity due to long cylindrical wire, due to a long solenoid. Differential and integral form of Faradays law of electromagnetic induction, Equation of continuity, Displacement current and its significance, Maxwells field equations (differential and integral forms), Betaron, Electromagnetic wave propagation in free space ( e.m wave equations for ---- & --- fields for free space and their solutions ( plane wave solution), velocity of e.m waves, relation between E o & Bo, Definition of pointing vector, pointing theorem. SECTION B 3. Applied Optics Interference in thin films (by reflection and transmission of light), theory of Newtons rings by reflected light, Determination of wave length and refractive index of mo nochromatic light by Newtons theory. Fraunhoffer & Fresnels diffraction Frenels half period zones and rectilinear propagation of light, Fraunhoffer diffraction due to a single slit, plane diffraction grading & its theory for secondary maxima and minima. Unpolarized and polarized light, Nicol Prism, Mathematical representation of polarization of different types, quarter and half wave plates. 4. Oscillations Free damped and forced oscillatios and their differential equations, Logarithmic decrement, power dissipation & quality factor, ultrasonic waves and their production by Piezoelectric method and applications (general). 5. Fibre Optics Proparation of light in fibres, numerical aperture, single mode and multimode fibres, general applications
Books Recommended :1. Vector Analysis 2. Mathematical Physics 3. Physics 4. Optics 5. Sound 6. Sound 7. Fiber Optics Spiegal Rajput and Gupta Hatliday & Reisnick Brijlal & Subramaniam Subramaniam Khanna & Bedi Ajay Ghatak & Tyagrajan
NOTE: There shall be total eight questions, four from each section. Each question carry 20 marks. Five questions will have to be attempted, selecting atleast two from each section. Use of calculator is allowed
Course Title : Engineering Chemistry I Course Code : CHM - 103 SECTION - A 1. Spectroscopy
L 3
T 1
P 2
Tr 100
S 25
P 50
UV Spectroscopy Electronics, transitions, spectrum, shift of bonds with solvents for double bonds, carbonyl compounds and aromatic compounds. IR- Spectroscopy Introduction, brief idea about instrumentation, applications and interpretation of IR Spectra, characterization of functional groups and frequency shift associated with structure changes. H-NMR Spectroscopy Theory of H-NMR spectroscopy, equivalent and non-equivalent protons, chemical shift, spin spin coupling, spin spin splitting, H-NMR spectrum of a few organic compounds. 2. Explosives Introduction, classification and types of explosives, requirement for good explosives, preparation and uses of following explosives Nitrocellulose, TNT, Dinitrobenzene, Picric Acid, Nitroglycerine and Dynamite, Gun Power, RDX, Tetracene. SECTION B 1. Stereochemistry Optical isomerism, recemerization, asymmetric synthesis, methods for resolution of racemic mixture, enantiomerism and diasteroisomerism 2. Alloys Introduction, purpose of making alloys, preparation of alloys, classification of alloys. (Ferrous and nonferrous alloys), alloy steels and copper alloys. 3. Lubricants Definitions, functions of lubricants, mechanism of lubricants, classification of lubricants ( lubricating oils, semi solid lubricants, solid lubricants) synthetic lubricants, flash and fire points, oiliness, cloud and pour points. 4. Dyes and Drugs Classification of dyes and its applications. Define drug and give the applications of following drugs. a) Narcotics b) Tranquilizers c) Antipyretics d) Antibiotics.
Books Recommended : 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Engineering Chemistry Engineering Chemistry Engineering Chemistry Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry - Jain and Jain - Sharma B. K. - Dara, S. S - Bahl B. S - Soni P. L - Jain M. K
Spectroscopy of organic Compounds - Silverstain Spectroscopy of organic Compounds - Kalsi P. S
NOTE: There shall be total eight questions, four from each section. Five questions will have to be attempted, selecting at least two from each section.
Course Title : Engineering Mechanics Course Code. : M- 104
L 3 SECTION A ( STATICS)
T 1
P 2
Tr 100
S 25
P 50
Scope and basic concepts (rigid body, force, units etc.) Concept of free body diagram. Resultant of coplanar concurrent forces in a plane and in space, moment of force, principle of moments, coplanar and spatial applications. Virtual work method and its applicatios. Equilibrium and its equations for planer and spatial systems, Analyst of trusses, method of joints and sections. Theory of friction, its laws and applications ( inclined plane). Square threaded screws, Belt friction. Centroids and centre of gravity, centroids of lines and composite areas, centroids determined by integration.
SECTION B (DYNAMIC)
Kinematics of a particle rectilinear motion, motion curves, Rectangular components of curvilinear motion, Flight of projectile, Normal and tangential components of acceleration, Radial and transverse components. Newtons law. D Alemberts Principle. Kinetics of rigid bodies: Types of rigid body motion, Angular motion, Fixed axis rotation, Analysis of plane motion and its applications, Instantaneous center and instantaneous axis of rotation. Kinetics of particle: Translation, analysis of a particle as a rigid body
Kinetics of rigid body: Equations of plane motion. fixed axis rotation, Rolling bodies, General plane motion, Impulse and momentum in plane motion, Angular momentum.
Books Recommended 1. 2. 3. 4. Engg. Mechanics (Statics & Dynamics) Engg. Mechanics (Statics & Dynamics) Engg. Mechanics (Statics & Dynamics) Engg. Mechanics (Statics & Dynamics) - Fredinand L. Singer - Mariam & Kraige - Timoshenko and Young - Beer and Johnson
NOTE: There shall be total eight questions, four from each section. Five questions will have to be attempted, selecting at least two from each section. Use of calculator is allowed
Course Title : Communication Skills Course No. : HUM - 105
L 3
T 1
P -
Tr 100
S 25
P -
Exercises in comprehension, grammar, vocabulary usage, pronunciation, spelling and composition based on the following texts: I. Contemporary English Prose: Edition by Menon, Oxford University Press.
II.
Developing English skills: Edition by Thanker, Desai and Purani, Oxford University Press. or English Through Reading - II Edition by Bhasker and Prabhu.
Note :- Text I and II carry 50% weightage each in the question paper.
Question Paper Format 1. Six short answer questions on Comprehension to be set from Text I. Students are expected to answer any (30 marks) from Text I to be used in sentences. Hundred percent choice
three in about 150 words each. 2. Phrases and Idioms
to be given. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Completing a Paragraph of which the first two or three short sentences are given. Exercise on Tenses from Text II. Exercise on Active / Passive transformation from Text II Forming Verbs or Adjectives or Nouns from the given word-Text II Prepositions from Text II Matching words and their meanings from Text II Forming words ending in -ify, -ize, -tion, etc. from Text II
(20 marks) (10 marks) (5 marks) (5 marks) (5 marks) (5 marks) (5 marks) (5 marks) (5 marks) II such as question tags,
10. Filling in the blanks with a given set of words in brackets -Text II. 11. Questions articles etc. or Marking Stress or Syllable in given words. on miscellaneous exercises from Text
( 5 marks)
Course Title : Engineering Graphics Course Code : M - 106 Unit I : Introduction
L 1
T -
P 3
Tr 100
S 0
P 50
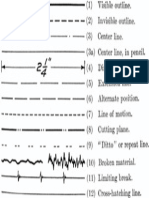
Conventional lines and signs used in engineering drawing, printing and lettering, Curves used in engineering practice: Cycloidals , Involutes; Spirals and Hellices, Locus of a point on simple mechanism.
Theory and Practice of Orthographic Projections: Projections of points and lines in different quadrant, w.r.t. principal reference planes, finding of true length, true inclinations and traces of lines.
Projections of Planes: Projections of planes w.r.t. the principal planes in simple and inclined positions. Rotation methods and simple auxiliary plane methods. Space relation of a plane and a line. To locate a point on a plane given its projections, parallel relation of lines and planes. Shortest distance between a line and a plane.
Unit II: Projections of Solids: Classification and main features Prisms and Pyramids. Projections of solids inclined to both the reference planes by (i) Rotation method and (ii) Auxiliary plane methods. Projection of solids in combination (Coaxial) in simple and inclined positions. Sectioning of Solids: Objects of sectioning, types of cutting planes, True shape of section, Auxiliary views in section of multiple co-axial solids in simple and tilted conditions.
Unit III : Interpenetration of Solid and Intersection of Surfaces Intersection of geometrical solids / hollow sections, Tracing of lines of intersection by line method and by section method. Development of surfaces: Classification of surfaces, mehods of development straight line method and radial line method, development of solids and hollow sections in full or part development of transition pieces. To draw projections from given development.
Unit IV : Isometric Projections: Isometric scale, Isometric axes and isometric planes, Isometric projections of solids and simple machine blocks. Orthographic Projections : Orthographic projection of simple blocks ( first & third angles), to draw the third view from given two views. Missing lines in projections.
Books Recommended 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Engineering Drawing Practical Geometry Engineering Graphics Principles of Engg. Graphics Engg. Graphics N. D. Bhat V. Laxminarayan & R.S. V. K. L. Narayan & P. Kamaiah P. E. Giesecks Fredrieck and Mischelle
NOTE: At least two questions to be attempted from Unit 1 and at least one question each of the Unit 2, Unit 3 and Unit 4 in the theory examination paper.
Course Title : Engineering Physics Lab-I Course Code : PHY- 107 List of Experiments 1.
L -
T -
P 2
Tr -
S -
P 50
To plot a graph between the distance of knife edges from the centre of gravity and the Time Period of a Compound Pendulum. Find from the graph:
i. ii. 2. 3. 4. 5.
(a). Acceleration due to gravity (b). The radius of the gyration & moment of inertia of the bar about an axis through the centre of gravity. To find the frequency of A.C mains using an Electrical Vibrator. To determine focal length of a convex mirror using a convex lens. To determine focal length of a concave lens using a concave mirror. To find the angle of given prism using a spectrometer.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12 13. 14. 15.
To find the dispersive power of a given prism using a spectrometer. To find refractive Index of a given liquid using a hollow prism/glass prism. To find the wavelength of Sodium Light by Newtons rings apparatus. To draw the V-I characteristics of a forward and reverse bias PN junction diode. To study the common base characteristics of PNP junction transistor. To study the common emitter characteristics of PNP junction transistor. To study the common base characteristics of NPN junction transistor. To study the common emitter characteristics of NPN junction transistor. To evaluate the value of Plancks constant To study the characteristics of a solar cell.
Note: A minimum of six experiments is to be performed in a semester Books Recommended 1. 2. 3. Practical Physics Practical Physics Bsc. Practical Physics Warsnop & Flint Chauhana & Singh ( Vol. I and Vol. II) C. L. Arora
Course Title : Engineering Chemistry Lab-I Course Code : CHM - 108 List of Experiments 1. 2. 3.
L -
T -
P 2
Tr -
S -
P 50
Determine the percentage of CaCO3 in precipitated chalk. You are provided with IN HCL and O.IN NaOH To analyses the given antacid tablets. Determine Volumetrically the percentage purity of given sample of Ferrous Sulphate, x gms of which have been dissolved per liter provided N/10 KMnO4
4.
Determine Volumetrically the number of molecules of water of crystallization present in a given sample of Mohrs salt, x gms of which have been dissolved per liter provided N/10 K2Cr2O7 (using an external indicator). Determine Volumetrically the percentage of Cu in a sample of CuSo4 crystals, Z gms of which have been dissolved per liter provided O.IN Na2S2O3.
5.
6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11.
To determine the coefficient of viscosity of an unknown liquid using Ostwalds Viscometer. Determine the surface tension of a unknown liquid using stalagmometer. To prepare a pure and dry sample of Aspirin. To prepare a pure and dry sample of Glucosazone Determine the method of purification of organic compounds by coloumn chromatography. Determine the aniline point of given lubricating oil.
Books Recommended 1. 2. Experimental Engg. Chemistry Lab manual on Engg. Chemistry Shashi Chawla Basin, S K & Sudha Rani
Course Title : Engineering Mechanics Lab Course Code : M - 109 List of Experiments 1.
L -
T -
P 2
Tr -
S -
P 50
To find the mechanical advantage, velocity ratio and percentage-effeciency of a single purchase Winch Crab.
2.
To find the mechanical advantage, velocity ratio and percentage-effeciency of a double purchase Winch Crab.
3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.
To find the mechanical advantage, velocity ratio and percentage-efficiency of a Worm and Worm Wheel. To verify Parallelogram law of forces using force board apparatus. To find the coefficient of friction between two surfaces i.e, glass and wood on an inclined plane To find the coefficient of friction between two surfaces i.e, glass and steel roller on an inclined plane. To find the reactions at supports in case of a simply supported beam. To verify Lami's Theorem using Jib Crane Apparatus. To find the moment of inertia in case of a Fly-Wheel.
Course Title : WORKSHOP TECHONOLOGY Course Code : WS - 110
L 1
T -
P 3
Tr -
S -
P 75
Introduction of workshop as fabrication unit. Information regarding various material of construction i.e. Ferrous and Non-Ferrous, wood, plastics etc. Basic fabrication process i.e. Castings, Mechanical working. Welding and Machining. Wood working and pattern making practice, Information about working hand and wood working machines, various methods of joining of wooden parts for the fabrication of patterns. Pattern materials and allowances, pattern construction procedures, preservation of Patterns. Moulding and casting practice. Sand moulding. Natural Foundry sands and synthetic sand, preparation of moulding sands, mould making procedures, cast iron and aluminum and pouring, melting crucible process, Extraction of Castings. Cold and Hot working process. Basic tools and equipment used in mechanical working. Forging furnaces operation, Smith forging operations.
Books Recommend: 1. Manufacturing Processes and Material 2. Manufacturing Processes 3. Workshop Technology Vol. I 4. Workshop Technology Vol I 5. Workshop Practice manual 6. Manufacturing Technology-I Campbell P.N.Rao Hajri & Chowdri B.S. Raghuwanshi V. Kapoor R. K. Kapur, P.K.
Shop Practice Unit I: Pattern Making (i) Bearing Block Pattern
(ii) Split pattern of Bench Vice ( Sliding Jaw) Unit ll: Moulding & Casting Moulding & Castings of pattern at Unit I Unit III: Hand Forging of (i) Hexagonal Headed bolt and nut from cylindrical rod. (ii) Cubical block from a cylindrical section.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 2 NdsemDocumento14 pagine2 NdsemAkshit GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Index: List of Practical Performed in The Work ShopDocumento2 pagineIndex: List of Practical Performed in The Work ShopAkshit GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 NdsemDocumento14 pagine2 NdsemAkshit GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Jammu University Mechanical Engineering SyllabusDocumento87 pagineJammu University Mechanical Engineering SyllabusAkshit GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- CAMPUS: RIICO Industrial Area, Opp. Chokhi Dhani, Tonk Road, Sitapura, JAIPUR-22Documento2 pagineCAMPUS: RIICO Industrial Area, Opp. Chokhi Dhani, Tonk Road, Sitapura, JAIPUR-22Akshit GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 NdsemDocumento14 pagine2 NdsemAkshit GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Memory UnitsDocumento1 paginaMemory UnitsAkshit GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Height and WeightDocumento16 pagineHeight and WeightAkshit GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- PassportApplicationForm Main English V2.0Documento2 paginePassportApplicationForm Main English V2.0Ramya NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Save Planet EarthDocumento1 paginaSave Planet EarthAkshit GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Alphabetline - TifDocumento1 paginaAlphabetline - TifAkshit GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hello: FrndsDocumento1 paginaHello: FrndsAkshit GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Straight Line Midpoint Solution3Documento1 paginaStraight Line Midpoint Solution3Akshit GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Banyan International School PaperDocumento5 pagineBanyan International School PaperAkshit GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- BrochureDocumento13 pagineBrochuresairamzambreNessuna valutazione finora
- Banyan International School - 2Documento2 pagineBanyan International School - 2Akshit GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Banyan International School 3Documento3 pagineBanyan International School 3Akshit GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Embedded Systems Online TestingDocumento6 pagineEmbedded Systems Online TestingPuspala ManojkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- KCG-2001I Service ManualDocumento5 pagineKCG-2001I Service ManualPatrick BouffardNessuna valutazione finora
- Unbound DNS Server Tutorial at CalomelDocumento25 pagineUnbound DNS Server Tutorial at CalomelPradyumna Singh RathoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Natural Cataclysms and Global ProblemsDocumento622 pagineNatural Cataclysms and Global ProblemsphphdNessuna valutazione finora
- CRISTIAN COLCERIU - PERSONALITATI CLUJENE Prof - Dr.ing - POMPILIU MANEADocumento21 pagineCRISTIAN COLCERIU - PERSONALITATI CLUJENE Prof - Dr.ing - POMPILIU MANEAcristian colceriu100% (2)
- Introducing The Thinkcentre M70A. A Desktop You DefineDocumento3 pagineIntroducing The Thinkcentre M70A. A Desktop You DefineSiti RohayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Play ClawDocumento2 paginePlay ClawFrenda SeivelunNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 20 AP QuestionsDocumento6 pagineChapter 20 AP QuestionsflorenciashuraNessuna valutazione finora
- Veritas™ High Availability Agent For WebSphere MQ Installation and Configuration Guide / WebSphere MQ InstallationDocumento64 pagineVeritas™ High Availability Agent For WebSphere MQ Installation and Configuration Guide / WebSphere MQ InstallationkarthickmsitNessuna valutazione finora
- Erosional VelocityDocumento15 pagineErosional VelocityGary JonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Paul Spicker - The Welfare State A General TheoryDocumento162 paginePaul Spicker - The Welfare State A General TheoryTista ArumNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Electronics Chapter 5Documento30 pagineDigital Electronics Chapter 5Pious TraderNessuna valutazione finora
- Stonehell Dungeon 1 Down Night Haunted Halls (LL)Documento138 pagineStonehell Dungeon 1 Down Night Haunted Halls (LL)some dude100% (9)
- Week - 2 Lab - 1 - Part I Lab Aim: Basic Programming Concepts, Python InstallationDocumento13 pagineWeek - 2 Lab - 1 - Part I Lab Aim: Basic Programming Concepts, Python InstallationSahil Shah100% (1)
- The Great Muslim Scientist - Imam Jaffer Sadiq (ADocumento78 pagineThe Great Muslim Scientist - Imam Jaffer Sadiq (ASalman Book Centre100% (2)
- STS Module 11Documento64 pagineSTS Module 11Desiree GalletoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lalit Resume-2023-LatestDocumento2 pagineLalit Resume-2023-LatestDrew LadlowNessuna valutazione finora
- Priest, Graham - The Logic of The Catuskoti (2010)Documento31 paginePriest, Graham - The Logic of The Catuskoti (2010)Alan Ruiz100% (1)
- Final Self Hypnosis Paperback For PrintDocumento150 pagineFinal Self Hypnosis Paperback For PrintRic Painter100% (12)
- Loop Types and ExamplesDocumento19 pagineLoop Types and ExamplesSurendran K SurendranNessuna valutazione finora
- Module-29A: Energy MethodsDocumento2 pagineModule-29A: Energy MethodsjhacademyhydNessuna valutazione finora
- 21 Tara Mantra-Wps OfficeDocumento25 pagine21 Tara Mantra-Wps OfficeAlteo FallaNessuna valutazione finora
- DR S GurusamyDocumento15 pagineDR S Gurusamybhanu.chanduNessuna valutazione finora
- Paul Wade - The Ultimate Isometrics Manual - Building Maximum Strength and Conditioning With Static Training-Dragon Door Publications (2020) - 120-146Documento27 paginePaul Wade - The Ultimate Isometrics Manual - Building Maximum Strength and Conditioning With Static Training-Dragon Door Publications (2020) - 120-146usman azharNessuna valutazione finora
- Operations Management Interim ProjectDocumento4 pagineOperations Management Interim ProjectABAYANKAR SRIRAM (RA1931201020042)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Changed Report 2015 PDFDocumento298 pagineChanged Report 2015 PDFAnonymous FKjeRG6AFnNessuna valutazione finora
- Microwave EngineeringDocumento2 pagineMicrowave Engineeringசுந்தர் சின்னையா0% (9)
- Newsletter 1-2021 Nordic-Baltic RegionDocumento30 pagineNewsletter 1-2021 Nordic-Baltic Regionapi-206643591100% (1)
- Nescom Test For AM (Electrical) ImpDocumento5 pagineNescom Test For AM (Electrical) Impشاہد یونسNessuna valutazione finora
- Operator'S Manual Diesel Engine: 2L41C - 2M41 - 2M41ZDocumento110 pagineOperator'S Manual Diesel Engine: 2L41C - 2M41 - 2M41ZMauricio OlayaNessuna valutazione finora