Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Head Injury 22
Caricato da
Permata Ayu Kamila0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
30 visualizzazioni0 pagineThis document provides guidelines for the initial management of mild head injuries in adults. It distinguishes between low and high risk injuries. Low risk injuries with normal CT scans and improving symptoms can be discharged after 4 hours of observation. High risk injuries require closer monitoring or CT scans and may need prolonged hospital admission depending on factors like abnormal vital signs, neurological symptoms or mechanisms of injury. The guidelines help determine which patients need imaging or further clinical observation versus those suitable for discharge.
Descrizione originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThis document provides guidelines for the initial management of mild head injuries in adults. It distinguishes between low and high risk injuries. Low risk injuries with normal CT scans and improving symptoms can be discharged after 4 hours of observation. High risk injuries require closer monitoring or CT scans and may need prolonged hospital admission depending on factors like abnormal vital signs, neurological symptoms or mechanisms of injury. The guidelines help determine which patients need imaging or further clinical observation versus those suitable for discharge.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
30 visualizzazioni0 pagineHead Injury 22
Caricato da
Permata Ayu KamilaThis document provides guidelines for the initial management of mild head injuries in adults. It distinguishes between low and high risk injuries. Low risk injuries with normal CT scans and improving symptoms can be discharged after 4 hours of observation. High risk injuries require closer monitoring or CT scans and may need prolonged hospital admission depending on factors like abnormal vital signs, neurological symptoms or mechanisms of injury. The guidelines help determine which patients need imaging or further clinical observation versus those suitable for discharge.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 0
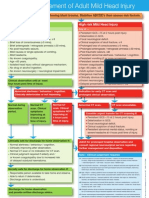
Low risk Mild Head Injury
Clinical observation until at least
four hours post time of injury.
Normal during
observation
period.
Normal CT
scan. Clinical
symptoms
improving at
4 hours post
time of injury.
Normal CT
scan. Clinical
symptoms NOT
improving at
4 hours post
time of injury.
Socially safe for discharge for home observation if:
1
Responsible person available to take home and observe.
1
Able to return if deteriorates.
1
Discharge advice is understood.
Clinically safe for discharge for home observation if:
1
Normal alertness / behaviour / cognition.
1
Clinically improving after observation.
1
Normal CT scan or no indication for CT scan.
1
Clinical judgment required if elderly and /
or known coagulopathy due to increased risk
of delayed subdural haematoma.
Consider urgent transfer for CT scanning if:
1
Persistent GCS <15 at 2 hours post injury.
1
Deterioration in GCS.
1
Focal neurological deficit.
1
Clinical suspicion of skull fracture.
1
Persistent abnormal mental status, vomiting or
severe headache at 4 hours post time of injury.
Admit for prolonged hospital observation and
consult regional neurosurgical service regarding
further management and disposition.
CT scan unavailable.
Initial Management of Adult Mild Head Injury
High risk Mild Head Injury
Any of ...
1
Persistent GCS <15 at 2 hours post injury.
1
Deterioration in GCS.
1
Focal neurological deficit.
1
Clinical suspicion of skull fracture. ::1
1
Prolonged loss of consciousness (>5 mins).
1
Prolonged anterograde / retrograde amnesia (>30 mins).
1
Post traumatic seizure. ::2
1
Persistent abnormal alertness / behaviour / cognition.
1
Persistent vomiting (2 or more occasions).
1
Persistent severe headache.
1
Known coagulopathy (eg warfarin / alcoholic).
1
Age >65 years. ::3
1
Multi-system trauma. ::4
1
Dangerous mechanism. ::5
1
Clinically obvious drug or alcohol intoxication. ::6
1
Known neurosurgery / neurological impairment. ::7
1
Delayed presentation or representation. ::8
Discharge for home observation
and provide written discharge advice.
Abnormal alertness / behaviour / cognition.
Clinically deteriorates or not improving.
Abnormal CT scan.
Note Clinical judgement required
::1 Clinical suspicion of skull fracture includes history of focal blunt assault
or injury; large scalp lacerations or haematomas; signs of base of skull fracture
haemotympanum / CSF leak / raccoon eyes / Battles sign.
::2 Post traumatic seizures prolonged, focal or delayed seizures are significant risk
factors for intracranial injury but brief generalised seizures immediately following
head injury are less concerning.
::3 Age >65yrs elderly patients have increased risk of significant intracranial injury;
routine CT scanning unless totally asymptomatic patient with no other risk factors.
::4 Multi-system trauma beware patients with unstable vital signs or distracting
injuries, as significant head injuries are easily missed.
::5 Dangerous mechanisms include MVA ejection / rollover; pedestrians / cyclists hit
by vehicle; falls >own height or five stairs; falls from horses / cycles etc; focal blunt
trauma, eg bat / ball / club.
::6 Clinically obvious drug or alcohol intoxication with altered mental status is an indication
for CT scanning but drug or alcohol ingestion with normal mental status is not.
::7 Known neurosurgery/neurological impairment conditions such as hydrocephalus
with shunt or AVM or tumour or cognitive impairment from any cause make clinical
assessment less reliable and may increase risk of intracranial injury.
::8 Delayed presentation or representation consider both intracranial injury
and post concussion symptoms and have a low threshold for CT scanning.
Indication for early CT scan and
prolonged clinical observation.
N
S
W
I
n
s
t
i
t
u
t
e
o
f
T
r
a
u
m
a
a
n
d
I
n
j
u
r
y
M
a
n
a
g
e
m
e
n
t
J
a
n
u
a
r
y
2
0
0
7
S
H
P
N
:
(
T
I
)
0
7
0
0
3
2
Initial GCS 14-15 on arrival following blunt trauma. Stabilise ABCDEs then assess risk factors.
All of ...
1
GCS 15 at 2 hours post injury.
1
No focal neurological deficit.
1
No clinical suspicion of skull fracture. ::1
1
Brief loss of consciousness (<5 mins).
1
Brief anterograde / retrograde amnesia (<30 mins).
1
No post traumatic seizure.
1
Mild nausea or single episode of vomiting.
1
Mild headache.
1
No known coagulopathy.
1
Age <65 years.
1
Isolated head injury without dangerous mechanism.
1
No drug or alcohol ingestion.
1
No known neurosurgery / neurological impairment.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- ITLS 9e Basic Pre-Test - Version 9.2Documento10 pagineITLS 9e Basic Pre-Test - Version 9.2Neil Thomas100% (1)
- ATLS Note Ed 10Documento51 pagineATLS Note Ed 10Nikko Caesario Mauldy Susilo100% (10)
- Neurology Notes - PassmedicineDocumento71 pagineNeurology Notes - PassmedicineMohammad SalehNessuna valutazione finora
- Syncope 08.29.2018Documento16 pagineSyncope 08.29.2018Emily EresumaNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Trauma Life Support (Atls)Documento44 pagineAdvanced Trauma Life Support (Atls)Danar Syahrial PradhiptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Closed Head Injury CPG 2nd Ed Algorithm 2Documento1 paginaClosed Head Injury CPG 2nd Ed Algorithm 2Nick PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- High Risk Mild Head InjuryDocumento1 paginaHigh Risk Mild Head InjuryMay JPNessuna valutazione finora
- Head Injury EciDocumento29 pagineHead Injury EciYullytia Galaksi MharyatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Initial Treatment For Closed Head Injuries PDFDocumento1 paginaInitial Treatment For Closed Head Injuries PDFdiaga081Nessuna valutazione finora
- Head Trauma: Types of Resulting Brain InjuryDocumento6 pagineHead Trauma: Types of Resulting Brain InjuryAnjali ParajuliNessuna valutazione finora
- Trauma KepalaDocumento43 pagineTrauma KepalaAray Al-AfiqahNessuna valutazione finora
- Head Injury GoulburnDocumento47 pagineHead Injury GoulburnSyarifah Maisyura100% (1)
- AISDocumento40 pagineAISMohamed AbdoNessuna valutazione finora
- Head Trauma: Kelompok 2: Andry Wongso Rhiza M.I.S Terri S. S PriscillaDocumento22 pagineHead Trauma: Kelompok 2: Andry Wongso Rhiza M.I.S Terri S. S PriscillaJenadi BinartoNessuna valutazione finora
- HEAD INJURY (Trauma Kepala) DR - AgusDocumento53 pagineHEAD INJURY (Trauma Kepala) DR - AgusSetyo RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurological EmergenciesDocumento11 pagineNeurological Emergenciespunit lakraNessuna valutazione finora
- Head Injury: Which Patients Need Imaging? Which Test Is Best?Documento5 pagineHead Injury: Which Patients Need Imaging? Which Test Is Best?crushnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurological CasesDocumento51 pagineNeurological CasesanisNessuna valutazione finora
- Update: Management of Head InjuriesDocumento38 pagineUpdate: Management of Head InjuriesWilly OematanNessuna valutazione finora
- Update: Management of Head InjuriesDocumento38 pagineUpdate: Management of Head InjuriesRoby Aditya SuryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)Documento48 pagineTraumatic Brain Injury (TBI)Alaa OmarNessuna valutazione finora
- CTC Lecture NotesDocumento28 pagineCTC Lecture NotesAda WongNessuna valutazione finora
- Head Injury 1Documento22 pagineHead Injury 1ahmedfarghaly909090Nessuna valutazione finora
- Head InjuryDocumento39 pagineHead InjuryYonathan asnakeNessuna valutazione finora
- A. Severe Migraine Attack B. Cluster Headache C. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage D. Hypertensive Encephalopathy E. EncephalitisDocumento4 pagineA. Severe Migraine Attack B. Cluster Headache C. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage D. Hypertensive Encephalopathy E. EncephalitisVgdgNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 NeurologyDocumento34 pagine03 Neurologyfire_n_iceNessuna valutazione finora
- IMhpncrisisDocumento8 pagineIMhpncrisischaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiology MS-III Case PresentationDocumento13 pagineCardiology MS-III Case PresentationGirl Oscar-WildeNessuna valutazione finora
- Head Trauma: Drs. Afnan Abdirahman MBBS Elrazi University General Surgery Resident (UOH/IMU)Documento30 pagineHead Trauma: Drs. Afnan Abdirahman MBBS Elrazi University General Surgery Resident (UOH/IMU)DrRahma Ali HeissNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential DiagnosisDocumento5 pagineDifferential Diagnosisjoanna gurtizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Head Injury: Dr. Farhad Bal'Afif, Spbs Bedah Saraf Fkub/Rssa MalangDocumento73 pagineHead Injury: Dr. Farhad Bal'Afif, Spbs Bedah Saraf Fkub/Rssa Malangzakfar evendyNessuna valutazione finora
- Transient Ischemic Attacks: Part I. Diagnosis and EvaluationDocumento10 pagineTransient Ischemic Attacks: Part I. Diagnosis and EvaluationAndi SaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- SubduralhematomaDocumento38 pagineSubduralhematomaNinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Head Injury .Documento26 pagineHead Injury .Lenjun100% (4)
- Head InjuryDocumento2 pagineHead InjuryPheiyi WongNessuna valutazione finora
- Head Trauma (Head Injury) : Thitinan LimchoopornwikulDocumento42 pagineHead Trauma (Head Injury) : Thitinan LimchoopornwikulPasut ChangeNessuna valutazione finora
- Transient Ischemic AttacksDocumento10 pagineTransient Ischemic AttacksfabianounifenasNessuna valutazione finora
- NeurologyDocumento37 pagineNeurologyDevangkumar PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Farin's Grand Round Presentation 31.09.23Documento75 pagineDr. Farin's Grand Round Presentation 31.09.23Anika TasnimNessuna valutazione finora
- Guideline Tce PedDocumento9 pagineGuideline Tce Pedcarolgc99Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cerebral ConcussionDocumento4 pagineCerebral Concussionnur_shakirin0% (1)
- Head Injury and Role of Anaesthesiologist in ManagementDocumento38 pagineHead Injury and Role of Anaesthesiologist in ManagementDeepak SolankiNessuna valutazione finora
- ASN 2016 UPDATE Flash DriveDocumento119 pagineASN 2016 UPDATE Flash DrivethisarNessuna valutazione finora
- ABC Emergency Differential DiagnosisdrererDocumento3 pagineABC Emergency Differential Diagnosisdrerersharu4291Nessuna valutazione finora
- 11.30 Brendan Davies, Acute and Chronic Headache Investigation and Management - 0 PDFDocumento46 pagine11.30 Brendan Davies, Acute and Chronic Headache Investigation and Management - 0 PDFamir ahmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuro Emergencies MccoydDocumento56 pagineNeuro Emergencies Mccoydgirolamoancorato84Nessuna valutazione finora
- Head InjuryDocumento50 pagineHead InjuryThiagarajah RaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Intracranial (Inside The Skull) Hemorrhage (Bleeding)Documento41 pagineIntracranial (Inside The Skull) Hemorrhage (Bleeding)MASIINessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Khairul P. Surbakti, SP.S Departemen Neurologi FK USU/RSUP H. Adam Malik MedanDocumento38 pagineDr. Khairul P. Surbakti, SP.S Departemen Neurologi FK USU/RSUP H. Adam Malik MedanviczNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurology Past Years Before EhsanDocumento345 pagineNeurology Past Years Before EhsanMohammad AlrefaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Head Injury 2022.Documento45 pagineHead Injury 2022.Alia QNessuna valutazione finora
- SAH RevisedDocumento41 pagineSAH RevisedZari NovelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Stroke Management by Carlos L ChuaDocumento61 pagineAcute Stroke Management by Carlos L ChuaRemaica Hernadez100% (1)
- A Case of Headache Turning Into Myeloproliferative Neoplasm-A Case ReportDocumento5 pagineA Case of Headache Turning Into Myeloproliferative Neoplasm-A Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNessuna valutazione finora
- NeuroemDocumento51 pagineNeuroemJameston BostreNessuna valutazione finora
- Cerebral Concussion (Mini Case Study)Documento8 pagineCerebral Concussion (Mini Case Study)Airalyn Chavez AlaroNessuna valutazione finora
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) : Epidural Hematoma Subdural HematomaDocumento62 pagineTraumatic Brain Injury (TBI) : Epidural Hematoma Subdural HematomaRey AlwiwikhNessuna valutazione finora
- ENLS Sub-Arachnoid Hemorrhage ProtocolDocumento22 pagineENLS Sub-Arachnoid Hemorrhage ProtocolFransiskus MikaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Fainting and Blacking Out (Near-Syncope and Syncope) .: - o o o o o o oDocumento3 pagineFainting and Blacking Out (Near-Syncope and Syncope) .: - o o o o o o oLILY MAINNessuna valutazione finora
- Ebp PresentationDocumento17 pagineEbp Presentationapi-252593358Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kuliah Head Injury MakasarDocumento113 pagineKuliah Head Injury MakasarJerrod WilsonNessuna valutazione finora
- MRCP(UK) and MRCP(I) Part II 200 CasesDa EverandMRCP(UK) and MRCP(I) Part II 200 CasesNessuna valutazione finora
- Transient Ischemic Attack, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandTransient Ischemic Attack, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Frequent and Rare Complications of Resuscitation Attempts: ReviewDocumento8 pagineFrequent and Rare Complications of Resuscitation Attempts: ReviewCarmen Garcia OliverNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 - Manejo de DVA en El Shock - Desde La Norepinefrina Al Azul de MetilenoDocumento72 pagine2 - Manejo de DVA en El Shock - Desde La Norepinefrina Al Azul de MetilenoJose Soto (Pepe S)Nessuna valutazione finora
- ALSDocumento35 pagineALSZainal ArifinNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing CS ABG-InterpretationDocumento1 paginaNursing CS ABG-InterpretationJanaNessuna valutazione finora
- DapusDocumento2 pagineDapusAdhi CandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Working at Height Rescue PlanDocumento1 paginaWorking at Height Rescue PlanAbbas AsadNessuna valutazione finora
- 2020 Covid Deaths Ffs EmsDocumento5 pagine2020 Covid Deaths Ffs EmsepraetorianNessuna valutazione finora
- Myocardial InfarctionDocumento1 paginaMyocardial InfarctionjljoioiuNessuna valutazione finora
- Airway Emergency ManagementDocumento47 pagineAirway Emergency ManagementTerefe AlemayehuNessuna valutazione finora
- r215 NremtDocumento1 paginar215 Nremtapi-538596708Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dsi Vs Rsi in TraumaDocumento7 pagineDsi Vs Rsi in TraumaAbhi JeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Apply Basic First AidDocumento17 pagineApply Basic First AidZOOMTECHVOC TRAINING&ASSESSMENTNessuna valutazione finora
- ABCDE ManagementDocumento26 pagineABCDE ManagementHilmy Haydar El-FauzyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 21 Emergency and Disaster Nursing LEWISDocumento22 pagineChapter 21 Emergency and Disaster Nursing LEWISMaythresha GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- 2009 Laerdal CatalogDocumento176 pagine2009 Laerdal CatalogEnerspect Medical Solutions100% (2)
- SOFA ScoreDocumento9 pagineSOFA ScoreIfone takahepisNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdominal and Pelvic Trauma ATLSDocumento36 pagineAbdominal and Pelvic Trauma ATLSlaura cintyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abg Interpretation 2Documento1 paginaAbg Interpretation 2Barbara Casqueira100% (2)
- cc2019b1 SampleDocumento27 paginecc2019b1 SampletanjudinNessuna valutazione finora
- Trauma Performance Rating ModuleDocumento5 pagineTrauma Performance Rating ModuleDayang Feineliza Samman BahjinNessuna valutazione finora
- II-C-1 Gastrointestinal (GI) BleedingDocumento4 pagineII-C-1 Gastrointestinal (GI) BleedingDharylle CariñoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hang Tuah Medical Journal: Research ArtikelDocumento9 pagineHang Tuah Medical Journal: Research ArtikelMaymay DamayNessuna valutazione finora
- National Course Dates 2024Documento2 pagineNational Course Dates 20245gr4wvbbg5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Poly-Trauma: by Dr. Elias Ahmed October 2003Documento14 paginePoly-Trauma: by Dr. Elias Ahmed October 2003Sisay FentaNessuna valutazione finora
- Multitrauma Case Report: Tn. Fauzan/ 27 Y.o/ 2843018 Team On DutyDocumento43 pagineMultitrauma Case Report: Tn. Fauzan/ 27 Y.o/ 2843018 Team On DutyNazila HanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Triage: Blessy Susan BabuDocumento21 pagineTriage: Blessy Susan BabuBlessy SusanNessuna valutazione finora
- ASSIGNMENT ON SHOCK (SEPTIC SHOCK) (AutoRecovered) (AutoRecovered)Documento17 pagineASSIGNMENT ON SHOCK (SEPTIC SHOCK) (AutoRecovered) (AutoRecovered)SabariNessuna valutazione finora