Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
DPSD 2marks
Caricato da
Toni GonzalezDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
DPSD 2marks
Caricato da
Toni GonzalezCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Department of Information Technology CS 2202- DIGITAL PRINCIPLES AND SYSTEM DESIGN Part-A Questions and Answers UNIT-I BOOLEAN
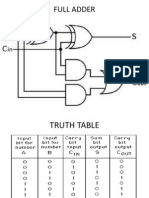
ALGEBRA AND LOGIC GATES 1. Define binary logic? Binary logic consists of binary variables and logical operations. The variables are designated by the alphabets such as A, B, C, x, y, z, etc., with each variable having only two distinct values: 1 and 0.There are three basic logic operations: AND, OR, and NOT. 2. What are the basic digital logic gates? The three basic logic gates are AND gate ,OR gate ,NOT gate 3. What is a Logic gate? Logic gates are the basic elements that make up a digital system. The electronic gate is a circuit that is able to operate on a number ofbinary inputs in order to perform a particular logical function. 4. Which gates are called as the universal gates? What are its advantages? The NAND and NOR gates are called as the universal gates. These gates are used to perform any type of logic application. 5.What do you mean by canonical form? The representation of Boolean function in SOP or POS form, i.e. each term in the expression must contain all the literals of the function either in normal form or complement form. 6.What is an Alpha numeric code? As most of the computers and their peripherals process both alphabetic and numeric information several coding techniques have been invented that represent this alphanumeric information as a series of 1s and 0s. Such codes are called Alpha numeric code. 7.What are error detecting codes? Digital systems should be accurate to the digit. So, detecting errors are very important. The simplest technique for detecting errors is that of adding an extra bit, known as parity bit. These codes are called error detecting codes.
8.What is sequential code? A code is said to be sequential when each succeeding code is one binary number greater than its preceding code. Ex. 8421 BCD, EXCESS 3. 9.What are prime implicants? Prime implicants are building blocks of minimum SOPexpression. 10.What is K- MAP? An arrangement of cells representing the combination of literals or variables in the Boolean expression and used for a systematic simplificationof the expression. 11.What are the advantages of K-map? 1) Kmap is a more orderly process with well definedsteps as compared with the trial and error process sometimes used in algebraic simplification. 2) Requires fewer steps especially for expressions containing many terms, and it always produces a minimum expression. 12.What are dont cares? Dont care term is a minterm for which the combinational logic may output either 1 or 0. 13.Explain about Tabulation method. It is a specific step by step procedure that is guaranteed to produce a simplified standard form expression for a function. It has two parts. The first is to find the terms for inclusion in the simplified function. These terms are called prime i mplicants. The second is to choose among the prime implicants that give an expression with the least number of literals. 14.Encode the number (2345)10 in BCD and excess 3. BCD equivalent : 0010 0011 0100 0101 Excess 3 : 0101 0110 0111 1000 15.State Duality principle. The dual of any Boolean function can be obtained bychanging each OR sign to an AND sign and vice versa and complementing any 0 or 1 appearing in the expression.
16.What is a weighted code? Give example. Weighted binary code are those which obey the positional weighting principle. Example. 8421 BCD code. 17.What is a non-weighted binary code ?Give example Non-weighted codes are the codes that are not positionally weighted. That is each position within the binary number is not assigned a fixed value. Example. Excess 3 code. 18.What is a gray code? The gray code is a binary code in which each successive number differs in only one bit position. It is a non-weighted code and not an arithmetic code. 19.What is signed binary number? In binary system, when the sign is represented by including an additional bit with the magnitude bits, usually a zero represents positive sign and a1 represents negative sign. These binary numbers are called as signed binary numbers. 20.What is a decimal number system? A decimal number system has a radix (Base r=10) anduses symbols 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9. Eg. (237) 10 UNIT-II COMBINATIONAL LOGIC 1.Define Positive Logic. When high voltage or more positive voltage level isassociated with binary 1 and while the low orless positive level is associated with binary 0 then the system adhere to this is called positive logic. 2.Define Negative Logic. When high voltage level is associated with binary 0 and while the low level is associated with binary 1 then the system adhering to this is called negative logic 3.List the characteristics of digital Ics i)propagation delay ii)power dissipation iii)Fan-in iv)Fan-out v)Noise margin
4. What is propagation delay? It is the average transition delay time for the signal to propagate from input to output when the signals change in value. 5. What is Noise margin? It is the limit of a noise voltage, which may bepresent with out impairing the proper operation ofthe circuit. 6. What is power dissipation? It is the power consumed by the gate, which mustbe available from the power supply. 7. Why parity checker is needed? Parity checker is required at the receiver side to check whether the expected parity is equal tothe calculated parity or not. If they are not equal then it is found that the received data has error. 8. What is meant by parity bit? Parity bit is an extra bit included with a binary message to make the number of 1s either odd or even. The message, including the parity bit is transmitted and then checked at the receiving and for errors.. 9. What is IC? An integrated circuit is a small silicon semiconductor crystal called a chip containing electrical components such as transistors, diodes, resistors a nd capacitors. The various components are interconnected inside the chip to form an electronic circuit. 10. What are the needs for binary codes? a.Code is used to represent letters, numbers and punctuation marks. b.Coding is required for maximum efficiency in singletransmission. c.Binary codes are the major components in the synthesis (artificial generation) of speech and video signals. d.By using error detecting codes, errors generated in signal transmission can be detected. e.Codes are used for data compression by which large amounts of data are transmitted in very short duration of time.
11. Mention the different type of binary codes? The various types of binary codes are, f.BCD code (Binary Coded decimal). g.Self-complementing code. h.The excess-3 (Xs-3) code. i.Gray code. j.Binary weighted code. k.Alphanumeric code. l.The ASCII code. m.Extended binary-coded decimal interchange code (EBCDIC). n.Error-detecting and error-correcting code. o.Hamming code. 12. List the advantages and disadvantages of BCD code? The advantages of BCD code are a.Any large decimal number can be easily converted into corresponding binary number b.A person needs to remember only the binary equivalents of decimal number from 0 to 9. c.Conversion from BCD into decimal is also very easy.The disadvantages of BCD code are a.The code is least efficient. It requires several symbols to represent even small numbers. b.Binary addition and subtraction can lead to wrong answer. c.Special codes are required for arithmetic operations. d.This is not a self-complementing code. e.conversion into other coding schemes requires special methods. 13. What is meant by self-complementing code? A self-complementing code is the one in which the members of the number system complement on themselves. This requires the following two conditions to be satisfied. a.The complement of the number should be obtained from that number by replacing 1s with 0s and 0s with 1s. b.The sum of the number and its complement should be equal to decimal 9. Example of a self-complementing code is i.2-4-2-1 code. ii.Excess-3 code.
14. Mention the advantages of ASCII code? The following are the advantages of ASCII code a.There are 27 =128 possible combinations. Hence, a large number of symbols, alphabets etc.., can be easily represented. b.There is a definite order in which the alphabets, etc.., are assigned to each code word. c.The parity bits can be added for error-detection and correction. 15. What are the disadvantages of ASCII code? The disadvantages of ASCII code are a.The length of the code is larger and hence more bandwidth is required for transmission. b.With more characters and symbols to represent, thisis not completely sufficient. 16. What is the truth table? A truth table lists all possible combinations of inputs and the corresponding outputs 17. Define figure of merit? Figure of merits is defined as the product of speedand power. The speed is specified in terms of propagation delay time expressed in nano seconds Figure of merits=Propagation delay time (ns) * Power (mw) It is specified in pico joules (ns*mw=PJ). 18. Define Combinational circuit. A combinational circuit consist of logic gates whose outputs at anytime are determined directly from the present combination of inputs without regard to previous inputs. 19. Define sequential circuits. Their outputs are a function of the inputs and thestate of memory elements. The state of memory elements, in turn, is a function of previous inputs . 20. What is Binary parallel adder? A binary parallel adder is a digital function thatproduces the arithmetic sum of two binary numbers in parallel.
UNIT-III DESIGN WITH MSI DEVICES 1.Define Decoder? A decoder is a multiple - input multiple output logic circuit that converts coded inputs into coded outputs where the input and output codes are different. 2.What is binary decoder? A decoder is a combinational circuit that converts binary information from n input lines to a maximum of 2n out puts lines. 3.Define Encoder? An encoder has 2n input lines and n output lines. In encoder the output lines generate the binary code corresponding to the input value. 4.What is priority Encoder? A priority encoder is an encoder circuit that includes the priority function. In priority encoder, if 2 or more inputs are equal to 1 at the same time, the in put having the highest priority will take precedence. 5.Define multiplexer? Multiplexer is a digital switch. If allows digital information from several sources to be routed onto a single output line. 6.What do you mean by comparator A comparator is a special combinational circuit designed primarily to compare the relative magnitude of two binary numbers. 7.List basic types of programmable logic devices. . Read only memory . Programmable logic Array . Programmable Array Logic 8.Explain ROM A read only memory(ROM) is a device that includes both the decoder and the OR gates within a single IC package. It consists of n input lines andm output lines. Each bit combination of the input variables is called an address. Each bit combination that comes out of the output lines is called a word. The number of distinct addresses possible with n input variables is 2n.
9.Define address and word: In a ROM, each bit combination of the input variable is called on address. Each bit combination that comes out of the output lines is called a word. 10.State the types of ROM . Masked ROM. . Programmable Read only Memory . Erasable Programmable Read only memory. . Electrically Erasable Programmable Read only Memory. 11.What is programmable logic array? How it differs from ROM? In some cases the number of dont care conditions is excessive, it is more economical to use a second type of LSI component called a PLA. A PLA is simila r to a ROM in concept; however it does not provide full decoding of the variables and does notgenerates all the minterms as in the ROM. 12.What is RAM? Random Access Memory. Read and write operations canbe carried out. 13.. What is programmable logic array? How it differs from ROM? In some cases the number of dont care conditions is excessive, it is more economical to use a second type of LSI component called a PLA. A PLA is similar to a ROM in concept; however it does not provide full decoding of the variables and does not generates all the minterms as in the ROM. 14.List the major differences between PLA and PAL PLA: Both AND and OR arrays are programmable and Complex Costlier than PAL PAL AND arrays are programmable OR arrays are fixed Cheaper and Simpler 15.Define PLD. Programmable Logic Devices consist of a large arrayof AND gates and OR gates that can be programmed to achieve specific logic functions. 16.Give the classification of PLDs. PLDs are classified as PROM(Programmable Read Only Memory), Programmable Logic Array(PLA), Programmable Array Logic (PAL), and Generic Array Logic(GAL)
17. Define PROM. PROM is Programmable Read Only Memory. It consists of a set of fixed AND gates connected to a decoder and a programmable OR array. 18. Define PLA PLA is Programmable Logic Array(PLA). The PLA is a PLD that consists of a programmable AND array and a programmable OR array. 19. Define PAL PAL is Programmable Array Logic. PAL consists of a programmable AND array and a fixed OR array with output logic. 20. Give the comparison between PROM and PLA. PROM PLA 1. And array is fixed and OR array is programmable. 2. Cheaper and simple to use. 1. Both AND and OR arrays are Programmable. 2. Costliest and complex than PROMS. UNIT IV SYNCHRONOUS SEQUENTIAL LOGIC 1. What are the classification of sequential circuits ? The sequential circuits are classified on the basis of timing of their signals into two types. They are, 1)Synchronous sequential circuit. 2)Asynchronous sequential circuit. 2. Define Flip flop. The basic unit for storage is flip flop. A flip-flo p maintains its output state either at 1
or 0 until directed by an input signal to change it s state. 3. .What are the different types of flip-flop? There are various types of flip flops. Some of them are mentioned below they are, RS flip-flop SR flip-flop D flip-flop JK flip-flop T flip-flop 4. .What is the operation of D flip-flop? In D flip-flop during the occurrence of clock pulse if D=1, the output Q is set and if D=0, the output is reset. 5. What is the operation of JK flip-flop? When K input is low and J input is high the Q outpu t of flip-flop is set. When K input is high and J input is low the Q outpu t of flip-flop is reset. When both the inputs K and J are low the output doe s not change When both the inputs K and J are high it is possibl e to set or reset the flip-flop (ie) the output toggle on the next positive clock edge. 6. What is the operation of T flip-flop? T flip-flop is also known as Toggle flip-flop.
When T=0 there is no change in the output. When T=1 the output switch to the complement state (ie) the output toggles. 7. Define race around condition. In JK flip-flop output is fed back to the input. Th erefore change in the output results change in the input. Due to this in the positive half of the cloc k pulse if both J and K are high then output toggle s continuously. This condition is called race around condition. 8. What is edge-triggered flip-flop? The problem of race around condition can solved by edge triggering flip flop. The term edge triggering means that the flip-flop changes state e ither at the positive edge or negative edge of the clock pulse and it is sensitive to its inputs only at this transition of the clock. 9. What is a master-slave flip-flop? A master-slave flip-flop consists of two flip-flops where one circuit serves as a master and the other as a slave. 10. .Define rise time. The time required to change the voltage level from 10% to 90% is known as rise time(t r ). 11. Define fall time. The time required to change the voltage level from 90% to 10% is known as fall time(t f ). 12. Define registers.
A register is a group of flip-flops flip-flop can s tore one bit information. So an n-bit register has a group of n flip-flops and is capable of storing any binary information/number containing n-bits. 13. Define shift registers. The binary information in a register can be moved f rom stage to stage within the register or into or out of the register upon application of clock pulse s. This type of bit movement or shifting is essenti al for certain arithmetic and logic operations used in microprocessors. This gives rise to group of registers called shift registers. 14. What are the different types of shift type? There are five types. They are, Serial In Serial Out Shift Register Serial In Parallel Out Shift Register Parallel In Serial Out Shift Register Parallel In Parallel Out Shift Register Bidirectional Shift Register 15. Explain the flip-flop excitation tables for RS FF. In RS flip-flop there are four possible transitions from the present state to the next state. They are , 0 to 0 transition: This can happen either when R=S= 0 or when R=1 and S=0. 0 to 1 transition: This can happen only when S=1 an d R=0.
1 to 0 transition: This can happen only when S=0 an d R=1. 1 to 1 transition: This can happen either when S=1 and R=0 or S=0 and R=0. 16. . Define sequential circuit? In sequential circuits the output variables depende nt not only on the present input variables but they also depend up on the past history of these input v ariables. 17. .Give the comparison between combinational circuits and sequential circuits. Combinational circuits Sequential circuits Memory unit is not required Memory unity is require d Parallel adder is a combinational circuit Serial ad der is a sequential circuit 18. What do you mean by present state? The information stored in the memory elements at an y given time defines the present state of the sequential circuit. 19. What do you mean by next state? The present state and the external inputs determine the outputs and the next state of the sequential circuit. 20. State the types of sequential circuits? 1. Synchronous sequential circuits 2. Asynchronous sequential circuits. Unit- V ASYNCHRONOUS SEQUENTIAL LOGIC 1. Define Asynchronous sequential circuit? In asynchronous sequential circuits change in input signals can affect memory element at any instant of time. 2.
What is race around condition? In the JK latch, the output is feedback to the inpu t, and therefore changes in the output results chan ge in the input. Due to this in the positive half of t he clock pulse if J and K are both high then output toggles continuously. This condition is known as ra ce around condition. 3. .What are secondary variables? present state variables in asynchronous sequential circuits 4. What are excitation variables? next state variables in asynchronous sequential cir cuits. 5. What is fundamental mode sequential circuit? input variables changes if the circuit is stable inputs are levels, not pulses only one input can change at a given time 6. What are pulse mode circuit? inputs are pulses width of pulses are long for circuit to respond to the input pulse width must not be so long that it is still pr esent after the new state is reached 7. What is the significance of state assignment? In synchronous circuits-state assignments are made with the objective of circuit reduction
Asynchronous circuits-its objective is to avoid cri tical races. 8. When do race conditions occur? two or more binary state variables change their val ue in response to the change in i/p variable 9. What is non critical race? final stable state does not depend on the order in which the state variable changes race condition is not harmful 10. What is critical race? final stable state depends on the order in which th e state variable changes race condition is harmful 11. When does a cycle occur? asynchronous circuit makes a transition through a s eries of unstable state 12.What are the different techniques used in state assignment? shared row state assignment one hot state assignment 13. What are the steps for the design of asyn chronous sequential circuit? construction of primitive flow table reduction of flow table state assignment is made realization of primitive flow table 14. What is hazard? What are its types
unwanted switching transients static, dynamic and essential. 15 .What is static 1 hazard and static 0 hazar d? output goes momentarily 0 when it should remain at 1 output goes momentarily 1 when it should remain at 0 16. What is dynamic hazard? output changes 3 or more times when it changes from 1 to 0 or 0 to 1 17. What are races? When 2 or more binary state variables change their value in response to a change in an input variable, race condition occurs in an asynchronous sequential circuit. In case of unequal delays, a race condition may cause the state variables to change i n an unpredictable manner. 18. Define non critical race. If the final stable state that the circuit reaches does not depend on the order in which the state variable changes, the race condition is not harmful and it is called a non critical race. 19. Define critical race? If the final stable state depends on the order in w hich the state variable changes, the race condition is harmful and it is called a critical race. 20. . Write a short note on fundamental mode asynchrono us circuit. Fundamental mode circuit assumes that. The input va riables change only when the circuit is stable. Only one input variable can change at a given time and inputs are levels and not pulses.
21. Write a short note on pulse mode circuit. Pulse mode circuit assumes that the input variables are pulses instead of level. The width of the pulses is long enough for the circuit to respond to the input and the pulse width must not be so long that it is still present after the new state is rea ched. 22. Define secondary variables The delay elements provide a short term memory for the sequential circuit. The present state and next state variables in asynchronous sequential circuits are called secondary variables. 23. Define flow table in asynchronous sequential circu it. In asynchronous sequential circuit state table is k nown as flow table because of the behaviour of the asynchronous sequential circuit. The stage changes occur in independent of a clock, based on the logic propagation delay, and cause the states to .f low. from one to another. 24. What is fundamental mode.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Combinational Logic CircuitsDocumento17 pagineCombinational Logic CircuitsAdarsha Bhattarai100% (1)
- Bebop to the Boolean Boogie: An Unconventional Guide to ElectronicsDa EverandBebop to the Boolean Boogie: An Unconventional Guide to ElectronicsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (3)
- PIC Projects and Applications using C: A Project-based ApproachDa EverandPIC Projects and Applications using C: A Project-based ApproachValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- DIgital Electronics Lab Exam Viva QuestionsDocumento6 pagineDIgital Electronics Lab Exam Viva Questionsmehek saba100% (19)
- Basic Digital Signal Processing: Butterworths Basic SeriesDa EverandBasic Digital Signal Processing: Butterworths Basic SeriesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Binary CodesDocumento32 pagineBinary CodesJatin Suri100% (1)
- Digital Principels and System DesignDocumento53 pagineDigital Principels and System Designnofeelingrahul100% (1)
- Object CounterDocumento39 pagineObject CounterNARESH WALIA100% (1)
- Digital Electronics: Question and Answers (Question Bank)Documento12 pagineDigital Electronics: Question and Answers (Question Bank)api-297153951100% (1)
- Channel Coding For Modern Communication Systems: Presented by Yasir Mehmood (200411018)Documento20 pagineChannel Coding For Modern Communication Systems: Presented by Yasir Mehmood (200411018)MaryamNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Electronics Question Bank, Digital Electronics 2 Mark Questions & AnswersDocumento22 pagineDigital Electronics Question Bank, Digital Electronics 2 Mark Questions & Answerssaipradeepkp92% (74)
- Digital Principle and System DesignDocumento26 pagineDigital Principle and System Designainugiri100% (4)
- DFT QnsDocumento6 pagineDFT QnsRajishaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dec Lab QuestionsDocumento25 pagineDec Lab QuestionsPrathiksha Harish Medical Electronics EngineeringNessuna valutazione finora
- Embedded Systems ExamDocumento3 pagineEmbedded Systems ExamHumberto ValadezNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 MarkDocumento28 pagine2 Markcoolrammi19Nessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Principles UNIT 1 FinalDocumento86 pagineDigital Principles UNIT 1 FinalSathish Kumar0% (1)
- Digital Principle and System Design 2marks and 12 MarksDocumento43 pagineDigital Principle and System Design 2marks and 12 MarksTamil Mani100% (1)
- Cs8351-Digital Principles and System DesignDocumento4 pagineCs8351-Digital Principles and System DesignsathishNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter I Review of Basics of Digital ElectronicsDocumento21 pagineChapter I Review of Basics of Digital ElectronicsMia LateNessuna valutazione finora
- DPSD 2 MarksDocumento19 pagineDPSD 2 MarksKavya DharshiniNessuna valutazione finora
- DIGITAL ELECTRONICS 2marksDocumento10 pagineDIGITAL ELECTRONICS 2marksHOD ECE JACSICENessuna valutazione finora
- Dpco Book1Documento4 pagineDpco Book1SELVAM SNessuna valutazione finora
- DC Unit Test 2 Question BankDocumento4 pagineDC Unit Test 2 Question BankSiva KrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Advantages of Digital SystemsDocumento26 pagineAdvantages of Digital Systemsayyanar7Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2 QB104321Documento4 pagine2 QB104321DevisriNessuna valutazione finora
- DownloadDocumento13 pagineDownloadArunNessuna valutazione finora
- DIGITAL-2marks Q&ADocumento12 pagineDIGITAL-2marks Q&Asai kiruthika KMNessuna valutazione finora
- Low-Complexity Low-Latency Architecture For Identical of Data Encoded With Hard Systematic Error-Correcting CodesDocumento104 pagineLow-Complexity Low-Latency Architecture For Identical of Data Encoded With Hard Systematic Error-Correcting CodesJaya SwaroopNessuna valutazione finora
- Iare de Lecture Notes PDFDocumento147 pagineIare de Lecture Notes PDFRajkumar RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice4 (Adder & SustractorDocumento7 paginePractice4 (Adder & SustractorManolo-Hues Diaz SNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment of Digital Techniques - Docx PrinceDocumento8 pagineAssignment of Digital Techniques - Docx PrincePranshu MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital ElectronicsDocumento28 pagineDigital Electronicspriya adhavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Principles and System DesignDocumento76 pagineDigital Principles and System Designraja rNessuna valutazione finora
- Which Uses Binary Number Systems To Store and ProcessDocumento19 pagineWhich Uses Binary Number Systems To Store and ProcessShahriyar ShantoNessuna valutazione finora
- TurboDocumento10 pagineTurboAlireza MovahedianNessuna valutazione finora
- DLD Unit 1 PDFDocumento14 pagineDLD Unit 1 PDFollata kalanoNessuna valutazione finora
- DL - Manual - 16-17Documento88 pagineDL - Manual - 16-17Aayush MahantNessuna valutazione finora
- Two Mark Questions 1Documento16 pagineTwo Mark Questions 1pl.babyshalini palanisamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Techniques VIVA ANSWERS 3rd SEMDocumento6 pagineDigital Techniques VIVA ANSWERS 3rd SEMOSA MEMBERNessuna valutazione finora
- A FEC Decoding in LTE and WiMAX SystemsDocumento4 pagineA FEC Decoding in LTE and WiMAX SystemsseventhsensegroupNessuna valutazione finora
- csc213 AssignmentDocumento8 paginecsc213 Assignmentstevefocus01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mod 1 2Documento20 pagineMod 1 2Naseef RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Gates Institute of Technology:: Gooty Digital Circuits and Systems 2 Marks With AnswersDocumento17 pagineGates Institute of Technology:: Gooty Digital Circuits and Systems 2 Marks With AnswersNaveen YallapuNessuna valutazione finora
- Gates Institute of Technology:: Gooty Digital Circuits and Systems 2 Marks With AnswersDocumento20 pagineGates Institute of Technology:: Gooty Digital Circuits and Systems 2 Marks With AnswersNaveen YallapuNessuna valutazione finora
- Dec Lab ManualDocumento5 pagineDec Lab ManualSam XingxnNessuna valutazione finora
- LDPC - Low Density Parity Check CodesDocumento6 pagineLDPC - Low Density Parity Check CodespandyakaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Logic Circuit DesignDocumento15 pagineLogic Circuit Designajas777BNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-1: 1.1: Coding TheoryDocumento35 pagineChapter-1: 1.1: Coding Theoryhari chowdaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Circuits & Logic DesignsDocumento23 pagineDigital Circuits & Logic DesignssamNessuna valutazione finora
- Channel Coding For Modern Communication SystemsDocumento4 pagineChannel Coding For Modern Communication SystemsMaryamNessuna valutazione finora
- Turbo Codes: Farah Ilyas Vohra (TC-28), Shafaq Mustafa (TC-13), Sabieka Rizvi (TC-61) and Zainab Qazi (TC-11)Documento5 pagineTurbo Codes: Farah Ilyas Vohra (TC-28), Shafaq Mustafa (TC-13), Sabieka Rizvi (TC-61) and Zainab Qazi (TC-11)Zainab QaziNessuna valutazione finora
- Turbo Codes: Lovely Professional University, Punjab Aman Gahoi, 11111771 A54Documento5 pagineTurbo Codes: Lovely Professional University, Punjab Aman Gahoi, 11111771 A54autorangersNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance Evaluation For Convolutional Codes Using Viterbi DecodingDocumento6 paginePerformance Evaluation For Convolutional Codes Using Viterbi Decodingbluemoon1172Nessuna valutazione finora
- QB104322Documento4 pagineQB104322abhirupnath666Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics ProjectDocumento24 paginePhysics ProjectSanskar BawniyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cour Se or Ient at Ion: Course Description: This Course Is The FirstDocumento55 pagineCour Se or Ient at Ion: Course Description: This Course Is The FirstLeonelyn Hermosa Gasco - CosidoNessuna valutazione finora
- Error-Correction on Non-Standard Communication ChannelsDa EverandError-Correction on Non-Standard Communication ChannelsNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 3: Assignment SolutionsDocumento4 pagineWeek 3: Assignment SolutionsTapti SoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Instruction Level Parallelism: Module 5: Chapter 12Documento13 pagineInstruction Level Parallelism: Module 5: Chapter 12yashu JNessuna valutazione finora
- AN 114: Board Design Guidelines For Intel Programmable Device PackagesDocumento35 pagineAN 114: Board Design Guidelines For Intel Programmable Device PackagesAymane FahmiNessuna valutazione finora
- DSD Syllabus - Calicut UniversityDocumento2 pagineDSD Syllabus - Calicut UniversityiammanuprasadNessuna valutazione finora
- Adama Science and Technology University School of Electrical Eng.& Computing Department of Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocumento3 pagineAdama Science and Technology University School of Electrical Eng.& Computing Department of Electronics & Communication EngineeringAlazar GetachewNessuna valutazione finora
- VLSI 100 QuestionsDocumento4 pagineVLSI 100 Questionsapi-3824368Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vlsisyll 22Documento91 pagineVlsisyll 22MaheshReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- VLSI Lab ManualDocumento46 pagineVLSI Lab ManualPriyam JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Logic Design: Latches, Flip-Flops, and TimersDocumento69 pagineDigital Logic Design: Latches, Flip-Flops, and TimersSheikh Jawwad AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Time TableDocumento7 pagineTime TablearupNessuna valutazione finora
- Docs Openhwgroup Org Openhw Group Cv32e41p en LatestDocumento100 pagineDocs Openhwgroup Org Openhw Group Cv32e41p en LatestSaheba ShaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Single Supply, Low Power Dual Comparators: Semiconductor Technical DataDocumento6 pagineSingle Supply, Low Power Dual Comparators: Semiconductor Technical DataNick DNessuna valutazione finora
- Full AdderDocumento4 pagineFull AdderMuniba Ahmad0% (1)
- Chapter 1: Further Sequential Logic Systems Synchronous CountersDocumento34 pagineChapter 1: Further Sequential Logic Systems Synchronous CountersKKK enNessuna valutazione finora
- Datasheet stm8s903k3Documento124 pagineDatasheet stm8s903k3Giban SeraosNessuna valutazione finora
- LPC1114 HandsOnDocumento68 pagineLPC1114 HandsOnKunil KudaNessuna valutazione finora
- W4823x SyllabusDocumento4 pagineW4823x Syllabuszhangtianyi199Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kongunadu College of Engineering and Technology, ThourpattiDocumento1 paginaKongunadu College of Engineering and Technology, ThourpattishankarNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Electronics - Final Assignment - American International University BangladdeshDocumento5 pagineAnalog Electronics - Final Assignment - American International University BangladdeshSHAHRIAR SHOVANNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review of Manchester, Miller, and FM0 Encoding TechniquesDocumento10 pagineA Review of Manchester, Miller, and FM0 Encoding TechniquesMusic LyricsNessuna valutazione finora
- SPI Verification Guide PDFDocumento3 pagineSPI Verification Guide PDFImtiyaz Pasha Shaik100% (1)
- Module 1: Mos Transistor Theory: Dr. G. Lakshmi Priya, AP (SG), SENSE, VIT, ChennaiDocumento14 pagineModule 1: Mos Transistor Theory: Dr. G. Lakshmi Priya, AP (SG), SENSE, VIT, ChennaiASHUTOSHNessuna valutazione finora
- بدون حل اسئلة الفصل االاول الدور الثاني - 2020Documento3 pagineبدون حل اسئلة الفصل االاول الدور الثاني - 2020Mohammed YounisNessuna valutazione finora
- Low Voltage and Low Power in Sram Read and Write Assist TechniquesDocumento9 pagineLow Voltage and Low Power in Sram Read and Write Assist TechniquesIJSTENessuna valutazione finora
- EE 552 (Logic Design and Switching Theory) Project: Quantitative Measurement of The Benefits of Reduction Techniques For Asynchronous Finite State MachinesDocumento9 pagineEE 552 (Logic Design and Switching Theory) Project: Quantitative Measurement of The Benefits of Reduction Techniques For Asynchronous Finite State MachinesTamiltamil TamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Study of SoIC and 3D PackagingDocumento11 pagineStudy of SoIC and 3D PackagingAllen SuNessuna valutazione finora
- Which Among Following Can Be Considered As Most Advanced ROM ?Documento5 pagineWhich Among Following Can Be Considered As Most Advanced ROM ?Krishnakumar VeerabathranNessuna valutazione finora
- VSD 2021 HW1 Explanation Ver1.2Documento24 pagineVSD 2021 HW1 Explanation Ver1.2N26112372崔哲瑋Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2nm Semiconductor TechnologyDocumento20 pagine2nm Semiconductor TechnologyYash ChaudhariNessuna valutazione finora