Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Frederick Taylor
Caricato da
Anna TongcoCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Frederick Taylor
Caricato da
Anna TongcoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Madaray, Magsambol, Salvacion, Santiago, Tongco
HRIM 112
FREDERICK WINSLOW TAYLOR Father of Scientific Management
Biography Early Life Born on 20 March 1856 in Germantown, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Parents: o Franklin Taylor o Emily Annette Taylor (ne Winslow) Marriage: o Louise M. Spooner of Philadelphia o 3 May 1884
Education Educated early by his mother Studied for 2 years in France and Germany; travelled Europe for 18 months 1872: entered Philips Exeter Academy (Exeter, New Hampshire) 1874: passed Harvard entrance examinations with honors Became an apprentice pattern-maker and machinist
Work Enterprise Hydraulic Works o Founded in Philadelphia o Pump-manufacturing company Death -
1878: Midvale Steel Works o Machine-shop labourer o Start of Taylors management observations o Recognized that workmen were not utilizing machines or skills efficiently 1890 1893: Manufacturing Investment Company of Philadelphia o General manager and consulting engineer to management o Company operations of large paper mills in Maine and Wisconsin 1893: independent consulting practice in Philadelphia 1898: Bethlehem Steel 1901: focused on promoting management and machining methods 1911: publication of The Principles of Scientific Management to The American Mechanical Engineering Society 19 October 1906: honorary degree of Doctor of Science by University of Pennsylvania; became a professor at Tuck School of Business in Dartmouth College
Date: 21 March 1915 Cause: pneumonia
Buried in West Laurel Hill Cemetary, Bala Cynwyd, Pennsylvania
Allocate work between managers and workers, so that the managers spend their time planning and training, and the workers actually perform the tasks efficiently.
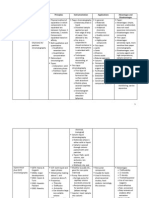
Scientific Management How did it start? Taylor and his associates were the first to study the work process scientifically Studied how work was performed and how this affected worker productivity Main philosophy: Making people work as hard as they could was not as efficient as optimizing the way the work was done Techniques Functional foremanship o Extension of principle of Division of Work/ specialization o Each worker takes orders from 8 foremen during production process o 8 specialists: Instruction card clerk Route clerk Time and cost clerk Disciplinarian Gang boss Repair boss Inspector Speed boss Standardization of work o Process of setting standards for every business activity o Ensures that they are of the required quality and quantity o Allows work to proceed at a faster pace with greater ease Simplification of work o Eliminate unnecessary diversity of products o Objectives: Effecting economy in the use of machines Bring down labor cost Affect economy in the staff
Main ideas Productivity increases when jobs are optimized and simplified Workers and managers need to cooperate with one another A fair days pay for a fair days work.
Four Principles of Scientific Management Replace rule-of-thumb work methods with methods based on a scientific study of the tasks. Scientifically select, train, and develop each employee rather than passively leaving them to train themselves. Monitor worker performance, and provide supervision to ensure that they are using the most efficient ways.
Scientific study of work o Conduct deep analysis of all activities being performed o Aims to produce maximum possible quality output at minimum costs o Studies conducted by Taylor: Method study Motion study Time study Fatigue study Differential piece wage system o Rewards efficient workers while motivating less efficient ones to improve performance Mental revolution o Change in mind-set of both employers and workers o Promote feelings of cooperation
Legacy One of the first attempts to treat management systematically Emphasized cooperation between workers and managers Studied workplace efficiency and systematic organizational design Allowed for advancement of quality assurance, modern quality control Led to creation of knowledge management, modern human resources
References Conclusion Benefits Increase in productivity Decrease in inaccuracy Better utilization of resources Harmonious relationship between workers and managers Piecework pay system provides incentives to maximize productivity Early working method and control http://notes.tyrocity.com/advantagesand-limitations-of-scientificmanagement/ http://www.mindtools.com/pages/arti cle/newTMM_Taylor.htm http://kalyancity.blogspot.com/2011/06/fredericktaylor-principles-of.html http://www.yourarticlelibrary.com/m anagement/6-different-techniques-ofscientific-management/887/ http://commerceedu.wordpress.com/ about/principles-ofmanagement/techniques-ofscientific-management/
Limitations Investment of huge capital Lack of flexibility Neglects human factor one right way to do something
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Anions TestingDocumento1 paginaAnions TestingAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- HACCP (Tagalog) - MPVAzanzaDocumento6 pagineHACCP (Tagalog) - MPVAzanzaAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Service Standard - City of Paranaque, PhilippinesDocumento23 pagineService Standard - City of Paranaque, PhilippinesAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Happy Birthday - KalimbaDocumento1 paginaHappy Birthday - KalimbaAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Remember Me (Coco OST) - KalimbaDocumento2 pagineRemember Me (Coco OST) - KalimbaAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Over The Rainbow - KalimbaDocumento2 pagineOver The Rainbow - KalimbaAnna Tongco100% (2)
- (Korea) Labeling of Unprocessed Commodities Enhanced Through BiotechnologyDocumento3 pagine(Korea) Labeling of Unprocessed Commodities Enhanced Through BiotechnologyAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- BLS Review and AEDsDocumento17 pagineBLS Review and AEDsAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Planning in ManagementDocumento22 paginePlanning in ManagementAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Reservation Form For Wedding in The Parish New PDFDocumento2 pagineReservation Form For Wedding in The Parish New PDFAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- PNS For Table EggsDocumento24 paginePNS For Table EggsAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ryan Caybyab - Araw GabiDocumento6 pagineRyan Caybyab - Araw GabiAnna Tongco81% (16)
- Birch Wedding Guide EbookDocumento52 pagineBirch Wedding Guide EbookAnna Tongco100% (2)
- Psalm 73Documento4 paginePsalm 73Anna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Behind The Scenes of CoffeeDocumento33 pagineBehind The Scenes of CoffeeAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Interaction With Oxidizing LipidsDocumento5 pagineProtein Interaction With Oxidizing LipidsAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Report: Electrochemistry and Electrode PotentialDocumento12 pagineLab Report: Electrochemistry and Electrode PotentialAnna Tongco100% (2)
- Electron and Molecular GeometryDocumento2 pagineElectron and Molecular GeometryAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Qualitative Analysis For AnionsDocumento1 paginaQualitative Analysis For AnionsAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- SodiumDocumento27 pagineSodiumAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Organization in ManagementDocumento38 pagineOrganization in ManagementAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Liquid ChromatographyDocumento17 pagineLiquid ChromatographyAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- ChlorideDocumento22 pagineChlorideAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Detection of Vibrio Spp. in Raw Maguro SashimiDocumento18 pagineDetection of Vibrio Spp. in Raw Maguro SashimiAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Frog Dissection: Skeletal and Muscular SystemsDocumento10 pagineFrog Dissection: Skeletal and Muscular SystemsAnna Tongco87% (15)
- MagnesiumDocumento30 pagineMagnesiumAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper CranesDocumento2 paginePaper CranesAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Instrumental Methods For Identification of Components in FoodDocumento15 pagineAdvanced Instrumental Methods For Identification of Components in FoodAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Histology, Frog MusculatureDocumento4 pagineHistology, Frog MusculatureAnna TongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Summary BMKT 525 Marketing ManagementDocumento112 pagineSummary BMKT 525 Marketing ManagementSobhi BraidyNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study On Business Model Adopted by The Pogo Travels: Abu Sufiyan 151GCMD006 R V Institute of ManagementDocumento12 pagineCase Study On Business Model Adopted by The Pogo Travels: Abu Sufiyan 151GCMD006 R V Institute of ManagementSUFIYANNessuna valutazione finora
- The Kurt Salmon Review Issue 05 VFSP PDFDocumento68 pagineThe Kurt Salmon Review Issue 05 VFSP PDFDuc NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Abm003 PT1Documento2 pagineAbm003 PT1Ma. Cristina CaraldeNessuna valutazione finora
- 2023 BusinessKids Convention ReportDocumento18 pagine2023 BusinessKids Convention ReportClaudia Isabel MirelesNessuna valutazione finora
- PsuDocumento2 paginePsuManas KapoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Transaction Event Keys pdf-1Documento4 pagineTransaction Event Keys pdf-1vedant maheshwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Feature Article: Value Analysis/Value Engineering: The Forgotten Lean TechniqueDocumento37 pagineFeature Article: Value Analysis/Value Engineering: The Forgotten Lean Techniquekish007rdNessuna valutazione finora
- The Measurement of Service Quality With Servqual For Different Domestic Airline Firms in TurkeyDocumento12 pagineThe Measurement of Service Quality With Servqual For Different Domestic Airline Firms in TurkeySanjeev PradhanNessuna valutazione finora
- BSBMGT608 Student Assessment Tasks 2020Documento45 pagineBSBMGT608 Student Assessment Tasks 2020Chirayu ManandharNessuna valutazione finora
- Entrepreneurship and Economic DevelopmentDocumento44 pagineEntrepreneurship and Economic Developmentgosaye desalegn100% (1)
- 5s As A Tool and Strategy For Improvising The Work PlaceDocumento3 pagine5s As A Tool and Strategy For Improvising The Work PlaceOscar PedrozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 Master DataDocumento13 pagineUnit 2 Master DatabalavenakatarajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Cebu Pacific Defense Paper 1Documento25 pagineCebu Pacific Defense Paper 1Paula Enriquez100% (2)
- Special Purpose Vehicle in Project Finance - Group 1-Batch 2Documento10 pagineSpecial Purpose Vehicle in Project Finance - Group 1-Batch 2Blesson PerumalNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Plan For Fertilizers DistributorsDocumento20 pagineBusiness Plan For Fertilizers DistributorsRanjan Shetty94% (17)
- Project Cutover PlanDocumento9 pagineProject Cutover PlanPrashant KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Weirich7e Casesolutions-3Documento37 pagineWeirich7e Casesolutions-3Connor Day50% (4)
- T3TMD - Miscellaneous Deals - R10Documento78 pagineT3TMD - Miscellaneous Deals - R10KLB USERNessuna valutazione finora
- Pas1192 6 2018Documento76 paginePas1192 6 2018JohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Demographics - The OpportunityDocumento4 pagineMarketing Demographics - The OpportunityVonderNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 - ThesisDocumento8 pagineChapter 1 - ThesisRed SecretarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Ijarah BNM PD 2018 PDFDocumento62 pagineIjarah BNM PD 2018 PDFaraary86Nessuna valutazione finora
- Peachtree AccountingDocumento170 paginePeachtree AccountingKyaw Moe Hain100% (4)
- Entry Strategies: Exporting Contractual Entry Modes Foreign Direct Investment (Documento10 pagineEntry Strategies: Exporting Contractual Entry Modes Foreign Direct Investment (DianaProEraNessuna valutazione finora
- SBIR Program OverviewDocumento13 pagineSBIR Program OverviewFernie1Nessuna valutazione finora
- How To Succeed at Retail - Winning Case Studies and Strategies For Retailers and Brands PDFDocumento224 pagineHow To Succeed at Retail - Winning Case Studies and Strategies For Retailers and Brands PDFPrashant SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- What You Should Know About The Cap RateDocumento4 pagineWhat You Should Know About The Cap RateJacob YangNessuna valutazione finora
- WEEK 6 Seminar Q&AsDocumento26 pagineWEEK 6 Seminar Q&AsMeenakshi SinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- MAS Answer KeyDocumento18 pagineMAS Answer KeyMitch Regencia100% (1)