Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Avob Q13
Caricato da
Christine DeVitoTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Avob Q13
Caricato da
Christine DeVitoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
AVOB Q13
Student: ___________________________________________________________________________ 1. Standardizing work through job descriptions and procedures: A. is a form of coordination. B. is more common when the work is complex and ambiguous. C. tends to reduce ualit! and consistenc!. ". is unnecessar! in large organizations. #. is more common in organic rather than mechanistic structures.
$. "ecentralization is more likel! to occur when: A. an organization becomes so complex that senior executi%es cannot process all the decisions that significantl! influence the business. B. corporate leaders want more consistent decisions across all work units. C. corporate leaders want to increase consistenc! and reduce costs across the organization. ". all of these occur. #. none of these occur.
&. 'hich organizational structure actuall! consists of se%eral organizations( A. "i%isionalized structure B. )unctional structure C. Simple structure ". *atrix structure #. +etwork structure
,. 'hich of these statements about team-based organizational structures is )A.S#( A. /eam-based structures ha%e %er! little formalization. B. /eam-based structures make extensi%e use of formal hierarch! as a coordinating mechanism. C. /eam-based structures impro%e communication and cooperation across skills and areas of expertise. ". /eam-based structures are usuall! more responsi%e and flexible than functional structures. #. /eam-based structures are usuall! found within larger di%isionalized structures.
0. A steel manufacturing firm with about 11222 emplo!ees operates in an en%ironment that is simple and integrated 3it makes a small number of steel products to a few ke! customers4 but also d!namic and hostile 3rapidl! changing technolog! and customer needs with man! competitors4. Based on the en%ironment in which this compan! operates1 it would be more successful with: A. an organic structure. B. a centralized structure. C. a di%isionalized structure. ". a matrix structure. #. a mechanistic structure.
5. 6ne problem with a functional structure is that: A. it is more difficult to directl! super%ise emplo!ees within each department. B. it produces higher d!sfunctional conflict and poorer coordination. C. it makes it difficult to permit greater specialization of skills. ". it pre%ents companies from creating economies of scale in their pool of talent. #. emplo!ees ha%e difficult! creating career paths within their area of knowledge.
7. 888888888888 establishes the chain of command1 that is1 the s!stem of common super%ision among positions and units within the organization. A. Span of control B. )ormalization C. /he organization9s en%ironment ". :ob specialization #. "epartmentalization
;. 'hich of the following is +6/ a feature of team-based organizations( A. /eams ha%e a high degree of autonom!. B. /eam members replace super%isors as conduits to senior management. C. *ost teams are formed around functional departments rather than work processes. ". /eam-based structures ha%e %er! few la!ers of hierarch!. #. #mplo!ees within each unit are encouraged to talk to each other.
<. A team-based organizational structure has: A. a %er! flat organizational hierarch!. B. %er! little formalization. C. extensi%e use of self-directed teams. ". all of the abo%e. #. 9B9 and 9C9 onl!.
12. /he current trend is for companies to shift their di%isionalized structures awa! from: A. functional specializations 3marketing1 accounting1 production1 etc.4 B. clients. C. geograph!. ". products. #. emerging forms of technolog!.
11. Creati%e Ad%ertising Corp. wants its 122 emplo!ees to work together around specific clients !et maintain an e ual emphasis on alignment with their skill specializations 3ad%ertising1 graphics1 cop!writing and public relations4. 'hich of the following organizational structures would work best for Creati%e Ad%ertising Corp.( A. *atrix structure that o%erla!s a geographic and client structure B. Simple structure C. +etwork structure ". Client-based di%isionalized form #. *atrix structure that o%erla!s project teams with a functional structure
1$. A team-based organization usuall! has: A. emplo!ees. B. self-directed teams. C. %er! little formalization. ". tasks o%er which teams ha%e semi-autonomous responsibilit!. #. all of the abo%e
1&. Coordination of work acti%ities is re uired: A. whene%er there is di%ision of labor. B. onl! in team-based organizations. C. whene%er the organization has more than approximatel! 122 emplo!ees. ". onl! when organizations operate in complex en%ironments. #. ne%er= coordination of work acti%ities is not found in organizations.
1,. An organization that wants to compete through inno%ation should: A. adopt an organic structure and make extensi%e use of informal communication to coordinate work. B. centralize and formalize its organizational structure. C. coordinate emplo!ees b! writing up formal rules and procedures. ". switch to a cost leadership strateg! as uickl! as possible. #. adopt a mechanistic structure with functional departmentalization.
10. A di%isionalized structure has all of the following problems #>C#?/: A. it increases the amount of duplication. B. it reduces cooperation across groups. C. it limits the abilit! to expand operations. ". it underutilizes resources. #. it creates 9silos of knowledge9 whereb! information is not shared to other units.
15. A di%isionalized structure is recommended mainl! for: A. stable en%ironments. B. di%erse en%ironments. C. munificent en%ironments. ". integrated en%ironments. #. none of these en%ironments.
17. 'hich organizational design element is most closel! related to standardization as a coordinating mechanism( A. "epartmentalization B. Span of control C. )ormalization ". Centralization #. "i%ision of labor
1;. 'hich of the following is +6/ a coordinating mechanism( A. :ob descriptions B. @nformal communication C. Centralization ". Sales targets #. #xtensi%e training
1<. As soon as people di%ide work among themsel%es1 the! need to: A. centralize. B. decentralize. C. form a team-based organizational structure. ". rel! increasingl! on a simple structure. #. rel! on one or more coordinating mechanisms.
$2. 6rganizations tend to form two clusters based on their span of control1 centralization1 and formalization. /he two clusters represented b! these organizational design features are called: A. hierarchical %ersus dela!ered. B. networked %ersus team-based. C. geographic %ersus productAclient di%isions. ". organic %ersus mechanistic. #. di%erse %ersus integrated.
$1. Simple structures usuall! rel! on which of the following to coordinate work acti%ities( A. "irect super%ision B. Standardization through formal instructions C. )ormal training 3standardizing skills4 ". Standardization of product or ser%ice outputs #. +one= simple structures are so-called because the! ha%e no coordinating mechanism
$$. As organizations grow1 which of the following does +6/ t!picall! occur( A. @nformal communication becomes more pre%alent as a coordinating mechanism. B. /here is increasing di%ision of labor. C. /he organization becomes more decentralized. ". /he organization becomes more formalized. #. /here is increasing job specialization.
$&. 'hich of the following is +6/ t!picall! a problem with a functional structure( A. @t tends to increase d!sfunctional conflict across work units. B. @t re uires higher le%els of interdependence than simple or di%isionalized forms1 thereb! increasing potentiall! d!sfunctional conflict. C. @t is more difficult to directl! super%ise emplo!ees within each department. ". #mplo!ees are less likel! to de%elop a broader understanding of the business. #. @t puts more emphasis on subunit goals than on organizational goals.
$,. 'hich coordinating mechanism is t!picall! most important among people working in hospital surgical operations( A. "irect super%ision B. @ntegrator roles C. :ob descriptions ". #xtensi%e training #. ?eople working in surgical operations do not use an! coordinating mechanism
$0. A wholesale grocer! business operates in one cit! and pro%ides one ser%ice stocking retailers with fresh produce. /he compan! wants to ensure that emplo!ees de%elop expertise in their skill specialization and that these specializations are used efficientl!. 'hat form of departmentalization would be most appropriate here( A. Simple structure B. *atrix structure C. Beographic di%isional structure ". )unctional structure #. ?roduct di%isional structure
$5. *ost emplo!ees at Cuokka S!stems are organized into project teams. #mplo!ees report to the project leader1 but the! also report to a leader responsible for their functional specialization 3such as engineering or marketing4. Cuokka S!stems likel! has a: A. simple structure. B. client-based di%isionalized structure. C. matrix structure. ". product-based di%isionalized structure. #. functional structure.
$7. As the number of emplo!ees increases1 the organization tends to ha%e: A. more job specialization. B. more elaborate coordinating mechanisms. C. more standardization rather than just informal communication as a coordinating mechanism. ". more decentralization. #. all of the abo%e.
$;. 'hich of the following is a coordinating mechanism( A. /raining. B. Clarif!ing work procedures. C. @nformal communication. ". All of these are coordinating mechanisms. #. +one of these is a coordinating mechanism.
$<. "epartmentalization does all of the following #>C#?/: A. "epartmentalization establishes a s!stem of common super%ision. B. "epartmentalization discourages coordination through informal communication. C. "epartmentalization creates common measures of performance among emplo!ees in the unit. ". "epartmentalization t!picall! determines which positions and units must share resources. #. "epartmentalization establishes interdependencies among emplo!ees and subunits.
&2. @ntegrator roles do which of the following( A. /he! increase formalization and centralization. B. /he! support informal communication as a coordinating mechanism. C. /he! reduce the need for %irtual corporations. ". /he! increase the amount of formal hierarch!. #. /he! do none of these things.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Basic Principles and Practice of Business AdministrationDa EverandBasic Principles and Practice of Business AdministrationNessuna valutazione finora
- Yahama Golf Cart G2e Parts ManualDocumento50 pagineYahama Golf Cart G2e Parts Manualtl3883100% (1)
- Defect EliminationDocumento4 pagineDefect EliminationHossein100% (1)
- TEST BANK: Daft, Richard L. Management, 11th Ed. 2014 Chapter 10 Designing AdaptDocumento62 pagineTEST BANK: Daft, Richard L. Management, 11th Ed. 2014 Chapter 10 Designing Adaptpolkadots93975% (4)
- The Outsourcing Revolution (Review and Analysis of Corbett's Book)Da EverandThe Outsourcing Revolution (Review and Analysis of Corbett's Book)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Open Book API 510 Practice Exam B Do Not Mark On Your Exam, Use The Answer Sheets ProvidedDocumento16 pagineOpen Book API 510 Practice Exam B Do Not Mark On Your Exam, Use The Answer Sheets ProvidedBeantickNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Organizational StructureDocumento17 pagineUnderstanding Organizational StructureSabriye ÇayırcıNessuna valutazione finora
- Mooring SystemsDocumento6 pagineMooring SystemsVinicius PessottiNessuna valutazione finora
- CRX Seat Diassembly & Assembly 1Documento9 pagineCRX Seat Diassembly & Assembly 1ocdank19806116Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Cross-Functional Workplace: Matrixed Project and Task SuccessDa EverandThe Cross-Functional Workplace: Matrixed Project and Task SuccessNessuna valutazione finora
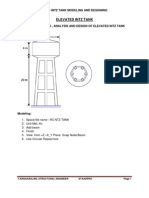
- Elevated Intz Tank 279Documento23 pagineElevated Intz Tank 279Navasivayam Sankar100% (2)
- Background Business Case Key Elements of Organizational Structures Types of Organizational StructuresDocumento15 pagineBackground Business Case Key Elements of Organizational Structures Types of Organizational StructuresKaterina Borodacheva100% (1)
- Structural Concept - Helix StructureDocumento6 pagineStructural Concept - Helix StructurebistsushantNessuna valutazione finora
- IT GOVERNANCE APPROACHES FOR AGILE SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT INVESTMENTSDa EverandIT GOVERNANCE APPROACHES FOR AGILE SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT INVESTMENTSValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- LiftingLugStress Rev 1.5Documento17 pagineLiftingLugStress Rev 1.5mohdshakir bahariNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Organization and ManagementDocumento12 pagineProject Organization and ManagementJ. VinceNessuna valutazione finora
- 'Company, August 200Z, Pp. 23-125 G. Edmondson, "BMW'sDocumento2 pagine'Company, August 200Z, Pp. 23-125 G. Edmondson, "BMW'sButetMasuliliNessuna valutazione finora
- Dubrin Review 08Documento10 pagineDubrin Review 08IRFAN KARIMNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.typology of OrganisationDocumento15 pagine3.typology of OrganisationVishal Singh JaswalNessuna valutazione finora
- BPSMDocumento18 pagineBPSMShakshi Arvind Gupta100% (1)
- TEST BANK Daft Richard L Management 11th Ed 2014 Chapter 10 Designing AdaptDocumento46 pagineTEST BANK Daft Richard L Management 11th Ed 2014 Chapter 10 Designing Adaptfoki_87100% (1)
- CH 15Documento63 pagineCH 15Tinatini BakashviliNessuna valutazione finora
- Organizational Structure 9Documento14 pagineOrganizational Structure 9teresaypilNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 15 - Activities/ Exercises Choose One Activity.: Organizational-ChangesDocumento5 pagineChapter 15 - Activities/ Exercises Choose One Activity.: Organizational-ChangessheeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample: Objective QuestionsDocumento5 pagineSample: Objective QuestionsjwcmadeincanadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Organizing NotesDocumento30 pagineOrganizing NotesJoseph WanderaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 10 StructureDocumento5 pagineChapter 10 Structureandresaguas19Nessuna valutazione finora
- David TIF Ch07Documento14 pagineDavid TIF Ch07harlloveNessuna valutazione finora
- Hbo Chapter 15Documento6 pagineHbo Chapter 15Diosdado IV GALVEZNessuna valutazione finora
- 17 - Modern Organization StructuresDocumento47 pagine17 - Modern Organization StructuresnarinderNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Manual For Understanding Management 9th EditionDocumento23 pagineSolution Manual For Understanding Management 9th EditionDanielKimqnob100% (42)
- OD SummariesDocumento40 pagineOD SummariesaaaaNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQS For The Mid Term Exams Chapter 6Documento10 pagineMCQS For The Mid Term Exams Chapter 6dort developersNessuna valutazione finora
- Students Copy Senior 11 Org and MGNT Q1 M7 1Documento13 pagineStudents Copy Senior 11 Org and MGNT Q1 M7 1Aljon AvestruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Organization Structure (Unit 3 Notes)Documento104 pagineOrganization Structure (Unit 3 Notes)ParakramNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3A - Business Analysis - Final NotesDocumento46 pagineUnit 3A - Business Analysis - Final NotesTushar BhatiNessuna valutazione finora
- MODULE 1 Student SlideDocumento37 pagineMODULE 1 Student SlideKamarul NizamNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 ReadingDocumento4 pagineUnit 1 Readingbaonguyen.erNessuna valutazione finora
- Designing Organisation Structures: John Van Rijn IndevelopmentDocumento14 pagineDesigning Organisation Structures: John Van Rijn IndevelopmentMohammed AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Operating ManualDocumento9 pagineOperating Manualmsn75Nessuna valutazione finora
- Icfai University Sample PapersDocumento21 pagineIcfai University Sample PapersIcfai Distance Learning DelhiNessuna valutazione finora
- (Template) 2ndQtr - QUIZ-1-ORGANIZINGDocumento3 pagine(Template) 2ndQtr - QUIZ-1-ORGANIZINGReyes, Aloysious Francis MVillarNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 3 Is The Continuation of Assignment 2Documento7 pagineAssignment 3 Is The Continuation of Assignment 2Ustaz Jibril YahuzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Key Notes: OrganisingDocumento8 pagineKey Notes: OrganisingSwapneel PanigrahiNessuna valutazione finora
- Organizational Behavior and Structure: Session #9 Assignment For #10Documento39 pagineOrganizational Behavior and Structure: Session #9 Assignment For #10Kav99Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 StructureDocumento35 pagineChapter 4 StructureXXXKUTI946Nessuna valutazione finora
- Structural ImplementationDocumento12 pagineStructural ImplementationSiddhartha Singhal057Nessuna valutazione finora
- Essentials of Contemporary Management 5th Edition Jones Test Bank DownloadDocumento48 pagineEssentials of Contemporary Management 5th Edition Jones Test Bank DownloadEstella Gouin100% (26)
- Final MCQs For Revision Answers All ChapterDocumento13 pagineFinal MCQs For Revision Answers All ChapterHằng Phạm Lê ThuNessuna valutazione finora
- ABB CaseDocumento4 pagineABB CaseAnirudh LikhiteNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.5 Emerging Faster and Stronger - Building Blocks of The "New Normal" Operating Model McKinsey & CompanyDocumento6 pagine3.5 Emerging Faster and Stronger - Building Blocks of The "New Normal" Operating Model McKinsey & CompanyJohn Gilbert GopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 15Documento7 pagineChapter 15gooyaaa13Nessuna valutazione finora
- Principle of Management Chapter Organizational ArchitectureDocumento27 paginePrinciple of Management Chapter Organizational ArchitectureSamy. E.N.DNessuna valutazione finora
- ARTICLES Organizational Orchestra StructureDocumento15 pagineARTICLES Organizational Orchestra Structuresoumya697Nessuna valutazione finora
- Key Principles Organization DesignDocumento4 pagineKey Principles Organization DesignAdams Collao DonosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ebert IMCh06Documento11 pagineEbert IMCh06Girish NarayananNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 TEST BANK Daft Richard L Manag, Jklhkhkhement 11th Ed 2014 Chapter 10 Designing AdaptDocumento93 pagine10 TEST BANK Daft Richard L Manag, Jklhkhkhement 11th Ed 2014 Chapter 10 Designing AdaptDat NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 5 - Managerial Roles - 19 August 2021Documento52 pagineClass 5 - Managerial Roles - 19 August 2021Priyanka AggarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Management 9th Edition Daft Solutions ManualDocumento23 pagineUnderstanding Management 9th Edition Daft Solutions Manualradleydiepwxq100% (30)
- Kinney 8e - IM - CH 19Documento15 pagineKinney 8e - IM - CH 19Analexa914Nessuna valutazione finora
- Latest Organization Designs: VsramaraoDocumento1 paginaLatest Organization Designs: VsramaraoShereen HossamNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 2Documento10 pagineChap 2Tú B Mai100% (2)
- Mbl93ar Assignment 2 - Courage ShoniwaDocumento20 pagineMbl93ar Assignment 2 - Courage ShoniwaCourage ShoniwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled 1Documento4 pagineUntitled 1Debasish BeheraNessuna valutazione finora
- The Customer Epic #9Documento7 pagineThe Customer Epic #9Thiago MachadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Raci AnalysisDocumento12 pagineRaci AnalysisAlbert NamoroNessuna valutazione finora
- KK Structural Frame WorksheetDocumento4 pagineKK Structural Frame Worksheetapi-720394088Nessuna valutazione finora
- Management Control with Integrated Planning: Models and Implementation for Sustainable CoordinationDa EverandManagement Control with Integrated Planning: Models and Implementation for Sustainable CoordinationNessuna valutazione finora
- PDS HEMPATEX ENAMEL 56360 en-GB PDFDocumento2 paginePDS HEMPATEX ENAMEL 56360 en-GB PDFMohamed ChelfatNessuna valutazione finora
- WAXESDocumento2 pagineWAXESPra YogaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Simulation of Attempts To Influence Crowd Dynamics'Documento6 pagineA Simulation of Attempts To Influence Crowd Dynamics'KhairulNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Related Topics Automatic IrrigationDocumento13 pagine2 Related Topics Automatic IrrigationSftvsn Giovanni TandogNessuna valutazione finora
- Gestrast 6Documento3 pagineGestrast 6iran1362Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hepworth Clay DoPs - Full SetDocumento54 pagineHepworth Clay DoPs - Full SetAnonymous XYAPaxjbYNessuna valutazione finora
- FMS 2009 Question Paper and Answer KeyDocumento6 pagineFMS 2009 Question Paper and Answer KeyHarish PotterNessuna valutazione finora
- Se MeterDataProcessingDocumento83 pagineSe MeterDataProcessingbzkxtNessuna valutazione finora
- CND - Clinical Round ChecklistDocumento2 pagineCND - Clinical Round ChecklistMona Ismail AlsomaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Babies of 2010Documento16 pagineBabies of 2010Sierra Nevada Media GroupNessuna valutazione finora
- NEMA Premium CatalogDocumento38 pagineNEMA Premium CatalogPedro SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Infopack 2016 enDocumento44 pagineInfopack 2016 enAlbertoNessuna valutazione finora
- American University of Beirut Aub Thesis TemplateDocumento12 pagineAmerican University of Beirut Aub Thesis TemplateHassane EzzeddineNessuna valutazione finora
- Catalog C60H-DCDocumento6 pagineCatalog C60H-DCNae MocioiNessuna valutazione finora
- Sumanta Chowdhury - CLS Aipmt-15-16 XIII Phy Study-Package-7 Set-1 Chapter-27Documento32 pagineSumanta Chowdhury - CLS Aipmt-15-16 XIII Phy Study-Package-7 Set-1 Chapter-27Rohit Raj0% (1)
- Maxstar140str (KK013519)Documento52 pagineMaxstar140str (KK013519)mrtans0% (1)
- Flextronics FINALDocumento25 pagineFlextronics FINALAnkit GauravNessuna valutazione finora
- Fabshield Offshore 71ni-1Documento2 pagineFabshield Offshore 71ni-1Anonymous ejnktktkY7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Formulation of Immediate Release Dosage Form of Ranitidine HCL Tabletsusing HPMC and Starch Acetate Film FormerDocumento11 pagineFormulation of Immediate Release Dosage Form of Ranitidine HCL Tabletsusing HPMC and Starch Acetate Film Formersunaina agarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- MMPB 730 RerollDocumento4 pagineMMPB 730 RerollLuis Padilla SandovalNessuna valutazione finora
- CS1 Course OutlineDocumento2 pagineCS1 Course Outlineapi-27149177Nessuna valutazione finora
- PR RTXDocumento27 paginePR RTXletanbaospkt06100% (1)