Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Glycolysis and TCA Cycle - Shuttles
Caricato da
Dr. SHIVA AITHALDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Glycolysis and TCA Cycle - Shuttles
Caricato da
Dr. SHIVA AITHALCopyright:
Formati disponibili
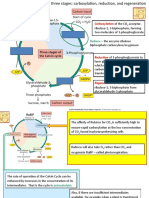
GLYCOLYSIS & TCA CYCLE-
SHUTTLES
GLUCOSE
ATP
ADP
Glucose-6-P
Fructose-6- P
ATP
ADP
Fructose-1,6-bis- P
Glycerone-3- P
(Di-OH-acetone- P)
2 3-P-Glyceraldehyde
2NAD
2 Pi
2 NADH+H+
2 1,3-bis-P-Glycerate 2 ADP
2 ATP
2 3-P-Glycerate
2 2-P-Glycerate
2H2O
2 P-enolpyruvate 2 ADP
2 ATP
2 PYRUVATE
NADH+H+
NAD+
PYRUVATE
-OOCCH(OH)CH COO- -OOCCH(OH)CH COO-
2 2
ACETYL-CoA Malate Malate
-OOCCOCH COO-
2
Oxaloacetate
MALATE-ASPARTATE
Oxaloacetate Oxaloacetate
2-Oxoglutarate
SHUTTLE
Citrate 2-Oxoglutarate
Malate
Aspartate Aspartate
NADH+H++
Isocitrate 1H+ 1H+
Glutamate Glutamate
Fumarate NAD+
GLYCEROL PHOSPHATE
2-Oxoglutarate HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OP
SHUTTLE
FADH2 FAD FAD Glycerol-3-P
H H HOCH2COCH2OP
OOCCH-CHCOO- Di-OH-acetone-P
UQ Succinate Succinyl-CoA FADH2
UQH2 Pi
2H+
GDP UQH2 UQ
2e- GTP
2H+
~1.5 ATP
~1.5ATP
2e-
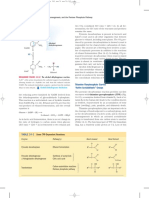
Malate-Aspartate Shuttle Operates when the NADH/NAD ratio is greater in the cytosol than in
the mitochondrial matrix. Electrons are transferred from cytosolic NADH via malate acoss the
the mitochondrial inner membrane and re-forms NADH in the matrix. This shuttle requires the
translocation of 1proton for each malate
Glycerol-phosphate Shuttle Operates if low ratio NADH/NAD in the cytosol - but at a cost.
Electrons are transferred (via FAD) to ubiquinone at the outer surface of the mitochondrial inner
membrane to give ubiquinol which remains in the membrane and feeds into the Electron
Transport Chain and forms ATP. This is a pathway similar to that in which succinate is aerobically
oxidised and they each result in the formation of approximately 1.5 mols of ATP
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Enzymes: A Practical Introduction to Structure, Mechanism, and Data AnalysisDa EverandEnzymes: A Practical Introduction to Structure, Mechanism, and Data AnalysisValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- Matabolic PathwaysDocumento11 pagineMatabolic PathwaysLevi100% (2)
- Sample ProblemDocumento1 paginaSample ProblemfintastellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Voet - Chapt - 12 Properties of EnzymesDocumento102 pagineVoet - Chapt - 12 Properties of Enzymestelmo flowNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Enzyme Kinetics-InhibitionDocumento40 pagine5 Enzyme Kinetics-InhibitionJoel SmolanoffNessuna valutazione finora
- Bibc102, Metabolic Biochemistry: Gen-Sheng Feng Fall, 2010Documento14 pagineBibc102, Metabolic Biochemistry: Gen-Sheng Feng Fall, 2010cool_trainerNessuna valutazione finora
- Excel 2007 TutorialDocumento5 pagineExcel 2007 TutorialromelcarvajalNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochem QbankDocumento16 pagineBiochem Qbank786waqar786Nessuna valutazione finora
- Amino Acids QuestionsDocumento5 pagineAmino Acids QuestionsKrishna KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzymology Quiz 1Documento5 pagineEnzymology Quiz 1Ryan Fortune AludaNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Exam Practice Dec 2012 - StudentDocumento15 pagineFinal Exam Practice Dec 2012 - StudentSeoAm HurNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Bioenergetics and Oxidative Metabolism IIDocumento3 pagine4 Bioenergetics and Oxidative Metabolism IILinus LiuNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 P-2 Enzyme-Inhibition 1Documento39 pagineChapter 2 P-2 Enzyme-Inhibition 1Raihan I. SakibNessuna valutazione finora
- Metabolism of Carbohydrate: Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Medicine University of YARSI JakartaDocumento60 pagineMetabolism of Carbohydrate: Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Medicine University of YARSI JakartaAmanda PutriNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 6 (Bioenergetics of Physical Exercise)Documento39 pagineLecture 6 (Bioenergetics of Physical Exercise)Helmi RaisNessuna valutazione finora
- EnzymeKinetics by P.C. Misra Professor, Department of Biochemistry Lucknow University, Lucknow-226 007Documento21 pagineEnzymeKinetics by P.C. Misra Professor, Department of Biochemistry Lucknow University, Lucknow-226 007Dr. SHIVA AITHALNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ MembranesDocumento10 pagineMCQ MembranesMarilyne RizkNessuna valutazione finora
- Cholesterol - Synthesis, Metabolism, Regulation PDFDocumento10 pagineCholesterol - Synthesis, Metabolism, Regulation PDFAdreiTheTripleA100% (1)
- Fa Lipid MetabDocumento4 pagineFa Lipid MetabJoy VergaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Amylase Assay 2Documento9 pagineAmylase Assay 2Rahman ImudaNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ in BioDocumento7 pagineMCQ in BioGiovanni Roccaforte100% (1)
- Lipids LehningerDocumento7 pagineLipids LehningerElla BangalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Metabolism WorksheetDocumento6 pagineMetabolism WorksheetJay DansNessuna valutazione finora
- B Y: - Idr. Megha Gaur BDS IDocumento89 pagineB Y: - Idr. Megha Gaur BDS IRishab GaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbohydrates SummaryDocumento9 pagineCarbohydrates SummaryHarold NagunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Answers Amino Acids PeptidesDocumento6 pagineAnswers Amino Acids PeptidesAnna LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzyme Kinetics Questions and Answers: 2 Year Undergraduates-Biology 2018-2019Documento8 pagineEnzyme Kinetics Questions and Answers: 2 Year Undergraduates-Biology 2018-2019Emmanuel JoyNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.carbohydrates and Lipid Metabolism-Converted - WatermarkDocumento97 pagine1.carbohydrates and Lipid Metabolism-Converted - WatermarkJuliyamol JoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Metabolism of Purine & Pyrimidine NucleotidesDocumento38 pagineMetabolism of Purine & Pyrimidine NucleotidesShimmering MoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Enzymes MCQ Topic Quiz Lesson ElementDocumento19 pagineEnzymes MCQ Topic Quiz Lesson ElementArvin DiNozzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 17-Multisubstrate Enzyme RXN KineticsDocumento13 pagineLecture 17-Multisubstrate Enzyme RXN KineticsAmogha G C 1SI19CH002Nessuna valutazione finora
- Question CH06+answer PDFDocumento8 pagineQuestion CH06+answer PDFCris-Anne Juangco III100% (1)
- Sella Turcica Releasing Factors Median Eminence Anterior Pituitary Paraventricular Supraoptic NucleiDocumento2 pagineSella Turcica Releasing Factors Median Eminence Anterior Pituitary Paraventricular Supraoptic NucleiDragan Petrovic0% (1)
- Chapter 14 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento6 pagineChapter 14 Multiple Choice QuestionsDawlat SalamaNessuna valutazione finora
- 06.disorder of Carbohydrate MetabolismDocumento47 pagine06.disorder of Carbohydrate MetabolismRizka NizarNessuna valutazione finora
- Dyslipidemia - HyperlipoproteinemiaDocumento43 pagineDyslipidemia - HyperlipoproteinemiaDarien LiewNessuna valutazione finora
- Creatine and Creatinine MetabolismDocumento108 pagineCreatine and Creatinine MetabolismMae Matira AbeladorNessuna valutazione finora
- SummaryDocumento21 pagineSummarydindaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochem 10A Lab QuestionsDocumento6 pagineBiochem 10A Lab QuestionsPaul A IBattledaily Scavella100% (1)
- Optimization of Cellulase Enzyme From Vegetable Waste by Using Trichoderma Atroviride in Solid State FermentationDocumento6 pagineOptimization of Cellulase Enzyme From Vegetable Waste by Using Trichoderma Atroviride in Solid State FermentationIOSRjournalNessuna valutazione finora
- s15 Miller Chap 3b LectureDocumento25 pagines15 Miller Chap 3b LectureDorice Clement100% (1)
- Cellular Respiration: Stage 1Documento20 pagineCellular Respiration: Stage 1anon_898682470Nessuna valutazione finora
- Enzyme Catalysis-Chapter 7 (Part 1)Documento22 pagineEnzyme Catalysis-Chapter 7 (Part 1)OmSilence2651Nessuna valutazione finora
- Some Answer of Problemset - 7 - KEYDocumento3 pagineSome Answer of Problemset - 7 - KEYNihir PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Study QuestionsDocumento13 pagineStudy QuestionsDawlat SlamaNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Overview of MOE Manual Conventions GUI Basics PDFDocumento15 pagine01 Overview of MOE Manual Conventions GUI Basics PDFAnand SolomonNessuna valutazione finora
- Concise Biochemistry: Fundamental Principles: March 2016Documento52 pagineConcise Biochemistry: Fundamental Principles: March 2016Sagar DeshmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- GluconeogenesisDocumento11 pagineGluconeogenesisMithilesh RautNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 - Metabolism & Bioenergetics (Part 2) PDFDocumento69 pagineChapter 2 - Metabolism & Bioenergetics (Part 2) PDFdarren100% (2)
- 2.2 Carbohydrate Metabolism Part 2Documento13 pagine2.2 Carbohydrate Metabolism Part 2John Louis PulidoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1Documento30 pagineLecture 1حموده ابراهيم يونسNessuna valutazione finora
- بايو بيبر 1 د.جميلة السمهريDocumento8 pagineبايو بيبر 1 د.جميلة السمهريOzgan SüleymanNessuna valutazione finora
- Amino SugarsDocumento2 pagineAmino SugarsNarasimha MurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- ART - Spectrophotometric Method For Determining GA in ..Documento4 pagineART - Spectrophotometric Method For Determining GA in ..Azahara Linares100% (2)
- Biochem HomeworkDocumento13 pagineBiochem Homeworkfcukingfranztastik50% (2)
- 3 LipidsDocumento44 pagine3 LipidsSuresh ChovatiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 Enzyme Mechanism & ControlDocumento37 pagineChapter 7 Enzyme Mechanism & ControlLiana ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- l08 Metabolism in Liver 2 - Fatty Acid Metabolism (Mod)Documento21 paginel08 Metabolism in Liver 2 - Fatty Acid Metabolism (Mod)Swapnil100% (4)
- Lactic and Alcoholic FermentationDocumento1 paginaLactic and Alcoholic FermentationDr. SHIVA AITHALNessuna valutazione finora
- GlycolysisDocumento1 paginaGlycolysisDr. SHIVA AITHALNessuna valutazione finora
- FOOD MICROBIOLOGY Spoilage Poisoning and PreservationDocumento13 pagineFOOD MICROBIOLOGY Spoilage Poisoning and PreservationDr. SHIVA AITHAL100% (1)
- Hanuman Chalisa English MeaningDocumento3 pagineHanuman Chalisa English MeaningSaurabh SaxenaNessuna valutazione finora
- EnzymeKinetics by P.C. Misra Professor, Department of Biochemistry Lucknow University, Lucknow-226 007Documento21 pagineEnzymeKinetics by P.C. Misra Professor, Department of Biochemistry Lucknow University, Lucknow-226 007Dr. SHIVA AITHALNessuna valutazione finora
- 50 Books For ChildrenDocumento32 pagine50 Books For ChildrenDr. SHIVA AITHALNessuna valutazione finora
- Microbiology of Water and Waste Water ManagementDocumento27 pagineMicrobiology of Water and Waste Water ManagementDr. SHIVA AITHAL100% (2)
- Air Microbiology 2009Documento13 pagineAir Microbiology 2009Dr. SHIVA AITHAL100% (9)
- Lactic and Alcoholic FermentationDocumento1 paginaLactic and Alcoholic FermentationDr. SHIVA AITHALNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycolysis and TCA Cycle Enzymes and EC Reference NumbersDocumento1 paginaGlycolysis and TCA Cycle Enzymes and EC Reference NumbersDr. SHIVA AITHALNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of DNA by CrickDocumento8 pagineStructure of DNA by CrickDr. SHIVA AITHALNessuna valutazione finora
- GlycolysisDocumento1 paginaGlycolysisDr. SHIVA AITHALNessuna valutazione finora
- Micro Teaching Skills ComponentsDocumento35 pagineMicro Teaching Skills ComponentsDr. SHIVA AITHAL89% (221)
- Management of Libraries and Information Sciences by Naznin BanuDocumento12 pagineManagement of Libraries and Information Sciences by Naznin BanuDr. SHIVA AITHALNessuna valutazione finora
- Visit To ISDN BayalaluDocumento16 pagineVisit To ISDN BayalaluDr. SHIVA AITHAL100% (2)
- 3G Wireless NetworksDocumento16 pagine3G Wireless NetworksAli QureshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Modelo Doble Helice Watson y CrickDocumento2 pagineModelo Doble Helice Watson y Crickangelferp100% (2)
- A Brief Foray Into The World of Nano Materials by Sarbari BhattacharyaDocumento17 pagineA Brief Foray Into The World of Nano Materials by Sarbari BhattacharyaDr. SHIVA AITHALNessuna valutazione finora
- Preamble To The Constitution of India by Prema NagaleDocumento12 paginePreamble To The Constitution of India by Prema NagaleDr. SHIVA AITHAL100% (1)
- Biotechnology in Agriculture Development by KS ManjunathDocumento15 pagineBiotechnology in Agriculture Development by KS ManjunathDr. SHIVA AITHAL100% (1)
- Worksheet: Cellular Respiration & Cell EnergyDocumento4 pagineWorksheet: Cellular Respiration & Cell Energyclaryl alexaNessuna valutazione finora
- MIT7 - 05S20 - Pset8 BIOCHEMDocumento9 pagineMIT7 - 05S20 - Pset8 BIOCHEMRejoice chekesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Book 2Documento101 pagineStudent Book 2helena coelho odaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gen Physics 1 2nd Quarter ExamDocumento5 pagineGen Physics 1 2nd Quarter ExamArvinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9 - Energy Metabolism and Membrane Physiology of The ErythrocyteDocumento5 pagineChapter 9 - Energy Metabolism and Membrane Physiology of The ErythrocyteAira UsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Aerobic Respiration: General BiologyDocumento12 pagineAerobic Respiration: General BiologyV KimNessuna valutazione finora
- C 04 Photosynthesis, Cellular Respiration and Biotechnological ApplicationsDocumento96 pagineC 04 Photosynthesis, Cellular Respiration and Biotechnological ApplicationsJenniferNessuna valutazione finora
- ICIMD ManuscriptDocumento23 pagineICIMD ManuscriptLAZARO INACIONessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis (Light and Dark Reaction) :: Concept Notes With Formative ActivitiesDocumento12 paginePhotosynthesis (Light and Dark Reaction) :: Concept Notes With Formative ActivitiesMonica SolomonNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise Questions Page Number - 224-225: NCERT Solution For Class 11 Biology Chapter 13 Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocumento4 pagineExercise Questions Page Number - 224-225: NCERT Solution For Class 11 Biology Chapter 13 Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsGuni GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- ABG Answers Sheet - 2Documento1 paginaABG Answers Sheet - 2khryss100% (1)
- ABGDocumento16 pagineABGIka ZulaikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocumento4 pagineProtein Synthesis WorksheetDen RoixNessuna valutazione finora
- Muhammad Wajid: Institute of Pharmacy Gulab Devi Educational Complex, LahoreDocumento36 pagineMuhammad Wajid: Institute of Pharmacy Gulab Devi Educational Complex, LahoreAhmed ImranNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Biology Chapter 10 Notes - PhotosynthesisDocumento5 pagineAP Biology Chapter 10 Notes - PhotosynthesisAustinNessuna valutazione finora
- Arterial Blood Gas InterpretationDocumento9 pagineArterial Blood Gas InterpretationSunny AghniNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiration Lec10 SlidesDocumento29 pagineRespiration Lec10 SlidesHussain IbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Mecanismo Tiamina LehningerDocumento2 pagineMecanismo Tiamina LehningerkpsantanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbohydrate, Lipid, Protein MetabolismDocumento3 pagineCarbohydrate, Lipid, Protein Metabolismtritone.paradoxNessuna valutazione finora
- 157 - Metabolism Physiology) Regulation of GlycolysisDocumento4 pagine157 - Metabolism Physiology) Regulation of Glycolysissaranya sankarNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis CR WKS KEY 28dnwi2Documento3 paginePhotosynthesis CR WKS KEY 28dnwi2Raye Shyn AsiloNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 4 Metabolic Stoichimetry and Energetics PDFDocumento51 pagineChap 4 Metabolic Stoichimetry and Energetics PDFUrgen TamangNessuna valutazione finora
- Bas 121 Biochemistry 2 - 0 - 2 3 TheoryDocumento1 paginaBas 121 Biochemistry 2 - 0 - 2 3 Theoryjyotiraditya palNessuna valutazione finora
- Detailed Lesson Plan in PeroxisomeDocumento8 pagineDetailed Lesson Plan in PeroxisomeKeannoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaplerotic and Cataplerotic Reactions of The Tca CycleDocumento4 pagineAnaplerotic and Cataplerotic Reactions of The Tca CyclebomabenediNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular RespirationDocumento6 pagineCellular RespirationBrian Reyes GangcaNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycogen MetabolismDocumento35 pagineGlycogen MetabolismMarawan MahmoudNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochem CH 27 Integration of MetabolismDocumento6 pagineBiochem CH 27 Integration of MetabolismSchat ZiNessuna valutazione finora
- Metabolism During Fasting and StarvationDocumento4 pagineMetabolism During Fasting and Starvationnicole castilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Calvin CycleDocumento14 pagineCalvin CycleWahyu ArifNessuna valutazione finora