Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Bio IC Lesson 7 - Mutation
Caricato da
Kurt KleinCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Bio IC Lesson 7 - Mutation
Caricato da
Kurt KleinCopyright:
Formati disponibili
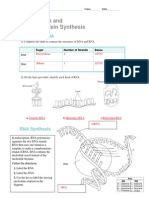
Student Page 7.1: DNA Replication and Transcription Procedure 1. 2. The DNA sequence below has a mutation.
Find the mutation and circle it. Use your knowledge of DNA replication to describe the base sequences of the two DNA molecules produced following one round of replication. In each box, list the DNA sequences of both strands. Indicate which DNA strands are new and which are old. Products of DNA Replication
DNA Strand
A -- T T -- A G -- C C -- G C -- G T -- A G -- C T -- A G -- A
3. In the space below, list the mRNA sequence that would result from transcription of this DNA sequence. DNA Template
T A C G G A C A A
mRNA Transcript
Student Page 7.2A: Assessing the Effects of Mutations Procedure 1. The mRNA sequence below represents the first part of a gene coding for a much longer protein. Use the genetic code table to translate this mRNA sequence into an amino acid sequence. Write the amino acid sequence in the space below. (You may use the amino acid abbreviations.) 1 10 20
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
Amino Acid Sequence
1. Next, consider (one at a time) the effects of the following three mutations. Make the changes indicated on the mRNA strand. Use the genetic code table and list the amino acid sequence that corresponds to each of the following three mutations: Mutation 1: Change base number 4 (C) to a U 1 10
20
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
Mutation 2: Change base number 8 (C) to an A 1 10
20
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
Student Page 7.2A: Assessing the Effects of Mutations (Cont.) Mutation 3: Change base number 12 (A) to a G 1 10
20
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
3.
In the space below, describe the effect of each mutation on the resulting protein. Explain which mutation you expect will have the greatest and least effect on the protein. Be sure to explain your reasoning. Base 4 (C) changes to a U
Mutation 1:
Mutation 2:
Base 8 (C) changes to an A
Mutation 3:
Base 12 (A) changes to a G
Student Page 7.2B: Assessing the Effects of Mutations Procedure 1. The mRNA sequence below represents the first part of a gene coding for a much longer protein. Use the genetic code table to translate this mRNA sequence into an amino acid sequence. Write the amino acid sequence in the space below. 1 10 20
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
Amino Acid Sequence
2.
Next, consider (one at a time) the effects of the following three mutations. Make the changes indicated on the mRNA strand. Use the genetic code table and list the amino acid sequence that corresponds to each of the following three mutations:
Mutation 1: Change base number 5 (U) to a G 1 10
20
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
Mutation 2: Change base number 9 (G) to an A 1 10
20
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
Student Page 7.2B: Assessing the Effects of Mutations (Cont.) Mutation 3: Insert a G base between base 12 (A) and base 13 (C) 1 10 20
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
3.
In the space below, describe the effect of each mutation on the resulting protein. Explain which mutation you expect will have the greatest and least effect on the protein. Be sure to explain your reasoning.
Mutation 1: Base 5 (U) changes to a G
Mutation 2: Base 9 (G) changes to an A
Mutation 3: Insertion of a G base after base 12 (A)
Student Page 7.2C: Assessing the Effects of Mutations Procedure 1. The mRNA sequence below represents the first part of a gene coding for a much longer protein. Use the genetic code table to translate this mRNA sequence into an amino acid sequence. Write the amino acid sequence in the space below. 1 10 20
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
Amino Acid Sequence
2.
Next, consider (one at a time) the effects of the following three mutations. Make the changes indicated on the mRNA strand. Use the genetic code table and list the amino acid sequence that corresponds to each of the following three mutations: 20
Mutation 1: Change base number 6 (U) to an A 1 10
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
Mutation 2: Delete base 7 (U) 1
10
20
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
Student Page 7.2C: Assessing the Effects of Mutations (Cont.) Mutation 3: Change base 19 (C) to an A 1 10 20
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
3.
In the space below, describe the effect of each mutation on the resulting protein. Explain which mutation you expect will have the greatest and least effect on the protein. Be sure to explain your reasoning. Base 6 (U) changes to an A
Mutation 1:
Mutation 2:
Deletion of Base 7 (U)
Mutation 3:
Base 19 (C) changes to an A
Student Page 7.2D: Assessing the Effects of Mutations Procedure 1. The mRNA sequence below represents the first part of a gene coding for a much longer protein. Use the genetic code table to translate this mRNA sequence into an amino acid sequence. Write the amino acid sequence in the space below. 1 10 20
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
Amino Acid Sequence
2.
Next, consider (one at a time) the effects of the following three mutations. Make the changes indicated on the mRNA strand. Use the genetic code table and list the amino acid sequence that corresponds to each of the following three mutations: 20
Mutation 1: Change base number 6 (U) to an A 1 10
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
Mutation 2: Change base number 8 (C) to an A 1 10
20
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
Student Page 7.2D: Assessing the Effects of Mutations (Cont.) Mutation 3: Delete bases 13 15 1 10 20
AUGCUUUCGGCAC C GGUACUA
3.
In the space below, describe the effect of each mutation on the resulting protein. Explain which mutation you expect will have the greatest and least effect on the protein. Be sure to explain your reasoning. Base 6 (U) changes to an A
Mutation 1:
Mutation 2:
Base 8 (C) changes to an A
Mutation 3:
Deletion of Bases 13 15
Student Page 7.3: Genetic Code Table
10
Student Page 7.4AB: Mutations and Their Effects Procedure: Circle the mutation that has the greatest and least effect. Explain the reasoning for your choice.
Greatest Effect
5.2A Change base number 4 (C) to a U Change base number 8 (C) to an A Change base number 12 (A) to a G 5.2B Change base number 5 (U) to a G Change base number 9 (G) to an A Insert a G base between base 12 (A) and base 13 (C) Reasoning:
Least Effect
5.2A Change base number 4 (C) to a U Change base number 8 (C) to an A Change base number 12 (A) to a G 5.2B Change base number 5 (U) to a G Change base number 9 (G) to an A Insert a G base between base 12 (A) and base 13 (C) Reasoning
Student Page 7.4CD: Mutations and Their Effects Procedure: Circle the mutation that has the greatest and least effect. Explain the reasoning for your choice.
Greatest Effect
5.2C Change base number 6 (U) to an A Delete base 7 (U) Change base 19 (C) to an A 5.2D Change base number 6 (U) to an A Change base number 8 (C) to an A Delete bases 13 15 Reasoning:
Least Effect
5.2C Change base number 6 (U) to an A Delete base 7 (U) Change base 19 (C) to an A 5.2D Change base number 6 (U) to an A Change base number 8 (C) to an A Delete bases 13 15 Reasoning
11
Teacher Page 7.4AB: Six Mutations Original mRNA 1 Met Leu Ser 10 Ala Pro Val 20 Leu
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
5.2A Mutation 1: Change base number 4 (C) to a U 1 10 Met Phe Ser Ala Pro Val
20 Leu 20
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
Mutation 2: Change base number 8 (C) to an A 1 10 Met Leu Stop 20 Val Leu
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
Mutation 3: Change base number 12 (A) to a G 1 10 Met Leu Ser Ala Pro
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
5.2B Mutation 1: Change base number 5 (U) to a G 1 10 Met Arg Ser Ala Pro Val
20 Leu 20 Val Leu 20
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
Mutation 2: Change base number 9 (G) to an A 1 10 Met Leu Ser Ala Pro
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
Mutation 3: Insert a G base between base 12 (A) and base 13 (C) 1 10 Met Leu Ser Ala Ala Gly Thr
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
12
Teacher Page 7.4CD: Six Mutations Original mRNA 1 Met Leu Ser 10 Ala Pro Val 20 Leu
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
5.2C Mutation 1: Change base number 6 (U) to an A 1 10 Met Leu Ser Ala 10 Pro Val
20 Leu 20
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
Mutation 2: Delete base 7 (U) 1
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
Met Leu Arg His Arg Tyr 20 Pro Val Ile
Mutation 3: Change base 19 (C) to an A 1 10 Met Leu Ser Ala
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
5.2D Mutation 1: Change base number 6 (U) to an A 1 10 Met Leu Ser Ala Pro Val
20 Leu 20
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
Mutation 2: Change base number 8 (C) to an A 1 10 Met Leu Stop 20 Val Leu
AUGCUUUCGGCACCGGUACUA
Mutation 3: Delete bases 13 15 1 10 Met Leu Ser Ala
AUGCUUUCGGCAC C GGUACUA
13
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Line Loss Analysis and Calculation of Electric Power SystemsDa EverandLine Loss Analysis and Calculation of Electric Power SystemsNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Multilevel Converters and Applications in Grid IntegrationDa EverandAdvanced Multilevel Converters and Applications in Grid IntegrationAli Iftekhar MaswoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics Sample Lab ReportDocumento10 pagineElectronics Sample Lab ReportLeo Marcelo VillalbaNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 13 Study Guide KeyDocumento5 pagineCH 13 Study Guide Keyi_wana_readNessuna valutazione finora
- Adamson University College of Engineering Electrical Engineering DepartmentDocumento8 pagineAdamson University College of Engineering Electrical Engineering DepartmentJohnBenedictRazNessuna valutazione finora
- Condenser Boundary For Part (D)Documento41 pagineCondenser Boundary For Part (D)gustavo_343297653Nessuna valutazione finora
- Part 6 Mutation Winter 2023Documento2 paginePart 6 Mutation Winter 2023tanusehdev17Nessuna valutazione finora
- 10 GHz Two-stage Class A RF Power Amplifier in a 0.25 μm CMOS ProcessDocumento5 pagine10 GHz Two-stage Class A RF Power Amplifier in a 0.25 μm CMOS Processmdr911Nessuna valutazione finora
- Delta - Wye TransformationsDocumento14 pagineDelta - Wye TransformationsGrae GonzagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Third HarmonicDocumento12 pagineThird HarmonicClasesFisicaUnabNessuna valutazione finora
- % Chapter 27: Molecular GeneticsDocumento39 pagine% Chapter 27: Molecular Geneticsdds uwuNessuna valutazione finora
- Modeling and Control Design of The Six-Phase Interleaved Double Dual Boost ConverterDocumento6 pagineModeling and Control Design of The Six-Phase Interleaved Double Dual Boost ConverterjyotheeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee 215 ADocumento8 pagineEe 215 AArjun Singhal100% (1)
- Methodology HifiDocumento6 pagineMethodology HifikrcdewanewNessuna valutazione finora
- Simulation and Experimental Results of 7-Level Inverter SystemDocumento8 pagineSimulation and Experimental Results of 7-Level Inverter Systembacuoc.nguyen356Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practical 1.1: Initial Setting-Up and Measurement of Transmission PowerDocumento9 paginePractical 1.1: Initial Setting-Up and Measurement of Transmission PowerKing MalikNessuna valutazione finora
- EXP3 - Symmetrical Fault AnalysisDocumento15 pagineEXP3 - Symmetrical Fault AnalysisLee Boon HongNessuna valutazione finora
- DNA RAN Prot Syn Web PracticeDocumento11 pagineDNA RAN Prot Syn Web PracticeTimothy MacdonaldNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Quality Improvement Using A Fuzzy Logic Control of A Series Active FilterDocumento9 paginePower Quality Improvement Using A Fuzzy Logic Control of A Series Active Filterankit407Nessuna valutazione finora
- Triaxial Digital Fluxgate MagnetometerDocumento87 pagineTriaxial Digital Fluxgate MagnetometershansovNessuna valutazione finora
- Power System Dissertation TopicDocumento5 paginePower System Dissertation TopicCollegePapersHelpSingapore100% (1)
- Harmonic Reduction in Three-Phase ParallelDocumento6 pagineHarmonic Reduction in Three-Phase ParallelAhmed JanadNessuna valutazione finora
- 1MRG009710 en Application Note Overall Differential Protection For Thermal Power PlantDocumento9 pagine1MRG009710 en Application Note Overall Differential Protection For Thermal Power Plantbdiaconu20048672Nessuna valutazione finora
- Systematic Design of A 200 MSs 8-Bit Interpolating AD ConverterDocumento5 pagineSystematic Design of A 200 MSs 8-Bit Interpolating AD ConverterThanos van RamNessuna valutazione finora
- 19.9% CIGS Solar Cell Made by NRELDocumento5 pagine19.9% CIGS Solar Cell Made by NRELcheah_shenNessuna valutazione finora
- Ame 3L Experiment 4 Speed Control of DC Motor by Armature Resistance Control AIMDocumento7 pagineAme 3L Experiment 4 Speed Control of DC Motor by Armature Resistance Control AIMCeline Kate BentayaoNessuna valutazione finora
- EE201Documento12 pagineEE201Iqmal Shah PutraNessuna valutazione finora
- Improved Power Quality For Renewable Power Generation Systems Presence of Non-Linear LoadsDocumento6 pagineImproved Power Quality For Renewable Power Generation Systems Presence of Non-Linear LoadsPhanikumar Bellam KondaNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of A Fully Differential High-Speed High-Precision AmplifierDocumento10 pagineDesign of A Fully Differential High-Speed High-Precision Amplifierkirkland1337Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maswood 01035144Documento9 pagineMaswood 01035144rahulanlNessuna valutazione finora
- Me2255 Electronics and MicroprocDocumento2 pagineMe2255 Electronics and MicroprocBalaji PalanisamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Naresh DC Re Injection FinalDocumento6 pagineNaresh DC Re Injection FinalRamu ThommandruNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee Sample PaperDocumento19 pagineEe Sample Paperjayapriyadarshni12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Upload Log in Sign Up: VHDL Ratings: (0) - Views: 1,302 - Likes: 8 Published byDocumento15 pagineUpload Log in Sign Up: VHDL Ratings: (0) - Views: 1,302 - Likes: 8 Published bydineshvhavalNessuna valutazione finora
- Predicting and Designing For The Impact of Process Variations and Mismatch On The Trim Range and Yield of BGRDocumento6 paginePredicting and Designing For The Impact of Process Variations and Mismatch On The Trim Range and Yield of BGRFatma HelmyNessuna valutazione finora
- Biquadratic FilterDocumento5 pagineBiquadratic FilterReece RevosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Marks: 0.00 User Answer Sheet Rank: 7: Report QuestionDocumento17 pagineMarks: 0.00 User Answer Sheet Rank: 7: Report Questionchandrachurom5538100% (1)
- Ade Lab Second Cycle FinalDocumento16 pagineAde Lab Second Cycle FinalAbin AntonyNessuna valutazione finora
- 9-Level Trinary DC Source Inverter Using Embedded ControllerDocumento6 pagine9-Level Trinary DC Source Inverter Using Embedded ControllerIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalNessuna valutazione finora
- 11e603 - Unit - 2Documento7 pagine11e603 - Unit - 2nandhakumarmeNessuna valutazione finora
- A New Passive 28-Step Current Shaper For Three-Phase RectificationDocumento8 pagineA New Passive 28-Step Current Shaper For Three-Phase Rectificationkishor reddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistical Analysis of Parameter Variations Using The Taguchi MethodDocumento18 pagineStatistical Analysis of Parameter Variations Using The Taguchi MethodMohamedKamalNessuna valutazione finora
- Folded CascodeDocumento4 pagineFolded Cascodeshivam12365Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1210 HFE SimulationProceduresDocumento6 pagine1210 HFE SimulationProceduressuper_lativoNessuna valutazione finora
- 325 Final Design Lab ReportDocumento11 pagine325 Final Design Lab Reportapi-241454978Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Methods in Power SystemsDocumento7 pagineComputer Methods in Power SystemssuhrudkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper 12Documento9 paginePaper 12Hari ShankarNessuna valutazione finora
- Open Loop Phase Control Circuit: DescriptionDocumento7 pagineOpen Loop Phase Control Circuit: DescriptionMuhammad NajibNessuna valutazione finora
- Open-Phase Fault-Tolerant Operation of The Three-Phase Dual Active Bridge ConverterDocumento12 pagineOpen-Phase Fault-Tolerant Operation of The Three-Phase Dual Active Bridge ConverterJaja LocoNessuna valutazione finora
- CE1000Documento581 pagineCE1000Mike WilsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Uwo Thesis RepositoryDocumento4 pagineUwo Thesis Repositoryqigeenzcf100% (2)
- Modelling and Analysis of Modular Multilevel Converter For Solar Photovoltaic Applications To Improve Power QualityDocumento12 pagineModelling and Analysis of Modular Multilevel Converter For Solar Photovoltaic Applications To Improve Power Qualitydishore312Nessuna valutazione finora
- ec2404-ESD Lab Course FileDocumento30 pagineec2404-ESD Lab Course Filejayaseelanj89Nessuna valutazione finora
- Analyses and Output ControlDocumento10 pagineAnalyses and Output ControlSezai Alper TekinNessuna valutazione finora
- TopSwitch Flyback Flyback Design Methodology AN16Documento32 pagineTopSwitch Flyback Flyback Design Methodology AN16Burlacu AndreiNessuna valutazione finora
- AC and DC Transistor Current Gain 1432 Exp 2Documento44 pagineAC and DC Transistor Current Gain 1432 Exp 2Rohit WadhwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- EE206-1012, Midterm, EE206 PDFDocumento2 pagineEE206-1012, Midterm, EE206 PDF820604jasonNessuna valutazione finora
- ADC816 m004405Documento5 pagineADC816 m004405JerichoNessuna valutazione finora
- United States Patent: (12) (10) Patent N0.: US 7,106,025 B1Documento17 pagineUnited States Patent: (12) (10) Patent N0.: US 7,106,025 B1Lava KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignDa EverandPower Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignBruno AllardNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio IC Lesson 1 - GriffithDocumento4 pagineBio IC Lesson 1 - GriffithKurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- Writing Recommendation LettersDocumento11 pagineWriting Recommendation LettersKurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio IC 1 Lesson 5 Central Dogma SPDocumento11 pagineBio IC 1 Lesson 5 Central Dogma SPKurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio IC 1 Lesson 4 Meselson SPDocumento7 pagineBio IC 1 Lesson 4 Meselson SPKurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio IC 1 Lesson 6 Translation SPDocumento5 pagineBio IC 1 Lesson 6 Translation SPKurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio IC 1 Lesson 2 - Avery SPDocumento4 pagineBio IC 1 Lesson 2 - Avery SPKurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Syllabus ApbiologyDocumento2 pagine12 Syllabus ApbiologyKurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- APChem ScheduleDocumento12 pagineAPChem ScheduleKurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics ScheduleDocumento12 paginePhysics ScheduleKurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- 13 Syllabus ChemistryDocumento2 pagine13 Syllabus ChemistryKurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem ScheduleDocumento12 pagineChem ScheduleKurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- APBio-pp1 6Documento92 pagineAPBio-pp1 6Kurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell CommunicationDocumento17 pagineCell CommunicationKurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- 13 Syllabus ApchemistryDocumento2 pagine13 Syllabus ApchemistryKurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- APBio-pp1 9Documento66 pagineAPBio-pp1 9Kurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- APES-Area2e-Natural Biogeochemical CyclesDocumento21 pagineAPES-Area2e-Natural Biogeochemical CyclesKurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- 13 Syllabus PhysicsDocumento2 pagine13 Syllabus PhysicsKurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- APES Area2a EcosystemsDocumento63 pagineAPES Area2a EcosystemsKurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- APES-Area2b-Energy FlowDocumento50 pagineAPES-Area2b-Energy FlowKurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- APES Area2c Ecosystem - DiversityDocumento91 pagineAPES Area2c Ecosystem - DiversityKurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- APBio-pp1 8Documento62 pagineAPBio-pp1 8Kurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- APBio-pp1 7Documento60 pagineAPBio-pp1 7Kurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecosystem Structure (Biomes)Documento100 pagineEcosystem Structure (Biomes)Kurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- APES-Area2d-Natural Ecosystem ChangeDocumento13 pagineAPES-Area2d-Natural Ecosystem ChangeKurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- APBio-pp1 5Documento78 pagineAPBio-pp1 5Kurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- APBio-pp1 4Documento92 pagineAPBio-pp1 4Kurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- APBio-pp1 3Documento92 pagineAPBio-pp1 3Kurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- APBio-pp1 1Documento34 pagineAPBio-pp1 1Kurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- APBio-pp1 2Documento44 pagineAPBio-pp1 2Kurt KleinNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Doping PPT PresentationDocumento26 pagineBlood Doping PPT Presentationee4254100% (1)
- HydrolasesDocumento446 pagineHydrolasesAchilles ThomasNessuna valutazione finora
- Circulatory SystemDocumento16 pagineCirculatory SystemHarinder KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Identification and Habitat Type of Mudskipper (Family: Gobiidae) at The Bali Beach, District of Batu Bara, North Sumatra ProvinceDocumento7 pagineIdentification and Habitat Type of Mudskipper (Family: Gobiidae) at The Bali Beach, District of Batu Bara, North Sumatra ProvinceFikran 31nusiNessuna valutazione finora
- Pant A Review Advances in Microbial Remediation of Trichloroethylene (TCE) 2010Documento11 paginePant A Review Advances in Microbial Remediation of Trichloroethylene (TCE) 2010kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOL 3121 - Lecture 13 - 081116Documento91 pagineBIOL 3121 - Lecture 13 - 081116Sara HuebnerNessuna valutazione finora
- Skin and Body Membranes: EssentialsDocumento43 pagineSkin and Body Membranes: EssentialsJohn Rex Lloyd TunaNessuna valutazione finora
- A New Species of Riverine Crab of The Genus Sundathelphusa Bott, 1969 (Crustacea: Brachyura: Gecarcinucidae) From Northeastern Luzon, PhilippinesDocumento10 pagineA New Species of Riverine Crab of The Genus Sundathelphusa Bott, 1969 (Crustacea: Brachyura: Gecarcinucidae) From Northeastern Luzon, PhilippinesNel YagosNessuna valutazione finora
- Sociology Handout 5Documento13 pagineSociology Handout 5Carzo Aggy MugyNessuna valutazione finora
- Recent DevelopmentsDocumento295 pagineRecent DevelopmentsGabriel PinheiroNessuna valutazione finora
- Kimia Daun PandanDocumento4 pagineKimia Daun Pandanlutfi_alhayathullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscle Biopsy A Diagnostic Tool in Muscle DiseasesDocumento9 pagineMuscle Biopsy A Diagnostic Tool in Muscle DiseasesRosa AquinoNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.1 MicrobiologyDocumento32 pagine6.1 MicrobiologyYsabelle BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Killing of Kangaroos For Meat and SkinDocumento34 pagineKilling of Kangaroos For Meat and SkinVegan FutureNessuna valutazione finora
- The Differences Between Asexual and Sexual ReproductionDocumento2 pagineThe Differences Between Asexual and Sexual ReproductionAmirul IkhwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell and Tissue Culture: Model Cells in Medicine - Stem Cells - Tissue EngineeringDocumento44 pagineCell and Tissue Culture: Model Cells in Medicine - Stem Cells - Tissue EngineeringCrasilia Yanti PadangNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition Label Worksheet PDFDocumento4 pagineNutrition Label Worksheet PDFCha Marie100% (2)
- Final Project Report Kiran MazumdarDocumento31 pagineFinal Project Report Kiran MazumdarPrajot Morajkar100% (3)
- Preparation of Histological SpecimensDocumento4 paginePreparation of Histological SpecimensAqilah HazwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Aims Stress - The SeedDocumento27 pagineAims Stress - The SeedFx KovacsNessuna valutazione finora
- Gender and PsychotherapyDocumento12 pagineGender and PsychotherapyEhh EnNaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chest TubesDocumento34 pagineChest TubesMuhd ShafiqNessuna valutazione finora
- Tomasello, M. (2000) - Culture and Cognitive Development.Documento4 pagineTomasello, M. (2000) - Culture and Cognitive Development.Roberto OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- Artikel SkripsiDocumento12 pagineArtikel SkripsiSari RofiqohNessuna valutazione finora
- NutritionDocumento5 pagineNutritionk,srikanthNessuna valutazione finora
- MSDS Ecaro-25Documento10 pagineMSDS Ecaro-25ValenteNessuna valutazione finora
- Alvin MDocumento2 pagineAlvin MRunmel Emmanuel Ramal DampiosNessuna valutazione finora
- G.B.Pant University of Agriculture & Technology, Pantnagar-263145, Distt. Udham Singh Nagar (Uttarakhand) University Website: WWW - Gbpuat.ac - inDocumento4 pagineG.B.Pant University of Agriculture & Technology, Pantnagar-263145, Distt. Udham Singh Nagar (Uttarakhand) University Website: WWW - Gbpuat.ac - inJeshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Understandings, Applications and Skills (This Is What You Maybe Assessed On)Documento10 pagineUnderstandings, Applications and Skills (This Is What You Maybe Assessed On)beaNessuna valutazione finora
- ART - Spectrophotometric Method For Determining GA in ..Documento4 pagineART - Spectrophotometric Method For Determining GA in ..Azahara Linares100% (2)