Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
SLC - Compulsory Math - Geometric Deduction
Caricato da
www.bhawesh.com.npTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
SLC - Compulsory Math - Geometric Deduction
Caricato da
www.bhawesh.com.npCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Downloaded From:- www.bhawesh.com.
np
Downloaded From:- www.bhawesh.com.np
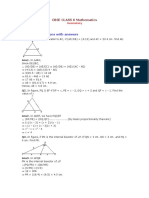
SLC Model Question
SLC _ Compulsory Math _ Geometric Deduction
[Short Questions]
# Section A
a) |+ =+= ABCD = CD |=s == - CD + +- - P c ~- APD + BCP = APB -c ~- +=-- =--=
In the given figure, ABCD is a parallelogram and P is any point on CD. Prove that APD + BCP = APB.
b) ABCD |== ==-- =-~= - AB + +- - P AD + +- - Q c ~- QBC = APD + CPB -c ~-
+=-- =--=
ABCD is a parallelogram. P is any point in AB and Q is any point on AD. Prove that. QBC = APD + CPB.
c) :|+ =+= ABCD |== == - === -+- BD = +- +- - X c +=-- =--=
AXB = =-~= ABCX.
In the given figure, ABCD is a parallelogram is which X is any point on the diagonal BD. Prove that : AXB = quadrilateral ABCX.
d) ==+ =+= PQRS|== ==-- =-~= - -+- PR + +- - M == Q S =:|+ c- =: =--=
PQM + ++= = PSM + ++=
In the adjoining diagram, PQRS is a parallelogram, Q and S are joined to any point M on the diagonal PR of the
parallelogram Prove that are of the PQM = area of PSM
e) =-~= ABCD = AO = Co ~| 2ABD = ABCD -c ~- +=-- =--=
In quadrilateral ABCD, AO = Co, prove that 2ABD = ABCD.
f) ABC + - A BC + |== - D =:|+ c AD + ==- E c ~- ABC = 2EBC -c ~- +=-- =--=
The vertex A of ABC is joined to a point D on the side BC. The midpoint of AD is E, Prove that ABC = 2EBC.
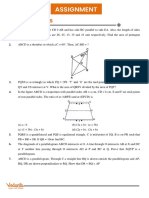
# Section B
a) ==+ =+= ABCD |== ==-- =-~= - CD = +- |== - N c AN = BC =: M -= c- = t:|+ c ~-
BNC + ++= = DNM + ++= -c ~- +=-- =--=
In the adjoining figure, ABCD is a parallelogram, N is any point CD AN and BC are produced to meet the point M. Prove that are of BNC =
the area of the DNM.
Downloaded From:- www.bhawesh.com.np
Downloaded From:- www.bhawesh.com.np
b) :|+ =+= ABCD |== == - = DC = CQ ~| PQC = BPQ -c ~- +=-- =--=
In the given figure, ABCD is a parallelogram IF DC = CQ, prove that PQC = BPQ.
c) == ABCD + ~= AD = +- - F c BF CD =: t| E -= ==:|+ c +=-- =--= BCE = ABDE.
ABCD is a parallelogram F is any point on side AD.BF and CD are produced to meet at E. Prove that BCE = ABDE.
d) ABC + ~= BC == ==-- XY c BE//AC CF//AB = XY =: E F = ~=c ~- ABE = ACF -c ~-
+=-- =--=
XY is a line parallel to side BC of ABC BE//AC and CF//AB meet XY in E and F respectively. Show that ABE = ACF
e) ABC = AB + ==- D BC + +- - P c = CQ//DP ~| 2BPQ = ABC -c ~- +=-- =--=
In ABC, D is the mid-point of AB and P is any point on BC. IF CQ//DP, prove that: 2BPQ = ABC.
f) :|+ +~= ABC =, BE CD = ==+-= - O = +-c- c- =: =--= BOC + ++= = =-~= ADOE + ++=
In the given triangle ABC, two medians BE and CD are intersect at O. Prove that area of BOC = area of quadrilateral ADOE.
g) ABC + ~=-= AB, BC, CA + ==--= += P, Q, R c- ~- +=-- =--=
P, Q and R are the midpoints of sides AB, BC and CA respectively of ABC, prove that,
APR = BPQ = CQR = PQR = ABC.
h) :|+ =+= AP, BP CP + ==--= += L, M N -- ~- ABC = 4LMN -c ~- +=-- =--=
In the given figure, L, M and N are the mid-points of AP, BP and CP respectively, prove that ABC = 4LMN.
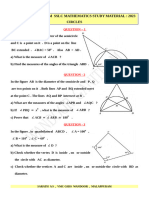
# Section C
a) =-~= ABCD + - C = -+- DB == ==-- -- = =|+ = AB =: ==:|+ + - E =
c|+ c =: =--= =-~= ABCD + ++= = DAE + ++=
The line drawn through the vertex. C of the quadrilateral ABCD parallel to the diagonal DB meets AB product at E. Prove that the quad
ABCD = DAE in area.
b) :|+ =+= PQRS ==== =-~= -, === PQ//MN//SR c- ~- =: =--=
Downloaded From:- www.bhawesh.com.np
Downloaded From:- www.bhawesh.com.np
PSN + ++= = QRM + ++=
In the given figure, PQRS is a trapezium in which PQ//MN//SR. Prove that area of PSN = area QRM.
# Section D
a) =+= =-~= ABCD = AP, BP, CR DR += A, B, C D + =++-: -+ =-~= QPRS +- =+= =-~= -c
~- +=-- =--=
In a cyclic quadrilateral ABCD AP, BP, DR, CR are the bisectors of A, B, D, C respectively. Prove that PQRS is also a cyclic quadrilateral.
b) :|+ =+= -a+ + - O, == AB DOAB ~| AEC = ODA -c ~- =: =--=
In the adjoining figure O is the center of a circle. AB is a diameter and DOAB. Prove AEC=ODA.
c) :|+ =+= AD//BC c ~- AYC = BXD -c ~- +=-- =--=
Given figure is a circle where AD//BC, Prove that AYC=BXD.
d) :|+ =+= AC = BC ABCD |== =+= =-~= - ~- CD = BDE =: =+ =c ~- +=-- =--=
In the given figure, AC=BC and ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral prove that DC bisects BDE.
e) : =-- AB CD +-+ == c- AOD + BOC = 180
0
-c ~- +=-- =--=
Two chords AB and CD are perpendicular to each other. Prove AOD+BOC=180
0
.
f) :|+ =+ |== -a+ - === PMS = QNR ~- PQ//RS -c ~- +=-- =--=
Given figure is a circle and PMS = QNR Prove PQ//RS.
g) :|+ =+= + - O ~|+ -a+ : ==- AB CD -- = =- CE == AB == ==-- BOC =++
+- -- ~- =+ DBE + == - B -c ~- =: =--=
In the figure, AB and CD are two diameters of a circle with center O. If the chord CE is parallel to AB and BOC is obtuse prove that B is the
mid point of arc DBE.
Downloaded From:- www.bhawesh.com.np
Downloaded From:- www.bhawesh.com.np
h) :|+ =+= ABCD |== =+= =-~= - = BC = DE CA = BCD =: ==:-~=- =c ~- ACE ==:-- +~=
-c ~- +=-- =--=
In the given figure, ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. If BC=DE and CA bisects BCD, prove that ACE is an isosceles triangle.
i) :|+ -a= AB == - OC OD ==+- --, =- =+ BC = =+ CD c ~- AD//OC -c ~- +=-- =--=
In the adjoining figure, AB is the diameter. OC and OD are radii where Arc BC= Arc CD, prove that AD//OC.
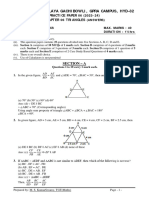
# Section E
a) :|+ -a= AB ==, OC OD ==- --, =- BOC =COD -- ~- AD//OC -c ~- =: =--=
In the adjoining figure, AB is the diameter. OC and OD are radii where BOC=COD, prove that AD//OC.
b) :|+ =+= BC, DBE + =++ - ABCD =+= =-~= - ~- +=-- =--= AC = DC
In the given figure BC is a bisector of DBE. ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral Prove that AC=DC.
c) O P +- ~|+ : -a- A B = +--c- ~|+ c- A B - O P =: C = +=|+ c- +=--
=--=
i) AC = BC ii) OCA = 90
0
Two circles having center O and P intersects at points A and B. AB meets OP at point C. Prove that (I) AC=BC (II) OCA=90
0.
d) O +- ~|+ -a XPY MQN =: XY = X Y - M N = +=+ c +=-- =--= XM = YN
O is the center of two circles XPY and MQN. XY cuts the circle XPY and MQN at X,Y and M,N respectively. Prove XM=YN.
e) ==+ =+= - A = AB AC -+ - =|+ c- -+ DE - F = -+ ~|+ c- ~-
+=-- =--=
In the adjoining figure A is the external point of the circle. AB, AC and DE are tangents of the circle at B, C and F. prove that
AB+AC=AD+DE+AE.
f) =+= AB, BC, CD DA -+ - -a+ + += P,Q,R S -+ -= -+ ~|+ c- +=-- =--= AB + CD =
BC + AD
In the given figure AB, BC, CD and DA are tangents of the circle at P, Q, R, S respectively. Prove that AB+CD=BC+AD.
Downloaded From:- www.bhawesh.com.np
Downloaded From:- www.bhawesh.com.np
g) :|+ =+= : -a- M N = +--c- c- PQ N = - M = + ~|+ c- R,P,S Q += - N
== =:|+ c- ~- =: =--=
In the given figure two circles intersects at M and N respectively PQ and RS pass through M. R, P, S, Q are joined with N. Prove that
PNR=SNQ.
h) :|+ =+= AEC = BFD c =: =--= i) ABC = BCD ii) AB//CD
In the given figure AEC=BFD. Prove that i) ABC = BCD ii) AB//CD
i) :|+ =+=, PQ = PR c- ~- QR//ST -c ~- =--=
In the given figure PQ=PR. Prove that QR//ST.
j) :|+ =+= : =-- PQ RS - X = == --= +=|+ c- +=-- =--=
=
In the adjoining figure chords PQ and RS intersects at X. Prove that, =
k) -= :|+ =+= ABCD |== =+= =-~= - = AB = AC ~| BDE + =++ AD - ~- =: =--=
In the given figure ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. If AB=AC. Prove that AD is the bisector of BDE.
l) :|+ =+= ABC |== +~= - === AB = AC c +=-- =--= AD = AE
In the given figure ABC is a triangle in which AB=AC. Prove that AD=AE.
# Section F
a) :|+ =+= PQ//RS ~| PTR = QUS -c ~- +=-- =--= In the given figure PQ//RS prove that PTR=QUS.
b) ==+ =+= ABCD |== == - a= AB =: E DC =: F = +=+ c ~-, +=-- =--= EFD = ABC
In the adjoining figure ABCD is a parallelogram. The Inscribed circle cuts AB at E and CD at F Prove that EFD=ABC.
Downloaded From:- www.bhawesh.com.np
Downloaded From:- www.bhawesh.com.np
c) :|+ =+= ABCD =+= =-~= - AB//DC c =: =--= (i) AD=BC. (ii) AC=BD.
In the adjoining figure ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral AB//DC. Prove that (i) AD=BC. (ii) AC=BD.
d) :|+ =+=, ABC ==-- +~= c BAC + =++ AD ~| BCE ==:-- +~= - ~- +=--
=--=
In the given figure, ABC is an inscribed equilateral triangle if AD is the bisector of BAC, prove that BCE is an isosceles triangle.
e) :|+ =+=, : -a- P Q --= |+ =+== +=|+ c- P Q = : - APB CQD =|+ c-
~- +=-- =--=
In the given figure, APB and CQD are the straight lines through the points of intersection of two circles. Prove that
(i) AC//BD (ii) CPD=AQB.
f) ==+ =+= O + ~|+ -a= AMOXOZ ~| ~- +=-- =--= OAZ=XYO.
In the adjoining figure, O is the center of circle. If AMOXOZ, then prove that OAZ=XYO.
g) :|+ =+= DE == c = BE = CE = AED = (ABC - ACB) -c ~- +=-- =--=
In the given figure, DE is a diameter. If arc BE=arc CE, then prove that AED= (ABC- ACB)
h) =+= +-- X Y ~|+ -a-+ -+- P ~| +=-- =--= XQ//YR.
In the figure the point of contact of two circles having center X and Y is P. Prove that XQ//YR.
i) :|+ -a= O +- - AB CD : -+ - -- +=-- =--= BAC = 2OBC
In the given figure O is the centre of the circle AB and CD are two tangents Prove that BAC = 2OBC.
Downloaded From:- www.bhawesh.com.np
Downloaded From:- www.bhawesh.com.np
j) =+= =+= =-~= ABCD + |+ ~= BC =: CP = AB -- = - P === ==:|+ c = ABC + =++
BD c ~- DBP ==:- +~= - ~- =: =--=
In the adjoining figure the side BC of a cyclic quadrilateral ABCD is produced to the point P making CP=AB. If BD bisects ABC, prove that
DBP is an isosceles triangle.
k) ==+ =+= AB + ==- X c SAT -+ - ST//XY c +=-- =--= i) AYX = ABC
ii) BXYC =+= =-~= -
In the adjoining figure X is the midpoint of AB, SAT is tangent & ST//XY. Prove that
(i) AYX=ABC (ii) BXYC is a cyclic quadrilateral.
l) ==+ =+= PT == - =+ SR = =+ RT ~| +=-- =--= PS//OR.
In the adjoining figure PT is a diameter Arc SR = Arc RT. Prove that PS//OR.
m) :|+ =+= -a+ =-- MN RS -= - X = +=|+ c- ~- =: =--= MXR=(Arc MR - Arc NS).
In the given figure chords MN and RS intersect at external point X. Prove that MXR = (Arc MR - Arc NS).
# Section G
a) =+= P Q += =+ AB =+ AC + ==-- -- ~- AX = AY -c ~- +=-- =--=
In the figure P and Q are the mid-points of arc AB and arc AC respectively. Prove that: AX = AY.
Hints: - VII(a) 1. Join PA and QA. 2. PQA = PAB =a 3. CAQ = QPA = b
4. AXY = PAB + QPA = a + b 5. AYX = CAQ + AQP = b + a
6. AXY = AYX 7. AX = AY
b) =+=, =-- PR QS +-+ ==+- ++- - E = +=|+ c- QR + == - X XE t= PS + Y = ~=c ~- EYPS -c
~- +=-- =--=
In the figure chords PR and QS of a circle intersect at point E at right angles. X is the mid-point of QR and XE is produced
meets PS in Y Prove that EYPS.
Downloaded From:- www.bhawesh.com.np
Downloaded From:- www.bhawesh.com.np
c) :|+ =+= PQ//AB ~| AY = BY -c ~- +=-- =--=
In the given figure, PQ//AB. Prove that AY = BY.
d) :|+ =+= PB = QB ~| MN//PQ -c ~- +=-- =--=
In the given figure, PB = QB. Prove that MN//PQ.
e) = :|+ =+= CMAB ~= MN//DE ~| AMNC |== =+= =-~= CNAE -c ~- +=-- =--=
In the given figure, CMAB and MN//DE, then prove that AMNC is a cyclic quadrilateral and CNAE.
Hints: VII(e) Join A & C (i) CAN = CMN (both are equals to CDE so, AMNC is a Cyclic quadrilateral (ii) AMC = CNA [since both are on the
same arc hence CNAE]
f) ABCD |== =+= =-~= -, === ~=- AD BC ==== - L = ~=- AB DC ==== - M =
~=+ c- ALB + =++= DC =: - P = AB =: R = AMD + =++= BC =: - Q = AD =: S = ~=+ c- ~- +=--
=--=
i) PR QS +-+ ==+- --= +=c-
ii) PQRS |+ ==-- =-~= -
ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral in which the sides AD and BC when produced meet at L and the sides AB and DC, when produced meet
at M. AMD meets BC in Q and AD in S. Prove that i) PR and QS intersect at right angles ii) PQRS is a rhombus.
Hints VII(f) 1. In LAR & LPC i. ALR =PLC ii. LAR = LCP
2. LAR LPC [by A.A case]
3. ARL = DPR
4. MPR = MRP 5. MP = MR 6. PN = RN & MNPR
7. Similarly SN = NQ & LNSQ 8. PQRS is a rhombus
g) A B = +--c- : -a-= |== -a= +- - P c PA PB ==== =+ -a= Q R = ~=c ~- P -= =+
-+ QR == ==-- -c ~- +=-- =--=
Two circles intersect at A and B. P is any point on one circle PA and PB produced & meet other circle at Q and R, prove that tangent drawn
on a point P is parallel to QR.
h) :|+ =+= O -a+ +- CE -+ D -+- c ~- +=-- =--=
In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle. CE is a tangent and D is the point of contact then prove that:
BOD = 2(AFD-ACD).
Hints : VII(h) Join BD & DA
Downloaded From:- www.bhawesh.com.np
Downloaded From:- www.bhawesh.com.np
1. Let AFD = ABD = a, BAD = PDC = b & BCD = c
2. BOD = 2BAD = 2b 3. a = b + c b = a - c 2b = 2a-2c
4. BOD = 2(a-c) or, BOD = 2(AFD-ACD)
# Section H
a) =+= A, B, C, D, P, Q, R, S +++ -- ~| P + Q + R + S = 540
0
-c ~- +=-- =--=
In the figure A, B, C, D, P, Q, R, S are the points at the circumference then prove that: P + Q + R + S = 540
0
Hints: VIII(a) Draw BD then opposite angles of cyclic quadrilateral is 180
0
so.
P + ADB = 180
0
, S + ABD = 180
0
, R + DBC = 180
0
and Q + CDB = 180
0
Adding all of them
(P + Q +S) + [(ADB + CBD) +(ABD + DBC)] = 720
0
or, (P + Q + R + S) + (ADC + ABC) = 720
0
or, (P + Q + R + S) + 180
0
= 720
0
P + Q + R + S = 540
0
b) =+= ABC ==- +~= - D E += =+ AB =+ AC + ==- ~| +=-- =--= 3XY = DE
In the adjoining figure, ABC is an equilateral triangle. D and E are the midpoints of arc AB and arc AC respectively. Prove that : 3XY = DE.
Hints: VIII(b)
(1) = = = =[Being ABC equilateral from given]
(2) DAX = ADX [Both are angles at the circumference and = ]
(3) DX = AX [From (ii)] (4) Similarly AY = YE[Same as above]
(5) AX = AY = XY [Sides of an equilateral triangle]
(6) DX = YE[From (iii), (iv) and (v)]
(7) DE = DX + XY + YE = XY + XY + XY = 3XY
c) ABC |== ==:- +~= -a=-=- c B C + =++- +++ - X Y = += ~= ~|+ c- -~= BXAYC + ===
~=- -c- ~- +=-- =--=
ABC is an isosceles triangle inscribed in the circle, the bisectors of B and C meet the circumference at X and Y respectively. Shoe that the
polygon BXAYC must have four of its sides equal.
Hints: VIII(c) 1) ACY = BCX [Being CX is a bisector of ACB]
2) ABY = YBC [Being BY is a bisector of ABC]
3) arc AX = arc BX = arc AY = arc YX [Corresponding areas of (i) and (ii)]
4) AX = BX = AY = YC [Corresponding segment of (iii)]
d) :|+ =+= BAC + =++ AP c ~- EF BC ==-- c- ~- +=-- =--=
In the given figure, AP is bisector of BAC. Prove that EF and BC are parallel.
Hints:VIII(d) (1) Join AD then being ABP = EAF and BAP = EDF we get EAF = EDF and AEFD is a cyclic quad.
(2) EFA = EDA and EDA = ACB gives EFA = ACB and EF//BC
e) ABCD |== -= AEF |== ==- +~= |== -a= =-=- c- EF//BD -c ~- +=-- =--=
Downloaded From:- www.bhawesh.com.np
Downloaded From:- www.bhawesh.com.np
ABCD is a square and AEF is an equilateral triangle inscribed in the same circle. Prove that EF//DB.
Hints:VIII(g) (1) Being AD = AB:AD = AB (2) AE = AF:ADE = ABF
(3) DE = BF(subtracting (i) from (ii) hence BD/EF.)
f) ABC =, x, y z += BC, AC AB + ==-- -- = AWBC ~| W,X,Y, Z -- =+= -- ~- +=-- =--=
In ABC, X, Y and Z are the mid-points of BC, AC and AB respectively. If AWBC, prove that W, X, Y and Z are co cyclic.
Hints:VIII(f) Join WZ
(1) AZ = BZ = WZ [Being ABW rt. angled ]
(2) ZBXY is a parm. so B = ZYX and
(3) Being BZ = ZW, B = ZWB hence ZWB = XYZ and W, X, Y, Z are con-cyclic.
g) ==+ =+= AB = BC, AC//XY, CX, AY, XD YD - =+- ~| +=-- =--= ACYX |== =+= =-~= -
In the adjoining figure, AB = BC, AC//XY, CX, AY, XD and YD are straight lines. Prove that: ACYX is a cyclic quadrilateral
Hints: VIII(g) (1) AB = BC, BAC = BCA and
being AC//XY, BAC = BYX
(2) Combing all we get BCA = BYX ACYX is a cyclic quadrilateral
h) =+= ABC |== =-=- +~= - === PMAB,PNAC PRBC c ~- MNR |== =+ -c ~- +=-- =--=
ABC is an inscribed triangle, PMAB,PNAC and PRBC. Prove that MNR is a straight line.
Hints:VIII(h) Join PA and PC
1) Show ANPM is a cyclic quad
2) Show PNRC is a cyclic quad.
3) PCB = PAM[Being ABCP is a cyclic quad.]
4) PCR = PAM
5) PNM = PAM
6) PCR = PNM
7) PNR + PCR = 180
0
[Being the opposite angles of a cyclic quad.]
8) PNR + PNM = 180
0
[from 6 & 7]
9) RNM is a straight line [Form (8)]
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- SLC - Compulsory Math - Model Question - AllDocumento29 pagineSLC - Compulsory Math - Model Question - Allwww.bhawesh.com.np75% (8)
- GeometeryDocumento28 pagineGeometerysaraswathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometery PDFDocumento27 pagineGeometery PDFSaugat KarNessuna valutazione finora
- TrianglesDocumento13 pagineTrianglessudhir_kumar_33Nessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 1 Basic ConceptDocumento1 paginaExercise 1 Basic ConceptDinesCidNessuna valutazione finora
- Traingle Class 10thDocumento6 pagineTraingle Class 10thAarthiKalyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mid-point Theorems and ConstructionsDocumento17 pagineMid-point Theorems and ConstructionsFahad pathanNessuna valutazione finora
- E5 AnswersDocumento24 pagineE5 AnswersIsrar AwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Vectors 13 14Documento41 pagineVectors 13 14Ramchandra MurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulas for triangles and circlesDocumento13 pagineFormulas for triangles and circlesAtithaya Chinchalongporn100% (1)
- Geomtery II AssignmentDocumento20 pagineGeomtery II AssignmentHimanshu Chahar100% (1)
- Vectors in Two Dimensions: PracticeDocumento4 pagineVectors in Two Dimensions: PracticeJohn GohNessuna valutazione finora
- AfrykaDocumento12 pagineAfrykaryszard_lubicz100% (1)
- CBSE IX Congruence of Triangle Solved QuestionsDocumento9 pagineCBSE IX Congruence of Triangle Solved Questionshimanshi swamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Vector Theory EDocumento26 pagineVector Theory EthinkiitNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems and Solutions: CRMO-2012, Paper 3: Solution: Let O be the centre of Γ. By symDocumento3 pagineProblems and Solutions: CRMO-2012, Paper 3: Solution: Let O be the centre of Γ. By symDoddy FeryantoNessuna valutazione finora
- PRMO - INCENTER - QuestionsDocumento4 paginePRMO - INCENTER - QuestionsAnshika MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry II AssignmentDocumento102 pagineGeometry II Assignmentkoushik reddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Goemetry 1 Revision Asssignment 2Documento7 pagineGoemetry 1 Revision Asssignment 2pv71705Nessuna valutazione finora
- SimilarityDocumento69 pagineSimilarityavinandan chandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytic Geometry Problem Booklet Week1 C.pinteaDocumento8 pagineAnalytic Geometry Problem Booklet Week1 C.pinteaCosminRusuNessuna valutazione finora
- Q 1 To 30Documento19 pagineQ 1 To 30Virtualy RichieNessuna valutazione finora
- TrianglesDocumento139 pagineTrianglessujaritha sureshNessuna valutazione finora
- Singapore Math Olympiad 2009 Senior Team Training QuizDocumento4 pagineSingapore Math Olympiad 2009 Senior Team Training QuizSerey KeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Areas of Parallelograms & TrianglesDocumento23 pagineAreas of Parallelograms & Trianglesthinkiit67% (3)
- CBSE Test Paper 04 Chapter 7 Coordinate GeometryDocumento9 pagineCBSE Test Paper 04 Chapter 7 Coordinate GeometryTanmay KatyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Circle - 1Documento5 pagineCircle - 1parthdbz2005Nessuna valutazione finora
- The E Tutor - Similarities of TrianglesDocumento22 pagineThe E Tutor - Similarities of Trianglesinfo5963Nessuna valutazione finora
- 10 TH Grade MathsDocumento164 pagine10 TH Grade MathsdarkdarkhbkNessuna valutazione finora
- Solutions to Problems in CRMO-2012 PapersDocumento10 pagineSolutions to Problems in CRMO-2012 Papersgeddam06108825Nessuna valutazione finora
- Triangles WorksheetDocumento20 pagineTriangles WorksheetRaghav GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Area of Parallelogram Assignment Class 9 CBSEDocumento1 paginaMaths Area of Parallelogram Assignment Class 9 CBSEgurdeepsarora8738Nessuna valutazione finora
- Solution of TrianglesDocumento35 pagineSolution of TrianglesSankar RanjanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9 (Circles)Documento10 pagineChapter 9 (Circles)vishal_bokaroNessuna valutazione finora
- GeometryDocumento22 pagineGeometrynitcvisheshNessuna valutazione finora
- Answers (EXTENSION 1 MATHEMATICS HSC MATHS IN FOCUS)Documento111 pagineAnswers (EXTENSION 1 MATHEMATICS HSC MATHS IN FOCUS)samiryounan3733% (6)
- Math AP ProblemsDocumento7 pagineMath AP ProblemsSUKUMAR GUCHHAITNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Sample Paper 2014Documento14 pagineCBSE Class 9 Mathematics Sample Paper 2014ravilullaNessuna valutazione finora
- Interpreting Numerical Expressions Math Presentation in Light Blue Math Do - 20240121 - 223657 - 0000Documento17 pagineInterpreting Numerical Expressions Math Presentation in Light Blue Math Do - 20240121 - 223657 - 0000tamorromeo908Nessuna valutazione finora
- Interpreting Numerical Expressions Math Presentation in Light Blue Math Do - 20240121 - 223657 - 0000Documento17 pagineInterpreting Numerical Expressions Math Presentation in Light Blue Math Do - 20240121 - 223657 - 0000tamorromeo908Nessuna valutazione finora
- Solution-U V - Practice Paper-2023Documento10 pagineSolution-U V - Practice Paper-2023akshitkk2Nessuna valutazione finora
- PHYS 510 A: Mathematical Methods of Physics Homework #1 Kristin Kathleen Creech LassondeDocumento35 paginePHYS 510 A: Mathematical Methods of Physics Homework #1 Kristin Kathleen Creech LassondeKristin Kathleen Creech Lassonde100% (1)
- Angles and Circles Geometry ProblemsDocumento8 pagineAngles and Circles Geometry Problemsgobinda prasad barmanNessuna valutazione finora
- G-9 Chapter 10 CirclesDocumento5 pagineG-9 Chapter 10 CirclesChetanNessuna valutazione finora
- Most Important Questions (Class 10 Maths) CircleDocumento13 pagineMost Important Questions (Class 10 Maths) CircleSreshta shreeNessuna valutazione finora
- Vector GeometryDocumento2 pagineVector GeometryAkira KobashiNessuna valutazione finora
- Appendix C VectororCrossProduct FinalDocumento8 pagineAppendix C VectororCrossProduct FinalMalik Nazim ChannarNessuna valutazione finora
- 373PR 02Documento2 pagine373PR 02George BasilaiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rectangle geometry and vector calculationsDocumento10 pagineRectangle geometry and vector calculationsNourNessuna valutazione finora
- Proofs and applications of sine and cosine formulaeDocumento22 pagineProofs and applications of sine and cosine formulaeMeenakshi ChaudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- SSLC Mathematics Important Questions Chap 2 EM CIRCLESDocumento11 pagineSSLC Mathematics Important Questions Chap 2 EM CIRCLESviruthaivikas matric schoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Triangles: Teacher: Devajaya GhoshDocumento42 pagineTriangles: Teacher: Devajaya GhoshHanako ChinatsuNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Class X Chapter 06 Triangles Practice Paper 06 AnswersDocumento8 pagineMaths Class X Chapter 06 Triangles Practice Paper 06 Answerssiddarthgavandalkar065Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vector Distributive Laws N Basics Etc PDFDocumento56 pagineVector Distributive Laws N Basics Etc PDFsound05Nessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry Theorems and Proportions ExplainedDocumento164 pagineGeometry Theorems and Proportions Explainedkalaikalai360Nessuna valutazione finora
- Class 9th Solved Questions Chapter QuadrilateralDocumento7 pagineClass 9th Solved Questions Chapter QuadrilateralSASIKALA RAVICHANDRANNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Revision AssignmentsDocumento17 pagineCBSE Class 9 Mathematics Revision AssignmentslauranistNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytic Geometry - Quarter 1 - Week 1Documento9 pagineAnalytic Geometry - Quarter 1 - Week 1L. RikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageDa EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNessuna valutazione finora
- Logo FinalDocumento3 pagineLogo Finalwww.bhawesh.com.np100% (1)
- Economics Notes Class 11 All in OneDocumento0 pagineEconomics Notes Class 11 All in Onewww.bhawesh.com.np84% (45)
- Economics Class 11 Unit 9-IndustryDocumento0 pagineEconomics Class 11 Unit 9-Industrywww.bhawesh.com.np100% (1)
- Economics Class 11 Unit 6-Human-ResourceDocumento0 pagineEconomics Class 11 Unit 6-Human-Resourcewww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- Economics Class 11 Unit 13-Development-PlanningDocumento0 pagineEconomics Class 11 Unit 13-Development-Planningwww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- Economics Class 11 Unit 4-Economic-DevelopmentDocumento0 pagineEconomics Class 11 Unit 4-Economic-Developmentwww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- Economics Class 11 Unit 12-Government-FinanceDocumento0 pagineEconomics Class 11 Unit 12-Government-Financewww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- Economics Class 11 Unit 15 Collection of DATADocumento0 pagineEconomics Class 11 Unit 15 Collection of DATAwww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- Economics Class 11 Unit 14-StatisticsDocumento0 pagineEconomics Class 11 Unit 14-Statisticswww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- Economics Class 11 Unit 11-Foreign-TradeDocumento0 pagineEconomics Class 11 Unit 11-Foreign-Tradewww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- Economics Class 11 Unit 7-AgricultureDocumento0 pagineEconomics Class 11 Unit 7-Agriculturewww.bhawesh.com.np0% (1)
- Economics Class 11 Unit 8-PovertyDocumento0 pagineEconomics Class 11 Unit 8-Povertywww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- Economics Class 11 Unit 2-Basic-Economic-IssuesDocumento0 pagineEconomics Class 11 Unit 2-Basic-Economic-Issueswww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- Economics Class 11 Unit 5 Natural Resources of NepalDocumento0 pagineEconomics Class 11 Unit 5 Natural Resources of Nepalwww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology - Unit 2 Origin and Evolution of LifeDocumento0 pagineBiology - Unit 2 Origin and Evolution of Lifewww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology - Zoology - Unit 8 Environmental PollutionDocumento0 pagineBiology - Zoology - Unit 8 Environmental Pollutionwww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Botany AngiospermDocumento0 pagineBiology Botany Angiospermwww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- Economics Class 11 Unit 1 - Basic-Concept-Of-EconomicDocumento0 pagineEconomics Class 11 Unit 1 - Basic-Concept-Of-Economicwww.bhawesh.com.np100% (5)
- Biology - Unit 10 Conservation of Wildlife ResourcesDocumento0 pagineBiology - Unit 10 Conservation of Wildlife Resourceswww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology - Zoology Unit 7 Detailed Study of FrogDocumento0 pagineBiology - Zoology Unit 7 Detailed Study of Frogwww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology - Botany - Kingdom MoneraDocumento0 pagineBiology - Botany - Kingdom Monerawww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology - Unit 9 Animal BehaviourDocumento0 pagineBiology - Unit 9 Animal Behaviourwww.bhawesh.com.np100% (1)
- SLC - OPT Math - PolynomialsDocumento0 pagineSLC - OPT Math - Polynomialswww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology - Unit 4 Kingdom ProtistaDocumento0 pagineBiology - Unit 4 Kingdom Protistawww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio-Logy - Unit 6 Detailed Study of EarthwormDocumento0 pagineBio-Logy - Unit 6 Detailed Study of Earthwormwww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- SLC - OPT Math - FunctionsDocumento0 pagineSLC - OPT Math - Functionswww.bhawesh.com.np100% (1)
- Biology - BiodiversityDocumento0 pagineBiology - Biodiversitywww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio-Logy - Unit 10 Biota and EnvironmentDocumento0 pagineBio-Logy - Unit 10 Biota and Environmentwww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- SLC - OPT Math - Natural NumbersDocumento0 pagineSLC - OPT Math - Natural Numberswww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- SLC - OPT Math - Geometric ProgressionDocumento0 pagineSLC - OPT Math - Geometric Progressionwww.bhawesh.com.npNessuna valutazione finora
- Class-10 SyllabusDocumento6 pagineClass-10 SyllabusUttam KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Gnomonic ChartDocumento3 pagineGnomonic ChartAMAZING GREATNESSNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Conic SectionsDocumento6 pagineApplication of Conic SectionsErlyn Grace RedobladoNessuna valutazione finora
- Bansal Classes Maths ProblemsDocumento5 pagineBansal Classes Maths ProblemsRahul Kumar SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Equations of A Straight LineDocumento6 pagineEquations of A Straight LineRose J. San JuanNessuna valutazione finora
- DGT Circle and ConicsDocumento52 pagineDGT Circle and ConicsHozaifa HamimNessuna valutazione finora
- Hamza Army Public School & College (B0Ys) Mcqs Mathematics Hssc-IiDocumento7 pagineHamza Army Public School & College (B0Ys) Mcqs Mathematics Hssc-IiIsbah INessuna valutazione finora
- Jee Mainmaths Paper With Solutions Paper 1Documento8 pagineJee Mainmaths Paper With Solutions Paper 1anuragNessuna valutazione finora
- 25 - Complex Locus of A CircleDocumento4 pagine25 - Complex Locus of A CircleJohnny GutsNessuna valutazione finora
- CircleDocumento59 pagineCircleMaliney PohsNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths November 2022 Question PaperDocumento6 pagineMaths November 2022 Question PaperKumar SubramanianNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus I With Analytic Geometry Test RevDocumento5 pagineCalculus I With Analytic Geometry Test Revarbee.iiooNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytical GeometryDocumento78 pagineAnalytical GeometryChinnaGurappaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ade 8 Consolidation Mathematics Student Workbook - FinalDocumento83 pagineAde 8 Consolidation Mathematics Student Workbook - FinalRHEA JANE A PILLADONessuna valutazione finora
- Senior 11 Pre-Calculus - Week-4 Module 8 For Printing PDFDocumento27 pagineSenior 11 Pre-Calculus - Week-4 Module 8 For Printing PDFRichard Bachar100% (2)
- Math 237 PreFinals Set ADocumento1 paginaMath 237 PreFinals Set AShunsui SyNessuna valutazione finora
- Circles Arcs and Sectors MediumDocumento5 pagineCircles Arcs and Sectors Mediumpoonam.upadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathalino: Spiral CurveDocumento6 pagineMathalino: Spiral CurveHaftu HadushNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 7: Coordinate Geometry: 7.1 Division of A Line SegmentDocumento19 pagineCHAPTER 7: Coordinate Geometry: 7.1 Division of A Line SegmentISMADI SURINNessuna valutazione finora
- The Planar Euler-Savary EquationDocumento9 pagineThe Planar Euler-Savary EquationaldoNessuna valutazione finora
- Parabolic Shapes and Their EquationsDocumento9 pagineParabolic Shapes and Their EquationsMohd Sofian MustaffaNessuna valutazione finora
- Edited AssignmentDocumento1 paginaEdited AssignmentPreethi SharmiNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 10 Circles Answer KeyDocumento1 paginaCH 10 Circles Answer KeyAlexie Mangalo100% (1)
- 9 4 Rotation and Systems of Quadratic EquationsDocumento15 pagine9 4 Rotation and Systems of Quadratic Equationsapi-317140261Nessuna valutazione finora
- 20-1 U1L1.1 - Worksheet Key - Graphing Quadratic FunctionsDocumento4 pagine20-1 U1L1.1 - Worksheet Key - Graphing Quadratic FunctionsPaige MayellNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3Documento95 pagineUnit 3KIRAN KUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 Intro To Conic Sections and Circles 1Documento11 pagineLesson 1 Intro To Conic Sections and Circles 1Markkhian GeveroNessuna valutazione finora
- Aits 2021 PT Ii JeemDocumento6 pagineAits 2021 PT Ii JeemTuoti DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Straight Line Equations Worksheet #01, Algebra Revision From GCSE Maths TutorDocumento2 pagineStraight Line Equations Worksheet #01, Algebra Revision From GCSE Maths TutorgcsemathstutorNessuna valutazione finora
- ME Math 10 Q2 1003 PSDocumento28 pagineME Math 10 Q2 1003 PSJazther Keishan RectoNessuna valutazione finora