Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Understanding MIL-F-8785C flying qualities requirements
Caricato da
Florence KwokTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Understanding MIL-F-8785C flying qualities requirements
Caricato da
Florence KwokCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Lecture 9 : Understanding MIL-F-8785C
Or the flying qualities of piloted airplanes
G. Leng, Flight Dynamics, Stability & Control
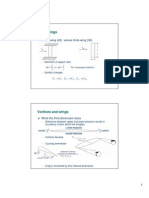
1.0 The concept of a reduced order approximation
1.1 Each stable real eigenvalue define a reduced (first) order approximation of the form: x T : + (1/T) x = 0
time constant
The real eigenvalue is of the form:
G. Leng, Flight Dynamics, Stability & Control
Figure 1.1 : 1st order system x(t)/x(0) = exp(-t/T)
t/T
G. Leng, Flight Dynamics, Stability & Control
1.2 Each complex pair of eigenvalues define a reduced (second) order approximation of the form: x + (2) x + 2 x : : damping ratio 01 = 0
undamped natural frequency
2. The complex pair of eigenvalues is of the form:
G. Leng, Flight Dynamics, Stability & Control
Fig 1.2 : 2nd order system x(t)/x(0) = exp[- () t ] cos(dt)
dt/ 2
G. Leng, Flight Dynamics, Stability & Control
In the complex plane, the damping ratio and the undamped natural frequency for a complex eigenvalue can be deduced as follows: j
(1 - 2 )
-
G. Leng, Flight Dynamics, Stability & Control
Important note 1. Eigenvalues with the same natural frequency are at the same distance from the origin. 2. Eigenvalues with the same damping ratio make the same angle with the imaginary axis. 3. MIL-F-8785C specifies flying qualities using these concepts.
G. Leng, Flight Dynamics, Stability & Control
2.0 MIL-F-8785C requirement for phugoid mode Recall that the phugoid mode is marginally stable or unstable...
Indicate these boundaries on the complex plane
G. Leng, Flight Dynamics, Stability & Control
2.1 MIL-F-8785C, Section 1.5 : Levels of Flying Qualities
G. Leng, Flight Dynamics, Stability & Control
2.2 MIL-F-8785C boundaries for phugoid mode
The angle of the constant damping with the imaginary axis is = =
G. Leng, Flight Dynamics, Stability & Control
3.0 MIL-F-8785C : Short period damping requirements
Note damping ratio 0.35 0.25 0.15
angle with imaginary axis (o)
G. Leng, Flight Dynamics, Stability & Control
3.1 MIL-F-8785C, Section 1.4 Flight Phase Categories Cat A : non terminal flight phase, rapid maneuvering, precision tracking, precise flight path control, ex: CO - air to air combat, GA ground attack Cat B : non terminal flight phase , gradual maneuvers, no precise tracking, may need precise flight path control, ex : CR - cruise, CL - climb, D - descent, LO - loiter Cat C : terminal flight phases, gradual maneuvers, accurate flight path control, ex : TO - takeoff, L - landing
G. Leng, Flight Dynamics, Stability & Control
4.0 MIL-F-8785C 3.3.1.1 Dutch roll requirements
G. Leng, Flight Dynamics, Stability & Control
4.1 MIL-F-8785C 1.3 Classification of Airplanes
G. Leng, Flight Dynamics, Stability & Control
The most demanding class of airplanes
G. Leng, Flight Dynamics, Stability & Control
5.0 MIL-F-8785C 3.3.1.2 Roll mode requirements
G. Leng, Flight Dynamics, Stability & Control
6.0 MIL-F-8785C 3.3.1.3 Spiral mode requirements Recall that the spiral mode affects the roll (bank) angle...
G. Leng, Flight Dynamics, Stability & Control
7.0 MIL-F-8785C 3.3.4.1.1 Roll performance (class IV airplanes)
G. Leng, Flight Dynamics, Stability & Control
7.1 MIL-F-8785C 3.3.4.1 Speed ranges for roll performance
Vmax , Vmin : maximum (minimum) service speed Vo : above as adjusted by a factor in Table 1
G. Leng, Flight Dynamics, Stability & Control
Question : Is there life after MIL-F-8785C ?
G. Leng, Flight Dynamics, Stability & Control
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- FLIGHT DYNAMICS EXAM RESULTSDocumento9 pagineFLIGHT DYNAMICS EXAM RESULTSAkshay KulkarniNessuna valutazione finora
- Transfer Function Form of Roll DynamicsDocumento9 pagineTransfer Function Form of Roll DynamicsD.Viswanath100% (1)
- Introduction To Aerial Vehicle Flight Mechanics, Stability and Control - CranfieldDocumento14 pagineIntroduction To Aerial Vehicle Flight Mechanics, Stability and Control - Cranfielddaus100% (1)
- A Effect of Elevator Deflection On Lift Coefficient IncrementDocumento17 pagineA Effect of Elevator Deflection On Lift Coefficient IncrementIJMERNessuna valutazione finora
- AE3212 I 2 Static Stab 1 AcDocumento23 pagineAE3212 I 2 Static Stab 1 AcRadj90Nessuna valutazione finora
- GATE Aerospace Forum's Delhi Test for GATE(AE) - 2017 QuestionsDocumento5 pagineGATE Aerospace Forum's Delhi Test for GATE(AE) - 2017 QuestionsharishNessuna valutazione finora
- Baehawk120 Flight Model DataDocumento6 pagineBaehawk120 Flight Model Datatomay777Nessuna valutazione finora
- Aircraft Control Surfaces CalculationDocumento16 pagineAircraft Control Surfaces Calculationlove2me20040% (1)
- Instrumentation For Flight TestingDocumento17 pagineInstrumentation For Flight TestingNambi RajanNessuna valutazione finora
- A Perspective On The Requirements and Design For Advanced Cruise MissilesDocumento7 pagineA Perspective On The Requirements and Design For Advanced Cruise Missilesgrindormh53100% (1)
- Uav CFD AnalysisDocumento15 pagineUav CFD AnalysisRanjeet SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- F16 Flight Control SystemDocumento16 pagineF16 Flight Control SystemARIJITNessuna valutazione finora
- Multhopp Method PDFDocumento18 pagineMulthopp Method PDFsizzleNessuna valutazione finora
- Autopilot HistoryDocumento20 pagineAutopilot HistoryKamesh PrasadNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review On Bird Strike Capability On Service-Age Aircraft CanopyDocumento14 pagineA Review On Bird Strike Capability On Service-Age Aircraft Canopytomzee1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Aerodynamic stability derivatives for aircraft roll and yawDocumento3 pagineAerodynamic stability derivatives for aircraft roll and yawGurunath AeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidance AlgorithmsDocumento12 pagineGuidance Algorithmsanil2383100% (1)
- Vought F7U-1 Jet FighterDocumento9 pagineVought F7U-1 Jet FighterqzakryaNessuna valutazione finora
- NACA AirfoilDocumento3 pagineNACA Airfoilmmaggiore3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Proportional Navigation Guidance (Cite:john H Blakelock)Documento7 pagineProportional Navigation Guidance (Cite:john H Blakelock)D.ViswanathNessuna valutazione finora
- APL Basic Principles of Homing Guidance PalumboDocumento17 pagineAPL Basic Principles of Homing Guidance PalumboÁlvaro Conti FilhoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lateral and Longitudinal Stability Analysis of UAV Using Xflr5-1163 PDFDocumento5 pagineLateral and Longitudinal Stability Analysis of UAV Using Xflr5-1163 PDFAlexandraAndreeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Whole Ac StructureDocumento22 pagineWhole Ac StructureLara SeverinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Schrenk Dan Gaya DalamDocumento7 pagineSchrenk Dan Gaya DalamandriaerospaceNessuna valutazione finora
- Aerodynamic Sections: (An Introduction Based On NACA Airfoils)Documento16 pagineAerodynamic Sections: (An Introduction Based On NACA Airfoils)jvila31Nessuna valutazione finora
- NR - Numerical Model of Single Main Rotor Helicopter DynamicsDocumento10 pagineNR - Numerical Model of Single Main Rotor Helicopter DynamicsHossam T BadranNessuna valutazione finora
- Tip Extensions, Winglets, and C-Wings: Conceptual Design and OptimizationDocumento33 pagineTip Extensions, Winglets, and C-Wings: Conceptual Design and Optimizationfelo82Nessuna valutazione finora
- Preliminary Design and Development of Small Class UAV For Testing of Different Payloads and SensorsDocumento6 paginePreliminary Design and Development of Small Class UAV For Testing of Different Payloads and SensorsAlg PRasadNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimization: of Joined-Wing AircraftDocumento10 pagineOptimization: of Joined-Wing AircraftSagar KulkarniNessuna valutazione finora
- FS2004 - The Aircraft - CFG FileDocumento5 pagineFS2004 - The Aircraft - CFG FiletumbNessuna valutazione finora
- AERO 2011 Q3 Article4 PDFDocumento9 pagineAERO 2011 Q3 Article4 PDFAmirAli MohebbiNessuna valutazione finora
- Determining Aircraft Excess Power CharacteristicsDocumento53 pagineDetermining Aircraft Excess Power CharacteristicsÇalanyalıoğluNessuna valutazione finora
- MATLAB SIMULATIONS FOR GARNELL's ROLL AUTOPILOTDocumento16 pagineMATLAB SIMULATIONS FOR GARNELL's ROLL AUTOPILOTD.ViswanathNessuna valutazione finora
- Airborne Doppler Radar Navigation of Jet Transport Aircraft-EftDocumento10 pagineAirborne Doppler Radar Navigation of Jet Transport Aircraft-Eftjulio perezNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 2 Problems SheetDocumento3 pagineCH 2 Problems SheetqzakryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Im Feld 1976Documento6 pagineIm Feld 1976Bill WongNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of The Full Scale Durability Tests On F-35 Lightning II ProgramDocumento21 pagineOverview of The Full Scale Durability Tests On F-35 Lightning II ProgrampuhumightNessuna valutazione finora
- Joined-Wing Aircraft Design and OptimizationDocumento11 pagineJoined-Wing Aircraft Design and OptimizationAli YıldırımNessuna valutazione finora
- Aircraft Flight Control System ModellingDocumento10 pagineAircraft Flight Control System ModellingMahmoudNessuna valutazione finora
- Control Techniques of Tilt Rotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Systems A ReviewDocumento18 pagineControl Techniques of Tilt Rotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Systems A Reviewchen4567Nessuna valutazione finora
- 14 01954MertMuameleciRapportDocumento72 pagine14 01954MertMuameleciRapportandredurvalandradeNessuna valutazione finora
- Modeling Future Aircraft Using OpenVSPDocumento23 pagineModeling Future Aircraft Using OpenVSPgustavojorge12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wing Theory Exercise PDFDocumento10 pagineWing Theory Exercise PDFthanesh01100% (1)
- Introduction To Flight Test Engineering: Dan HrehovDocumento30 pagineIntroduction To Flight Test Engineering: Dan HrehovmsrajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Missile Autopilot AerodynamicsDocumento12 pagineMissile Autopilot AerodynamicsD.ViswanathNessuna valutazione finora
- AerodynamicsDocumento11 pagineAerodynamicsAnuj KrNessuna valutazione finora
- Reducing Wave DragDocumento43 pagineReducing Wave DragJaredSagagaNessuna valutazione finora
- DCS JF-17 - Normal ProceduresDocumento17 pagineDCS JF-17 - Normal ProceduresJamoc0Nessuna valutazione finora
- Thank You.: Texstars, Inc. TEL: 972.647.1366 FAX: 972.641.2800Documento24 pagineThank You.: Texstars, Inc. TEL: 972.647.1366 FAX: 972.641.2800Balwinder GherhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aermacchi M-346 Brochure ENG NewDocumento11 pagineAermacchi M-346 Brochure ENG NewThallez100% (1)
- Adp Fighter AircraftDocumento35 pagineAdp Fighter Aircraftiyyappan rockNessuna valutazione finora
- Aircraft Design With Maneuver and Gust Load AlleviationDocumento15 pagineAircraft Design With Maneuver and Gust Load AlleviationNeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Maneuverable SuperSonic AircraftDocumento174 pagineManeuverable SuperSonic AircraftRahul KaruvingalNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods of Radar Cross-section AnalysisDa EverandMethods of Radar Cross-section AnalysisJ.W. Jr. CrispinNessuna valutazione finora
- A Much Unsung Hero, The Lunar Landing Training Vehicle: And Other NASA RecollectionsDa EverandA Much Unsung Hero, The Lunar Landing Training Vehicle: And Other NASA RecollectionsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Aerospace Actuators 1: Needs, Reliability and Hydraulic Power SolutionsDa EverandAerospace Actuators 1: Needs, Reliability and Hydraulic Power SolutionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Flight DynamicsDocumento33 pagineIntroduction To Flight DynamicsAnkita MundaNessuna valutazione finora
- NASA Exploration Systems Architecture Study - Final Report - November 2005Documento758 pagineNASA Exploration Systems Architecture Study - Final Report - November 2005sandrotanNessuna valutazione finora
- Avp Project (Moeez)Documento56 pagineAvp Project (Moeez)Faiq AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison of Orbital Launch SystemsDocumento173 pagineComparison of Orbital Launch SystemsgihadNessuna valutazione finora
- Jammin' Jets DesignDocumento2 pagineJammin' Jets DesignFyka RaufNessuna valutazione finora
- A300-600 FMS Pilot's GuideDocumento441 pagineA300-600 FMS Pilot's GuidePunthep Punnotok100% (1)
- Compressible Flow2 PDFDocumento7 pagineCompressible Flow2 PDFChaitanya Kishore ChitikenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aircraft DesignDocumento163 pagineAircraft Designsrbhdesh100% (9)
- Design principles for small aircraftDocumento34 pagineDesign principles for small aircraftMarion Nori MarallagNessuna valutazione finora
- Spacecraft Final ProjectDocumento25 pagineSpacecraft Final Projectapi-359883631Nessuna valutazione finora
- Airplane Wing Geometry and ConfigurationsDocumento7 pagineAirplane Wing Geometry and Configurationsh_mahdiNessuna valutazione finora
- Sonic BoomDocumento6 pagineSonic BoomSaifAdamz'sNessuna valutazione finora
- Helicopter RotorDocumento14 pagineHelicopter RotorRoshith Nair100% (1)
- From 2D To 3D WingsDocumento13 pagineFrom 2D To 3D Wingsentalto10% (2)
- X-Plane Helicopter Operation ManualDocumento22 pagineX-Plane Helicopter Operation ManualErnani KernNessuna valutazione finora
- NASA DSN Tracks Spacecraft Beyond EarthDocumento21 pagineNASA DSN Tracks Spacecraft Beyond EarthمحمدالنعيماتNessuna valutazione finora
- SatelliteDocumento38 pagineSatelliteapi-286215473Nessuna valutazione finora
- A320 TR SyllabusDocumento50 pagineA320 TR SyllabusMaalu Manohar100% (1)
- Livro Aerodynamics-Aeronautics-and-Flight-Mechanics-McCormick PDFDocumento666 pagineLivro Aerodynamics-Aeronautics-and-Flight-Mechanics-McCormick PDFLay AlmeidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biplanes vs. MonoplanesDocumento15 pagineBiplanes vs. Monoplaneslakshmi dileepNessuna valutazione finora
- Flight Vehicle Design: Module - 4Documento12 pagineFlight Vehicle Design: Module - 4vinuth nNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of Gemini Extravehicular ActivityDocumento336 pagineSummary of Gemini Extravehicular ActivityBob Andrepont100% (2)
- Basic Cold & Dark Preparation ProcedureDocumento6 pagineBasic Cold & Dark Preparation ProcedureMiguel Cayuela de PedroNessuna valutazione finora
- Ap 106 PDFDocumento298 pagineAp 106 PDFEleazar100% (2)
- Chapter 3 Satellite Subsystems 1Documento20 pagineChapter 3 Satellite Subsystems 1Akhil Mohanan71% (14)
- Science of Flight-White WingsDocumento14 pagineScience of Flight-White WingsMtzCarlosNessuna valutazione finora
- Boeing 757 Normal Checklist: Power Up & Preliminary PreflightDocumento4 pagineBoeing 757 Normal Checklist: Power Up & Preliminary PreflightАлексей ЯрлыковNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometric 3D Path-Following Control For A Fixed-Wing UAV On SODocumento30 pagineGeometric 3D Path-Following Control For A Fixed-Wing UAV On SOFikri Khairul AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- AeroDocumento556 pagineAeroLucas LazaméNessuna valutazione finora