Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Nursing Care Plan
Caricato da
Merfat AbubakarTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Nursing Care Plan
Caricato da
Merfat AbubakarCopyright:
Formati disponibili
NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT Subjective Cues: Masakit po at parang nangingilo ang legs ko, as verbalized by the patient. OBJECTIVE OF CARE At the end of 48 hours nursing intervention, the patient will be able to: NURSING INTERVENTION RATIONALE IMPLEMENTATION EVALUATION After implementing the nursing interventions: The patient have verbalized understanding of causative factors and demonstrated behaviors to resolve excess fluid volume.
Objective Cues verbalize assess patients general To determine assessed patients general - BP: 180/90 mmhg understanding of condition what approach to condition - T: 39C causative factors use in treatment - edematous leg of excess fluid - shortness of breath volume discuss the causative To give knowledge Discussed the causative - Urine Output: 500 factors of excess fluid factors of the excess fluid mL for 24 hour volume volume. period -Lab results: demonstrate monitor intake and I&O balance monitored intake and output Creatinine 6.3 adequate fluid output every 4 hours reflects fluid every 4 hours BUN 90 balance status Potassim 7.0
Nursing Diagnosis Fluid volume excess related to decrease urine out put and retention of sodium and water
weigh patient daily and compare to previous weights
Body weight is a weighed patient daily and sensitive compared to previous indicator of fluid weights balance and an increase indicates fluid volume excess
Auscultate breath When increased Auscultated breath sounds sounds q 2hr and pm for pulmonary q 2hr the presence of crackles capillary and monitor for frothy hydrostatic sputum production pressure exceeds oncotic pressure, fluid moves within the alveolar septum and is evidenced by the auscultation of crackles. Frothy, pink-tinged sputum is an indicator that the client is
developing pulmonary edema
Follow low-sodium diet Fluid restriction and/or fluid restriction may be used to decrease fluid intake, hence decreasing fluid volume excess.
Followed low-sodium diet and/or fluid restriction
Encourage or provide oral care q2
The client senses Encouraged or provide oral thirst because care q2 the body senses dehydration. Oral care can alleviate the sensation without an increase in fluid intake Inidicates fluid overload Monitored for distended neck veins and ascites
Monitor for distended neck veins and ascites
HEALTH TEACHING PLAN
SUBJECT MATTER: Acute Renal Failure TIME ALLOTMENT: 15 mins GENERAL OBJECTIVES: At the end of 15 minutes health teaching, the patient and his family will be able to acquire knowledge about acute renal failure. LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of health teaching, the patient should be able to: 1. Define acute renal failure The acute renal failure is an abrupt reduction in renal functions associated with oligurea (less than 400/day),fatigue,anorexia,nausea and vomiting 2 mins Explanation TIME ALLOTMENT
CONTENT
STRATEGIES
EVALUATION CRITERIA
ORAL QUESTIONING
In your own understanding, what is acute renal failure? -Ang acute renal failure po ay ang paunti-unting pagkawala ng function ng kidney natin. Can you give atleast 4 signs and symptoms? -fatigue -pagsusuka
2. Enumerate the signs and symptoms
Signs and Symptoms Oligurea (less than 400ml/day) Anuria(less than 50/day) Fatigue
4 mins
One on one discussion
3. Demonstrate understanding on the cause of acute renal failure
Anorexia Nausea Vomiting Increase creatinine and urea level in serum
-pagkonti ng dami ng ihi -walang ganang kumain
CAUSES AKI can be caused by disease, crush injury, contrast agents, some antibiotics, and more. The causes of acute kidney injury are commonly categorized into prerenal, intrinsic, and postrenal. Prerenal
6 mins
Explanation Any question about the causes of acute renal failure? -Wala po. Naiintidihan ko na isa sa mga rason kung bakit may acute renal failure ako ay dahil sa pagkakaroon ko ng diabetes.
Prerenal causes of AKI ("pre-renal azotemia") are
those that decrease effective blood flow to the kidney. These include systemic causes, such as low blood volume, low blood pressure, heart failure, and local changes to the blood vessels supplying the kidney. The latter include renal artery stenosis, or the narrowing of the renal arterywhich supplies the kidney with blood, and renal vein thrombosis, which is the formation of a blood clot in the renal vein that drains blood from the kidney. Intrinsic Sources of damage to the kidney itself are dubbed intrinsic. Intrinsic AKI can be due to damage to the glomeruli, renal tubules,
orinterstitium. Common causes of each are glomerulonephritis, acute tubular necrosis (ATN), and acute interstitial nephritis (AIN), respectively. A cause of intrinsic acute renal failure is tumor lysis syndrome.[7] Postrenal
Postrenal AKI is a consequence of urinary
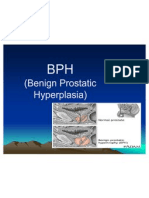
tract obstruction. This may be related to benign prostatic hyperplasia, kidney stones, obstructed urinary catheter, bladder stone, bladder, ureteral or renal malignancy. It is useful to perform a bladder scan or a post void residual to rule out urinary retention.
DIET: 4. Identify the importance of diet Low sodium Diet People with acute renal failure can improve their symptoms by reducing the amount of salt (sodium) in their diet. Sodium is a mineral found in many foods. Eating too much salt causes the body to keep or retain too much water, worsening the fluid build-up associated with heart failure. 3 mins One on one discussion How will it help you? -Sa pamamagitan ng pagkain ng tama ay kahit papaano mababawasan ang aking paghihirap sa mga sintomas.
GENERIC NAME -Furosemide
INDICATION
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES Observe the 10 rights in administering medications. Assess fluid status. Notify physician or other health care professional if thirst, dry mouth, hypotension, or oliguria occurs. Monitor blood pressure and pulse before and during administration. Monitor blood glucose closely; may cause increased blood glucose level. Caution patient to change positions slowly to minimize orthostatic hypotension. Advise patient to contact health care professional immediately if muscle weakness, cramps,nausea, dizziness and numbness occurs.
CLASSIFICATION - Loop diuretics
Edema d/t heart failure, hepatic impairment or renal disease. Hypertension.
blurred vision, dizziness, head ache, vertigo
DOSAGE - 1 tablet, 200 mg
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ADVERSE EFFECTS
ROUTE -PO
Hypersensitivity; Cross-sensitivity with thiazides and sulfonamides may occur; Hepatic coma or anuria; Some liquid products may contain alcohol, avoid in patients with alcohol intolerance.
CNS blurred vision, dizziness, head ache, vertigo EENT hearing loss, tinnitus CV hypotension GI anorexia, constipation, diarrhea, dry mouth, nausea, vomiting GU excessive urination Derm photosensitivity, rash F and E dehydration
GENERIC NAME: - Norfloxacin
INDICATION
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES Observe the 10 rights in administering medications. Instuct patient to take the drug on an empty stomach. Teach patient to drink a lot of fluids. Advise patient to contact health care professional immediately if muscle weakness, cramps,nausea, dizziness and numbness occurs.
CLASSIFICATION - Antibiotic - Fluoroquinolone DOSAGE - 4oo mg
FREQUENCY: -Q12
For the treatment of adults with UTIs caused by susceptible bacteria. Prostatitis caused by E. coli
blurred vision, dizziness, head ache, vertigo
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ADVERSE EFFECTS
ROUTE -PO
Contraindicated with allergy to norfloxacin, nalidixic acid or cinoxacin; lactation; history of tendonitis or tendon rupture. Use cautiously in patients with renal impairment, seizures, pregnancy.
CNS headache, dizziness, insomnia, fatigue, somnolence, depression, blurred vision GI anorexia, constipation, diarrhea, dry mouth, nausea, vomiting
GENERIC NAME: - Amlodipine besylate
INDICATION
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES Observe the 10 rights in administering medications. Monitor patients BP carefully while adjusting drug to therapeutic doses. Administer drug without regard to meals. Instruct patient to report immediately if he will have irregular heartbeat, shortness of breath, swelling of feet or hands
CLASSIFICATION - Antianginal - Antihypertensive DOSAGE - 5 mg
FREQUENCY: -QID
Essential hypertension, alone or in combination with other antihypertensives. Also for chronic stable angina.
Nausea, vomiting and headache
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ADVERSE EFFECTS
ROUTE -PO
Contraindicated with allergy to amlodipine. Use cautiously with heart failure and pregnancy.
CNS light-headedness, dizziness, asthenia, fatigue, lethargy CV peripheral edema, arrythmias GI nausea, abdominal discomfort Dermatologic flushing, rash
GENERIC NAME: - Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate
INDICATION
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES Observe the 10 rights in administering medications. Monitor serum electrolytes. Frequent blood tests will be needed to monitor drug effect. Report confusion, irregular heartbeats, constipation, severe GI upset.
Treatmentof hyperkalemia. CLASSIFICATION - Potassium removing resin DOSAGE - 15g
FREQUENCY: -QID
GI upset and constipation.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ADVERSE EFFECTS
ROUTE -PO
Contraindicated with allergy to any component of the drug, obstructive bowel, severe hypertension, severe HF, marked edema.
GI constipation, fecal impacation, gastric irritation, anorexia, nausea, vomiting Hematologic Hypokalemia, electrolyte abnormalities
HEALTH PROBLEM Possible preeclampsia
FAMILY NURSING PROBLEM 1.Inability to recognize the possible complication in pregnancy due to lack of knowledge. 2.Inability to provide adequate nursing care to a pregnant member due to: a. Failure to comprehend the nature and magnitude of the condition. b.Low salience of theproblem/ condition.
GOAL OF CARE After nursing intervention, the family will be able to take the necessary measures to properly manage preeclampsia.
OBJECTIVES OF CARE After nursing intervention, thefamily will be able to:
INTERVENTIONS
IMPLEMENTATIO N
EVALUATION
1.Acquire information about the complication including the signs and symptoms.
1.Discuss with the family the causes, signs and symptoms, on complications of pre-eclampsia. RATIONALE: -To educate family about the disease condition. 2. Allow the family to verbalize doubts, questions and others which can hinder them from addressing the problem properly. RATIONALE: -To recognize thought of the family members and to provide understanding about their questions and doubts.
2. Enumerate the ways in preventing preeclampsia.
The goal of care was met since the family demonstrated > Discussed with the understanding family the causes, regarding the signs and symptoms, disease on complications of conditin and pre-eclampsia. ways to prevent it by answering all the questions > Allowed the family I asked for to verbalize doubts, each family questions and member. others which can hinder them from addressing the problem properly.
3. Name the foods that are prohibited to Mrs. Tan.
3. Discuss with the family the ways in preventing preeclampsia. RATIONALE: -To provide information about in preventing the disease. 4. Provide written information and selflearning modules for client to refer as necessary. RATIONALE: -Reinforces learning process, allows clients proceed at own pace.
> Discussed with the family the ways in preventing preeclampsia.
> Provided written information and self-learning modules for client to refer as necessary.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Decrease Cardiac OutputDocumento6 pagineDecrease Cardiac OutputGerardeanne ReposarNessuna valutazione finora
- Small Bowel Obstruction Concept MapDocumento1 paginaSmall Bowel Obstruction Concept MapTessa Claire JaranowskiNessuna valutazione finora
- NCPDocumento7 pagineNCPmftaganasNessuna valutazione finora
- Manage Bronchiectasis Nursing Care PlanDocumento5 pagineManage Bronchiectasis Nursing Care PlanPaola Marie VenusNessuna valutazione finora
- NCPDocumento15 pagineNCPCamille PinedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 pagineStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationgreyciee은Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento14 pagineNursing Care PlanVin Landicho100% (1)
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related ToDocumento7 pagineIneffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related TohannahNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan EportfolioDocumento14 pagineNursing Care Plan Eportfolioapi-279212367Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan 2Documento6 pagineNursing Care Plan 2KM TopacioNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan FinalDocumento16 pagineNursing Care Plan FinalErickson OcialNessuna valutazione finora
- Managing Fever in a Child with PoliomyelitisDocumento4 pagineManaging Fever in a Child with PoliomyelitisMonica RamboyongNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 pagineImpaired Tissue PerfusionLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNessuna valutazione finora
- Case No 45: of Intermittent Abdominal Pain Abdominal Bloating and Nausea and Vomiting (NVDocumento17 pagineCase No 45: of Intermittent Abdominal Pain Abdominal Bloating and Nausea and Vomiting (NVPremiums of the RoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Healthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeDocumento4 pagineHealthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeBenjamin CañalitaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsDocumento3 pagineNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For CHF 3 Activity IntoleranceDocumento2 pagineNCP For CHF 3 Activity IntoleranceAngelyn ArdinesNessuna valutazione finora
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocumento3 pagineSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study 2Documento7 pagineCase Study 2desdav100% (1)
- ABG InterpretationDocumento23 pagineABG Interpretationprateekbatra0% (1)
- ARDS MANAGEMENT GUIDEDocumento2 pagineARDS MANAGEMENT GUIDETisha CarretteNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept Map - Abby !Documento2 pagineConcept Map - Abby !Abegail Abaygar100% (3)
- Hyponatremia Algorhythm Concept MapDocumento2 pagineHyponatremia Algorhythm Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento9 pagineNursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume DeficitGayu Patel0% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goal: IndependentDocumento4 pagineAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goal: IndependentNinaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP FVDDocumento1 paginaNCP FVDsisjing88510Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hemophilia N C P BY BHERU LALDocumento1 paginaHemophilia N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP DMDocumento6 pagineNCP DMstara123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Case PresentationDocumento5 pagineCase PresentationJARIETTA OCHOANessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment and InterventionsDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plan Assessment and InterventionsmandzkievonnieNessuna valutazione finora
- Actual Nursing Care Plan 2Documento16 pagineActual Nursing Care Plan 2Alyanna Evangelista100% (2)
- Actual NCPDocumento3 pagineActual NCPMabz BoholNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan WeeblyDocumento8 pagineNursing Care Plan Weeblyapi-277498943Nessuna valutazione finora
- GastroenteritisDocumento8 pagineGastroenteritistanlimdania100% (3)
- NCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thDocumento2 pagineNCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thRainier IbarretaNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 CaritosDocumento3 pagine10 CaritosDARREN EDMARK100% (4)
- A Renal Failure (NCP)Documento2 pagineA Renal Failure (NCP)Julie Aranda Hapin100% (1)
- HypokalemiaDocumento3 pagineHypokalemiaSergeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Oxygen Terapi Dan PrinsipelDocumento16 pagineOxygen Terapi Dan PrinsipelAmrita KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Ineffective Airway Clearance-Nursing Care Plan For COPDDocumento2 pagineIneffective Airway Clearance-Nursing Care Plan For COPDRnspeakcom100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis Care Plan HyponitremiaDocumento2 pagineNursing Diagnosis Care Plan HyponitremiaAbdallah AlasalNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento3 pagineNCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionPaul Cubacub0% (1)
- NCP2 - DengueDocumento4 pagineNCP2 - DengueSummer SuarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Medication ThalassemiaDocumento3 pagineMedication ThalassemiaDivya ToppoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For InjuryDocumento1 paginaNursing Care Plan Risk For InjuryAce Dioso TubascoNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary Tract Infection, (UTI) Is An Infection of One orDocumento4 pagineUrinary Tract Infection, (UTI) Is An Infection of One orLorebellNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento4 pagineNursing Care PlanKath RubioNessuna valutazione finora
- Asthma Nanda Diagnoses Goals InterventionsDocumento4 pagineAsthma Nanda Diagnoses Goals InterventionsZinya RobinsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Sclerosis Nursing Care PlanDocumento4 pagineMultiple Sclerosis Nursing Care PlanCHRISTIE MONTANONessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Short Term Short TermDocumento2 pagineAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Short Term Short TermFrancis Xavier S. MendezNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology: Circulatory SystemDocumento4 pagineAnatomy and Physiology: Circulatory SystemJordz PlaciNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric Nursing Care Plan Impaired Physical MobilityDocumento5 paginePediatric Nursing Care Plan Impaired Physical Mobilityapi-3077327050% (1)
- Cellulitis Concept MapDocumento3 pagineCellulitis Concept MapBien EstrellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Septic ShockDocumento1 paginaSeptic ShockShaine Wolfe100% (1)
- Care Plan September 25 Med-SurgDocumento19 pagineCare Plan September 25 Med-Surgapi-251516913Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lactulose Drug Info for Portalsystemic EncephalopathyDocumento9 pagineLactulose Drug Info for Portalsystemic EncephalopathyFrances Oscar GaviolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plans for Diarrhea, Dehydration & Acute PainDocumento13 pagineNursing Care Plans for Diarrhea, Dehydration & Acute PainRocel DevillesNessuna valutazione finora
- Remediation Essays - NursingDocumento12 pagineRemediation Essays - NursingLouis MatzNessuna valutazione finora
- Observation Report - Hemodialysis - Kit P. RoaquinDocumento15 pagineObservation Report - Hemodialysis - Kit P. Roaquineljhayar_18Nessuna valutazione finora
- Emergency Room Drugs Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento20 pagineEmergency Room Drugs Nursing ResponsibilitiestsikiNessuna valutazione finora
- Smoking: Psychological and Social Influences: One-Of-A-Kind MenswearDocumento289 pagineSmoking: Psychological and Social Influences: One-Of-A-Kind MenswearBernardo Villavicencio VanNessuna valutazione finora
- Immunosuppressant DrugsDocumento87 pagineImmunosuppressant DrugsNagu KopparapuNessuna valutazione finora
- Obgm Mar2018 Vol.30 No.3Documento57 pagineObgm Mar2018 Vol.30 No.3lcmurilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Monitoring Public Health Reporting: Data Tracking in Cancer RegistriesDocumento11 pagineMonitoring Public Health Reporting: Data Tracking in Cancer RegistriesMihaela BarbuNessuna valutazione finora
- Doctor-Scientist On Kangen PDFDocumento22 pagineDoctor-Scientist On Kangen PDFfredyagussusanto100% (2)
- Detailed Micro ChartDocumento6 pagineDetailed Micro Chartmatt100% (1)
- Handout - ADocumento13 pagineHandout - AMadhu UpadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- Silica Flour D66Documento4 pagineSilica Flour D66georgenzNessuna valutazione finora
- The Evolution of Mastectomy Surgical Technique - From Mutilation To MedicineDocumento8 pagineThe Evolution of Mastectomy Surgical Technique - From Mutilation To MedicineAnonymous LnWIBo1GNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical MCQ Question For 4-YearDocumento39 paginePractical MCQ Question For 4-Yearkhuzaima9100% (2)
- Angio Dysla SiaDocumento14 pagineAngio Dysla SiaNicoleta Popa-FoteaNessuna valutazione finora
- List Pasien Bedah RSUP H. Adam Malik: 27 September 2020Documento11 pagineList Pasien Bedah RSUP H. Adam Malik: 27 September 2020Yolanda RahayuNessuna valutazione finora
- WHEY PROTEIN INGREDIENT MARKET REPORTDocumento12 pagineWHEY PROTEIN INGREDIENT MARKET REPORTGaytan DaygoroNessuna valutazione finora
- MSDS QuartzDocumento4 pagineMSDS QuartzHero19Nessuna valutazione finora
- PCA Patient Checklist PDFDocumento14 paginePCA Patient Checklist PDFSuper SummonerNessuna valutazione finora
- Congenital Cystic Masses of The NeckDocumento48 pagineCongenital Cystic Masses of The NeckEsraa El ShemeNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.4.1. Symptom Distress ScaleDocumento1 pagina2.4.1. Symptom Distress ScaleMarni rongreNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug InteractionDocumento20 pagineDrug InteractionRajendra Moorthy RajendranNessuna valutazione finora
- Vulvar cancer clinical manifestations diagnosis pathologyDocumento2 pagineVulvar cancer clinical manifestations diagnosis pathologyAde YonataNessuna valutazione finora
- Male Genitourinary AssessmentDocumento46 pagineMale Genitourinary AssessmentNicole Victorino LigutanNessuna valutazione finora
- BPH Guide: Symptoms, Causes and Diagnostic TestsDocumento57 pagineBPH Guide: Symptoms, Causes and Diagnostic TestsDiannetotz MoralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison of Nursing and Medical DiagnosesDocumento14 pagineComparison of Nursing and Medical DiagnosesNeko NekoNessuna valutazione finora
- AirPollution88 Ch9 PDFDocumento15 pagineAirPollution88 Ch9 PDFEva Julian De GuzmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Weed The PeopleDocumento1 paginaWeed The PeopleJaycee PascualNessuna valutazione finora
- 402 Exam Notes 402 Exam NotesDocumento13 pagine402 Exam Notes 402 Exam NotesMSNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Talk On BSFDocumento11 pagineHealth Talk On BSFjyoti singh100% (1)
- Armour Thyroid (Thyroid Tablets, USP) RX Only: I I NHDocumento10 pagineArmour Thyroid (Thyroid Tablets, USP) RX Only: I I NHAdam GolsbyNessuna valutazione finora
- UAW Local 2600 and Kent County, MI 3-29-02Documento19 pagineUAW Local 2600 and Kent County, MI 3-29-02E Frank CorneliusNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnet TherapyDocumento13 pagineMagnet Therapyshabana100% (1)
- Section 7 4 Part IVDocumento10 pagineSection 7 4 Part IVapi-196193978Nessuna valutazione finora