Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Care Plan For Schizoaffective Disorder
Caricato da
Thalia PeartDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Care Plan For Schizoaffective Disorder
Caricato da
Thalia PeartCopyright:
Formati disponibili
LAGUARDIA COMMUNITY COLLEGE
CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK
DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL & APPLIED SCIENCE
PRACTICAL NURSING PROGRAM
DOCUMENTION OF THE NURSING PROCESS
STUDENT NAME: MANOLITO GULLA___________________ DATE: ____1/22/07____________
CLIENTS INTIALS:
MEDICAL DIAGNOSIS: _SCHIZOAFFECTIVE DISORDER (BIPOLAR TYPE)_______________________
INSTRUCTOR
L.M.
ALVIN BRADLEY
CLIENT CARE OBJECTIVE (S):TO RELIEVE CLIENTS SYMPTOMS THROUGH APPROPRIATE ANTIPSYCHOTIC MEDICATIONS AND BEHAVIOUR THERAPY.
_______
_______
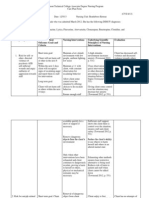
ASSESSMENT
(SUBJECTIVE/OBJECTIVE)
Data Collection
Subjective:
It is raining outside. John
Lennons spirit is inside my
body
I was feeling depressed thats
why they put me here
Objective:
CLIENTS PROBLEM
(S)/NEED(S)
(USE NURSING
DIAGNOSIS
STATEMENTS)
Disturbed Thought Processes
related to inability to evaluate
reality as evidenced by flight of
ideas and grandiose delusions.
CLIENT SHORT TERM
GOAL/OUTCOME
(PLANNING)
Have reality-based thinking.
Have a brief reality-based
conversations with staff
Take medications regularly
NURSING
INTERVENTION
(APPROACH)/ (ACTION)
Provide antipsychotic medications as
ordered and monitor effects.
It is the responsibility of nurses to
access the clients response to
medications for the purpose of
evaluating their effectiveness.
Look for the clients strengths and
abilities when providing nursing
care
It is important to look for the
persons strengths and to
acknowledge the normal parts of
the person.
Reinforce reality. Talk about what is
really happening.
Even conversations about the
simple realities of daily life focus
the clients attention away from
disorganized thoughts and into the
here and now.
Do not argue with the client about
delusional thoughts.
Clients do not recognize that they
are delusions, and arguments can
force the client to focus on
defending the false ideas. Change
the subject to reality-based topics.
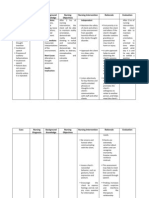
Disorganized sentences
Flight of ideas
Fast rambling speech
Internally preoccupied,
sometimes singing along the
hallway, other times performing
aerobic exercises
SCIENTIFIC RATIONALE
FOR
NURSING INTERVENTION
LAGUARDIA COMMUNITY COLLEGE
CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK
DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL & APPLIED SCIENCE
PRACTICAL NURSING PROGRAM
Encourage the client to express
feelings of fear or anxiety.
Expressing feeling to the nurse can
be affirming and helpful to clients.
Establish a trusting relationship in
which the client is safe to express
true feelings.
A non-threatening relationship
provides the opportunity to express
unresolved feelings
Offer medications in a confident
way, expecting the client to take
them.
The nurses confident attitude
promotes clients trust.
Teach clients stress management
techniques such as going to their
rooms and doing relaxation
exercises.
Practicing new coping behavior
teaches adaptive coping skills.
Keep in touch with family and
important friends
Approach client with an accepting
attitude. Be honest and sincere.
Acceptance, honesty, and sincerity
promotes trust.
Maintain healthy social
interactions with family, close
friends and neighbors
Interact with the client individually
and model appropriate social
behavior (body language, topics of
conversation).
Clients often lack social skills and
benefit from role modeling as a
way to learn them.
Give positive reinforcement for
clients voluntary interactions with
others.
Positive reinforcement is an
effective behavioral approach to
behavior change.
Encourage client to attend group
activities in the hospital. Accompany
client at first if necessary.
Client may respond positively to
encouragement from a trusted
nurse.
Grandiose delusions
Unpredictable and impulsive
Poor concentration, distractible
Ineffective Coping related to
internal conflicts as evidenced
by internal preoccupation and
by unpredictable and impulsive
behavior
Impaired Social Interactions
related to impulsivity and
hyperactivity as evidenced by
spontaneous singing and
performing aerobic exercises.
Client will use healthy coping
skills.
Have a routine daily and
weekly schedule
Include enjoyable activities in
schedule
Perform activities of daily
living independently
Reference:
Burke, Karen M., Priscilla LeMone, Elaine Mohn-Brown. Medical-Surgical Nursing Care. Upper Saddle River: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2006.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Schizoaffective DisorderDocumento8 pagineSchizoaffective Disorderapi-3797941100% (8)
- Shana Nichols - Girls Growing Up On The Autism Spectrum enDocumento353 pagineShana Nichols - Girls Growing Up On The Autism Spectrum enMaria Cozma100% (5)
- Psychological Assessment Report Reveals Major Depressive DisorderDocumento5 paginePsychological Assessment Report Reveals Major Depressive DisorderWaleedKhan100% (2)
- Theories of CounselingDocumento50 pagineTheories of CounselingSam Ahn100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan PsychDocumento12 pagineNursing Care Plan Psychblarehead88% (24)
- Schizophrenia Care Plan RNDocumento8 pagineSchizophrenia Care Plan RNlisa75% (4)
- The Control of AdhdDocumento92 pagineThe Control of Adhdminiloup05100% (1)
- Psychiatric Nursing Care PlansDocumento118 paginePsychiatric Nursing Care PlansUrlam Kumar100% (4)
- Case Study SchizophreniaDocumento3 pagineCase Study SchizophreniaCHRISANTO ARZANANNessuna valutazione finora
- Additional Nursing Care Plans - SchizophreniaDocumento26 pagineAdditional Nursing Care Plans - SchizophreniaJasmin Jacob100% (4)
- Ida Jean Orlando - Pelletier's Dynamic NurseDocumento16 pagineIda Jean Orlando - Pelletier's Dynamic NurseIan Randy Ferenal Gallego100% (1)
- Ineffective CopingDocumento5 pagineIneffective CopingIrish_Joy_Ari__301983% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For DepressionDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plan For DepressionCyrus De Asis87% (69)
- NCP SchizophreniaDocumento2 pagineNCP Schizophreniajoshua canja100% (5)
- MSE Sample PDFDocumento5 pagineMSE Sample PDFSam Raven AndresNessuna valutazione finora
- Care Plan For Schizoaffective Disorder Bipolar TypeDocumento4 pagineCare Plan For Schizoaffective Disorder Bipolar TypeAlrick Asentista100% (2)
- NCPDocumento8 pagineNCPTrixia Diaz67% (3)
- Dementia Nursing Care PlanDocumento2 pagineDementia Nursing Care Planmp175767% (3)
- Introduction To Psychology Course OutlineDocumento6 pagineIntroduction To Psychology Course OutlineGsdhdb100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Bipolar DisorderDocumento20 pagineNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Bipolar Disordermjk2100% (4)
- Case ManagementDocumento4 pagineCase ManagementPraveena.R100% (1)
- Mindful Month Calendar PDFDocumento1 paginaMindful Month Calendar PDFDomingo Juan de LeónNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plans SchizDocumento27 pagineNursing Care Plans SchizClariza Castro76% (17)
- Nursing Care Plans For Delusional DisorderDocumento4 pagineNursing Care Plans For Delusional Disorderkirill61195% (22)
- Taking Charge of Ones HealthDocumento34 pagineTaking Charge of Ones HealthNo One100% (1)
- Xi. Nursing Care PlansDocumento4 pagineXi. Nursing Care PlansNic Ji100% (1)
- Normal Personality Trait and Dark TriadDocumento9 pagineNormal Personality Trait and Dark TriadSakina Nusarifa TantriNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan 1 Risk For Violence, Self DirectedDocumento9 pagineNursing Care Plan 1 Risk For Violence, Self Directeddbryant010193% (14)
- NCP For Bipolar Risk For Injury Related To Extreme Hyperactivity As Evidenced by Excessive and Constant Motor ActivityDocumento3 pagineNCP For Bipolar Risk For Injury Related To Extreme Hyperactivity As Evidenced by Excessive and Constant Motor Activitydana75% (4)
- Paranoid Schizophrenia NCPDocumento8 pagineParanoid Schizophrenia NCPCherubim Lei DC Flores67% (3)
- NCPDocumento8 pagineNCPJayrald RosalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To PsychoeducationDocumento9 pagineIntroduction To PsychoeducationAneeh100% (1)
- NCP Disturbed Thought Process Related To SchizophreniaDocumento6 pagineNCP Disturbed Thought Process Related To Schizophrenianaishel0% (1)
- Altered Sensory and Disturbed Thought ProcessDocumento4 pagineAltered Sensory and Disturbed Thought ProcessRosecinie Torrente100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Paranoid SchizophreniaDocumento5 pagineNursing Care Plan For Paranoid SchizophreniaAyra Batore Laguitao88% (17)
- 4 NCP SchizophreniaDocumento9 pagine4 NCP SchizophreniaHazel Banday100% (4)
- Schizophrenia NCPDocumento2 pagineSchizophrenia NCPNicole cuencos100% (2)
- Psych Care PlanDocumento3 paginePsych Care Plancwarrington0967% (3)
- NURSING FUNDAMENTALSDocumento18 pagineNURSING FUNDAMENTALSAnthoinete AlbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plans For Acute ConfusionDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plans For Acute Confusionynecesity75% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan For Disturbed Thought ProcessesDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plan For Disturbed Thought Processesrinkai1377% (13)
- Bipolar Disorders Care Plan Nursing Care PlanDocumento4 pagineBipolar Disorders Care Plan Nursing Care PlanAnne de Vera0% (1)
- NCP BSN 3rd Yr Psychiatric WardDocumento9 pagineNCP BSN 3rd Yr Psychiatric WardMary Margarett BoadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Care Plan For SchizophreniaDocumento6 pagineCare Plan For SchizophreniaAllea Likestolaugh Brown100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For DepressionDocumento7 pagineNursing Care Plan For DepressionCatherineNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Psyche2Documento6 pagineNCP Psyche2Nica RTNessuna valutazione finora
- Jean Pearl R. Caoili Bsn3 NCB Diagnosis: Paranoid Schizophrenia Psychiatric Nursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals/ Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocumento9 pagineJean Pearl R. Caoili Bsn3 NCB Diagnosis: Paranoid Schizophrenia Psychiatric Nursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals/ Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluationpj casteNessuna valutazione finora
- Process RecordingDocumento8 pagineProcess Recordingapi-340063062Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan - SchizophreniaDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan - SchizophreniaJasmin Jacob80% (5)
- NCPDocumento1 paginaNCPNneka Andrea Datiles0% (2)
- NCP Assessment Diagnosis Planning Short-Term GoalDocumento4 pagineNCP Assessment Diagnosis Planning Short-Term GoalJessieRamosAnicetoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nurs 3021 - Final Evaluation - AkDocumento11 pagineNurs 3021 - Final Evaluation - Akapi-240864098Nessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For Bipolar DisorderDocumento1 paginaNCP For Bipolar DisorderJohn Carlo Santos100% (7)
- NCP PsychosisDocumento3 pagineNCP Psychosisinagasi100% (7)
- Care Plan - Arsenault 1031575Documento10 pagineCare Plan - Arsenault 1031575api-282962289100% (1)
- SCHIZOPHRENIA Nursing Care PlanDocumento1 paginaSCHIZOPHRENIA Nursing Care Planrinkai130% (1)
- NCP For SchizoDocumento6 pagineNCP For SchizoGILIANNE MARIE JIMENEANessuna valutazione finora
- Disturbed Thought Processes DescribeDocumento2 pagineDisturbed Thought Processes DescribePRINCESS LARA CASILAONessuna valutazione finora
- NCP SchizDocumento12 pagineNCP SchizKristine Reyes - MerleNessuna valutazione finora
- Scizophrenia NCP1Documento13 pagineScizophrenia NCP1Kholid Abu Mohammad AlfaizinNessuna valutazione finora
- Milieu TherapyDocumento5 pagineMilieu Therapyanimesh pandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ethics Assignment Sem 3Documento9 pagineEthics Assignment Sem 3api-314566363Nessuna valutazione finora
- PSYCH - Nursing ProblemsDocumento4 paginePSYCH - Nursing ProblemsKrystelle Jade ClerigoNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz No. 1 1 1Documento2 pagineQuiz No. 1 1 1Christine PagatpatanNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdellah's 21 Nursing Problem TheoryDocumento14 pagineAbdellah's 21 Nursing Problem TheoryJyoti Verma100% (1)
- Patient Centerd CareDocumento42 paginePatient Centerd Care21910589Nessuna valutazione finora
- Define Behaviour Change Communication: Concept and FunctionsDocumento15 pagineDefine Behaviour Change Communication: Concept and FunctionsshrutiNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Nursing: Dr. Abdul-Monim Batiha Assistant Professor Critical Care Nursing Philadelphia UniversityDocumento65 pagineIntroduction To Nursing: Dr. Abdul-Monim Batiha Assistant Professor Critical Care Nursing Philadelphia UniversityJohn peterNessuna valutazione finora
- PrintedFundamentals of NursingDocumento23 paginePrintedFundamentals of NursingAaron EspirituNessuna valutazione finora
- PHQ 9 en FRDocumento3 paginePHQ 9 en FRZICONessuna valutazione finora
- Edward GloverDocumento8 pagineEdward GloverIrayetzin HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Concepts of Mental Health and IllnessDocumento18 pagineConcepts of Mental Health and IllnessIbrahim R. Ayasreh67% (3)
- Branches of PsychologyDocumento7 pagineBranches of PsychologyNickhie BajadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Theoretical models in the etiology of phobiasDocumento21 pagineTheoretical models in the etiology of phobiasAna AchimNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaclitic Depression in An Infant Raised in An InstitutionDocumento9 pagineAnaclitic Depression in An Infant Raised in An Institutionyeremias setyawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Essay - Riley MDocumento13 pagineResearch Essay - Riley Mapi-519029225Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nur340 Eating Disorders and Social MediaDocumento8 pagineNur340 Eating Disorders and Social Mediaapi-449016971Nessuna valutazione finora
- Borderline Symptom List 23 (BSL-23) : Code: - DateDocumento2 pagineBorderline Symptom List 23 (BSL-23) : Code: - Datemsack leyNessuna valutazione finora
- My Dream JobDocumento3 pagineMy Dream Jobapi-481984077Nessuna valutazione finora
- Soapie Charting: Date/ Time/ ShiftDocumento2 pagineSoapie Charting: Date/ Time/ Shiftspain michaelisNessuna valutazione finora
- Bipolar Disorder: Presented By: Ashok Aswin, Aarsha Raj and Sneha Nair Group 51Documento23 pagineBipolar Disorder: Presented By: Ashok Aswin, Aarsha Raj and Sneha Nair Group 51Shambhu AshokNessuna valutazione finora
- Psychological Well-Being of Social Work ProfessionalsDocumento10 paginePsychological Well-Being of Social Work ProfessionalsKateryna Serhiivna BalakhtarNessuna valutazione finora
- K To 12 Nail Care Learning ModuleDocumento10 pagineK To 12 Nail Care Learning ModuleImelda BeraquitNessuna valutazione finora
- Your 20s Still Most Important for Career and Life PathDocumento4 pagineYour 20s Still Most Important for Career and Life PathCalvin KimNessuna valutazione finora
- By: Bradley, Heather, Joanne, Katelyn, StefanDocumento24 pagineBy: Bradley, Heather, Joanne, Katelyn, StefanHeather FleckensteinNessuna valutazione finora
- GC Eng Mar TempDocumento65 pagineGC Eng Mar TempAsma BadeNessuna valutazione finora
- References: Technostress: How Does It Affect You?Documento2 pagineReferences: Technostress: How Does It Affect You?coconutcrabNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review of Acceptance and Commitment TherapyDocumento14 pagineA Review of Acceptance and Commitment TherapyJuan Pablo Osorio SernaNessuna valutazione finora
- GE UTS Reflection Paper On The Mental Health Awareness Symposium Psychological SelfDocumento3 pagineGE UTS Reflection Paper On The Mental Health Awareness Symposium Psychological SelfAdrian Paul AstorgaNessuna valutazione finora
- First International congress on clinical Hypnosis & Related Sciences programDocumento91 pagineFirst International congress on clinical Hypnosis & Related Sciences programGolnaz BaghdadiNessuna valutazione finora