Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
NCP-Impaired Physical Mobility - E+ Imbalance
Caricato da
Rene John FranciscoTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
NCP-Impaired Physical Mobility - E+ Imbalance
Caricato da
Rene John FranciscoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
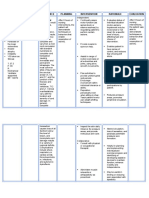
Patient: R.C.
Chief Complaints: Body weakness Assessment Actual/ Abnormal cues
Functional
Age: 90 years old
Gender: Female Admitting Diagnosis: Electrolyte Imbalance secondary to Poor intake
Level Classification: 3 (Requires help from another person and equipment device) Muscle strength of 3/5 score (muscle can contract and can move the body part fully against gravity but with limitations) Assisted with hourly turning to different
Nursing Diagnosis Impaired physical mobility of the upper and lower extremities r/t neuromuscular skeletal impairment as evidence by limitation in moving, decrease muscle strength, and assisted when turning and moving. Definition: Limitation in independent, purposeful physical movement of the body or of one or more extremities
Rationale Precipitating Factors: -(+) Diabetes Mellitus -Poor Intake of foods with essential vitamins and minerals Predisposing Factors: - Age: 90 years old (Old Age) -Gender (postmenopaus al period)
Desired Outcomes After 3 days of nursing interventions, the patient will be able to: 1.)Demonstrate techniques or behaviors that enable resumption of activities
Nursing Interventions Independent and Collaborative Nursing Interventions
Justifications Independent and Collaborative Nursing Interventions
Evaluation After 3 days of nursing interventions, the patient was able to:
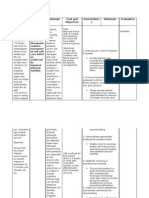
1.1 Assess degree of immobility produced by injury/treatment.
1.1 To initiate proper care and be able to assist in some part of the patients ADLs
Due to age related changes result to alteration of fast metabolism of micronutrients in the body plus low intake of foods rich in potassium
Low levels of circulating electrolyte to be disseminated to the different tissues and organs (esp. the brain)
1.2 Encourage participation in diversional/ recreational activities. Maintain stimulating environment, e.g., radio, TV, newspapers, personal possessions/pictures, clock, calendar, visits from family/friends. 1.3 Encourage use of isometric exercises starting with the unaffected limb.
1.2 Provides opportunity for release of energy, refocuses attention, enhances patients sense of self-control/selfworth, and aids in reducing social isolation.
Brain will be stimulated of the low levels of electrolyte (potassium)
1.3 Isometrics contract muscles without bending joints or moving limbs and help maintain muscle
positions. Facial mask of pain when turning the patient Weakness and limitation in motion of body parts Limited range of motion
Source: Doenges, M.E, et. Al. Nurses Pocket Guide Edition 11. F.A. Davis Company. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. 2008.
Changes in the nerve impulse state leading to slow conduction of electrical signals from the central nervous system to its periphery 2.)Participate in ADLs and desired activities 2.1 Instruct patient in/assist with active/passive ROM exercises of affected and unaffected extremities.
strength and mass. Note: These exercises are contraindicated while acute bleeding/edema is present. 2.1 Increases blood flow to muscles and bone to improve muscle tone, maintain joint mobility; prevent contractures/atrophy and calcium resorption from disuse 2.2 Improves muscle strength and circulation, enhances patient control in situation, and promotes selfdirected wellness. 3.1 Useful in maintaining functional position of extremities, hands/feet, and preventing complications (e.g., contractures/footdrop). 3.2 Prevents/reduces incidence of skin and respiratory complications (e.g., decubitus, atelectasis, pneumonia). 3.3 Bed rest, use of analgesics, and changes in
Marked weakness of the extremities
Impaired physical mobility of the upper and lower extremities r/t neuromuscular skeletal impairment Source: Medical-Surgical Book Edition 16 by Williams and Wilkins.
2.2 Assist with/encourage self-care activities (e.g., bathing, shaving).
Strengths: Strong family support Good compliance to treatment and medications 3.) Maintain position of function and skin integrity as evidenced by absence of contractures, footdrop, decubitus, and so forth. 3.1 Provide footboard, wrist splints, trochanter/hand rolls as appropriate.
3.2 Reposition periodically every 2 hours and encourage coughing/deepbreathing exercises. 3.3 Auscultate bowel sounds. Monitor
elimination habits and provide for regular bowel routine. Place on bedside commode, if feasible, or use fracture pan. Provide privacy.
dietary habits can slow peristalsis and produce constipation. Nursing measures that facilitate elimination may prevent/limit complications. Fracture pan limits flexion of hips and lessens pressure on lumbar region/lower extremity cast. 3.4 Creates positive assurance in maintaining the quality of care and update the current status of the patient.
3.4 Work hand in hand with other allied health care team in maintaining patients treatment and functionality
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Promoting Family Involvement in Long-Term Care Settings: A Guide To Programs That Work (Gaugler Excerpt)Documento22 paginePromoting Family Involvement in Long-Term Care Settings: A Guide To Programs That Work (Gaugler Excerpt)Health Professions Press, an imprint of Paul H. Brookes Publishing Co., Inc.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Surgical InstrumentsDocumento8 pagineSurgical InstrumentsSharmaine Simon91% (11)
- Gifts of the Holy Spirit ExplainedDocumento4 pagineGifts of the Holy Spirit ExplainedMauricio Rojas ValdiviaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Surgical InstrumentsDocumento37 pagineBasic Surgical Instrumentsapi-2658787991% (33)
- Drug Study For Paracetamol, Omeprazole and Vitamin B ComplexDocumento3 pagineDrug Study For Paracetamol, Omeprazole and Vitamin B ComplexMichelle Manibale R.N100% (4)
- Diazepam, Lanoxin, Hemostan, NaprexDocumento6 pagineDiazepam, Lanoxin, Hemostan, NaprexRene John Francisco100% (1)
- OT6 - Amyotrophic Lateral SclerosisDocumento19 pagineOT6 - Amyotrophic Lateral SclerosisAnnbe BarteNessuna valutazione finora
- Continuing Education in Nursing - EditedDocumento7 pagineContinuing Education in Nursing - EditedOnkwani DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocumento14 pagineDrug Study On Emergency DrugsRene John FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocumento11 pagineImpaired Physical MobilityAgronaSlaughter100% (1)
- Risk For FallsDocumento1 paginaRisk For FallsEugene UC100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan2 CVADocumento4 pagineNursing Care Plan2 CVAhermesdave1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study (Combivent)Documento2 pagineDrug Study (Combivent)Rene John Francisco100% (3)
- Spinal Cord Injury NCPDocumento2 pagineSpinal Cord Injury NCPEmmanuelRodriguez100% (1)
- College of Health Sciences Nursing Care Plan for Fractured FemurDocumento5 pagineCollege of Health Sciences Nursing Care Plan for Fractured FemurMae CeaesarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 04 - Immunologic ProblemsDocumento7 pagineChapter 04 - Immunologic ProblemscariNessuna valutazione finora
- Improving Physical Mobility Through Nursing InterventionsDocumento2 pagineImproving Physical Mobility Through Nursing InterventionsPrincess Averin Navarro50% (2)
- Omeprazole and Polynerv (B1,6,12)Documento3 pagineOmeprazole and Polynerv (B1,6,12)Rene John Francisco100% (1)
- Omeprazole and Polynerv (B1,6,12)Documento3 pagineOmeprazole and Polynerv (B1,6,12)Rene John Francisco100% (1)
- NCP-Impaired Physical MobilityDocumento3 pagineNCP-Impaired Physical MobilityRene John FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Bloom's TaxonomyDocumento26 pagineBloom's TaxonomyRene John FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Slides Surgical Instruments Update 1.7Documento43 pagineSlides Surgical Instruments Update 1.7Paul Christian P. Santos, RN100% (32)
- Nursing Care Plan for Activity IntoleranceDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plan for Activity Intolerancelouie roderos0% (1)
- Mpaired Physical Mobility (Amputation) : Nursing Care PlanDocumento3 pagineMpaired Physical Mobility (Amputation) : Nursing Care PlanTheSweetpea5010% (2)
- Impaired mobility assessmentDocumento2 pagineImpaired mobility assessmentVhin Lim100% (2)
- Research Priorities in Obstetrics SeminarDocumento7 pagineResearch Priorities in Obstetrics SeminarSharmistha Debnath83% (6)
- NCP FractureDocumento3 pagineNCP FractureDino V EscalonaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Chronic PainDocumento5 pagineNCP - Chronic PainJaye DangoNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocumento3 pagineImpaired Physical Mobilityvidagurl0% (1)
- FAIMER FELLOW 2020 - Kavita - Resubmission Final ProjectDocumento25 pagineFAIMER FELLOW 2020 - Kavita - Resubmission Final ProjectGreenThumbNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Pain - Nursing Intervention - RationaleDocumento2 pagineAcute Pain - Nursing Intervention - Rationaledonnaluna203315100% (4)
- NCP For Impaired Physical MobilityDocumento1 paginaNCP For Impaired Physical Mobilityitzme_andreaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rozzano C. Locsin: Technological Nursing As CaringDocumento29 pagineRozzano C. Locsin: Technological Nursing As Caringmonique100% (3)
- Potassium ChlorideDocumento2 paginePotassium ChlorideRene John FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Foundations of Nursing Research 7th Edition by Nieswiadomy Bailey ISBN 013416721X Test BankDocumento10 pagineFoundations of Nursing Research 7th Edition by Nieswiadomy Bailey ISBN 013416721X Test Bankcarol100% (23)
- NCP - OsteosarcomaDocumento5 pagineNCP - OsteosarcomaNelson Lacsamana100% (1)
- NCP Impaired Physical MobilityDocumento2 pagineNCP Impaired Physical MobilityJohn Michael FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study (Seretide)Documento1 paginaDrug Study (Seretide)Rene John Francisco100% (1)
- NCP-Impaired Physical MobilityDocumento3 pagineNCP-Impaired Physical MobilityradarsoulNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Impaired Physical Mobility-2Documento4 pagineNCP Impaired Physical Mobility-2ejoanbNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan (ImpairedphyssicalDocumento5 pagineNursing Care Plan (ImpairedphyssicalkuroroexileNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP ImmobilityDocumento2 pagineNCP Immobilityxxxcamzxxx67% (6)
- Impaired Physical Mobility RT Neuromuscular Skeletal Impairment.Documento3 pagineImpaired Physical Mobility RT Neuromuscular Skeletal Impairment.Abegail Abaygar100% (2)
- Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions Expected Outcome: (List 5 Unique To The Given Nursing DX)Documento3 pagineNursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions Expected Outcome: (List 5 Unique To The Given Nursing DX)joyrena ochondraNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study - Paracetamol Ambroxol, Ascorbic Acid, CefuroximeDocumento4 pagineDrug Study - Paracetamol Ambroxol, Ascorbic Acid, Cefuroximeapi-3701489100% (12)
- Nursing Care for Impaired Physical MobilityDocumento3 pagineNursing Care for Impaired Physical MobilityMeljonesDaan100% (1)
- Impaired Physical Mobility Related To Pain and DiscomfortDocumento2 pagineImpaired Physical Mobility Related To Pain and DiscomfortRis NapolisNessuna valutazione finora
- Integrative Medicine and Patient Centered Care PDFDocumento35 pagineIntegrative Medicine and Patient Centered Care PDFCristobal Carrasco100% (1)
- Drug Study (Budesonide)Documento1 paginaDrug Study (Budesonide)Rene John Francisco33% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan - AnxietyDocumento1 paginaNursing Care Plan - AnxietyPauPauNessuna valutazione finora
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalDocumento1 paginaNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie riveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan for Mr. Ying to Prevent FallsDocumento1 paginaNursing Care Plan for Mr. Ying to Prevent Fallsjanna mae patriarca100% (1)
- Mechanism, Indications, Contraindications and Adverse Effects of TramadolDocumento5 pagineMechanism, Indications, Contraindications and Adverse Effects of TramadolDenise EspinosaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP LocDocumento2 pagineNCP LocMel RodolfoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Acute PainDocumento3 pagineNCP Acute PainDyanne BNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 pagineAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationGiselle EstoquiaNessuna valutazione finora
- SunStar News Doctors May Lose Their Licenses Over Surgery ScandalDocumento4 pagineSunStar News Doctors May Lose Their Licenses Over Surgery Scandalseigelystic100% (12)
- Diagnostic TestDocumento57 pagineDiagnostic TestPam ArauneNessuna valutazione finora
- Body Weakness NCPDocumento1 paginaBody Weakness NCPArnold Christian QuilonNessuna valutazione finora
- Constipation NCPDocumento2 pagineConstipation NCPKaren Pili100% (1)
- Activity IntoleranceDocumento2 pagineActivity IntoleranceSenyorita KHaye100% (4)
- NCP For Ruptured AppendicitisDocumento2 pagineNCP For Ruptured AppendicitisJansen Arquilita RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Pain Relief Combo of Tramadol and ParacetamolDocumento1 paginaPain Relief Combo of Tramadol and Paracetamolenirdnas14100% (2)
- NCP For CTTDocumento1 paginaNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Physical Mobility...Documento3 pagineImpaired Physical Mobility...Christy BerryNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute PainDocumento5 pagineAcute PainJan Heartini SalvadorNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP 2Documento3 pagineNCP 2klawdin100% (1)
- Biperiden Generic and Brand Names, Uses, Side EffectsDocumento1 paginaBiperiden Generic and Brand Names, Uses, Side EffectsMFQ.RN100% (2)
- Week 10 Drug Card - Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ)Documento2 pagineWeek 10 Drug Card - Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ)RCurry09Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan ADocumento6 pagineNursing Care Plan ACrystal WyattNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Acute Pain Stomach CancerDocumento2 pagineNCP - Acute Pain Stomach CancerJohn Michael TaylanNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity IntoleranceDocumento3 pagineActivity Intolerancelouie roderosNessuna valutazione finora
- Ncp-For-Sle-Fatigue-And-Pain EDITEDDocumento4 pagineNcp-For-Sle-Fatigue-And-Pain EDITEDJordz PlaciNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDocumento5 pagineNCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDarkCeades100% (2)
- NXCP Disturbed Sensory Perception3Documento2 pagineNXCP Disturbed Sensory Perception3marielle_dellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity IntoleranceDocumento3 pagineActivity IntoleranceRheegell Ellar-Fuertes50% (2)
- NCP BkaDocumento4 pagineNCP BkaKeeshia CesnerosNessuna valutazione finora
- DRUG Kalium Durule (Potasium Chloride)Documento1 paginaDRUG Kalium Durule (Potasium Chloride)rholiboiNessuna valutazione finora
- FdarDocumento1 paginaFdarRoxas Cedrick100% (1)
- Improving Comfort with Endotracheal TubeDocumento1 paginaImproving Comfort with Endotracheal TubeSelwynVillamorPatenteNessuna valutazione finora
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)Documento29 pagineAmyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)Krisia Mhel Buyagao MollejonNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plans for Neurological PatientDocumento9 pagineNursing Care Plans for Neurological PatientJam AbantaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Body Mechanics & ROM ExercisesDocumento8 pagineBody Mechanics & ROM ExercisesRaisa GravadorNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For Impaired MobilityDocumento4 pagineNCP For Impaired MobilityBettinaFernandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Dressing For Job Interview and ResignationDocumento7 pagineDressing For Job Interview and ResignationRene John FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Genexpert TestDocumento2 pagineGenexpert TestRene John FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- OR EquipmentsDocumento8 pagineOR EquipmentsRene John FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- MSPPP 12913337842396 Phpapp01Documento26 pagineMSPPP 12913337842396 Phpapp01RI NANessuna valutazione finora
- Scientific Death of JesusDocumento7 pagineScientific Death of JesusRene John FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Surgical Instrumentation - R. ILADODocumento54 pagineSurgical Instrumentation - R. ILADOrhenier_ilado100% (1)
- Stress ManagementDocumento17 pagineStress Managementanon_469843072Nessuna valutazione finora
- Facts of The RealityDocumento11 pagineFacts of The RealityRene John FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Delivery Set (Nullipara)Documento1 paginaBasic Delivery Set (Nullipara)Rene John FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Naloxone, MorphineDocumento7 pagineNaloxone, MorphineRene John FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- ErythromycinDocumento6 pagineErythromycinapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Study for Psychosis and Bipolar DisorderDocumento4 pagineDrug Study for Psychosis and Bipolar DisorderJowel Cruz De LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 45 - Drugs For HypertensionDocumento14 pagineChapter 45 - Drugs For Hypertensiondlneisha61100% (1)
- Drug Study - MirceraDocumento2 pagineDrug Study - MirceraRene John FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- CMC Vellore Prospectus for Admissions 2021-2022Documento168 pagineCMC Vellore Prospectus for Admissions 2021-2022Food FactoryNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 9 BIOETHICAL PRINCIPLEDocumento10 pagineModule 9 BIOETHICAL PRINCIPLEColeen TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Megan Crump: Clinical ExperienceDocumento2 pagineMegan Crump: Clinical Experiencemegan crumpNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 5 - Nursing ResearchDocumento16 pagineCHAPTER 5 - Nursing ResearchCharlz ZipaganNessuna valutazione finora
- Prof Ad Chapter 1: Nursing As A ProfessionDocumento11 pagineProf Ad Chapter 1: Nursing As A ProfessionJulia Mariz BadicNessuna valutazione finora
- ETHICAL & PROF. Responsibilities of RNDocumento5 pagineETHICAL & PROF. Responsibilities of RNEvan Lloyd Cedeno MirafloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Nursing 2-Sir ToniDocumento7 pagineFundamentals of Nursing 2-Sir Tonijed_cute30Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Informatics and Healthcare Policy: Information, and Computer Sciences To Manage andDocumento2 pagineNursing Informatics and Healthcare Policy: Information, and Computer Sciences To Manage andSOLIVEN KING JAMESNessuna valutazione finora
- Compassion in PracticeDocumento29 pagineCompassion in PracticeAndreea GheorghiuNessuna valutazione finora
- JPN 321 Autumn 2019 PDFDocumento60 pagineJPN 321 Autumn 2019 PDFjumantoNessuna valutazione finora
- CV Muhammad Afkar HDDocumento2 pagineCV Muhammad Afkar HDNur AmiinNessuna valutazione finora
- Records in Family Health Nursing PracticeDocumento3 pagineRecords in Family Health Nursing PracticeSophia Nicole AranasNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutri - Lec and LabDocumento11 pagineNutri - Lec and LabJuzhley PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Perspective of AgingDocumento21 paginePerspective of AgingMarianne Joyce ManzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mental Health Quiz Online - Psychiatric Disorders - Mental Health Nursing - Nursing OfficerDocumento26 pagineMental Health Quiz Online - Psychiatric Disorders - Mental Health Nursing - Nursing OfficermanishjeswalNessuna valutazione finora
- Holland Area Chamber Business DirectoryDocumento68 pagineHolland Area Chamber Business DirectoryRaymart AauinoNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Child Abuse Nursing Care Plan PDFDocumento7 pagine1 Child Abuse Nursing Care Plan PDFMAHESH KOUJALAGINessuna valutazione finora
- Asses MentDocumento3 pagineAsses MentNaufal AlbabNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.01 Historical Development and Background of Health EducationDocumento5 pagine2.01 Historical Development and Background of Health EducationLUISA JULIA SAGUMNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Life Support Training and AssessmentDocumento6 pagineAdvanced Life Support Training and AssessmentwilmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assign 2Documento19 pagineAssign 2Ajmal FareedNessuna valutazione finora