Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Strain-Based Fatigue Analysis: Dr. Nuri Ersoy
Caricato da
zalazullahDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Strain-Based Fatigue Analysis: Dr. Nuri Ersoy
Caricato da
zalazullahCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Strain-Based Fatigue Analysis
Dr. Nuri Ersoy
Material Models
Material Models
Material Models
Mechanical Behavior of Materials: Engineering Methods for Deformation, Fracture, and Fatigue, Third Edition,
by Norman E. Dowling. ISBN 0-13-186312-6.
2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ . All rights reserved.
This material is protected by Copyright and written permission should be obtained from the publisher prior to any prohibited reproduction, storage in a retrieval system,
or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or likewise. For information regarding permission(s),
write to: Rights and Permissions Department, Pearson Education Inc., Upper Saddle river, NJ 07458.
c
c
o
A
B
C
c
y
<c<2c
o
c
o
c
c
o
A
B
C
c>2c
o
c
o
c
o
Ac
p
Ac
e
c
a
Ac =
2c
a
c
a
A
o
=
2
o
a
o
a
o
a
Stress-Strain Hystheresis Loop
Testing the Materials for Strain Life Approach
o
c
c
a
N
f
c
a
c
f
o
f
/E
plastic
elastic
N
f3
N
f2
N
f1
Ac
Ac
p
Ao
Ao/
E
E
1
c
1
b
1
o
c
c
a
=Ac/2, o
a
=Ao/2
(d)
cyclic
monotonic
Ramberg-Osgood equation
The cyclic stress strain curve is
represented by Ramberg-Osgood
equation:
n n
a a
a
H E H E
' '
|
.
|
\
|
'
A
+
A
=
A
|
.
|
\
|
'
+ =
/ 1 / 1
2 2 2
o o c o o
c
where
c
a
is the strain amplitude
o
a
is the stress amplitude
H
'
is the Cyclic Strength Coefficient
n
'
is the Strain Hardening Exponent.
o
c
(c)
Mechanical Behavior of Materials: Engineering Methods for Deformation, Fracture, and Fatigue, Third Edition,
by Norman E. Dowling. ISBN 0-13-186312-6.
2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ . All rights reserved.
This material is protected by Copyright and written permission should be obtained from the publisher prior to any prohibited reproduction, storage in a retrieval system,
or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or likewise. For information regarding permission(s),
write to: Rights and Permissions Department, Pearson Education Inc., Upper Saddle river, NJ 07458.
Mechanical Behavior of Materials: Engineering Methods for Deformation, Fracture, and Fatigue, Third Edition,
by Norman E. Dowling. ISBN 0-13-186312-6.
2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ . All rights reserved.
This material is protected by Copyright and written permission should be obtained from the publisher prior to any prohibited reproduction, storage in a retrieval system,
or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or likewise. For information regarding permission(s),
write to: Rights and Permissions Department, Pearson Education Inc., Upper Saddle river, NJ 07458.
Cycle Dependent Material Response
Cycle Dependent Material Response
Strain Control Stress Control
Cyclic
Hardening
Cyclic
Softening
D
r
i
v
e
R
e
s
p
o
n
s
e
0 100 200 300 400
-5E-3
0
5E-3
strain(mm/mm)
Secs.
0 100 200 300 400
-400
-200
0
200
400
600
stress(MPa)
Secs.
-0.01 -5E-3 0 5E-3 0.01
-600
-400
-200
0
200
400
600
800
strain (mm/mm)
Time range : 0 secs to 435 secs
1
3
5
7
9
2
4
6
8
Cyclic Softenening
Stable Hysteresis Loops
Stable Hysteresis Loops
Mechanical Behavior of Materials: Engineering Methods for Deformation, Fracture, and Fatigue, Third Edition,
by Norman E. Dowling. ISBN 0-13-186312-6.
2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ . All rights reserved.
This material is protected by Copyright and written permission should be obtained from the publisher prior to any prohibited reproduction, storage in a retrieval system,
or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or likewise. For information regarding permission(s),
write to: Rights and Permissions Department, Pearson Education Inc., Upper Saddle river, NJ 07458.
Stable Hysteresis Loops
Effect of Notches
Effect of Notches-Neubers rule
Notched Components: Neubers Rule
Ao,Ac
As,Ae
o
c
Ac
Ao
As
Ae
o c
o
c
o
c
k k
s
k
e
k
>
A
A
=
A
A
=
constant
2
2
=
A
= A A
A
A A
=
A
A
A
A
=
A
A
A
A
=
=
E
s k
E
s
k
E
E
e s e s
k
k k k
t
t
t
t
c o
c o
c o c o
o c
Stress and Strain Concentration Factors: Neubers
Rule
1
2
3
K
f
Ao
Ae
As
Ac
Cyclic oc Curve
Neuber Equation
Solution point
Graphical Solution for Local o and c
constant = A A c o
n
H E
'
|
.
|
\
|
'
A
+
A
=
A
/ 1
2 2 2
o o c
o
c
constant = a ac o
Construction of the Local Hysteresis Loop
Using Neubers Rule
n
a a a
H E
'
|
.
|
\
|
'
+ =
/ 1
2
o o c
constant = A A c o
n
H E
'
|
.
|
\
|
'
A
+
A
=
A
/ 1
2 2 2
o o c
Ao
Ac
Ao
Ac
Strain Life Results from a Series of LCF Tests
1E0 1E1 1E2 1E3 1E4 1E5 1E6 1E7 1E8
1E-4
1E-3
1E-2
1E-1
1E0
Life Curve Display
L
o
g
S
t
r
a
i
n
Log Life (Reversals)
Total strain curve fit
Elastic strain curve fit
Plastic strain curve fit
Total strain data
Elastic strain data
Plastic strain data
Sf': 670 MPa
b : -0.0582
(X/Y)
Ef': 0.374
c : -0.54
E : 2.05E5 MPa
(X/Y)
: Run-out pts
c
f
o
f
/E
plastic
elastic
N
f3
N
f2
N
f1
c
1
b
1
( ) ( )
c
N
b
N
E
f f f
f
a
2 2 c
o
c
'
+
'
=
L
o
g
S
t
r
a
i
n
Log Life
Strain Life Results from a Series of LCF Tests
( ) ( )
exponent ductility fatigue
t coefficien ductility fatigue
cycle 1 reversals 2
failure to reversals of number 2
exponent strength fatigue
t coefficien strength fatigue
amplitude strain
2 2
c
N
b
c
N
b
N
E
f
f
f
a
f f f
f
a
c
o
c
c
o
c
'
=
'
'
+
'
=
Coffin-Manson Strain-Life Equation
( ) ( )
exponent ductility fatigue
t coefficien ductility fatigue
cycle 1 reversals 2
failure to reversals of number 2
exponent strength fatigue
stress mean
t coefficien strength fatigue
amplitude strain
2 2
) (
c
N
b
c
N
b
N
E
f
f
m
f
a
f f f
m f
a
c
o
o
c
c
o o
c
'
=
'
'
+
'
=
Coffin-Manson Strain-Life Equation
Modified for Mean Stress Effect
Effect of Mean Stress
( ) ( )
strength ultimate
failure strain to ultimate
cycle 1 reversals 2
failure to reversals of number 2
amplitude strain
2 2 5 . 3
u
6 . 0 6 . 0 12 . 0
S
N
N N
E
S
f
f
a
f f f
u
a
c
c
c c
=
+
|
.
|
\
|
=
Generalized Strain-Life Equation:
Method of Universal Slopes
Mechanical Behavior of Materials: Engineering Methods for Deformation, Fracture, and Fatigue, Third Edition,
by Norman E. Dowling. ISBN 0-13-186312-6.
2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ . All rights reserved.
This material is protected by Copyright and written permission should be obtained from the publisher prior to any prohibited reproduction, storage in a retrieval system,
or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or likewise. For information regarding permission(s),
write to: Rights and Permissions Department, Pearson Education Inc., Upper Saddle river, NJ 07458.
General Procedure
for calculating life for
constant amplitude
strain histories
Rainflow Counting and Stress/Strain Space
Fatigue is
the process where repeated variations in
loading cause failure even when the nominal
stresses are below the material yield strength;
Damage is
The inverse of life for a given strain amplitude
and is cumulative until failure
Damage and Life
N
f3
N
f1
L
o
g
S
t
r
a
i
n
Log Life Ac
1
Ac
2
Ac
1
Ac
2
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
1
i
i
N
n
Miners Rule
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Sterling Test Prep College Physics Practice Questions: Vol. 2, High Yield College Physics Questions with Detailed ExplanationsDa EverandSterling Test Prep College Physics Practice Questions: Vol. 2, High Yield College Physics Questions with Detailed ExplanationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Box Culvert As Per Aashto LRFDDocumento39 pagineDesign of Box Culvert As Per Aashto LRFDRafique MundeNessuna valutazione finora
- r5 Led KasapDocumento65 paginer5 Led KasaptonikNessuna valutazione finora
- HB D KomplettDocumento181 pagineHB D KomplettGabriel BourguignonNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Electrophysiological Methods and InstrumentationDa EverandIntroduction to Electrophysiological Methods and InstrumentationNessuna valutazione finora
- STP1303 Eb.1415051 1 PDFDocumento157 pagineSTP1303 Eb.1415051 1 PDFpaolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Plasma Scattering of Electromagnetic Radiation: Theory and Measurement TechniquesDa EverandPlasma Scattering of Electromagnetic Radiation: Theory and Measurement TechniquesNessuna valutazione finora
- 0132497468-Ch12 ISMDocumento29 pagine0132497468-Ch12 ISMJeison Rincón Garzón75% (4)
- Residual Stresses: Technology — Applications — EffectsDa EverandResidual Stresses: Technology — Applications — EffectsNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Behaviour and Testing of MaterialsDocumento811 pagineMechanical Behaviour and Testing of MaterialsMohammed AbdulkedirNessuna valutazione finora
- Spectral method for fatigue damage estimation with non-zero mean stressDa EverandSpectral method for fatigue damage estimation with non-zero mean stressNessuna valutazione finora
- Dowling Material PropertiesDocumento17 pagineDowling Material PropertiesCarlos A CuencaNessuna valutazione finora
- HDPE FatigueDocumento5 pagineHDPE Fatiguegk218Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computational Fluid Dynamics: Principles and ApplicationsDa EverandComputational Fluid Dynamics: Principles and ApplicationsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- A Practical Method For Statistical Analysis of Strain-Life Fatigue DataDocumento10 pagineA Practical Method For Statistical Analysis of Strain-Life Fatigue DatabloomdidoNessuna valutazione finora
- SolManEngineering Vibration 4th Edition by InmanDocumento36 pagineSolManEngineering Vibration 4th Edition by Inmansmirnov2591100% (1)
- W200 Casing Design Day 3 PDFDocumento106 pagineW200 Casing Design Day 3 PDFYosef ShaabanNessuna valutazione finora
- Offshore GeotechnicsDocumento124 pagineOffshore GeotechnicsthiyakiNessuna valutazione finora
- 0132497468-Ch13 ISMDocumento48 pagine0132497468-Ch13 ISMJeison Rincón Garzón100% (2)
- Stable Numerical Schemes for Fluids, Structures and their InteractionsDa EverandStable Numerical Schemes for Fluids, Structures and their InteractionsNessuna valutazione finora
- DIN 18800-02 - Structural Steelwork Design Construction - DIN (1990)Documento41 pagineDIN 18800-02 - Structural Steelwork Design Construction - DIN (1990)rapaig100% (4)
- Resistance and Deformation of Solid Media: Pergamon Unified Engineering SeriesDa EverandResistance and Deformation of Solid Media: Pergamon Unified Engineering SeriesNessuna valutazione finora
- ISIS Manual - FRP Concrete ReinforcementDocumento158 pagineISIS Manual - FRP Concrete Reinforcementmenumorut173012Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hemp CreteDocumento30 pagineHemp CreteMahaManthra100% (3)
- A Complete Course in Power PointDocumento18 pagineA Complete Course in Power Pointphantom_nc91Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 14Documento97 pagineChapter 14Steven Sun50% (2)
- Lecture 8 FinalDocumento49 pagineLecture 8 FinalKittikun JitpairodNessuna valutazione finora
- Experimental and Analytical Aspects of Strain Localization For Cohesive Frictional MaterialsDocumento20 pagineExperimental and Analytical Aspects of Strain Localization For Cohesive Frictional MaterialsLTE002Nessuna valutazione finora
- HWork03 SolDocumento7 pagineHWork03 SolBen CarltonNessuna valutazione finora
- Appendix C: DX T I T QDocumento3 pagineAppendix C: DX T I T QKelly HoffmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Presentation Dario CulapDocumento11 pagineResearch Presentation Dario CulaptutorialinformationNessuna valutazione finora
- On The Aharonov-Casher Scattering in A CPT-odd Lorentz-Violating BackgroundDocumento14 pagineOn The Aharonov-Casher Scattering in A CPT-odd Lorentz-Violating BackgroundFrontiersNessuna valutazione finora
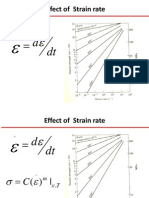
- Effect of Strain RateDocumento22 pagineEffect of Strain Rateanupam.agrawal4959Nessuna valutazione finora
- Optoelectronics and Photonics Principles and Practices 2nd Edition Kasap Solutions ManualDocumento36 pagineOptoelectronics and Photonics Principles and Practices 2nd Edition Kasap Solutions Manualmatte.caudalebvf100% (32)
- Resonancia SubsincronaDocumento16 pagineResonancia SubsincronaSheyla Elizabeth Santamaria RoqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Block 1 Lessons 1-16: Appendix A.6 & Residual Stress Reading On TeamsDocumento19 pagineBlock 1 Lessons 1-16: Appendix A.6 & Residual Stress Reading On TeamsBenNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5Documento94 pagineChapter 5GülinNessuna valutazione finora
- 13e Chap 03Documento77 pagine13e Chap 03Al- DhaheriNessuna valutazione finora
- SM ch7Documento225 pagineSM ch7nav4evrNessuna valutazione finora
- Strain TransformationDocumento81 pagineStrain TransformationDevout PrakosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Fatigue Failure of Cold Forging Tooling Causes and PossibleDocumento15 pagineFatigue Failure of Cold Forging Tooling Causes and PossibleMarcin ŚledźNessuna valutazione finora
- 3MIT PresentationDocumento23 pagine3MIT PresentationLTE002Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Continuum Damage Mechanics CAP 1 (Kachanov)Documento36 pagineIntroduction To Continuum Damage Mechanics CAP 1 (Kachanov)Raul Robledo AlvaradoNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamical Analysis and Allowable Vibration Determination For The Piping SystemsDocumento31 pagineDynamical Analysis and Allowable Vibration Determination For The Piping SystemsChirag ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- S. V. Bulanov-Extreme Light - Matter Interactionthrough The Lensesof The Relativistic Flying Mirror ConceptDocumento67 pagineS. V. Bulanov-Extreme Light - Matter Interactionthrough The Lensesof The Relativistic Flying Mirror ConceptELI BeamlinesNessuna valutazione finora
- Sedra/Smith Microelectronic Circuits 6/E: Chapter 4-A Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS)Documento61 pagineSedra/Smith Microelectronic Circuits 6/E: Chapter 4-A Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS)Allen ChandlerNessuna valutazione finora
- FATEMI Lecture On Fatigue (Must Read Again and Again)Documento94 pagineFATEMI Lecture On Fatigue (Must Read Again and Again)masoodkamal100% (1)
- Ocean Thermal Fronts and Sonar Range PredictionDocumento2 pagineOcean Thermal Fronts and Sonar Range PredictionZahid Hameed QaziNessuna valutazione finora
- Strain Life ApproachDocumento65 pagineStrain Life Approachsjdjd ddjdjfNessuna valutazione finora
- Método Deformacion VidaDocumento68 pagineMétodo Deformacion VidaNohora jimenez abrilNessuna valutazione finora
- 17 Lecture Hardening Soil Model PDFDocumento20 pagine17 Lecture Hardening Soil Model PDFAbdelmoez ElgarfNessuna valutazione finora
- Bab 5 Slide 1Documento25 pagineBab 5 Slide 1Rosyid RidhoNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 - Fatigue of MetalsDocumento55 pagine12 - Fatigue of Metalsvoldemorts100% (1)
- Influence of Strain Rate On Mechanical Properties of 6061-T6 Aluminum Under Uniaxial and Biaxial States of StressDocumento8 pagineInfluence of Strain Rate On Mechanical Properties of 6061-T6 Aluminum Under Uniaxial and Biaxial States of StressNancy TabataNessuna valutazione finora
- On The Inter-Relationship Between Fiber Fracture and Ply Cracking in Graphite - Epoxy LaminatesDocumento22 pagineOn The Inter-Relationship Between Fiber Fracture and Ply Cracking in Graphite - Epoxy Laminatesn_kosmasNessuna valutazione finora
- Optoelectronics and Photonics Principles and Practices 2nd Edition Kasap Solution ManualDocumento59 pagineOptoelectronics and Photonics Principles and Practices 2nd Edition Kasap Solution Manualryan100% (23)
- Solution Manual For Optoelectronics and Photonics Principles and Practices 2Nd Edition Kasap 0132151499 9780132151498 Full Chapter PDFDocumento32 pagineSolution Manual For Optoelectronics and Photonics Principles and Practices 2Nd Edition Kasap 0132151499 9780132151498 Full Chapter PDFrichard.parga191100% (16)
- Finite Elements in Engineering ChandrupatlaDocumento17 pagineFinite Elements in Engineering ChandrupatlaTahsinul Haque Tasif40% (5)
- Multipole Expansion of Magnetic Vector PotentialDocumento12 pagineMultipole Expansion of Magnetic Vector Potentialabserer0% (1)
- Machine Design I Ch3Documento36 pagineMachine Design I Ch3Shitnu SuwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento46 pagineChapter 2Bong Kuek KongNessuna valutazione finora
- Frequency Based Fatigue: Professor Darrell F. SocieDocumento59 pagineFrequency Based Fatigue: Professor Darrell F. SocieSunilkumar ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- 06-Fatigue and Creep of Materials - F17 PDFDocumento23 pagine06-Fatigue and Creep of Materials - F17 PDFsabavoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Manson DLDRDocumento41 pagineManson DLDRBairZubairNessuna valutazione finora
- Critical State Soil Mechanics (CSSM)Documento14 pagineCritical State Soil Mechanics (CSSM)Tomasz CzNessuna valutazione finora
- 13e Chap 08Documento144 pagine13e Chap 08kaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Field Effect in Semiconductor-Electrolyte Interfaces: Application to Investigations of Electronic Properties of Semiconductor SurfacesDa EverandField Effect in Semiconductor-Electrolyte Interfaces: Application to Investigations of Electronic Properties of Semiconductor SurfacesNessuna valutazione finora
- Colloquium Spectroscopicum Internationale: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XVIII Colloquium Spectroscopicum International, Grenoble, France, 15 - 19 September 1975Da EverandColloquium Spectroscopicum Internationale: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XVIII Colloquium Spectroscopicum International, Grenoble, France, 15 - 19 September 1975J. P. RobinNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Report Draft 2Documento97 pagineFinal Report Draft 2LiNessuna valutazione finora
- Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Lower Limb Prosthetic Foot Made From Composite Polymer Blends1Documento12 pagineExperimental and Numerical Investigation of Lower Limb Prosthetic Foot Made From Composite Polymer Blends1Jawad K. OleiwiNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Properties of Batu Pahat Soft Clay Stabilized With Lime, Cement and Bentonite For Subgrade in Road ConstructionDocumento46 pagineEngineering Properties of Batu Pahat Soft Clay Stabilized With Lime, Cement and Bentonite For Subgrade in Road ConstructionHawaiiChongNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Datasheet LITEN BB 85 F - EngDocumento2 pagineTechnical Datasheet LITEN BB 85 F - EngTo RaNessuna valutazione finora
- Extrusion Guides 01Documento6 pagineExtrusion Guides 01Praveen ChathurangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sesion 3 - Tabla Concentrador de EsfuerzosDocumento10 pagineSesion 3 - Tabla Concentrador de EsfuerzosĞôřqûî ĀğūîřřêNessuna valutazione finora
- Shaban Booklet 1-6-2016Documento162 pagineShaban Booklet 1-6-2016Mariwan MirNessuna valutazione finora
- Base PlateDocumento15 pagineBase PlateHSY79Nessuna valutazione finora
- Concrete Fundamental: Bfs 40603 Concrete Technology Semester Ii Session 2015/2016Documento25 pagineConcrete Fundamental: Bfs 40603 Concrete Technology Semester Ii Session 2015/2016Qayyum Uzear UsinNessuna valutazione finora
- Lightweight Concrete PDFDocumento5 pagineLightweight Concrete PDFShamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Stress Concentration and FatigueDocumento22 pagineStress Concentration and FatiguelosoceNessuna valutazione finora
- Buderus 7225Documento4 pagineBuderus 7225Ajeng GaleriNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Tensile TestingDocumento7 pagineChapter 4 Tensile TestingعلياسماعيلNessuna valutazione finora
- Mortars in Norway From The Middle Ages To The 20th Century: Con-Servation StrategyDocumento8 pagineMortars in Norway From The Middle Ages To The 20th Century: Con-Servation StrategyUriel PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- HIT-HY 200 RV3 Injection Mortar: Technical DatasheetDocumento31 pagineHIT-HY 200 RV3 Injection Mortar: Technical DatasheetHafizul ZaidanNessuna valutazione finora
- IPD Liner Sales Sheet v5bDocumento2 pagineIPD Liner Sales Sheet v5bKhun khaiNessuna valutazione finora
- LooPUB31 PDFDocumento71 pagineLooPUB31 PDFAbdallah AlrifaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced-PP 1102LQ - 0Documento1 paginaAdvanced-PP 1102LQ - 0Narender RawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Stainless Steels and Super AlloysDocumento44 pagineStainless Steels and Super AlloysRenan AlmeidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Design of Offshore Ships: DNV-OS-C102Documento66 pagineStructural Design of Offshore Ships: DNV-OS-C102Allan SousaNessuna valutazione finora
- An Sys NotesDocumento4 pagineAn Sys NotesbalabooksNessuna valutazione finora