Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Answer Gerak Gempur Chemistry 2013
Caricato da
ryder1man6433Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Answer Gerak Gempur Chemistry 2013
Caricato da
ryder1man6433Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Mark scheme 1 (a) (i) (ii) (b) (i) (ii) The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom 17 2.8.
1 Group 1, because it has one valence electron Marks 1 1 1 1+1
(iii) Reacts with water to produce hydrogen and metal hydroxide Reacts with oxygen to form metal oxide Reacts with chlorine gas to produce metal chloride [ Any one] (c) (d) (e) Q and R because they have the same proton number but different nucleon number/ number of neutrons S S, Q, P Total 2 a b alkane (i) (ii) 58 No. of mole of CO2 = 12 0 cm3 24000 cm3 // = 0.005 mol
1 1+1 1 1 10 1 1
1 No of mole of C4H10. = 0.005 / 4 // = 0.00125 mol Mass of C4H10. = 0.0125 x 58 = 0.0725 g (c) (i) (ii) (d) Butene // But 2 - ene C = C // Double bond between carbon atoms Accept any one of the isomers 1 1 1 1 1
(I) (e)
(i) (ii)
Hydration Catalyst - phosphoric acid Temperature 300 oC Pressure - 60 atm.
Any one1 Total 10
(a) (i)
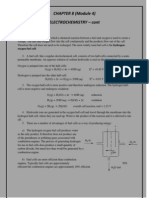
Diagram : functional apparatus : label - copper(II) chloride solution - carbon electrodes : draw test tube to collect gas at anode
1 1 1 1 1
(ii)
Gas produced is tested with a glowing (wooden) splinter Gas relights the glowing (wooden) splinter
(iii)
Hydroxide ions will be attracted to the anode and discharged to form oxygen molecules 1 Cl, OH 1 1
(b) (i) (ii)
Cl- // chloride ion
Cl- ion // chloride ion is more concentrated than OH- ion // 1 hydroxide ion (iii) 2 Cl Cl2 + 2e Total a From pink to colourless 1 1 10
Experiment 1= 22.40 cm3
2= 22.20 cm3
3= 22.00 cm3
All correct with two decimal places - 2 marks All correct with one decimal place / 2 correct with 2 decimal places - 1 mark c H2SO4 + 2 NaOH K2 SO4 + 2H2O Correct formula for reactants and products Balanced equation d (i) Average volume = ( 22.40 + 22.20 + 22.00 ) / 3 = 22.30 cm3
2 1 1
1 ii) The number of mol of sulphuric acid = ( 22.30 1.0) / 1000 = 0.0223 mol 1 e f Methyl orange 1 Functional apparatus set- up : conical flask, burette Label : Sulphuric acid, Potassium hydroxide and phenolphthalein 1 1
Total10 5 (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution // Manganate(VII) ions Fe2+ Fe3+ + e Green solution turns tbrown // Purple coloured solution becomes colourless From electrode carbon X to Y [ show on diagram 4.1] Reduction 1 1 1 1 1
(f )
because the oxidation number of MnO4- changes from +7 to +2 / 1 decreases ( i ) Cl2 + 2II2 + 2CI2 ( ii ) Acts as an oxidizing agent ( iii ) -1 to 0 1 1
Total
10
6 (a)
[able to explain how to measure a fixed quantity of sulphur produced correctly] Example: - A piece of white paper marked X was placed under the conical flask - Time taken for (enough sulphur to produce and cover) the mark X disappear from sight
1 1
(b)
Rate of reaction is the time taken for the X mark to disappear 1 from sight
(c)
(i)
[able to calculate the 1/ time correctly ] Example: 1/ time (s 1 ) 0.030 0.042 0.053
0.063
0.071 1
(ii)
[able to draw the graph correctly] both axes are labelled correctly All 5 points transferred correctly a straight line [able to state the relationship correctly] Example: When the temperature increases, the rate of reaction increases [able to explain using the collision theory correctly] Example: - Increase in temperature increases the kinetic energy of
1 1 1
(d)
(i)
(ii)
1 thiosulphate ions / particles // Thiosulphate ions move faster - Frequency of collision between thiosulphate ions and hydrogen ions increase. 1 - Frequency of effective collision increases Total 10
7 (a)
#Atom of element# Y has three shells containing electrons Y is in Period 3 The number of electron valence of #atom# Y is 7 Y is in Group 17
1 1 1 1 4
(b)
X is in Group 1 1 When going down the group, the number of shells containing electrons 1 increases So atomic size increases. 1 Atom of each element in the group has 1 valence electron 1 The valence electron becomes further away from the nucleus. 1 Therefore, the force of attraction between nucleus and valence electron becomes weaker 1 It is easier for the atom to donate electron, 1 so reactivity increases 1 Max 7
(c)
X and oxygen form ionic bond Atom X donates one electron to form X+ ion to achieve a stable /octet electron arrangement // (electron arrangement of 2.8) Oxygen atom has an electron arrangement of 2.6 and accept two electrons from two X atoms to form ion O2 to achieve a stable/octet electron arrangement // (electron arrangement of 2.8) X+ and O2- are attracted to each other and form X2O // [Can be inferred from correct electron arrangement diagram]
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 max 7
(d)
Cannot 1 Atom Z has achieved the stable electron arrangement // Atom Z does not need to (donate), accept or share electron with X or Y 1 2 Total 20
(a) Metal: copper. Alloy: brass//bronze (b) Average diameter: 3.10 cm 1.95 cm
1 1 2 1 1
The size of atoms in metal block are the same// The atoms are arranged in an orderly manner. The atoms/layers of atoms can slide easily over each other (when 1 kg weight hit on it.)
As a result the average diameter of dent on metal/copper block 1 is larger/bigger//the metal block is softer. The sizes of atoms in alloy/bronze/brass block are not the same//alloy/brass/bronze are made up of different elements/copper and zinc/copper and tin
The foreign /zinc/tin atoms disrupt the orderly arrangement of 1 copper/metal atoms The atoms/layers of atoms cannot slide easily /hardly slide over each other when 1 kg weight hit on it. As a result the average diameter of dent on alloy/brass/bronze block is smaller//lthe metal block is harder. 1 Max: 8
(c) 1 1 1 1
Substance/ingredients aspartame tartazine octyl butanoate citric acid (d)
Food additives sweetener Colouring Flavouring agent anti oxidant
X : antibiotic 1 - the patient must complete the whole course 1 - immunization/ prevent the disease from coming back 1 Y : anti depressant 1 - taken only when needed/ do not overdose/ stop when 1 calmer - could cause addiction/ death if overdose 1 Jumlah 6 20 1 1 1 1 1 1 6
9 (a)
1. Redox reaction is a chemical reaction where oxidation and reduction takes place simultaneously. 2. Half equation at negative terminal: Mg Mg2+ + 2e 3. So, oxidation occurs at the negative terminal. 4. Half equation at the positive terminal: Cu2+ + 2e Cu 5. Reduction occurs at the positive terminal. 6. Thus , the reaction in this cell is a redox reaction. Cell P Energy Change Chemical energy to electrical energy Observation Negative terminal: Zinc strip becomes smaller/ mass of zinc decreases Positive terminal: A brown solid is deposited// mass of copper increases Negative terminal: Zn Zn2+ + 2e Positive terminal: Cu2+ + 2e Cu Cell Q Electrical energy to chemical energy Cathode : A brown solid is deposited// mass of copper increases Anode: Anode/ copper strip dissolves Cathode : Cu2+ + 2e Cu Anode: Cu Cu2+ + 2e
(b)
1+1
1+1
Half equation
1+1 6
Procedure: Iron spoon is connected to the negative terminal on the battery while the silver plate is connected to the positive terminal of the battery//Iron spoon is made as cathode while silver plate is made as anode. 1 Both plates are immersed into the silver nitrate solution. 1 The circuit is completed 1
Functional apparatus set-up Label correctly: silver plate Silver nitrate solution Iron spoon Observation: Grey /silvery solid is deposited Cathode: Ag+ + e Ag Anode : Ag Ag+ + e 1 1 1 Jumlah 1 (a) Heat released when 1 mol of a alcohol is completely burnt in excess 8 20 1 1 1
0 (b)
oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water. Heat of combustion of alcohol Y is higher than alcohol X The molecular size/ number of carbon atom per molecule Alcohol Y is bigger/ higher than alcohol X Alcohol Y produce more carbon dioxide and water molecule than alcohol X // release more heat energy. (c) Methanol/ ethanol / propanol / any alcohol Diagram : functional apparatus : label - thermometer , copper can , spirit lamp, water, alcohol Procedure : 1. (100-250 cm3 ) of water is measured and poured into a copper/tin can and the copper can is placed on a tripod stand . 2. The initial temperature of the water is measured and recorded . 3. A spirit lamp with ethanol/ any alcohol is weighed and its mass is recorded.
1 2 1 1 1 3 1 1 1
1 1 1
4. The lamp is then placed under the copper can and the wick of the lamp is light up immediately. 1 5. The water in the can is stirred continuously until the temperature of the water increases by about 30 C 1 6.The flame is put off and the highest temperature reached by the water is recorded.. 7.The lamp and its content is weighed and the mass is recorded. Max 5 Data: The highest temperature of water The initial temperature of water Increase in temperature, Mass of lamp after burning Mass of lamp before burning Mass of ethanol burnt, m = t2 = t1 = t2-t1 = = m2 = m1 = m2 m1 = m 1 1 1 1 1
Calculation: Number of mole of ethanol / any alcohol, C2H5 OH, n = m/46 The heat energy given out during combustion by ethanol = the heat energy absorbed by water = 100 c J Heat of combustion of ethanol = mc / n Jmol-1 = p = -p/1000 kJ
1 1 Max 12
(d) Number of mol silver nitrate = 100 0.5/1000 // 0.05 1 mol of silver nitrate reacted to release 105kJ heat Therefore, 0.05 mol silver nitrate reacted to produce 1050.05/1 / = -5.2kJ /mol 5250 = 100 4.2 = 12.5 C 1 1
Total
20
END OF MARK SCHEME
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 2010 Chemistry Perak (Gerak Gempur)Documento67 pagine2010 Chemistry Perak (Gerak Gempur)qalanisNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry SPM 2016 SaltDocumento2 pagineChemistry SPM 2016 SaltAzie Nurul AkhtarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry (The Mole)Documento44 pagineChemistry (The Mole)Aisya AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Answer Scheme P123 Trial SBP 07Documento21 pagineChemistry Answer Scheme P123 Trial SBP 07hudazzakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Modul Galus Chem 2014Documento83 pagineModul Galus Chem 2014Juni Farhana100% (2)
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Documento22 pagineSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Ck OoiNessuna valutazione finora
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 4 (BL)Documento8 pagineIT Bio F4 Topical Test 4 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 62 Rate of Reaction Concentration Effect - DwiDocumento2 pagineModule 62 Rate of Reaction Concentration Effect - Dwirudi_zNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 9 ExerciseDocumento7 pagineChemistry Form 4 Chapter 9 ExerciseAngie Kong Su MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Skema Jawapan Kertas 3 PatDocumento10 pagineSkema Jawapan Kertas 3 PatSitinorsyahidah JantanNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 4 Chemistry PracticesDocumento122 pagineForm 4 Chemistry PracticesVANESSA VOON MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOLOGY 2 (4551/2) : Answering Questions Techniques SECTION A: STRUCTURED QUESTIONS (5 Compulsory Questions)Documento6 pagineBIOLOGY 2 (4551/2) : Answering Questions Techniques SECTION A: STRUCTURED QUESTIONS (5 Compulsory Questions)Jedidah Jong100% (2)
- Chemistry Exercise - Chap 3Documento2 pagineChemistry Exercise - Chap 3eddielawNessuna valutazione finora
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocumento10 pagineAcids, Bases and Saltsshehryar khanNessuna valutazione finora
- SPM Physics Terms and DefinitionDocumento12 pagineSPM Physics Terms and Definitionnursuhailah100% (3)
- Kimia Module 1 5 Diagnostik f4 PDFDocumento70 pagineKimia Module 1 5 Diagnostik f4 PDFJuan DavisNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 4 - Salts (+experiment)Documento4 pagineForm 4 - Salts (+experiment)kanryu_zonasNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Chemical Formulae and EquationDocumento43 pagine3 Chemical Formulae and EquationmawarhanifNessuna valutazione finora
- IT Bio F4 Topical Test 8 (BL)Documento9 pagineIT Bio F4 Topical Test 8 (BL)Ismaliza IshakNessuna valutazione finora
- Form 4 Science Chapter 8Documento6 pagineForm 4 Science Chapter 8elineNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 6Documento9 pagineChemistry Form 4 Chapter 6Steven Wong50% (2)
- Physics Paper 3 SPMDocumento13 paginePhysics Paper 3 SPMChaste TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Mistakes Made by Students in SPM Chemistry Paper 2Documento9 pagineCommon Mistakes Made by Students in SPM Chemistry Paper 2leemayjuin100% (1)
- Chemistry (Chapter 3 - Notes)Documento2 pagineChemistry (Chapter 3 - Notes)Daniel Wong Sai Meng100% (1)
- Exercise Physics Form 4 Chapter 1Documento7 pagineExercise Physics Form 4 Chapter 1Wa Wa Jackson WongNessuna valutazione finora
- KimDocumento104 pagineKimBayby SiZzle'zNessuna valutazione finora
- Add Math Mid Year SPM Form 5 P2 2015Documento18 pagineAdd Math Mid Year SPM Form 5 P2 2015smkpthoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Section A p3Documento8 pagineSection A p3Zunaidi JaafarNessuna valutazione finora
- PMR 2012 Science 108 MantraDocumento16 paginePMR 2012 Science 108 MantraJun MingNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics P2 SPM 2014 MelakaDocumento9 paginePhysics P2 SPM 2014 MelakaLeeZiangNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuideDocumento39 pagineChapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuideMuhd Rifaie RodzilNessuna valutazione finora
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 2Documento11 pagineSPM Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 2kslpeter87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Form 4 - Paper 1Documento13 pagineChemistry Form 4 - Paper 1adikmuk0% (1)
- REDOXDocumento67 pagineREDOXLeo PietroNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 7Documento5 pagineChemistry Form 4 Chapter 7Azsyerrah Jahini67% (3)
- Trial Paper 2 MS PerlisDocumento8 pagineTrial Paper 2 MS PerlisZaiton RoslanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Perfect Score 2011 Module AnswerDocumento43 pagineChemistry Perfect Score 2011 Module Answersarahrozaimi100% (1)
- Kedah Skema Modul 2 Kimia Paper 2 Trial SPM 2015Documento10 pagineKedah Skema Modul 2 Kimia Paper 2 Trial SPM 2015azmibhr100% (1)
- Perfect Score Chemistry SBP 2012 - ANSWERDocumento61 paginePerfect Score Chemistry SBP 2012 - ANSWERAhmad RawiNessuna valutazione finora
- 2015 PSPM Kedah Kimia2 W AnsDocumento38 pagine2015 PSPM Kedah Kimia2 W Ansjee2kk100% (2)
- 2811 Jan 01MSDocumento10 pagine2811 Jan 01MSThatchani GundasamyNessuna valutazione finora
- SPM Trial 2012 Chemistry Qa SelangorDocumento49 pagineSPM Trial 2012 Chemistry Qa SelangorzerosakuraNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer For Chemistry Paper 2 Negeri Sembilan 2012Documento6 pagineAnswer For Chemistry Paper 2 Negeri Sembilan 2012ryder1man6433Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sec 4EXP Pure Chemistry Paper Marking SchemeDocumento7 pagineSec 4EXP Pure Chemistry Paper Marking SchemeHui XiuNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Scheme Chemistry Trial SPM Terengganu 2011Documento22 pagineAnswer Scheme Chemistry Trial SPM Terengganu 2011Cik Mieyrarif100% (1)
- Trial Kedah Chemistry SPM 2013 K2 SKEMADocumento12 pagineTrial Kedah Chemistry SPM 2013 K2 SKEMACikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Chemical Engineering Board Exam Questions (Edited)Documento11 pagineChemical Engineering Board Exam Questions (Edited)AkiNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrochemistry - Cont Module 4 STPMDocumento10 pagineElectrochemistry - Cont Module 4 STPMPavithiranNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper 2 Marking Scheme 2013Documento18 paginePaper 2 Marking Scheme 2013Jaaizah JaafarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2010 A Level H2 P3 Suggested AnswersDocumento10 pagine2010 A Level H2 P3 Suggested AnswersMichelle LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Eletrochemistry Previous Qns With AnswersDocumento8 pagineEletrochemistry Previous Qns With AnswersAkshay SureshNessuna valutazione finora
- Structured Questions AnswersDocumento23 pagineStructured Questions AnswersNg Swee Loong StevenNessuna valutazione finora
- Solutions To Problem Set 2Documento5 pagineSolutions To Problem Set 2Andy Nguyen100% (1)
- Che Ans 1Documento9 pagineChe Ans 1Aditi KrishnamurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- CHE1501 2018 S2 Memo Ass4andExamPrepDocumento18 pagineCHE1501 2018 S2 Memo Ass4andExamPrepZethu Khah100% (1)
- HKDSE Chem FX Mock Exam Paper 1 2012 Set 1 Eng AnsDocumento10 pagineHKDSE Chem FX Mock Exam Paper 1 2012 Set 1 Eng Ansleung_ting_2Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4541 123 Skema Kim Trial SPM 2013Documento22 pagine4541 123 Skema Kim Trial SPM 2013Robert HicksNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem Prepa 1Documento10 pagineChem Prepa 1Kubra KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionDa EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Experiment 1: Change of Iron (Ii) Ion To Iron (Iii) IonDocumento12 pagineExperiment 1: Change of Iron (Ii) Ion To Iron (Iii) Ionryder1man6433100% (1)
- Diffusion and Melting PointDocumento6 pagineDiffusion and Melting Pointryder1man6433Nessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 1: Change of Iron (Ii) Ion To Iron (Iii) IonDocumento12 pagineExperiment 1: Change of Iron (Ii) Ion To Iron (Iii) Ionryder1man6433100% (1)
- Please Choose One Item From The List AboveDocumento3 paginePlease Choose One Item From The List Aboveryder1man6433Nessuna valutazione finora
- Exam Chemistry Form 4 Paper 2Documento8 pagineExam Chemistry Form 4 Paper 2ryder1man643367% (6)
- Rate of Reaction EexercisDocumento6 pagineRate of Reaction Eexercisryder1man6433Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3: Oxidation and Reduction Form 5 Chemistry Title: Rusting As A Redox ReactionDocumento3 pagineChapter 3: Oxidation and Reduction Form 5 Chemistry Title: Rusting As A Redox Reactionryder1man6433Nessuna valutazione finora
- Language of ChemistryDocumento51 pagineLanguage of Chemistryryder1man6433Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Form 6 Chap 01 PDFDocumento44 pagineChemistry Form 6 Chap 01 PDFryder1man6433Nessuna valutazione finora
- Natural RubberDocumento3 pagineNatural Rubberryder1man6433Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Matter & The Atomic Structure ModulDocumento43 pagine1 Matter & The Atomic Structure Modulryder1man6433100% (1)
- CBSE Class X (Science) Page 1 30Documento30 pagineCBSE Class X (Science) Page 1 30Nitesh Bhardwaj0% (1)
- SPM Kimia Tingkatan, 5 Rate of Reaction ExerciseDocumento7 pagineSPM Kimia Tingkatan, 5 Rate of Reaction Exerciseryder1man6433Nessuna valutazione finora
- Answer For Chemistry Paper 2 Negeri Sembilan 2012Documento6 pagineAnswer For Chemistry Paper 2 Negeri Sembilan 2012ryder1man6433Nessuna valutazione finora
- RTS Chemistry SPM Question Bank Chapter 5Documento10 pagineRTS Chemistry SPM Question Bank Chapter 5ryder1man64330% (1)
- Trial Kedah Chemistry SPM 2013 K2 SKEMADocumento12 pagineTrial Kedah Chemistry SPM 2013 K2 SKEMACikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Chemistry SPM Trial Examination Pahang 2012 AnswersDocumento8 pagineChemistry SPM Trial Examination Pahang 2012 Answersryder1man6433Nessuna valutazione finora
- Yearly Plan 2013 Nama: Chemistry (Form Four)Documento12 pagineYearly Plan 2013 Nama: Chemistry (Form Four)ryder1man6433Nessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Chemical Reactions Class 7.Documento19 pagineSimple Chemical Reactions Class 7.ZUNI100% (4)
- Chem ch31 9 33Documento2 pagineChem ch31 9 33Tang Hon Kit WilsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Reactions of Copper and Percent Yield KeyDocumento9 pagineChemical Reactions of Copper and Percent Yield KeysibtainNessuna valutazione finora
- ResonanceCalcGraph Fixed (Joe Champion Transmutation ExperimentsDocumento218 pagineResonanceCalcGraph Fixed (Joe Champion Transmutation ExperimentsDonald Smith100% (2)
- BIsmuthDocumento3 pagineBIsmuthtyler.mcclainNessuna valutazione finora
- NEET UG Chemistry P Block ElementsDocumento47 pagineNEET UG Chemistry P Block ElementskamalNessuna valutazione finora
- Acids 1 QPDocumento12 pagineAcids 1 QPihana.k2008Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment ChemistryDocumento12 pagineAssignment ChemistrySayyad Dawar100% (1)
- Using Your Text Book and These Descriptions of Chemical Reactions, Complete This Worksheet Parts 1,2 and 3Documento2 pagineUsing Your Text Book and These Descriptions of Chemical Reactions, Complete This Worksheet Parts 1,2 and 3MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Trio Reality 2017Documento96 pagineTrio Reality 2017elektrospecNessuna valutazione finora
- Questions From Previous Chemistry 116 ExamsDocumento21 pagineQuestions From Previous Chemistry 116 ExamsBindu JayachandranNessuna valutazione finora
- 0620 s17 QP 43Documento16 pagine0620 s17 QP 43Aryan Shah0% (1)
- Exercise No. 1 Mole To GramDocumento5 pagineExercise No. 1 Mole To GramJoyae ChavezNessuna valutazione finora
- Perhitungan Status Mutu Air Metode Indeks Pencemaran Pada Hilir Sungai Tempat Pembuangan Air Limbah Rsu Permata Hati Parameter Ci Lix Ci/Lix Ci/Li Ukur Baru (Ci/Lix) R (Ci/Lix) M Pij Ci/LixDocumento2 paginePerhitungan Status Mutu Air Metode Indeks Pencemaran Pada Hilir Sungai Tempat Pembuangan Air Limbah Rsu Permata Hati Parameter Ci Lix Ci/Lix Ci/Li Ukur Baru (Ci/Lix) R (Ci/Lix) M Pij Ci/LixDafy ZainiNessuna valutazione finora
- Edexecel IAL Lesson 1Documento20 pagineEdexecel IAL Lesson 1Pevin De silvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Stainless Steel TypesDocumento20 pagineStainless Steel Typessushant_jhawerNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocumento12 pagineCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelThaarvena RetinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Alternative Do MeasurementDocumento3 pagineAlternative Do Measurementfendi setyoNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 10 Science - Acids Bases and SaltsDocumento2 pagineCBSE Class 10 Science - Acids Bases and SaltsAnuska SaxenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aluminum Toxic Heavy Metals Fact SheetDocumento1 paginaAluminum Toxic Heavy Metals Fact SheetosumexNessuna valutazione finora
- Difference Between Rust and CorrosionDocumento5 pagineDifference Between Rust and Corrosionhutsonianp100% (2)
- Dha Senior School For Girls Online MOCK-Examinations: There Are FORTY Questions On This Paper. Answer All QuestionsDocumento12 pagineDha Senior School For Girls Online MOCK-Examinations: There Are FORTY Questions On This Paper. Answer All QuestionsaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aqua Comparador Catalogo Orbeco Hellige Aguas ColombiaDocumento10 pagineAqua Comparador Catalogo Orbeco Hellige Aguas ColombiaRmao CINessuna valutazione finora
- Lassaigne's Test Is Used ToDocumento4 pagineLassaigne's Test Is Used ToGroup SixNessuna valutazione finora
- Studying Gold Ores: Mineralogy, Cyanidation, Toxicity and Environmental IssuesDocumento34 pagineStudying Gold Ores: Mineralogy, Cyanidation, Toxicity and Environmental IssuesFitria Putri DwiNessuna valutazione finora
- Specification of Phosphor Bronze StripDocumento3 pagineSpecification of Phosphor Bronze Stripsaleemnel100% (1)
- C-CS - 20 - 011 - Galvanized Flashing & Sheet Metal Rev - 0Documento12 pagineC-CS - 20 - 011 - Galvanized Flashing & Sheet Metal Rev - 0Yvan Nuñez EscobedoNessuna valutazione finora
- History of The Development of The Periodic Table of ElementsDocumento16 pagineHistory of The Development of The Periodic Table of ElementsJerry Delos Reyes100% (1)
- Unit 3 Chem Lab 1 PDFDocumento4 pagineUnit 3 Chem Lab 1 PDFapi-239721624Nessuna valutazione finora
- Raku Glaze ListDocumento9 pagineRaku Glaze ListRobson Lamosa CesarNessuna valutazione finora