Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Nervous System Outline
Caricato da
Mark Angelo Tacorda CabreraCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Nervous System Outline
Caricato da
Mark Angelo Tacorda CabreraCopyright:
Formati disponibili
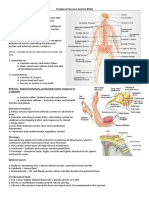
NERVOUS SYSTEM OUTLINE I. Nervous System = 2 Parts A. Central Nervous System (CNS) 1. Brain 2. Spinal Cord B.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) 1. Nerves to parts of the body 2. Nerves from parts of the body C. Functions 1. Sensory a. receptors for stimuli (receive stimulus) b. peripheral nerves (carry impulses to CNS) c. activities monitored 1. light intensity (visual) 2. sound intensity (auditory) 3. temperature 4. oxygen concentration 5. internal fluid conditions 2. Motor a. peripheral nerves (carry impulses from CNS) b. effectors (muscles & glands) 3. Integration (CNS) a. create sensations (awareness) b. add to memory c. help produce thoughts d. make decisions (conscious & subconscious) 4. Importance = maintain homeostasis Nerve Tissue A. Neurons (structural & functional units of nervous system) B. Neuroglial Cells (accessory cells: support neurons) 1. Astrocytes (star shaped cell) a. found between neurons and blood vessels b. provide nutrition c. support d. form scar tissue after brain tissue injury (multiply) 2. Oligodendrocytes a. smaller than astrocytes with fewer processes b. found along neurons c. form myelin sheath (brain and spinal cord neurons) 3. Microglia a. very small cells with even fewer processes b. found throughout CNS c. phagaocytosis
II.
d. increase in numbers during inflammation 4. Ependymal Cells a. cube to columnar shaped cells b. found lining ventricles & central canal of spinal cord c. cover choroids plexuses in brain III. Synaptic Transmission C. Neurotransmitters 1. acetylcholine 2. monoamines a. epinephrine b. norepinephrine c. dopamine d. serotonin 3. amino acids a. glycine b. glutamic acid c. aspartic acid d. gama amino butyric acid (GABA) 4. peptides a. enkephalins b. substance P D. Release of neurotransmitters 1. action potential reaches synaptic knob 2. calcium channels open 3. calcium moves in 4. synaptic vesicles release neurotransmitter 5. neurotansmitter binds to receptor on next neuron 6. action potential occurs on next neuron
III.
Peripheral Nervous System A. 2 parts 1. somatic nervous system a. cranial & spinal nerves 1. skin & skeletal system b. conscious activity 2. autonomic nervous system a. central nervous system nerves 1. visceral organs b. subconscious activity B. cranial & spinal nerves 1. 12 cranial nerves a. origen 1. cerebrum & brain stem
b. classification 1. sensory 2. motor 3. mixed c. sensory cell bodies outside CNS 1. in ganglia d. motor cell bodies 1. in gray matter of cerebral cortex 2. 31 spinal nerves a. origen 1. in spinal cord b. classification 1. all mixed c. sensory cell bodies outside CNS 1. in dorsal root ganglia d. motor cell bodies 1. in gray matter of spinal cord
IV.
Autonomic Nervous System A. functions = control visceral activities 1. heart rate 2. blood pressure 3. respiration rate 4. body temperature 5. homeostasis 6. stressful responses B. 2 parts 1. sympathetic a. energy expending stressful conditions 2. parasympathetic a. restful conditions b. restores/maintain normal state 3. antagonistic actions a. heart rate 1. sympathetic increases 2. parasympathetic decreases b. digestive actions 1. sympathetic decreases 2. parasympathetic increases C. Sympathetic (fight or flight response) 1. pupils dilate 2. heart rate increases 3. vasoconstriction
a. skin b. viscera 4. vasodilation a. heart b. lungs c. brain d. skeletal muscles 5. blood pressure increases 6. respiration rate increases 7. bronchioles dilate 8. blood sugar increases a. glycogenolysis in liver 9. gastrointestinal tract slows or stops 10. adrenal glands a. release epinephrine & norepinephrine D. parasympathetic set-up 1. preganglionic neuron cell body a. location 1. brain stem 2. 2 4 sacral vertebrae 2. postganglionic neuron cell body a. location 1. terminal ganglia a) close to or within visceral organs
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Nervous System NotesDocumento6 pagineNervous System NotesAlex Whitwam100% (3)
- Nervous System WorksheetDocumento12 pagineNervous System WorksheetLeamae ObinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Physiology II MCQS66Documento11 pagineHuman Physiology II MCQS66Jany SNessuna valutazione finora
- Summative Test 2.1 Nervous System For NotebookDocumento4 pagineSummative Test 2.1 Nervous System For NotebookJonalvin KE100% (2)
- Long Test No. 4 (Nervous System) Ready To PrintDocumento3 pagineLong Test No. 4 (Nervous System) Ready To Printjayrald cruzada100% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocumento2 pagineNervous System234iagiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1Da EverandIntro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ana 211 Anatomy For NursesDocumento96 pagineAna 211 Anatomy For NursestonylizzyNessuna valutazione finora
- Circulatory Cloze WoorsheetDocumento2 pagineCirculatory Cloze WoorsheetAmarpreet Kaur100% (1)
- B Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 2 (Week 3)Documento17 pagineB Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 2 (Week 3)Daisy Soriano PrestozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous SystemDocumento11 pagineNervous SystemMabesNessuna valutazione finora
- History of BiologyDocumento30 pagineHistory of BiologyErl D. MelitanteNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous System: The Dog Stole the Professor's NotesDa EverandNervous System: The Dog Stole the Professor's NotesNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous System - Free Printable TestsDocumento1 paginaNervous System - Free Printable TestsRayan KassamNessuna valutazione finora
- KS4 The Heart and Circulatory SystemDocumento49 pagineKS4 The Heart and Circulatory SystemjtNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 PDFDocumento20 pagineModule 3 PDFSuiluj Omatsodlab100% (1)
- Medical SurgicalDocumento180 pagineMedical SurgicalCorinne Adriano100% (2)
- Coordination System Encircle The Best Answer of The Following QuestionsDocumento13 pagineCoordination System Encircle The Best Answer of The Following Questionsnon elfNessuna valutazione finora
- 3rdQ Test Sci10Documento4 pagine3rdQ Test Sci10Enrick PestilosNessuna valutazione finora
- PE 1 Midterm Exam 2022Documento3 paginePE 1 Midterm Exam 202212 S1 Delos Santos Doreen Claire M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Frog Dissection Lab Sheet #1: Pre/Post Questions NameDocumento2 pagineFrog Dissection Lab Sheet #1: Pre/Post Questions NameFrancis ArceoNessuna valutazione finora
- Histology-World! Histology Testbank-Nervous System 1Documento3 pagineHistology-World! Histology Testbank-Nervous System 1Kat JornadalNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment of The AbdomenDocumento22 pagineAssessment of The AbdomenTerence Shane AcodNessuna valutazione finora
- Internal Parts of A FishDocumento2 pagineInternal Parts of A FishBohna FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- DLP 1 For 3rd GradingDocumento3 pagineDLP 1 For 3rd GradingMarivic Guillermo - LongaresNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ Hap-II, Bp201tDocumento39 pagineMCQ Hap-II, Bp201tANUJ DEVNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1: Human Body System Lesson 5: The Nervous and Endocrine SystemDocumento9 pagineUnit 1: Human Body System Lesson 5: The Nervous and Endocrine SystemeisachannelestNessuna valutazione finora
- BioPsych Handout 4 RESTRUCTUREDDocumento7 pagineBioPsych Handout 4 RESTRUCTUREDMarial JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 3Documento15 pagineScience 10 Quarter 3 Module 3Zahra Alexä DavidsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral Quiz10Documento2 pagineOral Quiz10Jel SuarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Notes 12 Sem2Documento11 pagineBiology Notes 12 Sem2josmanlilyNessuna valutazione finora
- BiopsychologyDocumento28 pagineBiopsychologyElysia ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Biological ScienceDocumento6 pagineBiological ScienceMae Quibod PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous System CNS 1481841Documento5 pagineNervous System CNS 1481841Jglacier godNessuna valutazione finora
- Cns Notes UclaDocumento4 pagineCns Notes UclaJulieNessuna valutazione finora
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocumento23 pagineAutonomic Nervous SystemPIOZRNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Psychology Chapter 3 Notes: BiopsychologyDocumento5 pagineAP Psychology Chapter 3 Notes: BiopsychologyKloie WalkerNessuna valutazione finora
- NSLNDocumento7 pagineNSLNhandel21Nessuna valutazione finora
- Summative Exam On Nervous System and Endocrine SystemDocumento3 pagineSummative Exam On Nervous System and Endocrine SystemKhiyah RhueNessuna valutazione finora
- Clin Phys Exam 2Documento5 pagineClin Phys Exam 2Paloma GuijarroNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology: Nervous SystemDocumento48 pagineBiology: Nervous SystemThanush KarthikNessuna valutazione finora
- 3rd Preliminary Examination 2023 - 2024 Grade 10 ScienceDocumento4 pagine3rd Preliminary Examination 2023 - 2024 Grade 10 ScienceJerome Tala-oc100% (1)
- Long Test No. 4 (Nervous System)Documento3 pagineLong Test No. 4 (Nervous System)Yaj CruzadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Central Nervous SystemDocumento25 pagineCentral Nervous SystemKhairulbariah AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurology - The Study of The Nervous SystemDocumento3 pagineNeurology - The Study of The Nervous SystemMizchelle Angeles VilladorNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 3rd QTR Day 3Documento43 pagineScience 3rd QTR Day 3A S HNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology - The Nervous SystemDocumento16 pagineAnatomy and Physiology - The Nervous Systemxuxi dulNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 10Documento2 pagineGrade 10letty louNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurological System588 PDFDocumento14 pagineNeurological System588 PDFTanwir HoussaynNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 01 Final RevDocumento8 pagine9 01 Final RevAna MariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Autonomic Nervous System QuestionsDocumento6 pagineAutonomic Nervous System Questions202210034Nessuna valutazione finora
- Neurophysiology Practice Questions (Multiple Choice) Flashcards - QuizletDocumento23 pagineNeurophysiology Practice Questions (Multiple Choice) Flashcards - Quizletblackkcat308Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sistem Saraf TepiDocumento39 pagineSistem Saraf TepiPradista HariniNessuna valutazione finora
- General Anatomy Test 5Documento3 pagineGeneral Anatomy Test 5Hamza TareenNessuna valutazione finora
- Central Nervous SystemDocumento48 pagineCentral Nervous SystemPIOZRNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz#4Documento3 pagineQuiz#4jhacetin775Nessuna valutazione finora
- Peripheral Nervous System 5187471101Documento2 paginePeripheral Nervous System 5187471101Jglacier godNessuna valutazione finora
- 5PRI LL NATURAL SC - Term1 - GEN - Worksheets - AnswerKeyDocumento11 pagine5PRI LL NATURAL SC - Term1 - GEN - Worksheets - AnswerKeyEisiyi MMNessuna valutazione finora
- Parasympathetic Divisions Which Are Anatomically and FunctionallyDocumento35 pagineParasympathetic Divisions Which Are Anatomically and Functionallyzepoli_zepoly6232Nessuna valutazione finora
- THE Nervous System: Nervous System Is A Complex Network That Transmit NervesDocumento12 pagineTHE Nervous System: Nervous System Is A Complex Network That Transmit NervesLeean HizonNessuna valutazione finora
- 751-vdg ch13 AnsDocumento3 pagine751-vdg ch13 AnsCPCL24Nessuna valutazione finora
- Full Download Introduction To Drugs and The Neuroscience of Behavior 1st Edition Adam Prus Test BankDocumento36 pagineFull Download Introduction To Drugs and The Neuroscience of Behavior 1st Edition Adam Prus Test Bankthomasstonetyy6100% (29)
- Organisation of The Nervous System: Form 5 Biology Chapter 3 Body Coordination (A)Documento24 pagineOrganisation of The Nervous System: Form 5 Biology Chapter 3 Body Coordination (A)Mei QiiNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of Nervous SystemDocumento59 pagineAnatomy of Nervous SystemSeema ChapagainNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer 6 ScienceDocumento6 pagineReviewer 6 ScienceJhanna Gil BuctolanNessuna valutazione finora
- Zly106 CA Questions & Answers by Evans Kelly & DiligeceDocumento40 pagineZly106 CA Questions & Answers by Evans Kelly & DiligeceSHERIFF BAKARENessuna valutazione finora
- Dwnload Full Introduction To Drugs and The Neuroscience of Behavior 1st Edition Adam Prus Test Bank PDFDocumento36 pagineDwnload Full Introduction To Drugs and The Neuroscience of Behavior 1st Edition Adam Prus Test Bank PDFdog.starstiflero3wsf6100% (11)
- Notes - Animals and Their Young OnesDocumento4 pagineNotes - Animals and Their Young OnesAnitha KanumilliNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 - The Human BodyDocumento43 pagineModule 1 - The Human BodyRHONENessuna valutazione finora
- HIBERNACIONDocumento29 pagineHIBERNACIONMariana MuñozNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 Activities (Anatomy and PHYSIOLOGY)Documento19 pagineModule 3 Activities (Anatomy and PHYSIOLOGY)FloraNessuna valutazione finora
- Science6 q2 Mod1 Lesson1-2 Human Body System v1Documento32 pagineScience6 q2 Mod1 Lesson1-2 Human Body System v1HONEYLENE ORNOSNessuna valutazione finora
- Phil Wildlife Jan 10, 2012 NotesDocumento15 paginePhil Wildlife Jan 10, 2012 NotesAbigail CuyacotNessuna valutazione finora
- Gambar 3.2. Anatomi Rongga Mulut Kadal (Eutropis Multifasciata) Keterangan GambarDocumento5 pagineGambar 3.2. Anatomi Rongga Mulut Kadal (Eutropis Multifasciata) Keterangan GambarrefestufuNessuna valutazione finora
- Araling PanlipunanDocumento89 pagineAraling PanlipunanAlyce AjthaNessuna valutazione finora
- PlacentaDocumento21 paginePlacentaAttiqaQureshiNessuna valutazione finora
- AmphibiansDocumento12 pagineAmphibianskldwujezycznaNessuna valutazione finora
- MGW 5 PDFDocumento26 pagineMGW 5 PDFSuhana SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 32 Introduction To AnimalsDocumento22 pagineChapter 32 Introduction To AnimalsMoses GoldenkeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Q2 at Mapeh6Documento4 pagineQ2 at Mapeh6Marhco Tumandao LumanasNessuna valutazione finora
- Digestive System - Part 1Documento20 pagineDigestive System - Part 1AndrewNessuna valutazione finora
- Trivers 1971. The Evolution of Reciprocal AltruismDocumento24 pagineTrivers 1971. The Evolution of Reciprocal AltruismHenry TantaleánNessuna valutazione finora
- 0 Echinoderms-FinalDocumento18 pagine0 Echinoderms-FinalMark Robert MagsinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Day 4-Animal Life CyclesDocumento22 pagineDay 4-Animal Life CyclesKevin Diamante FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Illuatrated Keys To Genera of The Male Wasps in The Subfamily Thynninae - TiphiidaeDocumento69 pagineIlluatrated Keys To Genera of The Male Wasps in The Subfamily Thynninae - TiphiidaeManu AmaroNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomechanics of Musculoskeletal SystemDocumento76 pagineBiomechanics of Musculoskeletal SystemGovinda PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- 1. გენდერ განსხDocumento9 pagine1. გენდერ განსხთეკლა გაბრავაNessuna valutazione finora
- Module III - Lesson 1 Fitness ConceptDocumento4 pagineModule III - Lesson 1 Fitness ConceptPancho RJNessuna valutazione finora
- Changes in The Body: What Is Puberty?Documento4 pagineChanges in The Body: What Is Puberty?Mitch MarananNessuna valutazione finora
- Further Observations On EupelminaeDocumento14 pagineFurther Observations On EupelminaeManu AmaroNessuna valutazione finora