Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Online Shopping System
Caricato da
Dapborlang MarweinDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Online Shopping System
Caricato da
Dapborlang MarweinCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM Page No.
1
CONTENTS :
1. SCOPE 1.1 AUDIENCE 1.2 ORGANISATION 1.3 APPLICABLE DOCUMENTS 2. SOFTWARE REQUIREMENT SPECIFICATION 3. FUNCTIONAL MODEL 4. ACTIVITY DIAGRAM 5. USE CASE DIAGRAM 6. INTERACTION DIAGRAM 6.1.1 6.1.2 SEQUENCE DIAGRAM COLLABORATION DIAGRAM
2 3 8 11 19 23 26 28 29 31
7. STATE CHART DIAGRAM 8. CLASS DIAGRAM 9. IMPLEMENTATION DIAGRAM 9.1 COMPONENT DIAGRAM 9.2 DEPLOYMENT DIAGRAM
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 1
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
1. Scope :
The following subsections describe the scope of the fast food outlet system in terms of its audience, organization, and applicable documents
1.1 Audience : Customers, Administrators, Sellers. 1.2 Organization : ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM 1.3 Applicable Documents : The following documents provide information necessary to understand this documentation:
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 2
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design 2 Software Requirement Specification:
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
System Abstract The Online Shopping Cart system facilitates the Customer to view the Items Products, inquire about the item details, availability of seats and many more. The major functionality of system is to allow the user to book and cancels the flights as per user requirements. It also provides the administrator or manager to modify existing flights or to introduce a new flights in the schedule. Major features provided by the system are : 1. Customer The system allows the user or member to perform flight qnuiry including flight scheduling, seats availability status, fare details, etc. 2. Administrator It allows the customer to register in order to give the services to its member . 3. Online shopping system The system allows the member to order the product as per his/her requirements. The customer is prompt to enter the customer details and credit card details. The member then receives the unique cart number . 4. Product Listing This process gives the details about the purchasing process made by the customer at the details of the shipping and taxes involved with the cost
5. Administrator The administrator module of the system allows the admin/manager to manage the products item It provides the admin /manger to modify or change the existing items or to introduce a new items. Apart from modifying the category it also allow the admin/manager to take the taxes and include the shipping charges along with the h/w s/w and service requirements.
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 3
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design 3. Functional Model.
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
Fig 3.1 Data Flow Diagram for Online Shopping Cart Software
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 4
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
Fig 3.2 Data Flow Diagram for Product Listing
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 5
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
Fig 2.3 Fig : 3.3Data Flow Diagram for Administrator.
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 6
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
Fig Fig: 3.4 Data Flow Diagram for Secure Gateway Provider.
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 7
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design 4. Activity Diagram.
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
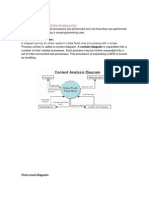
An Activity diagram is a visual representation of any system's activities and flows of data or decisions between activities. Activity diagrams provide a very broad view of a business process. They represent the dynamics of a system. They are flow charts that are used to show the work flow of a system. They show the flow of control from activity to activity in the system. They show what activities can be done in parallel, and any alternative paths through the flow. Purpose Model business workflows Model operations Activity diagrams commonly contain Activity states and action states Transitions Objects
Action States and Activity States Action states are atomic and cannot be decomposed Work of the action state is not interrupted. Activity states can be further decomposed Their activity being represented by other activity diagrams They may be interrupted Represented in UML by a rounded rectangle.
Activity represents the performance of some behavior in the work flow.
Transitions Transitions are used to show the passing of the flow of control from activity to activity. They are typically triggered by the completion of the behavior in the originating activity. When the action or activity of a state completes, flow of control passes immediately to the next action or activity state
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 8
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
A flow of control has to start and end at some place initial state -- a solid ball stop state -- a solid ball inside a circle
Branching When modeling the workflow of a system, it is often necessary to show where the flow of control branches based on a decision point.
The transition from a decision point contain a guard condition. The guard condition is used to determine which path from the decision point is taken. Decisions along with their guard conditions allow you to show alternative paths through a work flow. A branch specifies alternate paths taken based on some Boolean expression A branch may have one incoming transition and two or more outgoing ones
Synchronization Bars In a workflow there are typically some activities that may be done in parallel. A synchronization bar allows you to specify what activities may be done concurrently. A synchronization bar may have many incoming transition and one outgoing transition, or one incoming transition and many outgoing transitions. It is use to specify the forking and joining of parallel flows of control A synchronization bar is rendered as a thick horizontal or vertical line
A fork may have one incoming transitions and two or more outgoing transitions each transition represents an independent flow of control conceptually, the activities of each of outgoing transitions are concurrent either truly concurrent (multiple nodes) or sequential yet interleaved (one node) Page 9 Department of MCA.
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
A join may have two or more incoming transitions and one outgoing transition above the join, the activities associated with each of these paths continues in parallel at the join, the concurrent flows synchronize each waits until all incoming flows have reached the join, at which point one flow of control continues on below the join
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 10
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
Fig 4.1 Activity Diagram :
customer view the product want to purchase? no yes product avilable in india? yes go through the product details yes no Register Login no visit faq Item not found
are u member?
shopping cart is assigned to customer
item get added to shopping cart no confirm the shopp... yes generate purchase details do you want to cancel the product? yes Cancel Product no payment details
paying by creditcard? yes
no
payment on delivery
getway system activated no varification of customer? yes yes want to purchase? no final bill
want to fill feedback?
no yes
Fill feedback
signout
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 11
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
5. Use-Case Diagram.
The use-case concept was introduced by Ivar Jacobson in the object-oriented software engineering (OOSE) method. A use-case diagram is a graph of actors, a set of use cases enclosed by a system boundary, communication (participation) associations between the actors and the use cases, and generalization among the cases. Use case diagrams show how users interact with the system. Use case diagrams describe what a system does from the standpoint of an external observer. The emphasis is on what a system does rather than how. Use case diagrams are closely connected to scenarios. A scenario is an example of what happens when someone interacts with the system. Here is a scenario for a medical clinic. "A patient calls the clinic to make an appointment for a yearly checkup. The receptionist finds the nearest empty time slot in the appointment book and schedules the appointment for that time slot. " Used during requirements elicitation to represent external behavior Actors represent roles, that is, a type of user of the system Use cases represent a sequence of interaction for a type of functionality The use case model is the set of all use cases. It is a complete description of the functionality of the system and its environment
Actors
An actor models an external entity which communicates with the system: o User o External system o Physical environment An actor has a unique name and an optional description. Customer Examples: Passenger: A person in the train GPS satellite: Provides the system with GPS coordinates
Use Cases
A use case represents a class of functionality provided by the system as an event flow. A use case consists of: Unique name Participating actors Pre-conditions Entry conditions (triggers) Flow of events Exit conditions (success guarantees) Page 12
Item Purchased
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design Special requirements The Use Case diagram for whole system is as shown in fig 5.3 The <<extend>> Relationship
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
<<extend>> relationships represent exceptional or seldom invoked cases. The exceptional event flows are factored out of the main event flow for clarity. Use cases representing exceptional flows can extend more than one use case. The direction of a <<extend>> relationship is to the extended use case
The <<include>> Relationship An <<include>> relationship represents behavior that is factored out of the use case. An <<include>> represents behavior that is factored out for reuse, not because it is an exception. The direction of a <<include>> relationship is to the using use case (unlike <<extend>> relationships).
Choose shipping type Online customer <<include>>
<<include>>
Add shipping address
Select shipping address
Select credit card <<include>>
e>> clud n i <<
Add credit card <<include> >
<<include>>
Add Credit card type
Add Credit card number
Add Expiration date
Fig :5.1 Use Case Diagram
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 13
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
Update Items Administrator
Register Customer Customer
Search Item <<include>>
<<include>> Validate Customer <<include>>
Registered Customer
<<include>> Buy Item Prepare Bill
Pay Bill
Fig 5.2 Use case Diagram
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 14
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
USE CASE DESCRIPTION : Actors: 2.1 New Customers 2.2 Registered Customer 2.3 Administrator
Use cases: 1. Search Item 2. Register Item 3. Buy Item 4. Update Item
1. Search Item Any user can search the item. User can search the item by name or company. 2. Register Customer To buy the item, the customer has to be a registered customer. This process is used to register a customer. 3. Buy Item A registered customer can buy a item using this process. This process include search item, validate customer, prepare bill, pay bill.
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 15
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design Use Case Table Use case ID Use case name Actor Pre-condition Post-condition Flow of events 1 View shopping cart Online customer Open the website Search for product open the website of online shopping cart
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
Use case ID Use case name Actor Pre-condition Post-condition Flow of events
2 Search for product Online customer View shopping cart Select the product Open the website, search the product from list
Use case ID Use case name Actor Pre-condition Post-condition Flow of events
3 Create new user Online customer Select the product Select credit card Open the website, search the product from list, select the product, create new user
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 16
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
Use case ID Use case name Actor Pre-condition Post-condition Flow of events
4 Purchase item Online customer Select credit card Review order information Open the website, search the product from list, select the product, create new user, select credit card, purchase the selected item
Use case ID Use case name Actor Pre-condition Post-condition Flow of events
5 Login as registered user Online seller and online customer Open the website Sell or purchase the product Open the website, Login as registered user
Use case ID Use case name Actor Pre-condition Post-condition Flow of events
6 Item registration Online seller Login into the shopping cart system Confirm the registration Open the website, Login as registered user, register the item into system
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 17
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
Use case ID Use case name Actor Pre-condition Post-condition Flow of events Use case ID Use case name Actor Pre-condition Post-condition Flow of events
7 Change the information administrator Login into the system as administrator Update the system Open the website, Login as administrator, make changes in the information 8 Block users administrator Select the user Update the system Open the website, Login as administrator, select the user, block the user
Use case ID Use case name Actor Pre-condition Post-condition Flow of events
9 Inform the deal to seller Online Seller and shopping cart system Check the availability of item Make a deal Open the website, login as shopping cart system , seller sell the item to shopping cart system, inform the deal to seller
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 18
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
View shopping cart
Search for product
Add item to shopping cart
Create new user Online Customer Change item information
Administrator
Select credit card
Purchase item Review order confirmation Choose shipping type Login as registered user
Block users
Shopping Cart system Inform the deal to seller
Register Item
Online seller
fig 5.3. Use case diagram for Online Shopping System
6. UML Interaction Diagram
6.1 Sequence Diagram :
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 19
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
Shopping cart system Administrator
user
User Login user name & password
gives the details give access to member
Fig.6.1.1 Sequence Diagram for User registeration
Administrator : Online seller Item Registration
Log out();
Fig.6.1.2 Sequence Diagram for Seller registeration
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 20
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
Shopping cart : Online Customer Adds Item Gets Item
Cart item
Process order
Logout
Order summary
Product Details Add the products Shipping Charges
Taxes Taxes Payment Details
Processes Processes
Displays the ordered item
Displays the Orderd Item
Confirms
Confirms
Checks Out
Checkout
Fig.6.1.3 Sequence Diagram for Online Customer
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 21
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
Shopping system
: Online Customer Login Add item
Cart system
Ordering system
Add category Add user
Delete user Change password
Delete item
Delete category
Logout
Fig.6.1.4 Sequence Diagram for Online Administrator
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 22
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design 6.2 Collaboration diagrams:
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
They are also interaction diagrams. They convey the same information as sequence diagrams, but they focus on object roles instead of the times that messages are sent. In a sequence diagram, object roles are the vertices and messages are the connecting links. Collaboration diagrams show (used to model) how objects interact and their roles. They are very similar to sequence diagrams. Actually they are considered as a cross between class and sequence diagram. Sequence Diagrams are arranged according to Time. Collaboration Diagrams represent the structural organization of object. [Both sequence and collaboration diagrams are called interaction diagrams] Forms a context for interactions o May realize use cases o May be associated with operations o May describe the static structure of classes Collaboration diagrams contain the following: o Class roles (subsystems/objects/classes/actors/ external systems) as before. o Association roles (pathways or links over which messages flow) o Message flows (messages sent between class roles)
1: user
User Login Shopping cart system
4: give access to member
3: gives detail
2:
user name & password
Administrator
Fig.6.2.1 Collaboration Diagram for User registration
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 23
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
1: 2:
Item registration log out(); Administrator
: Online seller
Fig.6.2.2Collaboration Diagram for Seller registeration
Shopping cart 1: Adds Item 11: Checkout 2: Gets Item Logout
: Online customer
10: Confirms 9: Displays the Orderd Item 8: Processes
Cart item
Order summary 3: Product Details 4: Add the products 5: Shipping Charges 6: Taxes Process order
7: Payment Details
Fig.6.2.3 Collaboration Diagram for Online Customer
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 24
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
Shopping system
1: Logiin
: Online Customer
9: Logout 2: Add item 3: Add category 7: Delete item 8: Delete category
Cart system
4: Add user 5: Delete user 6: Change password
Ordering system
Fig.6.2.4 Collaboration Diagram for Online Administrator
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 25
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
7. Statechart Diagram:
The name of the diagram itself clarifies the purpose of the diagram and other details. It describes different states of a component in a system. The states are specific to a component/object of a system. A Statechart diagram describes a state machine. Now to clarify it state machine can be defined as a machine, which defines different states of an object, and these states are controlled by external or internal events.
Member Logging
Member Login
Verifying
Valid login
Accessing the account
Invalid Login
Member Access managing account Perform Reservation Reserving Perform cancellation
Re-Logging Member Relogin
Invalid >3 times
Cancelling
Process credit card details Credit card Processing Transaction Processing Transaction Performing
Process credit card details
transaction Processed Printing Ticket
Fig.7.1 State Chart diagram for Online Shopping System
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 26
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
Searching
registered customer
Selecting
buy the item new customer Register
more items Buying
buy item
item selection over Pay bill
Fig7.2 State diagram for customer.
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 27
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design 8. CLASS DIAGRAM :
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM HTTP CUSTOMER Number of Item : Integer cusid : Integer Shipnname : String Company : String Address : String Payment() CartAddition() Cancellation()
USER Email id : String password : String First name : String Last Name : String Street Address : String ZipCode : Integer City : String State : String Country : String Phone : String Login() Registration() Logout()
SELLER Item name : String Item id : Integer Discount : Integer Categoty : Integer CANCELLATION cusno : Integer Item id : Integer amount : Integer retrive() update() CREDIT CARD HOLDER cardno issuedate expirydate verifydtls() perform_transaction()
CartAddition Creidtno : String Description : String ItemId : String Amount : Integer Category : String Get_to_cart() Check_out()
Payment System custno custid custname creditcardno BillingAddress VeiwOrder() PaymentDetails() TRANSACTION transid pnrno transdate amt commit() rollback()
Fig 8.1 Class diagram for Online Shopping System
RGIT, MUMBAI. Page 28 Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
9.Implementation Diagram. 9.1Component Diagram :
Component diagrams are different in terms of nature and behavior. Component diagrams are used to model physical aspects of a system. Physical aspects are the elements like executables, libraries, files, documents etc that resides in a node. So component diagrams are used to visualize the organization and relationships among components in a system. These diagrams are also used to make executable systems. Description of the component diagram for online shopping system is as follows : Data base server contains all the database tables. It contains Administrator, Registered Customer, Seller, Item and Payment. Application server contains Access classes package and Business classes package and view layer classes, i.e. view classes package. Clients are the nodes having no processing capabilities. Only browser is there on this node to send a request
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 29
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
Component Diagram :
View Classes Home Page Login Form Updation Form Registration Form
Searching Form
Ordering Form
Payment form
Business Classes Registered Customer Seller
Administrator
Payment
Access Classes Access Database
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 30
Department of MCA.
Object Oriented Modeling and Design
ONLINE SHOPPING CART SYSTEM
9.2 Deployment Diagram :
Deployment diagrams are used to visualize the topology of the physical components of a system where the software components are deployed. So deployment diagrams are used to describe the static deployment view of a system. Deployment diagrams consist of nodes and their relationships.
Client
<<Private Network>>
Data Base Server
<<LAN>>
Application Server
<<Private Network>>
Client
Oracle Server
Application Server.exe <<Private Network>>
Client
Fig 9..2 Deployment diagram for Online Shopping System.
RGIT, MUMBAI.
Page 31
Department of MCA.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Online Shopping SystemDocumento25 pagineOnline Shopping SystemShatha H Rabaya20% (5)
- Different Diagrams of Online Shopping SystemDocumento9 pagineDifferent Diagrams of Online Shopping SystemRXT STORMNessuna valutazione finora
- UML Diagrams For Railway ReservationDocumento7 pagineUML Diagrams For Railway ReservationNagaraju50% (2)
- CaseStudy Online Shopping CartDocumento21 pagineCaseStudy Online Shopping Cartakash_mohan87% (53)
- Online Shopping Uml ExamplesDocumento12 pagineOnline Shopping Uml ExamplesPLegendTiger67% (3)
- Online Shopping System SRS DocumentDocumento30 pagineOnline Shopping System SRS Documenttejas m50% (2)
- Online Shopping SystemDocumento21 pagineOnline Shopping SystemAnuj Kumar Singh50% (2)
- SRS For Hospital Management SystemDocumento3 pagineSRS For Hospital Management Systemnilanjan199179% (14)
- Report Cafe Management SystemDocumento20 pagineReport Cafe Management SystemSaad Khan100% (1)
- Course Management SystemDocumento65 pagineCourse Management Systemhardikpadhy100% (1)
- Online Shopping System 1Documento28 pagineOnline Shopping System 1Ailyn Fe GolosinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Online Shopping System Project ReportDocumento34 pagineOnline Shopping System Project ReportUvaise Basheer72% (54)
- Case Study of Library Management SystemDocumento12 pagineCase Study of Library Management Systemridihima50% (2)
- Book Shop Automation Software Requirements SpecifcationDocumento12 pagineBook Shop Automation Software Requirements SpecifcationUtkal Sinha100% (1)
- This Is A SRS Document For Hospital Patient Information Management SystemDocumento5 pagineThis Is A SRS Document For Hospital Patient Information Management SystemviniNessuna valutazione finora
- Online Library Management System SRSDocumento36 pagineOnline Library Management System SRSAkash Jain100% (7)
- E-Book MaanagementDocumento12 pagineE-Book MaanagementSangeethRaj PS100% (1)
- Online Library Management System (SRS)Documento16 pagineOnline Library Management System (SRS)Bharath Palaksha87% (23)
- Hospital Management System (SRS)Documento16 pagineHospital Management System (SRS)usman100% (6)
- Uml Diagrams For Hospital Management SystemDocumento9 pagineUml Diagrams For Hospital Management Systemjitendra jha100% (1)
- Book Bank Management System: Ex No: DateDocumento23 pagineBook Bank Management System: Ex No: Datethebhas1954100% (1)
- Book Shop Automation - SRSDocumento41 pagineBook Shop Automation - SRSVivek Kushwaha100% (22)
- Book Shop Management System Vb6Documento43 pagineBook Shop Management System Vb6qazplm200767% (3)
- Srs University Management SystemDocumento13 pagineSrs University Management Systemankitjauram0% (1)
- Project ProposalDocumento6 pagineProject ProposalMadara Kandaudahewa100% (2)
- Online Shopping Store Project ReportDocumento18 pagineOnline Shopping Store Project ReportDiwakar_Singh5567% (6)
- Online Shopping Project ReportDocumento17 pagineOnline Shopping Project ReportAcharyaSP0% (2)
- Foreign Trading SystemsDocumento16 pagineForeign Trading SystemsAravind SivaNessuna valutazione finora
- Online Shopping Project DFD Data Flow DiagramsDocumento9 pagineOnline Shopping Project DFD Data Flow Diagramsvaleriaramosg0% (1)
- Online Shopping SystemDocumento89 pagineOnline Shopping SystemShreyanshNessuna valutazione finora
- Conference Management System (UML Sequence and Collaboration Diagram)Documento12 pagineConference Management System (UML Sequence and Collaboration Diagram)Siva siva100% (2)
- Blood Donation Management SystemDocumento55 pagineBlood Donation Management SystemMounika50% (18)
- Fast Food Billing SystemDocumento6 pagineFast Food Billing SystemSubhadeep ChatterjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Uml Diagrams of Hospital ManagmentsDocumento34 pagineUml Diagrams of Hospital Managmentsshakir54491% (68)
- Online Shopping System Software RequirementsDocumento3 pagineOnline Shopping System Software RequirementsAnshuman Biswas50% (8)
- Point of Sale Terminal Management System Construct A Design Element For PointDocumento5 paginePoint of Sale Terminal Management System Construct A Design Element For Pointdarshana gulhaneNessuna valutazione finora
- SRS - Scientific Calculator v1.0Documento14 pagineSRS - Scientific Calculator v1.0Gopalakrishna Rapaka29% (7)
- Courier Manegment SystemDocumento30 pagineCourier Manegment Systemkrawariya0% (1)
- Goods Transport CompanyDocumento19 pagineGoods Transport CompanyRajdeep ChakrabortyNessuna valutazione finora
- Onlineshopping: Home ExploreDocumento5 pagineOnlineshopping: Home Explorepraim chandNessuna valutazione finora
- CabDocumento65 pagineCabRamanna Aakasa67% (3)
- Online ShoppingDocumento16 pagineOnline ShoppingRevathi DuraiNessuna valutazione finora
- Automated Grocery StoreDocumento9 pagineAutomated Grocery StoreAbhay tiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1.2.1Documento5 pagineLecture 1.2.1Ashutosh mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 Chapter 3-GoodsDocumento44 pagine9 Chapter 3-GoodsJesha Pauline BaatenNessuna valutazione finora
- Designing PhaseDocumento35 pagineDesigning PhaseDavid RajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 4Documento12 pagineAssignment 4dr. waingNessuna valutazione finora
- Mall SeDocumento30 pagineMall Seharshshah316Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sds FDocumento52 pagineSds FShraddha BhandariNessuna valutazione finora
- Smart Cloth Mall ApplicationDocumento44 pagineSmart Cloth Mall ApplicationbabasahebNessuna valutazione finora
- Softwareegg SampleDocumento19 pagineSoftwareegg Samplefeed my mindNessuna valutazione finora
- Use Case ModelingDocumento10 pagineUse Case ModelingrealsutanNessuna valutazione finora
- Stock MaintenanceDocumento19 pagineStock Maintenancethebhas1954Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter III UpdatedDocumento11 pagineChapter III UpdatedLilian May MalfartaNessuna valutazione finora
- Software Production: Software Requirements Visually Modeling Use Cases With Activity DiagramsDocumento20 pagineSoftware Production: Software Requirements Visually Modeling Use Cases With Activity Diagramstieungunhi139Nessuna valutazione finora
- Shubham SeDocumento13 pagineShubham SeSIDDHANT GUPTANessuna valutazione finora
- Class, State Trans, UsecaseDocumento18 pagineClass, State Trans, Usecasearunkumar1100155Nessuna valutazione finora
- Checkpost Management SystemDocumento68 pagineCheckpost Management SystemVivek Kumar100% (1)
- Online Supermarket SystemDocumento26 pagineOnline Supermarket SystemG.D.M.Madushantha73% (11)
- AuctionDocumento3 pagineAuctionRajesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 3 Building An EC Presence 30 Nov 19Documento20 pagineChap 3 Building An EC Presence 30 Nov 19KY10NANessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Commerce SystemsDocumento48 pagineElectronic Commerce SystemsYasir HasnainNessuna valutazione finora
- Survey On Development of Android Based Mobile App For Prestashop Ecommerce Shopping Cart (Alc)Documento6 pagineSurvey On Development of Android Based Mobile App For Prestashop Ecommerce Shopping Cart (Alc)herziNessuna valutazione finora
- Books4u: Fast Track Shopping Software SystemDocumento18 pagineBooks4u: Fast Track Shopping Software SystemRrr320Nessuna valutazione finora
- Online Book StoreDocumento24 pagineOnline Book Storeshravanidussa2006Nessuna valutazione finora
- IT8005 EC Notes UNIT 4Documento27 pagineIT8005 EC Notes UNIT 4Arunsunai ComputerNessuna valutazione finora
- Multivendor Ecommerce WebsiteDocumento50 pagineMultivendor Ecommerce WebsiteCedCommerce Document100% (4)
- Design and Implementation of E-Commerce Site For Online ShoppingDocumento23 pagineDesign and Implementation of E-Commerce Site For Online ShoppingShariar Parvez TonmoyNessuna valutazione finora
- JPR ProjectDocumento26 pagineJPR ProjectShriram Sonwane100% (3)
- E-Commerce Client Server ArchitectureDocumento29 pagineE-Commerce Client Server ArchitectureVipul MaheshwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Online Shopping Project ReportDocumento86 pagineOnline Shopping Project ReportVivek Sahu78% (18)
- Online ShoppingDocumento25 pagineOnline ShoppingArushi KapoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Social Media Strategies For OnlineDocumento69 pagineSocial Media Strategies For OnlineNamitaGupta100% (2)
- DiagnosticLink Instruction Guide PDFDocumento24 pagineDiagnosticLink Instruction Guide PDFEduardo VillatoroNessuna valutazione finora
- E BusinessDocumento15 pagineE BusinessJia_AminNessuna valutazione finora
- E-Commerce Glossary PDFDocumento5 pagineE-Commerce Glossary PDFwefWENessuna valutazione finora
- Risk Register TemplateDocumento1 paginaRisk Register Templatealfan666Nessuna valutazione finora
- I-Parcel User GuideDocumento57 pagineI-Parcel User GuideBrian GrayNessuna valutazione finora
- Documentation of E-Commerce Website Requirements and DesigningDocumento14 pagineDocumentation of E-Commerce Website Requirements and DesigningM Ayaz Khan74% (72)
- Chapter 4: Evaluation of Shopee and Prudential Websites 4.1 ShopeeDocumento4 pagineChapter 4: Evaluation of Shopee and Prudential Websites 4.1 ShopeeHuiTong LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Sehrish Sana - Online Shopping at Daraz - SDDDocumento99 pagineSehrish Sana - Online Shopping at Daraz - SDDRabiaNessuna valutazione finora
- E-Commerce BookDocumento61 pagineE-Commerce BookYasin YoseffNessuna valutazione finora
- Online ShoppingDocumento32 pagineOnline ShoppingKr Sandy100% (3)
- Amrapali Aadya TradingDocumento7 pagineAmrapali Aadya Tradingpiyanjan88Nessuna valutazione finora
- Shopping Cart Software Requirement SpecificationDocumento13 pagineShopping Cart Software Requirement Specificationnaveendkt80% (5)
- 006 Ghar BanaoDocumento224 pagine006 Ghar Banaomansha99Nessuna valutazione finora
- WBBML Final ReportDocumento69 pagineWBBML Final ReportAyush PremjithNessuna valutazione finora
- A&D High Tech Import FileDocumento22 pagineA&D High Tech Import FileproskuneoNessuna valutazione finora
- Virtual Pos Tech SheetDocumento2 pagineVirtual Pos Tech SheetJonathan VardouniotisNessuna valutazione finora
- Srs E-Market WebsiteDocumento13 pagineSrs E-Market WebsitePratik HepatNessuna valutazione finora