Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
CB - Model
Caricato da
sasaluDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CB - Model
Caricato da
sasaluCopyright:
Formati disponibili
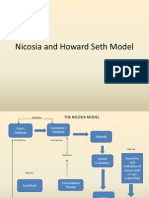
CB - MODEL The model is important because it highlights the importance of inputs to the consumer buying process and suggests
ways in which the consumer orders these inputs before making a final decision. Schiffman and Kanuk (1997) mentioned that many early theories concerning consumer behavior were based on economic theory, on the notion that individuals act rationally to maximize their benefits (satisfactions) in the purchase of goods and services. A consumer is generally thought of as a person who identifies a need or desire, makes a purchase, and then disposes of the product during the three stages in the consumption process in Figure2.2 (Solomon, 1996)
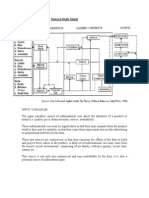
HOWARD-SHETH MODEL Inputs Stimuli display
Significative a. Quality b. Price c. Distinctive d. Service e. Availability Symbolic a. Quality b. Price c. Distinctive d. Service e. Availability Social a. Family b. Reference groups c. Social class Attention Intention Purchase
Perceptual Constructs
Learning Constructs
Outputs
Confidence Overt search Intention
Attitude Stimulus ambiguity Motives Brand Comprehension Choice Criteria
Attitude
Brand Comprehe n- sion
Attention
Perceptual bias
Figure 2-3 A Simplified Description of the Theory of Buyer Behavior Source: Howard, and Sheth,Pp32 (1969)
This model suggests three levels of decision making: 1. The first level describes the extensive problem solving. At this level the consumer does not have any basic information or knowledge about the brand and he does not have any preferences for any product. In this situation, the consumer will seek information about all the different brands in the market before purchasing.
2. The second level is limited problem solving. This situation exists for consumers who have little knowledge about the market, or partial knowledge about what they want to purchase. In order to arrive at a brand preference some comparative brand information is sought. 3. The third level is a habitual response behavior. In this level the consumer knows very well about the different brands and he can differentiate between the different characteristics of each product, and he already decides to purchase a particular product. According to the Howard-Sheth model there are four major sets of variables; namely:
Input Output model
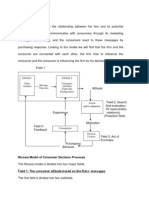
A Model of Consumer Decision Making
1. 2.
Input & Output Model
The process of consumer decision making can be viewed as three distinct but interlocking stages: the input stage, the process stage, and the output stage. The input stage influences the consumers recognition of a product need and consists of two major sources of information: a) The firms marketing efforts (the product itself, its price, promotion, and where it is sold). b) The external sociological influences on the consumer (family, friends, neighbors, other informal and noncommercial sources, social class, cultural and subcultural memberships).
3.
4.
The process stage focuses on how consumers make decisions. a) The psychological factors inherent in each individual (motivation, perception, learning, personality, attitude) affect how the external inputs influence the consumers recognition of a need, prepurchase search for information, and evaluation of alternatives. b) The experience gained through evaluation of alternatives, in turn, affects the consumers existing psychological attributes. The output stage of the consumer decision-making model consists of two closelyrelated post decision activities: a) Purchase behavior, which can be a trial purchase or a repeat purchase. b) The postpurchase evaluation of the product feeds directly into the consumers experience in the process stage of the model.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Consumer Behavior Models and Consumer Behavior in TourismDocumento41 pagineConsumer Behavior Models and Consumer Behavior in TourismShwetaBajiraoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - Iii Consumer Behaviour ModelsDocumento11 pagineChapter - Iii Consumer Behaviour ModelsRAGHU M SNessuna valutazione finora
- Nicosia Model: Subfield 1 Firms Attribute Subfield 2 Consumers Attributes (Especially PredispositionDocumento6 pagineNicosia Model: Subfield 1 Firms Attribute Subfield 2 Consumers Attributes (Especially Predispositionanon_80127205Nessuna valutazione finora
- Howard ShethDocumento5 pagineHoward Shethjmpnv007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Howard Sheth ModelDocumento12 pagineHoward Sheth ModelibmahapatraNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic: Howard Sheth ModelDocumento12 pagineTopic: Howard Sheth ModelPhaniraj Lenkalapally100% (1)
- Topic: Howard Sheth ModelDocumento12 pagineTopic: Howard Sheth ModelPhaniraj Lenkalapally87% (15)
- CIA-1 CB ResentDocumento15 pagineCIA-1 CB ResentAnuraag KulkarniNessuna valutazione finora
- No Knowledge N PreferencesDocumento7 pagineNo Knowledge N PreferenceskaranbhattalNessuna valutazione finora
- ModelDocumento22 pagineModelArchana DeepakNessuna valutazione finora
- ModelDocumento22 pagineModelArchana DeepakNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumerdecisionmakingandbeyond 110214023948 Phpapp01Documento18 pagineConsumerdecisionmakingandbeyond 110214023948 Phpapp01Gosai JaydeepNessuna valutazione finora
- Identification of Secondary Factors That Influence Consumer's Buying Behavior For Soaps and ChocolatesDocumento19 pagineIdentification of Secondary Factors That Influence Consumer's Buying Behavior For Soaps and ChocolatesTrung cấp Phương Nam0% (1)
- Unit 2Documento23 pagineUnit 2Bhuvaneswari ANessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Chapter SummariesDocumento23 pagineMarketing Chapter Summarieseholmes80Nessuna valutazione finora
- Howard Sheth Model of Consumer BehaviorDocumento13 pagineHoward Sheth Model of Consumer BehaviorRiya RahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cia-1 CBDocumento14 pagineCia-1 CBAnuraag KulkarniNessuna valutazione finora
- Howard and Sheth Model of Consumer BehaviourDocumento2 pagineHoward and Sheth Model of Consumer BehaviourGauri sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Behaviour Unit - 2 PDFDocumento22 pagineConsumer Behaviour Unit - 2 PDFPrashant TripathiNessuna valutazione finora
- MODEL OF CONSUMER by MadhuDocumento6 pagineMODEL OF CONSUMER by MadhuRadhika RocksNessuna valutazione finora
- Piyush Consumer BehaviourDocumento19 paginePiyush Consumer BehaviourNehal SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Buyerbehaviourmodels1 150926125257 Lva1 App6892Documento29 pagineBuyerbehaviourmodels1 150926125257 Lva1 App6892KrishnakaparNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Behaviour Models: Mayank Sharma Assistant Professor - Marketing, IMS GhaziabadDocumento11 pagineConsumer Behaviour Models: Mayank Sharma Assistant Professor - Marketing, IMS GhaziabadManish AroraNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Behaviour NotesDocumento14 pagineConsumer Behaviour NotesNavaneetha KrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Models of Consumer Behaviour: UNIT-2Documento11 pagineModels of Consumer Behaviour: UNIT-2Karthick PNessuna valutazione finora
- Howard Sheth ModelDocumento4 pagineHoward Sheth ModelDipjyoti TalukdarNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Decision Making Andb EyondDocumento25 pagineConsumer Decision Making Andb Eyondmurary123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Behavour Ch-3Documento5 pagineConsumer Behavour Ch-3Ilma GirmaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Consumer Decision Making Process Consists of The Following StagesDocumento29 pagineThe Consumer Decision Making Process Consists of The Following StagesSHIVPRATAPNessuna valutazione finora
- The Buying Decision, Consumer Behaviour RefinedDocumento23 pagineThe Buying Decision, Consumer Behaviour RefinedJoshNessuna valutazione finora
- Howard Sheth ModelDocumento5 pagineHoward Sheth Modelrahul viju100% (1)
- Howard Sheth Model NotesDocumento5 pagineHoward Sheth Model NotesarunvisaalNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Behavior ModelsDocumento21 pagineConsumer Behavior ModelsPankaj AggarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Behaviour: Mini Project On Howard Seth ModelDocumento10 pagineConsumer Behaviour: Mini Project On Howard Seth ModelLokesh KrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Howard Shet ModelDocumento4 pagineHoward Shet ModelGirija mirjeNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Behaviour MM-4Documento19 pagineConsumer Behaviour MM-4anujbeniwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Motives Which Influence Purchasing DecisionsDocumento31 pagineMotives Which Influence Purchasing Decisionsayushi gargNessuna valutazione finora
- 1) Extensive Problem SolvingDocumento1 pagina1) Extensive Problem SolvingAkshay bhondeNessuna valutazione finora
- Nicosia and Howard Seth ModelDocumento7 pagineNicosia and Howard Seth Modelshanti2699Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3, Consumer Behaviour RefinedDocumento23 pagineLecture 3, Consumer Behaviour RefinedShiro WanjiruNessuna valutazione finora
- Models of Consumer Behavior: - Engel, Blackwell and Miniard (EBM) - Howard Sheth Model of Buying BehaviourDocumento20 pagineModels of Consumer Behavior: - Engel, Blackwell and Miniard (EBM) - Howard Sheth Model of Buying BehaviourroshniNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 CBDocumento13 pagineUnit 4 CBAnilBahugunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Stimuli - GilletteDocumento11 pagineMarketing Stimuli - GilletteAfsheen Danish NaqviNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Roles:-Importance of Consumer BehaviourDocumento7 pagineConsumer Roles:-Importance of Consumer BehaviourPravin SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Howard Sheth ModelDocumento8 pagineHoward Sheth ModelSaurabh PoteNessuna valutazione finora
- Models of Consumer BehaviourDocumento22 pagineModels of Consumer BehaviourZoheb Ali KNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Behaviour Unit3Documento10 pagineConsumer Behaviour Unit3Sumit YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2Documento24 pagineUnit 2Pranay ChhetriNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Decision PeocessDocumento3 pagineConsumer Decision PeocessNageshwar YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Howard Seth ModalDocumento10 pagineHoward Seth ModalgnmadaviNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.2 The Buying Decision Process-The Five-Stage ModelDocumento5 pagine6.2 The Buying Decision Process-The Five-Stage ModelSanjeev JayaratnaNessuna valutazione finora
- PIM COBB Unit 3MGSE01 Buying ModelsDocumento10 paginePIM COBB Unit 3MGSE01 Buying ModelspiyushsithaNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Decision Making 6Documento40 pagineConsumer Decision Making 6yaduvanshiak05Nessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Buying ProcessDocumento6 pagineConsumer Buying ProcessMAHENDRA SHIVAJI DHENAKNessuna valutazione finora
- Individual Assignment - C2Documento4 pagineIndividual Assignment - C2Radescu MalinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Behaviour and Rural Marketing AssignmentDocumento15 pagineConsumer Behaviour and Rural Marketing Assignmentjainpiyush_1909Nessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Behavior Models and Consumer Behavior in TourismDocumento42 pagineConsumer Behavior Models and Consumer Behavior in TourismDecu IoanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Howard Sheth ModelDocumento4 pagineHoward Sheth ModelSalim SarkiNessuna valutazione finora