Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Assignment 2 - Basic Electronic Components
Caricato da
Rafael PereiraDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Assignment 2 - Basic Electronic Components
Caricato da
Rafael PereiraCopyright:
Formati disponibili
05/10/13
MECH 207
Assignment 2 Basic Electronic Components
Objective : The objective of this assignment is to become familiar with passive circuit and semiconductor-based components, common circuits using these components, typical applications of these components, and the appropriate analytic techniques used to design systems with these components. Read: Text Chp 2 & 3. Problems : You are REQUIRED to use the HW2 Solution Summary Sheet for your solutions. Please make this the cover sheet for your submission. 1. What is the resistance of a 100m long piece of 12-gage copper wire? You will need to use reliable resources for determining some of the required values. 2. Determine the resistance values (and the tolerance) for each of the following: a - Resistor R1 has color bands: brown, black, orange. What is its value? b - Resistor R2 has color bands: black, violet, orange. What is its value? c - R1 and R2 are in series. What is the equivalent value? d - R1 and R2 are in parallel. What is the equivalent value? 3 . Derive the expression (using Kirchhoff's Laws and the V-I constitutive relationships) for the equivalent inductance of two parallel inductors. 4. You have a voltage divider with a 5V supply voltage, a "top" resistor R1 = 2 kOhms and a "bottom" resistor R2 = 3 kOhms. a - What is the output voltage? b - What is the current through R1? c - What is the current through R2? d - What is the power dissipated by R2? 5. Examine the dynamics of a high pass passive RC filter by completing the following exercises: a. Use Kirchhoff's Laws to derive the governing dynamics equations (reviewed in class). Let R=1 Kohms and C=.00001F. b. Use Simulink to plot the filter's time response to a sine wave with frequency 10 rad/sec, a sine wave with frequency 100 rad/sec, and a sine wave with frequency of 1000 rad/sec (assume a magnitude of 1 for all inputs). Your Simulink plot should have both the input and output signals for the purposes of comparison. Comment on how the filter affects the magnitude and phase of the signal. Show a screen shot of your Simulink model. Note - if your Simulink time responses don't look as smooth as they should be (given that these signals are sine waves), try going to Simulation - Configuration Parameters via the menus and changing the "Max step size"; for example, you might try 1e-4. Also, you might want to change the duration of your simulation from the default of 10 sec to something more appropriate in order to show enough (the "interesting" parts) of the signal (e.g., you should be able to see transients die out, you should see at least a few wavelengths of oscillatory signals, etc.). c. Use Matlab to generate a Bode plot of the filter. What information does a Bode plot provide? How does your Bode plot compare with the outputs from the previous bullet? d. Explain why this circuit is called a high pass filter. 6. Examine the dynamics of the RLC filter shown in the Figure below by completing the following exercises: a. Use Kirchhoff's Laws to derive the governing dynamics equations (reviewed in class). Let R=10 Kohms, C=.000001F, and L=1H.
mech207.engr.scu.edu/hw/hw2/hw2.htm 1/3
05/10/13
MECH 207
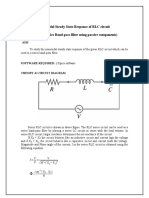
b. Use Simulink to plot the filter's time response to a sine wave with frequency 10 rad/sec, a sine wave with frequency 1000 rad/sec, and a sine wave with frequency of 100,000 rad/sec (assume a magnitude of 1 for all inputs). Your Simulink plot should have both the input and output signals for the purposes of comparison. Comment on how the filter affects the magnitude and phase of the signal. Show a screen shot of your Simulink model. c. Use Matlab to generate a Bode plot of the filter. How does your Bode plot compare with the outputs from the previous bullet? d. Explain why this is called a "bandpass filter".
R L C
7. You want to turn on a DC motor (24 V, 1 A) using a power transistor that acts like a switch, with a digital control signal that is either 0 or 5 V. In the figure below, each numbered box represents a very specific component that should be used. To begin, for each number 1-4, state what the component should be. You should make your choice from the following list: power supply, ground, resistor, capacitor, inductor, diode, transistor. Second, for each component, state why each of these components are needed in those locations, and provide some sort of numerical value or rating or capacity for each (the only component that does not require a quantitative rating is ground).
8. For the circuit below, R = 1 kohm and Vin = 10sin(pi*t)V. Sketch (or accurately describe) the amplitude and frequency of the Vout signal. You may assume that the diodes are ideal.
mech207.engr.scu.edu/hw/hw2/hw2.htm 2/3
05/10/13
MECH 207
9. For the circuit below, assume that the zener diode is ideal with a breakdown voltage of 5.1V. Sketch (or accurately describe) the output amplitude for the following input voltage signals: a. Vin = 6*sin(pi*t) V b.Vin = sin(pi*t) V c. Vin = 10 + 2*sin(2pi*t) V
10. Analyze the circuit below in order to determine the values described below. Assume that the LED has a forward bias of 1V when lit. Assume that the transistor has an amplification ratio of 100, Vbe = 0.7V and Vce = 0.2V when saturated. a. When the LED is on and the transistor is fully saturated, what is Vb and Vc? b. Given this, what are Ibe and Ice? c. Given this, what must Vin be in order to turn on the LED?
mech207.engr.scu.edu/hw/hw2/hw2.htm
3/3
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Da EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Nessuna valutazione finora
- EDN Design Ideas 2006Documento142 pagineEDN Design Ideas 2006chag1956100% (1)
- Block DiagramDocumento1 paginaBlock DiagramDimaz Hanggoro0% (2)
- Esp32-S3 Technical Reference Manual enDocumento787 pagineEsp32-S3 Technical Reference Manual enANessuna valutazione finora
- DPR2900B-48 User ManualDocumento9 pagineDPR2900B-48 User ManualAnonymous mazgh1R100% (1)
- HVDC Transmission FiltersDocumento5 pagineHVDC Transmission FiltersGnanaseharan ArunachalamNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Circuit ElementsDocumento30 pagineBasic Circuit ElementsRafael PereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexsim TutorialDocumento122 pagineFlexsim TutorialZougoulougou100% (5)
- CSS 7 - 8 SSLMs 4 PDFDocumento4 pagineCSS 7 - 8 SSLMs 4 PDFLouise MaglantayNessuna valutazione finora
- EE 230 - Analog Circuits Lab - 2021-22/I (Autumn) Experiment 1: Familiarization With NGSPICE Circuit Simulator and Lab EquipmentDocumento7 pagineEE 230 - Analog Circuits Lab - 2021-22/I (Autumn) Experiment 1: Familiarization With NGSPICE Circuit Simulator and Lab EquipmentTanmay JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Procedure - AC Circuits and Signal Modulation - W20Documento6 pagineProcedure - AC Circuits and Signal Modulation - W20ChocoNessuna valutazione finora
- Radio Frequency and Microwave Circuits:: Ananthv@iisermohali - Ac.inDocumento3 pagineRadio Frequency and Microwave Circuits:: Ananthv@iisermohali - Ac.inElectronic BoyNessuna valutazione finora
- RLC Circuit Simulation Using PSpiceDocumento8 pagineRLC Circuit Simulation Using PSpiceRudra MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 4 Filter DesignDocumento6 pagineLab 4 Filter DesignSandeep PatwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ece 334 ManualDocumento37 pagineEce 334 ManualZelalem GirmaNessuna valutazione finora
- EC Lab ManualsDocumento53 pagineEC Lab ManualsArish AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Ansoft Designer Harmonic BalanceDocumento9 pagineAnsoft Designer Harmonic BalanceAbdul Kadir Ramos FaisalNessuna valutazione finora
- SRMSCET Bareilly Electrical Simulation Lab ExperimentsDocumento28 pagineSRMSCET Bareilly Electrical Simulation Lab Experimentssachin10dulkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Integrator Circuits: 7.0.1 ReadingDocumento5 pagineIntegrator Circuits: 7.0.1 Readingnaveenkv10_105528408Nessuna valutazione finora
- RLC and Bandpass circuitsDocumento4 pagineRLC and Bandpass circuitscuamiNessuna valutazione finora
- IES CONV Electronic Comm. 2000Documento11 pagineIES CONV Electronic Comm. 2000gateandiesNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied Analogue Electronics QuestionsDocumento5 pagineApplied Analogue Electronics QuestionsKerera DeograciousNessuna valutazione finora
- L211 Series Resonance and TimeFrequency Response of Passive Networks PDFDocumento25 pagineL211 Series Resonance and TimeFrequency Response of Passive Networks PDFglenlcy100% (1)
- Circuit Analysis 2 Lab Report 2 Pieas PakistanDocumento6 pagineCircuit Analysis 2 Lab Report 2 Pieas PakistanMUYJ NewsNessuna valutazione finora
- Two StageDocumento6 pagineTwo StageSiphosethuSidloyiNessuna valutazione finora
- Equency Response of A Common-Emitter BJT AmplifierDocumento5 pagineEquency Response of A Common-Emitter BJT AmplifierThomas SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab8 EEDocumento4 pagineLab8 EEhaha2012Nessuna valutazione finora
- 9A04604 Electronic Measurements and InstrumentationDocumento4 pagine9A04604 Electronic Measurements and InstrumentationsivabharathamurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Circuits & Logic Design Lab ManualDocumento83 pagineElectronic Circuits & Logic Design Lab ManualsunandaalurNessuna valutazione finora
- 9A04502 Linear IC ApplicationsDocumento4 pagine9A04502 Linear IC ApplicationssivabharathamurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- RF and Microwave Systems IntroductionDocumento38 pagineRF and Microwave Systems IntroductionAbdul Hafiz AnuarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ids and Net Names in The Multisim Network. Furthermore, The Use of TransientDocumento3 pagineIds and Net Names in The Multisim Network. Furthermore, The Use of TransientMaxNessuna valutazione finora
- Elvis and Bode PlotsDocumento7 pagineElvis and Bode PlotsKashif AmjadNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog System Design ExperimentsDocumento27 pagineAnalog System Design ExperimentsAnsh BhaganiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Project EE310Documento9 pagineProject EE310Engr Muhammad ArslanNessuna valutazione finora
- RC Circuits: J H U, P ADocumento6 pagineRC Circuits: J H U, P APavan PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Eee312 Eee282 Lab7 Spring2015Documento6 pagineEee312 Eee282 Lab7 Spring2015vognarNessuna valutazione finora
- Transformer Windings' RLC Parameters Calculation and Lightning Impulse Voltage Distribution SimulationDocumento4 pagineTransformer Windings' RLC Parameters Calculation and Lightning Impulse Voltage Distribution SimulationOscar PieruzziniNessuna valutazione finora
- IES Conventional Electrical Engineering 2012Documento28 pagineIES Conventional Electrical Engineering 2012Srujan BobbyNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution of Guessing Paper 2018 PDFDocumento17 pagineSolution of Guessing Paper 2018 PDFVidyasagar AcademyNessuna valutazione finora
- Course: EC2P001 Introduction To Electronics Lab: Indian Institute of Technology Bhubaneswar School of Electrical ScienceDocumento5 pagineCourse: EC2P001 Introduction To Electronics Lab: Indian Institute of Technology Bhubaneswar School of Electrical ScienceAnik ChaudhuriNessuna valutazione finora
- December 2016: AMIETE - ET (Current & New Scheme)Documento3 pagineDecember 2016: AMIETE - ET (Current & New Scheme)mraavulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Function Generator Op-Amp Summing Circuits Pulse Width Modulation LM311 ComparatorDocumento7 pagineFunction Generator Op-Amp Summing Circuits Pulse Width Modulation LM311 ComparatorMuhammad JunaidNessuna valutazione finora
- Prework Questions For KI-1Documento5 paginePrework Questions For KI-1Danial SadiqNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 06 Bode PlotDocumento8 pagineLab 06 Bode PlotfarhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Measurement - Instrumentation Rec403Documento2 pagineElectronic Measurement - Instrumentation Rec403Brahmanand SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- ECA ManualDocumento62 pagineECA ManualAnonymous gP8ivl7fNessuna valutazione finora
- EE-Conventional Paper-IIDocumento7 pagineEE-Conventional Paper-IISoumyabrataPatraNessuna valutazione finora
- 9A04502 Linear IC ApplicationsDocumento4 pagine9A04502 Linear IC ApplicationssivabharathamurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- 06 CSL38 Manual LDDocumento68 pagine06 CSL38 Manual LDSwathi N SudarshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ec 303Documento2 pagineEc 303jeetendrasidhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper - I: Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 200Documento8 paginePaper - I: Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 200h9emanth4Nessuna valutazione finora
- ELE341 Project OPAmpDocumento4 pagineELE341 Project OPAmpbabycryyNessuna valutazione finora
- Twin T NetworkDocumento2 pagineTwin T NetworkVijayalakshmi PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Jntuworld: Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocumento30 pagineJntuworld: Electrical and Electronics EngineeringRajeev BujjiNessuna valutazione finora
- RLC Circuit Band-Pass Filter Design and AnalysisDocumento10 pagineRLC Circuit Band-Pass Filter Design and AnalysisDivya KNessuna valutazione finora
- 9A04402 Electronic Circuit AnalysisDocumento8 pagine9A04402 Electronic Circuit AnalysissivabharathamurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Modeling and Simulation of PWM Converter CircuitsDocumento27 pagineComputer Modeling and Simulation of PWM Converter CircuitsskrtamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic and Pulse Circuits Lab PDFDocumento2 pagineElectronic and Pulse Circuits Lab PDFAparna LakshmiNessuna valutazione finora
- MATLAB-Spice Project - EE310 - Spring 2021Documento9 pagineMATLAB-Spice Project - EE310 - Spring 2021Muhammad hashimNessuna valutazione finora
- Control Systems Group Project 2Documento3 pagineControl Systems Group Project 2Yu-Yun ChangNessuna valutazione finora
- Small-Signal Transistor Amplifiers PDFDocumento14 pagineSmall-Signal Transistor Amplifiers PDFManoj Singh RawatNessuna valutazione finora
- 9A04502 Linear IC ApplicationsDocumento1 pagina9A04502 Linear IC ApplicationssivabharathamurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- ECEN325 Lab ManualDocumento66 pagineECEN325 Lab ManualIrwan RamliNessuna valutazione finora
- Rafael Alves Pereira - RESUMEDocumento1 paginaRafael Alves Pereira - RESUMERafael PereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Rafael Alves Pereira - RESUMEDocumento1 paginaRafael Alves Pereira - RESUMERafael PereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- EMGT 373 Technology Entrepreneurship: Weekly Guidebook Summary Week 2 - Team Formation and DevelopmentDocumento2 pagineEMGT 373 Technology Entrepreneurship: Weekly Guidebook Summary Week 2 - Team Formation and DevelopmentRafael PereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- EMGT 373 Technology Entrepreneurship: Weekly Guidebook Summary Week 1 - Career PathDocumento2 pagineEMGT 373 Technology Entrepreneurship: Weekly Guidebook Summary Week 1 - Career PathRafael PereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework 4 Solutions Winter2014 v5Documento11 pagineHomework 4 Solutions Winter2014 v5Rafael PereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- EMGT 346 HW#1 SolutionsDocumento7 pagineEMGT 346 HW#1 SolutionsRafael PereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework #6 - Elen 234 Rafael Pereira - W1064769: Problem 3Documento33 pagineHomework #6 - Elen 234 Rafael Pereira - W1064769: Problem 3Rafael PereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Course EnrollmentDocumento2 pagineCourse EnrollmentRafael PereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- EMGT 346 Homework #2 Ans 5-8Documento11 pagineEMGT 346 Homework #2 Ans 5-8Rafael PereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework #7 - Elen 234 Rafael Pereira - W1064769Documento116 pagineHomework #7 - Elen 234 Rafael Pereira - W1064769Rafael PereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- VerbsDocumento2 pagineVerbsRafael PereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ltu RocketDocumento8 pagineLtu Rocketluis milanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cool ReaperDocumento34 pagineCool Reaper9to5MacNessuna valutazione finora
- 2400 Master ClockDocumento10 pagine2400 Master ClockFlipside4100% (4)
- Technical Facts HIQuad X PU00012692Documento2 pagineTechnical Facts HIQuad X PU00012692Sadegh AkbariNessuna valutazione finora
- Microcontroller Based Applied Digital Control Dogan IbrahimDocumento313 pagineMicrocontroller Based Applied Digital Control Dogan Ibrahimkz300Nessuna valutazione finora
- 03 Assembler (UPDATED)Documento12 pagine03 Assembler (UPDATED)Saurabh100% (1)
- 62445e PDFDocumento323 pagine62445e PDFBinh DuongNessuna valutazione finora
- GPS Receiver Components and TypesDocumento12 pagineGPS Receiver Components and TypesSuresh PallemkotaNessuna valutazione finora
- Testing The PIC Microcontroller (Pic 16F877A)Documento6 pagineTesting The PIC Microcontroller (Pic 16F877A)Matt ImriNessuna valutazione finora
- System Software Lab ManualDocumento22 pagineSystem Software Lab ManualShantheri BhatNessuna valutazione finora
- BM8701 diagnostic and therapeutic equipment unit I patient monitoringDocumento9 pagineBM8701 diagnostic and therapeutic equipment unit I patient monitoringnandhini zechNessuna valutazione finora
- Project ReportDocumento14 pagineProject ReportAkshit VarmoraNessuna valutazione finora
- LogDocumento69 pagineLogVera WatiNessuna valutazione finora
- EWS101 DatasheetDocumento4 pagineEWS101 DatasheetZaw Lin HtutNessuna valutazione finora
- Features General Description: High Slew Rate Rail-to-Rail Dual Operational AmplifiersDocumento8 pagineFeatures General Description: High Slew Rate Rail-to-Rail Dual Operational AmplifiersOrkys TenorioNessuna valutazione finora
- Open Source GSMDocumento6 pagineOpen Source GSMSaadat RehmanNessuna valutazione finora
- EventDocumento1.256 pagineEventmilmat1966Nessuna valutazione finora
- DVB-S2/ACM Technology Brief - Dramatically Improved Bandwidth EfficiencyDocumento2 pagineDVB-S2/ACM Technology Brief - Dramatically Improved Bandwidth EfficiencyShahzaib AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Amazon Aws ListDocumento40 pagineAmazon Aws ListHarshal GunjalNessuna valutazione finora
- Hospital Management SystemDocumento11 pagineHospital Management SystemHemi AngelicNessuna valutazione finora
- Wifi - BVDK - Agg Project ReportDocumento19 pagineWifi - BVDK - Agg Project ReportDũng HuỳnhNessuna valutazione finora
- Monostable MultivibratorDocumento4 pagineMonostable MultivibratorSakshi GosaviNessuna valutazione finora
- ON Icon: Inline Ultrasonic Flow MeterDocumento4 pagineON Icon: Inline Ultrasonic Flow MeterJayaminNessuna valutazione finora
- Protocol Driver Sheet - Gardner DenverDocumento2 pagineProtocol Driver Sheet - Gardner DenverKelvin ArizaNessuna valutazione finora
- SRS Template V11.04.18Documento20 pagineSRS Template V11.04.18LydiaNessuna valutazione finora