Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Climate of The Philippines: Temperature
Caricato da
Nielsen Jose MarcelinoTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Climate of The Philippines: Temperature
Caricato da
Nielsen Jose MarcelinoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Climate of the Philippines
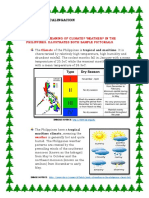
The Climate of the Philippines is tropical and maritime. It is characterized by relatively high temperature, high humidity and abundant rainfall. It is similar in many respects to the climate of the countries of Central America. Temperature, humidity, and rainfall, which are discussed hereunder, are the most important elements of the country's weather and climate. Temperature Based on the average of all weather stations in the Philippines, excluding Baguio, the o mean annual temperature is 26.6 C. The coolest months fall in January with a mean o temperature of 25.5 C while the warmest month occurs in May with a mean temperature o of 28.3 C. Latitude is an insignificant factor in the variation of temperature while altitude shows greater contrast in temperature. Thus, the mean annual temperature of Baguio with o an elevation of 1,500 meters is 18.3 C. This makes the temperature of Baguio comparable with those in the temperate climate and because of this, it is known as the summer capital of the Philippines. The difference between the mean annual temperature of the southernmost station in Zamboanga and that of the northermost station in Laoag is insignificant. In other words, there is essentially no difference in the mean annual temperature of places in Luzon, Visayas or Mindanao measured at or near sea level. Humidity Humidity refers to the moisture content of the atmosphere. Due to high temperature and the surrounding bodies of water, the Philippines has a high relative humidity. The average monthly relative humidty varies between 71 percent in March and 85 percent in September. The combination of warm temperature and high relative and absolute humidities give rise to high sensible temperature throughout the archipelago. It is especially uncomfortable during March to May, when temperature and humidity attain their maximum levels. Rainfall Rainfall is the most important climatic element in the Philippines. Rainfall distribution throughout the country varies from one region to another, depending upon the direction of the moisture-bearing winds and the location of the mountain systems. The mean annual rainfall of the Philippines varies from 965 to 4,064 millimeters annually. Baguio City, eastern Samar, and eastern Surigao receive the greatest amount of rainfall while the southern portion of Cotabato receives the least amount of rain. At General Santos City in Cotabato, the average annual rainfall is only 978 millimeters. The Seasons Using temperature and rainfall as bases, the climate of the country can be divided into two
major seasons: (1) the rainy season, from June to November; and (2) the dry season, from December to May. The dry season may be subdivided further into (a) the cool dry season, from December to February; and (b) the hot dry season, from March to May. Climate Types Based on the distribution of rainfall, four climate types are recognized, which are described as follows:
The flood alerts Under the heavy rainfall warning system, a yellow rainfall advisory is raised when the expected rainfall amount is between 7.5 mm and 15 mm within one hour and likely to continue. Communities given this advisory are advised to be aware of the weather condition and warned that flooding may be possible in low-lying areas.
The orange rainfall advisory is raised in areas where rainfall is between 15 mm and 30 mm within one hour. Flooding is a definite threat in communities under the orange alert. A red rainfall advisory is issued when downpours constitute an emergency. This is raised when observed rainfall is more than 30 mm within one hour or if rainfall has continued for the past three hours and is more than 65 mm. When PAGASA raises a Red warning, communities should be prepared to respond. It means serious flooding is seen and that residents should be ready to evacuate to safety. How it works: Based on the advisory level, find out if your area is affected. For example, if you live in Marikina, go to Project Noah. The real-time flood reference for Marikina can be seen if you click flood maps and go to flood inundation. PAGASAgenerates flood scenario for Marikina river every 10 min. In cases of alerts, its the LGU in charge: MMDA Flood Control 882-4177, Paraaque DPOS Manila Traffic Hotline Cainta Traffic Hotline 646-0044, 655-7368 Las Pias Traffic 874-5756, 874-3957, Mandaluyong Hotline Taguig Traffic 838-4301 loc. Marikina STOC Pasig Traffic 643-0000, 724-5813 Makati Public Safety Dept. 844-3146, 819-3270 All LGUs have identified evacuation areas to be used in case of flooding. These are the barangay multi-purpose court, selected barangay halls, and public schoolselementary and H.S. 882-0925 829-2056 527-3087 loc. 164 874-3927 534-2993 7112 646-1651
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Basics of - AntennasDocumento196 pagineBasics of - AntennasNielsen Jose Marcelino50% (2)
- Keiilf: Training ManualDocumento53 pagineKeiilf: Training ManualGary GouveiaNessuna valutazione finora
- 12.5 Collision Theory - ChemistryDocumento15 pagine12.5 Collision Theory - ChemistryAri CleciusNessuna valutazione finora
- Immigrant Italian Stone CarversDocumento56 pagineImmigrant Italian Stone Carversglis7100% (2)
- Biophoton RevolutionDocumento3 pagineBiophoton RevolutionVyavasayaha Anita BusicNessuna valutazione finora
- Implicit Explicit SignalsDocumento8 pagineImplicit Explicit SignalsVersoza Nel100% (2)
- Tropical DesignDocumento201 pagineTropical DesignFrancis Grant ReladoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tropical DesignDocumento12 pagineTropical DesignjohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate of The PhilippinesDocumento25 pagineClimate of The PhilippinesCMarie Cachero PazNessuna valutazione finora
- Precautionaryandsafetymeasuresfor Hydrometeorological HazardsDocumento35 paginePrecautionaryandsafetymeasuresfor Hydrometeorological HazardsNikki CrystelNessuna valutazione finora
- Adaptation to Climate Change: Agricultural Ecosystems and Gender DimensionsDa EverandAdaptation to Climate Change: Agricultural Ecosystems and Gender DimensionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Arbor APS STT Unit 01 Design Basics 25 Jan2018Documento31 pagineArbor APS STT Unit 01 Design Basics 25 Jan2018masterlinh2008Nessuna valutazione finora
- VBAC MCQsDocumento3 pagineVBAC MCQsHanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Philippine ClimateDocumento22 paginePhilippine ClimateJulia ObregonNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate in The PhilippinesDocumento2 pagineClimate in The Philippinesmisayestuaria11Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reyes RRL Me-ElectiveDocumento5 pagineReyes RRL Me-ElectiveMarc GajudoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tropical Des.Documento4 pagineTropical Des.jairahguiab0516Nessuna valutazione finora
- Climate of The PhilippinesDocumento12 pagineClimate of The PhilippinesABUAN, NOWEL T.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Climate of The PhilippinesDocumento13 pagineClimate of The PhilippinesAngel Anne AlcantaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Philippine Climate Data & AnalysisDocumento14 paginePhilippine Climate Data & AnalysisJulia ObregonNessuna valutazione finora
- Handout For Trop DesignDocumento4 pagineHandout For Trop DesignAidan MalamugNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes On The Climate of The PhilippinesDocumento4 pagineNotes On The Climate of The PhilippinesAnonymous HXLczq3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 6 Weather and Climate in The Phil 1Documento13 pagineChap 6 Weather and Climate in The Phil 1secretzNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate in The Philippines: TemperatureDocumento6 pagineClimate in The Philippines: TemperatureKukishin KrimNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study Tropical DesignDocumento1 paginaCase Study Tropical Designmimo.deleon.upNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate of The PhilippinesDocumento10 pagineClimate of The PhilippinesApple ColladoNessuna valutazione finora
- Objectives Main Objective: Sagunto, Sison, Pangasinan Namcamaliran East, Urdaneta, PangasinanDocumento21 pagineObjectives Main Objective: Sagunto, Sison, Pangasinan Namcamaliran East, Urdaneta, PangasinanJayvee Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Impact of Global Warming OnDocumento7 pagineImpact of Global Warming OnKiran MittalNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Ii Eed 18Documento19 pagineUnit Ii Eed 18Rishel AlamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate Refers To The LongDocumento26 pagineClimate Refers To The LongReuNessuna valutazione finora
- Weather Basics (Meteorology) : Atmospheric Waters MeteorologyDocumento6 pagineWeather Basics (Meteorology) : Atmospheric Waters Meteorologyglaydelle100% (1)
- Group 4-ShaneDocumento3 pagineGroup 4-ShaneAngeline CuriosoNessuna valutazione finora
- ELEMENTS of WEATHER and CLIMATEDocumento71 pagineELEMENTS of WEATHER and CLIMATEMel DridNessuna valutazione finora
- The Climate and Weather of The PhilippinesDocumento8 pagineThe Climate and Weather of The PhilippinesZahra Margrette SchuckNessuna valutazione finora
- Factsheet AdaptationDocumento9 pagineFactsheet AdaptationMichael SiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate ChangeDocumento5 pagineClimate ChangeCristine Joy CalingacionNessuna valutazione finora
- Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : Hydrometeorological HazardsDocumento7 pagineSelf-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : Hydrometeorological HazardsAnnabella Quevedo CampomanesNessuna valutazione finora
- (PARGAD) Weather and Climatic Elements of Philippine ArchipelagoDocumento28 pagine(PARGAD) Weather and Climatic Elements of Philippine ArchipelagoTrisha Cristi Ramos AlmoniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 3 MeteorologyDocumento30 paginePart 3 Meteorologyxhero 71Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 9 - Geographic Profile of The Philippines: Learning ObjectivesDocumento3 pagineLesson 9 - Geographic Profile of The Philippines: Learning ObjectivesMary Antonette MulingtapangNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is ClimateDocumento12 pagineWhat Is ClimateDannielyn BuayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate ChangeDocumento84 pagineClimate ChangeKyla Ellen CalelaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Rainfall Warnings and Climate Type of PhilippinesDocumento2 pagineRainfall Warnings and Climate Type of Philippinesprinz ViterboNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate: Sagurit, Saraiah Luy, Camille Del Valle, Laia Villanueva, Roi Alvarez, ArvinDocumento21 pagineClimate: Sagurit, Saraiah Luy, Camille Del Valle, Laia Villanueva, Roi Alvarez, ArvinSaraiah SaguritNessuna valutazione finora
- Tropical CyclonesDocumento34 pagineTropical CyclonesDavis ShamolmolNessuna valutazione finora
- Conomic Ssue of The Ay: Basics On Philippine ClimatologyDocumento2 pagineConomic Ssue of The Ay: Basics On Philippine ClimatologyRandy CamaclangNessuna valutazione finora
- El Niño - WPS OfficeDocumento8 pagineEl Niño - WPS OfficeEnah Sazi Ale ArbalNessuna valutazione finora
- ARC-03-1485 - Adedeji - Climatic Zones For Architectural DesignDocumento16 pagineARC-03-1485 - Adedeji - Climatic Zones For Architectural DesignResame EdimNessuna valutazione finora
- Esemen Earth N Space 2015Documento11 pagineEsemen Earth N Space 2015Zulfazakmalhusna Ibnu MaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate of The PhilippinesDocumento82 pagineClimate of The PhilippinesBabylyn MordenNessuna valutazione finora
- ScienceDocumento5 pagineScienceAaron Jarque JesalvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Klima I PoljoprivredniciDocumento11 pagineKlima I PoljoprivredniciNevena NeškovićNessuna valutazione finora
- ClimateDocumento3 pagineClimateHazel CordanoNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are The Future Changes in The Northeast Monsoon Rainfall Is Expected and What Are The Areas in The Phil. Will Be Affected?Documento5 pagineWhat Are The Future Changes in The Northeast Monsoon Rainfall Is Expected and What Are The Areas in The Phil. Will Be Affected?Aaron Jarque JesalvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate Edit 2Documento17 pagineClimate Edit 2Malemeko GriffinNessuna valutazione finora
- EXPLORE ACTIVITY 2: Rainforest Climates: ProcedureDocumento3 pagineEXPLORE ACTIVITY 2: Rainforest Climates: ProcedureKyle BanceNessuna valutazione finora
- Uruguay ArgentinaDocumento2 pagineUruguay ArgentinaIbni SabilNessuna valutazione finora
- Heavy Rainfall Index 1Documento19 pagineHeavy Rainfall Index 1ROBERT TOMARONessuna valutazione finora
- Geo ProjDocumento9 pagineGeo ProjSnigdha DasNessuna valutazione finora
- ClimateDocumento26 pagineClimateJenny ManagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 3 Soc. Stud 4Documento14 pagineWeek 3 Soc. Stud 4Asther Jane B. VillacastinNessuna valutazione finora
- UNW-DPC NDMP Country Report Philippines 2014Documento7 pagineUNW-DPC NDMP Country Report Philippines 2014Anonymous z0jnPUhANessuna valutazione finora
- Climate Change Vulnerability and Impact Analysis in NepalDocumento8 pagineClimate Change Vulnerability and Impact Analysis in Nepalsabitri sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate Classification PDFDocumento12 pagineClimate Classification PDFAndrea Louise VergelNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate Profiles of Countries in Southern Africa ZimbabweDocumento6 pagineClimate Profiles of Countries in Southern Africa ZimbabweJohn MuseredzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Title - Understanding Kampala's Weather PatternsDocumento2 pagineTitle - Understanding Kampala's Weather PatternsmusobotrekNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 2Documento13 pagineAssignment 2SiyathokozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate of The Philippines: PagasaDocumento3 pagineClimate of The Philippines: PagasaJoan Reyes CarimpongNessuna valutazione finora
- Expt - 1introduction To MATLABDocumento10 pagineExpt - 1introduction To MATLABNielsen Jose MarcelinoNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Marriage? Explain: RelationshipsDocumento7 pagineWhat Is Marriage? Explain: RelationshipsNielsen Jose MarcelinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Micro Weather Systems - MWS: Good Morning !Documento19 pagineMicro Weather Systems - MWS: Good Morning !Nielsen Jose MarcelinoNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Force & ExtensionDocumento13 pagine4 Force & ExtensionSelwah Hj AkipNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar On Solar Mobile Charger: Submitted To: Submitted byDocumento16 pagineSeminar On Solar Mobile Charger: Submitted To: Submitted byAkhila GottemukkulaNessuna valutazione finora
- 外贸专业术语Documento13 pagine外贸专业术语邱建华Nessuna valutazione finora
- User'S Guide: Tm4C Series Tm4C129E Crypto Connected Launchpad Evaluation KitDocumento36 pagineUser'S Guide: Tm4C Series Tm4C129E Crypto Connected Launchpad Evaluation KitLương Văn HưởngNessuna valutazione finora
- G1CDocumento12 pagineG1CKhriz Ann C ÜNessuna valutazione finora
- SSDsDocumento3 pagineSSDsDiki Tri IndartaNessuna valutazione finora
- NAT-REVIEWER-IN-PHYSICAL EDUCATIONDocumento4 pagineNAT-REVIEWER-IN-PHYSICAL EDUCATIONMira Rochenie CuranNessuna valutazione finora
- Sika - Bitumen: Bitumen Emulsion Waterproof & Protective CoatingDocumento3 pagineSika - Bitumen: Bitumen Emulsion Waterproof & Protective Coatingdinu69inNessuna valutazione finora
- 300 PSI CTS (MP-1115) Operation Manual Rev1.3Documento18 pagine300 PSI CTS (MP-1115) Operation Manual Rev1.3Juan Manuel VizosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1Documento3 pagineAssignment 1farhang_tNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Syllabus: Course Code Course Title ECTS CreditsDocumento3 pagineCourse Syllabus: Course Code Course Title ECTS CreditsHanaa HamadallahNessuna valutazione finora
- 2015 Nos-Dcp National Oil Spill Disaster Contingency PlanDocumento62 pagine2015 Nos-Dcp National Oil Spill Disaster Contingency PlanVaishnavi Jayakumar100% (1)
- Drilling & GroutingDocumento18 pagineDrilling & GroutingSantosh Laxman PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Flight Vehicle Design:: Example 2 (Uav)Documento43 pagineFlight Vehicle Design:: Example 2 (Uav)Anmol KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- SDHI18 - Komparativna Analiza Primene Vodostana I Sinhronih Regulatora TurbinaDocumento13 pagineSDHI18 - Komparativna Analiza Primene Vodostana I Sinhronih Regulatora TurbinaAleksandar PetkovicNessuna valutazione finora
- Passenger Lift Alert - Health and Safety AuthorityDocumento4 paginePassenger Lift Alert - Health and Safety AuthorityReginald MaswanganyiNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric ScootorDocumento40 pagineElectric Scootor01fe19bme079Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electrowetting - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento5 pagineElectrowetting - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDwane AlmeidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Shandong Baoshida Cable Co, LTD.: Technical ParameterDocumento3 pagineShandong Baoshida Cable Co, LTD.: Technical ParameterkmiqdNessuna valutazione finora
- Module-4 (PDFDrive)Documento67 pagineModule-4 (PDFDrive)Divya priya KNessuna valutazione finora
- DMDWLab Book AnswersDocumento44 pagineDMDWLab Book AnswersNarpat Makwana Pune100% (1)
- Introduction To LCCDocumento32 pagineIntroduction To LCCGonzalo LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Semi Finals in Tle 2015Documento3 pagineSemi Finals in Tle 2015LoraineTenorioNessuna valutazione finora