Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Brain Bee
Caricato da
Ye Rim WonCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Brain Bee
Caricato da
Ye Rim WonCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Brain Bee The Nervous System Basic Structure: Consists of brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves Made
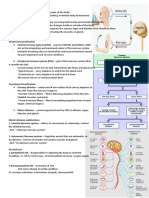
de up of nerve cells called neurons and supporting cells called glial cells Three main neurons types: Sensory neurons: - Attached to receptors - They are specialised to respond to different attributes of the internal and external environment - Sensitive to changes in light, sound, mechanical and chemical stimuli which promote sensory procedures of vision, hearing, touch, smell and taste - When mechanical, thermal or chemical stimuli to the skin exceed a certain intensity, they can cause tissue damage - Nociceptors are activated which triggers protective reflections and sensation of pain Motor neurons: - Control muscle activity - Responsible for all forms of behaviour eg. speech Interneurons: - They influence simple reflexes - Responsible for the highest functions of the brain - Most in numbers in the human brain Glial cells support neurons Make an important contribution to the development of the nervous system and function in the adult brain Do not transmit information like neurons Neuron architecture: Cell body Axons - A process, an additional compartment to the neuron - Transmits information to other neurons when connected Dendrites - Receive information transmitted by axons Both make up a specialised contact called synapses Neurons are organised into complex chains and networks which are pathways for information to be transmitted through in the nervous system Peripheral nerves: - Long axons - Brain and spinal cords are connected to sensory receptors and muscles by peripheral nerves Spinal cord: - Has two functions - 1) triggers simple reflexes eg. knee jerk, pulling away from hot object or pinprick and other complex reflexes
2) forms a highway between body and brain for information travelling in both directions
Anatomy of the Brain: Brain Stem: Hind-brain - Extension of the spinal cord - Contains networks of neurons that establish centres which control vital functions eg. breathing, blood pressure - Neurons within these networks controls these functions - From the roof of the hind-brain is the cerebellum Mid-brain - Contains groups of neurons - Each mainly use a particular type of chemical messenger but they all project up to the cerebral hemispheres - Thought to moderate activity of neurons in the higher centres of the brain to influence functions like sleep, attention or reward Between-brain, Diencephalon - Divided into: - Thalamus: Passes impulses from all sensory systems to cerebral cortex which sends messages back to thalamus Information travels both ways - Hypothalamus: Controls functions eg. eating, drinking Controls the release of hormones involved in sexual functions
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- NeuroscienceDocumento169 pagineNeuroscienceSalam Matalka100% (17)
- Brain Bee Sample QuestionsDocumento4 pagineBrain Bee Sample QuestionsThasaRatha100% (3)
- Quiz Neuroscience Part 2 of 4Documento31 pagineQuiz Neuroscience Part 2 of 4MedShare80% (5)
- Neuroanatomy: and The Peripheral Nervous SystemDocumento24 pagineNeuroanatomy: and The Peripheral Nervous Systemnamya mehan0% (1)
- Introduction To The BrainDocumento109 pagineIntroduction To The BrainHelenSCNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 Olympiad Training Genetics (Student)Documento73 pagine2016 Olympiad Training Genetics (Student)dimpledblissNessuna valutazione finora
- Glass Menagerie Study GuideDocumento36 pagineGlass Menagerie Study Guidejdwright20170% (1)
- E-Magazine: Terra RosaDocumento55 pagineE-Magazine: Terra RosaTerra RosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz Neuroscience Part 1 of 4Documento55 pagineQuiz Neuroscience Part 1 of 4MedShare80% (5)
- Psychology I Brain Test Review Mrs. ForbesDocumento2 paginePsychology I Brain Test Review Mrs. ForbesKPNessuna valutazione finora
- Brain Bee NotesDocumento10 pagineBrain Bee Notesapi-534972164Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 BrainBeeUSM MBBC2019 Learning Resources PDFDocumento157 pagine1 BrainBeeUSM MBBC2019 Learning Resources PDFwan muhd100% (1)
- Module 3 PDFDocumento20 pagineModule 3 PDFSuiluj Omatsodlab100% (1)
- HomeostasisDocumento16 pagineHomeostasisDr M K GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- PurvesNeuroscienceWebsiteQuestionsCh9 13answersDocumento3 paginePurvesNeuroscienceWebsiteQuestionsCh9 13answersPK32145987100% (4)
- Brain Bee Quiz Chapter 7-16 PDFDocumento7 pagineBrain Bee Quiz Chapter 7-16 PDFMartyna Petrulytė83% (6)
- Computational Neuroscience and Cognitive ModellingDocumento241 pagineComputational Neuroscience and Cognitive Modellingaajkljkl100% (8)
- Brainbee Study Outline PDFDocumento5 pagineBrainbee Study Outline PDFanon_578778160Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz Neuroscience Part 4 of 4Documento59 pagineQuiz Neuroscience Part 4 of 4MedShare100% (2)
- Nervous System Part 1Documento6 pagineNervous System Part 1rb YangzonNessuna valutazione finora
- 2014 Alabama Brain Bee Mock Test AnswersDocumento5 pagine2014 Alabama Brain Bee Mock Test Answersbrainbeeuab80% (10)
- Brain Bee Questions CH 1 - 11Documento13 pagineBrain Bee Questions CH 1 - 11Martyna Petrulytė88% (8)
- USABO 18 Open Exam - Final Wo AnsDocumento17 pagineUSABO 18 Open Exam - Final Wo AnsJ.Chang ChangNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication and Presentation Skill 1Documento229 pagineCommunication and Presentation Skill 1shanthakumargcNessuna valutazione finora
- BrainbeeDocumento269 pagineBrainbeeTianli Jiang100% (1)
- Vermont Brain Bee Studyprep GuideDocumento1 paginaVermont Brain Bee Studyprep Guideterran2020100% (1)
- 2017 Brain Bee Competition QuestionsDocumento63 pagine2017 Brain Bee Competition QuestionsRama Bodapati100% (3)
- Brain BeeDocumento1 paginaBrain Beeapi-303151625Nessuna valutazione finora
- Brain Bee Sample QuestionsDocumento1 paginaBrain Bee Sample QuestionsDivineDoctorNessuna valutazione finora
- Brain BeeDocumento2 pagineBrain BeeJulia Alexsandra GalizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuroanatomy Quiz BeeDocumento55 pagineNeuroanatomy Quiz BeeJulienne Sanchez-Salazar100% (3)
- Program - Stanford Brain Bee 2015Documento2 pagineProgram - Stanford Brain Bee 2015KelLYSNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 NS Objective QuestionsDocumento8 pagineChapter 1 NS Objective QuestionsSadasivarao GaddeNessuna valutazione finora
- BB2019 Multiple ChoiceDocumento14 pagineBB2019 Multiple Choicebrainbeeuab100% (5)
- British Brain Bee Revision Session PowerpointDocumento118 pagineBritish Brain Bee Revision Session PowerpointMartyna Petrulytė100% (16)
- Brianbee Sample Questions 1 PDFDocumento2 pagineBrianbee Sample Questions 1 PDFLigeia100% (1)
- Cerebrum MCQDocumento5 pagineCerebrum MCQSrinivasa Rao BollaNessuna valutazione finora
- U3 - Lab Project Leech NeuronsDocumento6 pagineU3 - Lab Project Leech NeuronsAmandaShermanNessuna valutazione finora
- Brain Bee 2013 Study Guide FULLDocumento12 pagineBrain Bee 2013 Study Guide FULLmsawickaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 NS Objective AnswersDocumento6 pagineChapter 2 NS Objective AnswersSadasivarao GaddeNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz Neuroscience Part 3 of 4Documento47 pagineQuiz Neuroscience Part 3 of 4MedShare75% (4)
- Writeup by National Brain Bee Winner IBB2012Documento2 pagineWriteup by National Brain Bee Winner IBB2012terran2020Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vermont Brain Bee Practice QuestionsDocumento1 paginaVermont Brain Bee Practice QuestionsVishurockNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Brain Basics QuestionsDocumento9 pagine1 Brain Basics QuestionsEster RustemiNessuna valutazione finora
- Brain Bee Study QuestionsDocumento13 pagineBrain Bee Study QuestionsMartyna Petrulytė88% (25)
- EBB 2020 Phase 1 TestDocumento9 pagineEBB 2020 Phase 1 TestMohamed Hamed IssaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2014 Alabama Brain Bee Mock TestDocumento7 pagine2014 Alabama Brain Bee Mock Testbrainbeeuab67% (3)
- Physioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsDocumento5 paginePhysioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsJoashan Vac100% (2)
- Purves Neuroscience Website Questions CH 11 AnswersDocumento3 paginePurves Neuroscience Website Questions CH 11 AnswersPK32145987100% (3)
- Brain Bee QuizDocumento4 pagineBrain Bee QuizЗулааХонгорооNessuna valutazione finora
- Brain BeeDocumento2 pagineBrain Beebubblegumlover96Nessuna valutazione finora
- Brain Bee Quiz by Neil JainDocumento1 paginaBrain Bee Quiz by Neil Jainneiljainhd100% (2)
- Purves Neuroscience Website Questions CH 6 AnswersDocumento4 paginePurves Neuroscience Website Questions CH 6 AnswersPK32145987Nessuna valutazione finora
- Epilepsy: Alabama Brain BeeDocumento15 pagineEpilepsy: Alabama Brain Beebrainbeeuab100% (1)
- Study Guide Anatomy 2015Documento5 pagineStudy Guide Anatomy 2015KelLYSNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug of Abuse Substance of AbuseDocumento10 pagineDrug of Abuse Substance of AbuseCARL ANGELA SISONNessuna valutazione finora
- Purves Neuroscience Website Questions CH 7 AnswersDocumento4 paginePurves Neuroscience Website Questions CH 7 AnswersPK32145987100% (1)
- Huntington's DiseaseDocumento9 pagineHuntington's DiseasebrainbeeuabNessuna valutazione finora
- Schizophrenia: Alabama Brain BeeDocumento10 pagineSchizophrenia: Alabama Brain BeebrainbeeuabNessuna valutazione finora
- Purves Neuroscience Website Questions CH 8 AnswersDocumento4 paginePurves Neuroscience Website Questions CH 8 AnswersPK3214598750% (2)
- Chapt 09 AnswersDocumento7 pagineChapt 09 AnswersJerimiah MirandaNessuna valutazione finora
- CogNeuro2e Ch03 Online QuizDocumento4 pagineCogNeuro2e Ch03 Online Quizgoss9Nessuna valutazione finora
- CogNeuro2e Ch01 Online QuizDocumento4 pagineCogNeuro2e Ch01 Online Quizgoss9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide For Science BowlDocumento48 pagineStudy Guide For Science BowlAnonymous xxfTSo5aNessuna valutazione finora
- Pertemuan 8 - Sistem Saraf MinDocumento43 paginePertemuan 8 - Sistem Saraf MinErsha PutriNessuna valutazione finora
- Physiology ReviewDocumento65 paginePhysiology ReviewNandita KNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is The Nervous SystemDocumento3 pagineWhat Is The Nervous SystemSittie Asleah SandiganNessuna valutazione finora
- Functions of The Nervous SystemDocumento5 pagineFunctions of The Nervous SystemJungkookie BaeNessuna valutazione finora
- In Time Film EssayDocumento2 pagineIn Time Film EssayYe Rim WonNessuna valutazione finora
- Stardust Film EssayDocumento2 pagineStardust Film EssayYe Rim WonNessuna valutazione finora
- 12ENGX - Mister Pip EssayDocumento1 pagina12ENGX - Mister Pip EssayYe Rim Won0% (1)
- Obesity Anorexia ReportDocumento3 pagineObesity Anorexia ReportYe Rim WonNessuna valutazione finora
- In Time Film EssayDocumento2 pagineIn Time Film EssayYe Rim WonNessuna valutazione finora
- Diem Regime EssayDocumento3 pagineDiem Regime EssayYe Rim WonNessuna valutazione finora
- Kawau IslandDocumento13 pagineKawau IslandYe Rim WonNessuna valutazione finora
- Win From John: Take A ChanceDocumento8 pagineWin From John: Take A ChanceYe Rim WonNessuna valutazione finora
- MCDDocumento14 pagineMCDYe Rim WonNessuna valutazione finora
- Diem Regime EssayDocumento3 pagineDiem Regime EssayYe Rim WonNessuna valutazione finora
- JC Science 2018-2020 PDFDocumento17 pagineJC Science 2018-2020 PDFLindela M Buz-BèéNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Cns 1 Receptor 1 1Documento95 pagine1 Cns 1 Receptor 1 1SanketNandaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Brain and Behavior 4e PrefaceDocumento26 pagineBrain and Behavior 4e Prefaceboka987Nessuna valutazione finora
- Scientific Reconciliation of The Concepts and Principles of Rood ApproachDocumento11 pagineScientific Reconciliation of The Concepts and Principles of Rood ApproachNaveen KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Reviewer Reviewer 2Documento15 pagineScience Reviewer Reviewer 2LyrMa NCNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 The Nervous System 2Documento6 pagine10 The Nervous System 2Cristina AdolfoNessuna valutazione finora
- BiopotentialsDocumento35 pagineBiopotentialsramyarakiNessuna valutazione finora
- CNS and PNSDocumento4 pagineCNS and PNSDeepshikhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Pack Science Form 1 + Form 2Documento21 pagineRevision Pack Science Form 1 + Form 2Shureen Baskaran100% (1)
- Nervous System 2Documento51 pagineNervous System 2وجد عمرNessuna valutazione finora
- The Molecular and Cellular Basis of Cold Sensation: David D. MckemyDocumento10 pagineThe Molecular and Cellular Basis of Cold Sensation: David D. MckemyAlyanah AloveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Vision and Other Sensory SystemsDocumento8 pagineVision and Other Sensory SystemsMerryNessuna valutazione finora
- Physiological Basis of Behavior ScribDocumento12 paginePhysiological Basis of Behavior ScribJJ WoodruffNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanisms of Neuropathic PainDocumento14 pagineMechanisms of Neuropathic Painfahri azwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 33Documento13 pagineExperiment 33KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Nerve Cells 2Documento22 pagineNerve Cells 2Paulo Justin Tabangcora OropillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Integumentary SystemDocumento7 pagineIntegumentary SystemKristine MerhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Physiology FC PainDocumento4 paginePhysiology FC Painiqz saniomeNessuna valutazione finora
- From Neuron To Brain 5editionDocumento13 pagineFrom Neuron To Brain 5editionJuan Carrillo Cruz19% (16)
- Biology 3Documento126 pagineBiology 3khaledNessuna valutazione finora
- PHA 618 Laboratory Human Physiology and Pathophysiology: Muscular SystemDocumento42 paginePHA 618 Laboratory Human Physiology and Pathophysiology: Muscular SystemROSEMARIE ONGNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaphy - Lesson 4 - Topic 4 and 5Documento21 pagineAnaphy - Lesson 4 - Topic 4 and 5Rica Abigail DagosNessuna valutazione finora