Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
What Is A Digital Signature?
Caricato da
ajhiredTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
What Is A Digital Signature?
Caricato da
ajhiredCopyright:
Formati disponibili
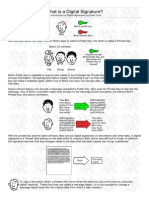
What is a Digital Signature?
An introduction to Digital Signatures, by David Youd
(Bob's public key)
Bob
(Bob's private key)
Bob has been given two keys. One of Bob's keys is called a Public Key, the other is called a Private Key. Bob's Co-workers:
Anyone can get Bob's Public Key, but Bob keeps his Private Key to himself
Pat
Doug
Susan
Bob's Public key is available to anyone who needs it, but he keeps his Private Key to himself . Keys are used to encrypt inf ormation. Encrypting inf ormation means "scrambling it up", so that only a person with the appropriate key can make it readable again. Either one of Bob's two keys can encrypt data, and the other key can decrypt that data. Susan (shown below) can encrypt a message using Bob's Public Key. Bob uses his Private Key to decrypt the message. Any of Bob's coworkers might have access to the message Susan encrypted, but without Bob's Private Key, the data is worthless.
"Hey Bob, how about lunch at Taco Bell. I hear they have free refills!" HNFmsEm6Un BejhhyCGKOK JUxhiygSBCEiC 0QYIh/Hn3xgiK BcyLK1UcYiY lxx2lCFHDC/A HNFmsEm6Un BejhhyCGKOK JUxhiygSBCEiC 0QYIh/Hn3xgiK BcyLK1UcYiY lxx2lCFHDC/A "Hey Bob, how about lunch at Taco Bell. I hear they have free refills!"
With his private key and the right sof tware, Bob can put digital signatures on documents and other data. A digital signature is a "stamp" Bob places on the data which is unique to Bob, and is very dif f icult to f orge. In addition, the signature assures that any changes made to the data that has been signed can not go undetected.
To sign a document, Bob's sof tware will crunch down the data into just a f ew lines by a process called "hashing". These f ew lines are called a message digest. (It is not possible to change a message digest back into the original data f rom which it was created.)
Bob's sof tware then encrypts the message digest with his private key. The result is the digital signature.
Finally, Bob's sof tware appends the digital signature to document. All of the data that was hashed has been signed.
Bob now passes the document on to Pat. First, Pat's sof tware decrypts the signature (using Bob's public key) changing it back into a message digest. If this worked, then it proves that Bob signed the document, because only Bob has his private key. Pat's sof tware then hashes the document data into a message digest. If the message digest is the same as the message digest created when the signature was decrypted, then Pat knows that the signed data has not been changed.
Plot complication...
Doug (our disgruntled employee) wishes to deceive Pat. Doug makes sure that Pat receives a signed message and a public key that appears to belong to Bob. Unbeknownst to Pat, Doug deceitf ully sent a key pair he created using Bob's name. Short of receiving Bob's public key f rom him in person, how can Pat be sure that Bob's public key is authentic? It just so happens that Susan works at the company's certif icate authority center. Susan can create a digital certif icate f or Bob simply by signing Bob's public key as well as some inf ormation about Bob. Bob Inf o:
Name Department Cubical Number
Certif icate Inf o:
Expiration Date Serial Number
Bob's Public Key:
Now Bob's co-workers can check Bob's trusted certif icate to make sure that his public key truly belongs to him. In f act, no one at Bob's company accepts a signature f or which there does not exist a certif icate generated by Susan. This gives Susan the power to revoke signatures if private keys are compromised, or no longer needed. There are even more widely accepted certif icate authorities that certif y Susan. Let's say that Bob sends a signed document to Pat. To verif y the signature on the document, Pat's sof tware f irst uses Susan's (the certif icate authority's) public key to check the signature on Bob's certif icate. Successf ul de-encryption of the certif icate proves that Susan created it. Af ter the certif icate is de-encrypted, Pat's sof tware can check if Bob is in good standing with the certif icate authority and that all of the certif icate inf ormation concerning Bob's identity has not been altered. Pat's sof tware then takes Bob's public key f rom the certif icate and uses it to check Bob's signature. If Bob's public key de-encrypts the signature successf ully, then Pat is assured that the signature was created using Bob's private key, f or Susan has certif ied the matching public key. And of course, if the signature is valid, then we know that Doug didn't try to change the signed content.
Although these steps may sound complicated, they are all handled behind the scenes by Pat's user-f riendly sof tware. To verif y a signature, Pat need only click on it.
(c) 1996, David Youd Permission to change or distribute is at the discretion of the author Warning: You may be missing a few lines of text if you print this document. This seems to occur on pages following pages that have blank space near the bottom due to moving tables with large graphics in them to the next page so that the images are not split across pages. If this happens to you, simply print out document in sections. (Ex: I have the problem on page 4, so I print pages 1- 3, then pages 4- 5.)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Best Torrent Sites 2019Documento9 pagineBest Torrent Sites 2019gda gdaNessuna valutazione finora
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Hacker's Manual 2015Documento146 pagineThe Hacker's Manual 2015Amanda Dean100% (7)
- Introduction to Cyber Security ConceptsDocumento5 pagineIntroduction to Cyber Security ConceptsnadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Java Tutorial PDFDocumento124 pagineAdvanced Java Tutorial PDFrabirm77Nessuna valutazione finora
- CNS Book by BrainheatersDocumento240 pagineCNS Book by Brainheatersanjana DeviNessuna valutazione finora
- Durga Software Solutions Spring MaterialDocumento0 pagineDurga Software Solutions Spring Materialpvkchakravarthi100% (5)
- Multithreading and Concurrency QuestionsDocumento26 pagineMultithreading and Concurrency QuestionsZsolt BokorNessuna valutazione finora
- Sec 2 - Lec 32 - Viewing-Files-And-The-Nano-Editor PDFDocumento7 pagineSec 2 - Lec 32 - Viewing-Files-And-The-Nano-Editor PDFdenyuuuNessuna valutazione finora
- Web Scripts Student GuideDocumento63 pagineWeb Scripts Student GuideajhiredNessuna valutazione finora
- 054 Getting Help PDFDocumento20 pagine054 Getting Help PDFajhiredNessuna valutazione finora
- Sec 2 Lec 34 1 Editing-Files-With-ViDocumento17 pagineSec 2 Lec 34 1 Editing-Files-With-VidenyuuuNessuna valutazione finora
- Karaf Commands2Documento1 paginaKaraf Commands2ajhiredNessuna valutazione finora
- 048 Backfround and Introduction PDFDocumento15 pagine048 Backfround and Introduction PDFajhiredNessuna valutazione finora
- 071 Switching Users and Sudo PDFDocumento15 pagine071 Switching Users and Sudo PDFajhiredNessuna valutazione finora
- 076 Installing SoftwareDocumento8 pagine076 Installing SoftwareajhiredNessuna valutazione finora
- Gautam Buddha University Late Admission Schedule July 2014Documento1 paginaGautam Buddha University Late Admission Schedule July 2014ajhiredNessuna valutazione finora
- Karaf CommandsDocumento1 paginaKaraf CommandsajhiredNessuna valutazione finora
- 073 Installing SoftwareDocumento18 pagine073 Installing SoftwarenykazNessuna valutazione finora
- Id Name Location Date Type 400 Rock XXX 5/1/2016 401 Austin Yyy 5/2/2016 II 402 Paul ZZZ 5/3/2016 III 403 Brock Aaa 5/4/2016 IV 404 Don 5/5/2016 VDocumento1 paginaId Name Location Date Type 400 Rock XXX 5/1/2016 401 Austin Yyy 5/2/2016 II 402 Paul ZZZ 5/3/2016 III 403 Brock Aaa 5/4/2016 IV 404 Don 5/5/2016 VajhiredNessuna valutazione finora
- Java AbstractionDocumento34 pagineJava AbstractionZsolt BokorNessuna valutazione finora
- Alfresco in An Hour: Jared Ottley Solutions EngineerDocumento41 pagineAlfresco in An Hour: Jared Ottley Solutions EngineerajhiredNessuna valutazione finora
- Karaf CommandsDocumento1 paginaKaraf CommandsajhiredNessuna valutazione finora
- OOPS ConceptDocumento1 paginaOOPS ConceptajhiredNessuna valutazione finora
- Disk SpaceDocumento1 paginaDisk SpaceajhiredNessuna valutazione finora
- List PortletDocumento1 paginaList PortletajhiredNessuna valutazione finora
- Apachechemistrywebinar 110713114739 Phpapp01Documento46 pagineApachechemistrywebinar 110713114739 Phpapp01ajhiredNessuna valutazione finora
- ANT Interview Questions and Answers: Ques:1 Give Example How We Can Deploy File On Server Using Ant? AnsDocumento10 pagineANT Interview Questions and Answers: Ques:1 Give Example How We Can Deploy File On Server Using Ant? AnsajhiredNessuna valutazione finora
- New Text DocumergegdfgdfgentDocumento2 pagineNew Text DocumergegdfgdfgentajhiredNessuna valutazione finora
- SignatureyryretyDocumento3 pagineSignatureyryretyajhiredNessuna valutazione finora
- IBPS RRB CWE Clerk Exam Paper Held 09-09-2012Documento22 pagineIBPS RRB CWE Clerk Exam Paper Held 09-09-2012ajhiredNessuna valutazione finora
- CsirDocumento9 pagineCsiryp20007Nessuna valutazione finora
- ADocumento5 pagineAjagadishksNessuna valutazione finora
- Category:: Central Bank of IndiaDocumento2 pagineCategory:: Central Bank of IndiaajhiredNessuna valutazione finora
- Ciphertext Policy Attribute Based Encryption: KeywordsDocumento4 pagineCiphertext Policy Attribute Based Encryption: Keywordssucheta pandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Handwritten Cipher ProgramsDocumento14 pagineHandwritten Cipher ProgramsRuby ShakyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hacker JobDocumento7 pagineHacker JobTom HasNessuna valutazione finora
- Balite DecDocumento75 pagineBalite DecAngelika CalingasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Website Vulnerability Scanner Report (Light) Security IssuesDocumento6 pagineWebsite Vulnerability Scanner Report (Light) Security Issuesalex681219Nessuna valutazione finora
- KAVACH'23: Team: Key KeepersDocumento9 pagineKAVACH'23: Team: Key Keeperspro coder MinecraftNessuna valutazione finora
- Key Distribution and User AuthenticationDocumento32 pagineKey Distribution and User AuthenticationdanielNessuna valutazione finora
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - DOEACC B Level-Network Management & Information Security Sample Paper 1Documento2 pagine(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - DOEACC B Level-Network Management & Information Security Sample Paper 1DEBLEENA VIJAYNessuna valutazione finora
- Crypto VizDocumento19 pagineCrypto Vizpipul36Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To SigncryptionDocumento27 pagineIntroduction To SigncryptionSara AbozeidNessuna valutazione finora
- IctDocumento5 pagineIctHenryPDTNessuna valutazione finora
- Diffie Hellman Algorithm RileyDocumento16 pagineDiffie Hellman Algorithm RileyShiva Prasad100% (1)
- Module 5 CryptographyDocumento14 pagineModule 5 CryptographyCIELICA BURCANessuna valutazione finora
- Digital SignatureDocumento14 pagineDigital SignatureAakash SaxenaNessuna valutazione finora
- IS Unit-2Documento125 pagineIS Unit-2Sarath Chandra BanalaNessuna valutazione finora
- CSB451 Ca4Documento8 pagineCSB451 Ca4s AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- INS Journal VikasDocumento54 pagineINS Journal Vikashaashboi5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Network Security Fundamentals QuizDocumento17 pagineNetwork Security Fundamentals Quizaqprincess89Nessuna valutazione finora
- Signature Image Hiding in Color Image Using Steganography and Cryptography Based On Digital Signature ConceptsDocumento5 pagineSignature Image Hiding in Color Image Using Steganography and Cryptography Based On Digital Signature ConceptsMarisna N. FadhilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Wsec01 PDFDocumento427 pagineWsec01 PDFRaoni Timo de CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- Summative Assessment Answers: CybersecurityDocumento4 pagineSummative Assessment Answers: CybersecurityZenyangNessuna valutazione finora
- Cryptography: Principles of Information Security, 2nd Edition 1Documento20 pagineCryptography: Principles of Information Security, 2nd Edition 1Nishanth KrishnamurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Nintendo Server Bug Bounty Program - Bug Bounty Program - HackerOneDocumento9 pagineNintendo Server Bug Bounty Program - Bug Bounty Program - HackerOneMariuxi RomeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Phishing Techniques and ToolsDocumento13 pagineIntroduction to Phishing Techniques and ToolsPerfect BoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networks 13 Security in The Internet IPSec SSLTLS PGP VPN and FirewallsDocumento34 pagineComputer Networks 13 Security in The Internet IPSec SSLTLS PGP VPN and FirewallsRittu TomNessuna valutazione finora
- 15 526 Topic14Documento26 pagine15 526 Topic14Alexandre FranckNessuna valutazione finora