Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Chapter 06
Caricato da
Kabil RajDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chapter 06
Caricato da
Kabil RajCopyright:
Formati disponibili
76
CHAPTER 6
CHAPTER
VEHICLE LIFTING AND HOISTING
OBJECTIVES
After studying Chapter 6, the reader will be able to: 1. Identify vehicle hoisting and lifting equipment. 2. Discuss safety procedures related to hoisting or lifting a vehicle. 3. Describe the proper methods to follow to safely hoist a vehicle.
KEY TERMS
Creeper (p. 77) Floor Jack (p. 77) Jack Stands (p. 77) Safety Stands (p. 77)
Vehicle Lifting and Hoisting
77
FLOOR JACK
A floor jack is a hand-operated hydraulic device that is used to lift vehicles or components, such as engines, transmissions, and rear axle assemblies. Most floor jacks use four casters, which allow the jack to be easily moved around the shop. See Figure 6-1.
Safe Use of Floor Jacks
Floor jacks are used to lift a vehicle or major vehicle component, but they are not designed to hold a load. Therefore safety stands, also called jack stands, should always be used to support the vehicle. After the floor jack has lifted the vehicle, safety stands should be placed under the vehicle, and then, using the floor jack, lowered onto the safety stands. The floor jack can be lifted in position as another safety device but the load should be removed from the floor jack. If a load is retained on the floor jack, hydraulic fluid can leak past seals in the hydraulic cylinders, which would lower the vehicle, possibly causing personal injury. See Figure 6-2.
FIGURE 6-2 Safety stands are being used to support the rear of this vehicle.Notice a creeper also.
Safe Use of Creepers
Creepers can create a fall hazard if left on the floor. When a creeper is not being used, it should be picked up and placed vertically against a wall or tool box to help prevent accidental falls.
CREEPERS
When working underneath a vehicle, most service technicians use a creeper, which consists of a flat or concaved surface equipped with low-profile casters. A creeper allows the technician to maneuver under the vehicle easily.
VEHICLE HOISTS
Vehicle hoists include older in-ground pneumatic/hydraulic (air pressure over hydraulic) and aboveground units. Most of the vehicle hoists used today use an electric motor to pressurize hydraulic fluid, which lifts the vehicle using hydraulic cylinders. Hoists are rated by the maximum weight that they can safely lift, such as 7,000 lbs to 12,000 lbs or more. Hoists can also have equal length arms or can be equipped with different length arms allowing the vehicle to be set so the doors can be opened and not hit the center support column. Many chassis and underbody service procedures require that the vehicle be hoisted or lifted off the ground. The simplest methods involve the use of drive-on ramps or a floor jack and safety (jack) stands, whereas in-ground or surface-mounted lifts provide greater access.
Setting the Pads Is a Critical Part of This Procedure
All automobile and light-truck service manuals include recommended locations to be used when hoisting (lifting) a vehicle. Newer vehicles have a triangle decal on the drivers door indicating the recommended lift points. The recommended standards for the lift points and lifting procedures are found in SAE Standard JRP-2184. See Figure 6-3. These recommendations typically include the following points: 1. The vehicle should be centered on the lift or hoist so as not to overload one side or put too much force either forward or rearward. See Figure 6-4.
FIGURE 6-1 A hydraulic hand-operated floor jack.
78
CHAPTER 6
2. The pads of the lift should be spread as far apart as possible to provide a stable platform. 3. Each pad should be placed under a portion of the vehicle that is strong and capable of supporting the weight of the vehicle. a. Pinch welds at the bottom edge of the body are generally considered to be strong.
CAUTION: Do not look away from the vehicle while it is being raised (or lowered) on a hoist. Often one side or one end of the hoist can stop or fail, resulting in the vehicle being slanted enough to slip or fall, creating physical damage not only to the vehicle and/or hoist but also to the technician or others who may be nearby.
CAUTION: Even though pinch weld seams are the recommended location for hoisting many vehicles with unitized bodies (unit-body), care should be taken not to place the pad(s) too far forward or rearward.Incorrect placement of the vehicle on the lift could cause the vehicle to be imbalanced, and the vehicle could fall. This is exactly what happened to the vehicle in Figure 6-5.
b. Boxed areas of the body are the best places to position the pads on a vehicle without a frame. Be careful to note whether the arms of the lift might come into contact with other parts of the vehicle before the pad touches the intended location. Commonly damaged areas include the following: 1. Rocker panel moldings 2. Exhaust system (including catalytic converter) 3. Tires or body panels. (See Figures 6-6 and 6-7.) 4. The vehicle should be raised about a foot (30 centimeters [cm]) off the floor, then stopped and shaken to check for stability. If the vehicle seems to be stable when checked at a short distance from the floor, continue raising the vehicle and continue to view the vehicle until it has reached the desired height. The hoist should be lowered onto the mechanical locks, and then raised off of the locks before lowering.
(a)
LIFT POINT LOCATION SYMBOL
(b)
FIGURE 6-3 Most newer vehicles have a triangle symbol indicating the recommended hoisting lift points.
FIGURE 6-4 (a) Tall safety stands can be used to provide additional support for a vehicle while on a hoist. (b) A block of wood should be used to avoid the possibility of doing damage to components supported by the stand.
Vehicle Lifting and Hoisting
79
(a)
FIGURE 6-5 This vehicle fell from the hoist because the pads were not set correctly.No one was hurt,but the vehicle was a total loss.
(b)
FIGURE 6-7 (a) In this photo the pad arm is just contacting the rocker panel of the vehicle.(b) This photo shows what can occur if the technician places the pad too far inward underneath the vehicle.The arm of the hoist has dented in the rocket panel.
(a)
NOTE: Most hoists can be safely placed at any desired height as long as it is high enough for the safety latches to engage.For ease while working, the area in which you are working should be at chest level. When working on brakes or suspension components,it is not necessary to work on them down near the floor or over your head.Raise the hoist so that the components are at chest level.
(b)
FIGURE 6-6 (a) An assortment of hoist pad adapters that are often necessary to safely hoist many pickup trucks,vans,and sport utility vehicles.(b) A view from underneath a Chevrolet pickup truck showing how the pad extensions are used to attach the hoist lifting pad to contact the frame.
5. Before lowering the hoist, the safety latch(es) must be released and the direction of the controls reversed. The speed downward is often adjusted to be as slow as possible for additional safety.
80
CHAPTER 6
DRIVE-ON RAMPS
Ramps are an inexpensive way to raise the front or rear of a vehicle. See Figure 6-8. Ramps are easy to store, but they can be dangerous because they can kick out when driving the vehicle onto the ramps.
CHOCK DRIVE-ON RAMPS
CAUTION: Professional repair shops do not use ramps because they are dangerous to use.Use only with extreme care.
FIGURE 6-8 Drive-on-type ramps. The wheels on the ground level must be chocked (blocked) to prevent accidental movement down the ramp.
Vehicle Lifting and Hoisting
81
HOISTING THE VEHICLE Step-by-Step
Step 1
The first step in hoisting a vehicle is to properly align the vehicle in the center of the stall.
Step 2
Most vehicles will be correctly positioned when the left front tire is centered on the tire pad.
Step 3
Most pads at the end of the hoist arms can be rotated to allow for many different types of vehicle construction.
Step 4
The arms of the lifts can be retracted or extended to accommodate vehicles of many different lengths.
Step 5
Most lifts are equipped with short pad extensions that are often necessary to use to allow the pad to contact the frame of a vehicle without causing the arm of the lift to hit and damage parts of the body.
Step 6
Tall pad extensions can also be used to gain access to the frame of a vehicle. This position is needed to safely hoist many pickup trucks,vans,and sport utility vehicles.
(continued)
82
CHAPTER 6
HOISTING THE VEHICLE continued
Step 7
An additional extension may be necessary to hoist a truck or van equipped with running boards to give the necessary clearance.
Step 8
Position the front hoist pads under the recommended locations as specified in the owners manual and for service information for the vehicle being serviced.
Step 9
Position the rear pads under the vehicle under the recommended locations.
Step 10
This photo shows an asymmetrical lift where the front arms are shorter than the rear arms. This design is best used for passenger cars and allows the driver to exit the vehicle easier because the door can be opened wide without it hitting the vertical support column.
Step 11
After being sure all pads are correctly positioned, use the electromechanical controls to raise the vehicle.
Step 12
Raise the vehicle about 1 foot (30 cm) and stop to double-check that all pads contact the body or frame in the correct positions.
Vehicle Lifting and Hoisting
83
HOISTING THE VEHICLE continued
Step 13
With the vehicle raised about 1 foot off the ground, push down on the vehicle to check to see if it is stable on the pads. If the vehicle rocks,lower the vehicle and reset the pads. Be sure the safety is engaged before working on or under the vehicle.
Step 14
This photo shows the pads set flat and contacting the pinch welds of the body.
Step 15
Where additional clearance is necessary for the arms to clear the rest of the body,the pads can be raised and placed under the pinch weld area as shown.
Step 16
When the service work is completed, the hoist should be raised slightly and the safety released before using the hydraulic lever to lower the vehicle.
Step 17
After lowering the vehicle, be sure all arms of the lift are moved out of the way before driving the vehicle out of the work stall.
Step 18
Notice that all of the lift arms have been neatly moved out of the way to provide clearance so that the tires will not contact the arms when the vehicle is driven out of the stall.
84
CHAPTER 6
Summary
1. Whenever a vehicle is raised off the ground, it must be supported using safety stands. 2. Creepers should be stored vertically to prevent the possibility of stepping on it, which could cause a fall and personal injury. 3. Always adhere to the specified hoisting locations as found in service information. 4. Adapters or extensions are often needed when hoisting pickup trucks or vans.
Review Questions
1. Why must safety stands be used after lifting a vehicle with a floor jack? 2. What precautions should be adhered to when storing a creeper? 3. What precautions should be adhered to when hoisting a vehicle?
Chapter Quiz
1. A safety stand is also called a _____. a. Jack b. Jack stand c. Bottle jack d. Safety stool 2. A creeper should be stored _____. a. Vertically b. Under a vehicle c. Flat on the floor d. Upside down on the floor 3. The SAE standard for hoist location is _____. a. J-1980 b. SAE-2009 c. JRP-2184 d. J-14302 4. Tall safety stands would be used to _____. a. Support an engine while the vehicle is hoisted b. Lift a vehicle c. Lift a component such as an engine high off the ground d. Both b and c 5. Commonly damaged areas of a vehicle during hoisting include _____. a. Rocker panels b. Exhaust systems c. Tires or body panels d. All of the above 6. Pad extensions may be needed when hoisting what type of vehicle? a. Small cars b. Pickup trucks c. Vans d. Either b or c 7. Technician A says that a hoist can be stopped at any level as long as the safety latch engages. Technician B says that the vehicle should be hoisted to the top of the hoist travel for safety. Which technician is correct? a. Technician A only b. Technician B only c. Both Technicians A and B d. Neither Technician A nor B
Vehicle Lifting and Hoisting
8. Before lowering the vehicle, what should the technician do? a. Be sure nothing is underneath the vehicle b. Raise the vehicle enough to release the safety latch c. Be sure no one will be walking under or near the vehicle d. All of the above 9. Technician A says that a creeper should be stored vertically. Technician B says that a creeper should be stored on its casters. Which technician is correct? a. Technician A only b. Technician B only c. Both Technicians A and B d. Neither Technician A nor B
85
10. When checking for proper pad placement, how high should the vehicle be raised? a. About 2 inches (5 cm) b. About 6 inches (15 cm) c. About 1 foot (30 cm) d. About 3 feet (91 cm)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Paccar 2010 Multiplexed Electrical System Sevice Manual - (P30-1011)Documento104 paginePaccar 2010 Multiplexed Electrical System Sevice Manual - (P30-1011)gustavo88% (32)
- Alternate Carry ManualDocumento405 pagineAlternate Carry Manualmetallicfoam88% (8)
- NSX1991 Service ManualDocumento1.420 pagineNSX1991 Service ManualRobert LaRueNessuna valutazione finora
- E007 h800xlDocumento21 pagineE007 h800xlHector Peña0% (1)
- Assembly & Operator'S Manual: Liftgator XTR 1200Lbs Removable LiftgateDocumento12 pagineAssembly & Operator'S Manual: Liftgator XTR 1200Lbs Removable LiftgateGilberto Ceballos100% (1)
- John DeereDocumento610 pagineJohn DeereMMM-MMM50% (2)
- Liebherr L544 Operating Manual PDFDocumento247 pagineLiebherr L544 Operating Manual PDFGoran Klemčić100% (4)
- Operator Manual sp4000 Na en PDFDocumento21 pagineOperator Manual sp4000 Na en PDFEmmanuel Chavez VargasNessuna valutazione finora
- Loader Backhoe Student ManualDocumento25 pagineLoader Backhoe Student ManualSanket Pujari100% (2)
- Lift System & EscalatorDocumento18 pagineLift System & EscalatorJamal DinNessuna valutazione finora
- Safe Practices in Operating Fork-Lift TrucksDocumento17 pagineSafe Practices in Operating Fork-Lift TrucksThomas Baby100% (2)
- 777 2 PDFDocumento280 pagine777 2 PDFAlif Yunis S100% (2)
- Rre 250e PDFDocumento366 pagineRre 250e PDFCergey100% (4)
- PLAN-TM-001 5W Traffic Management PlanDocumento84 paginePLAN-TM-001 5W Traffic Management PlanCeek Hanif100% (1)
- Forklift TrainingDocumento29 pagineForklift Trainingmirrao100% (2)
- CAT 777E Vs HD785-7 - CM20161202-52722-10061Documento2 pagineCAT 777E Vs HD785-7 - CM20161202-52722-10061pendekar_hijau100% (1)
- Fassi Crane: Use and MaintenanceDocumento55 pagineFassi Crane: Use and MaintenanceJaime Sua100% (1)
- Forklift Operator Training-VelosiRev0Documento65 pagineForklift Operator Training-VelosiRev0shahbaz akram100% (1)
- Stand Up Forklift Student ManualDocumento37 pagineStand Up Forklift Student ManualBiniyam12100% (2)
- Material Stacker Operator Training-StudentDocumento58 pagineMaterial Stacker Operator Training-Studentshahbaz akramNessuna valutazione finora
- DecantingDocumento2 pagineDecantingPrakash ChoudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Bank Nifty Option Strategies BookletDocumento22 pagineBank Nifty Option Strategies BookletSneha SinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- ENG7cranesgen Volvo Body Builder Cat Crane MountingDocumento13 pagineENG7cranesgen Volvo Body Builder Cat Crane MountingL.kolekar0% (1)
- Epiroc DB40-80 Light Spec Brochure A4 - LoRes - Spreads PDFDocumento7 pagineEpiroc DB40-80 Light Spec Brochure A4 - LoRes - Spreads PDFDavid MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Linde e 16 02 - 335Documento2 pagineLinde e 16 02 - 335Eryx0% (1)
- Forklift SafetyDocumento61 pagineForklift SafetyMohammed AtefNessuna valutazione finora
- Cric Hidraulic Rulant Ian89880 Ro BG El CyDocumento29 pagineCric Hidraulic Rulant Ian89880 Ro BG El CyMBAlexNessuna valutazione finora
- SC4000 Forklift ManualDocumento16 pagineSC4000 Forklift ManualpetromechanicsnjNessuna valutazione finora
- Carga Suspensiones PDFDocumento82 pagineCarga Suspensiones PDFmarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Tipper InstructionDocumento29 pagineTipper InstructionAnangtri WahyudiNessuna valutazione finora
- H2000 5-10t Service and Operation ManualDocumento111 pagineH2000 5-10t Service and Operation ManualArnaldo Benitez100% (1)
- Forklift ReportDocumento18 pagineForklift Reportkalam230% (1)
- Wheel & Hub TTLMDocumento24 pagineWheel & Hub TTLMMeseret SisayNessuna valutazione finora
- MachineS and EquipmentSDocumento19 pagineMachineS and EquipmentSAriel AdriaticoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lift SafetyDocumento3 pagineLift SafetyDiego JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- Vehicle Lift and Support Locations: Introduction - Repair InstructionDocumento4 pagineVehicle Lift and Support Locations: Introduction - Repair InstructionKevin StrongNessuna valutazione finora
- Manteniemiento PeriodicoDocumento41 pagineManteniemiento PeriodicoEmil AlvearNessuna valutazione finora
- Lift Car Hidrolis Dan SelingDocumento32 pagineLift Car Hidrolis Dan SelingMuhammad Arief PrasetyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Installation Instructions: 5568 Rear Anti-Swaybar 67-'69 Camaro & FirebirdDocumento3 pagineInstallation Instructions: 5568 Rear Anti-Swaybar 67-'69 Camaro & Firebirdkkg4782Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ifting Ehicles DescriptionDocumento7 pagineIfting Ehicles DescriptionManiNessuna valutazione finora
- Vehicle Lift and Support Locations: Introduction - Repair InstructionDocumento4 pagineVehicle Lift and Support Locations: Introduction - Repair InstructiondiemnganNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic StabilizationDocumento16 pagineBasic StabilizationGuillermo VilumbralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Bell Cantilever 200 300 ManualDocumento20 pagineBell Cantilever 200 300 Manualjimmie65Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pittsburgh Hydraulic Jack Manual 66482Documento12 paginePittsburgh Hydraulic Jack Manual 66482linx316Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hydraulic Hitch Crane: Owner'S ManualDocumento12 pagineHydraulic Hitch Crane: Owner'S Manualramses9Nessuna valutazione finora
- NORMAS - JACK - STAND - The Ultimate Guide To Industrial Jack Stands - SafeRackDocumento8 pagineNORMAS - JACK - STAND - The Ultimate Guide To Industrial Jack Stands - SafeRackJose Luis FulledaNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual de Servicio y Mantenimiento Serie M Térmica FD200-320T - enDocumento74 pagineManual de Servicio y Mantenimiento Serie M Térmica FD200-320T - enJose ValeroNessuna valutazione finora
- VMR 6SPDocumento24 pagineVMR 6SPLeonard ReinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Report (Tire Change)Documento4 paginePractical Report (Tire Change)Rohan BhanotNessuna valutazione finora
- Ehs Forklift TrainingDocumento100 pagineEhs Forklift TrainingAbdel Rahman SalahNessuna valutazione finora
- Rotary Aro14 - Smo14 Owners ManualDocumento8 pagineRotary Aro14 - Smo14 Owners ManualCarlos Alberto100% (1)
- Challenger Pallet Truck - Instruction ManualDocumento16 pagineChallenger Pallet Truck - Instruction ManualReubz FishingNessuna valutazione finora
- 6000 LB Capacity Portable Mid-Rise Scissor Lift: Operation ManualDocumento28 pagine6000 LB Capacity Portable Mid-Rise Scissor Lift: Operation Manualeu si atatNessuna valutazione finora
- 2009 Hollywood Racks ExpressDocumento6 pagine2009 Hollywood Racks ExpresschristianmseseNessuna valutazione finora
- The Concepts and Specification of Maintainance Ramp For Military VehicleDocumento5 pagineThe Concepts and Specification of Maintainance Ramp For Military VehicleRestu PutraNessuna valutazione finora
- EDocumento8 pagineEiconoclasticjarheadNessuna valutazione finora
- CPCQD Operation ManualDocumento44 pagineCPCQD Operation ManualZii RamNessuna valutazione finora
- J1 - Joey-Operator PDFDocumento24 pagineJ1 - Joey-Operator PDFDmitryNessuna valutazione finora
- Jacking and Lifting - Jacking: Safety PrecautionsDocumento4 pagineJacking and Lifting - Jacking: Safety PrecautionsEimantasNessuna valutazione finora
- CPC (Q) D20-35T3 Operation ManualDocumento40 pagineCPC (Q) D20-35T3 Operation ManualАлександр ФтомовNessuna valutazione finora
- Carga Suspensiones PDFDocumento82 pagineCarga Suspensiones PDFmarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Installation Instructions: 1520 Hoist W/ SubframeDocumento14 pagineInstallation Instructions: 1520 Hoist W/ SubframeHugo RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Auto LiftDocumento32 pagineAuto LiftKs KarthikeyanNessuna valutazione finora
- G3 Series CPD15-20SQ-GE2LiDocumento169 pagineG3 Series CPD15-20SQ-GE2Liuri.cruz.zamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Automotive Workshop Practice 1 Report - AlignmentDocumento8 pagineAutomotive Workshop Practice 1 Report - AlignmentIhsan Yusoff Ihsan0% (1)
- Lift ManualDocumento24 pagineLift Manualnaik_shreyNessuna valutazione finora
- Scissor Jack: 1 Tonne (1000Kg)Documento4 pagineScissor Jack: 1 Tonne (1000Kg)Bruno PowerNessuna valutazione finora
- Santafe 2.7L 2007Documento1.241 pagineSantafe 2.7L 2007Joe TateauNessuna valutazione finora
- Install Manual For PEP50 PDFDocumento44 pagineInstall Manual For PEP50 PDFRafael Sotelo BNessuna valutazione finora
- Du Lackierroboter en LowresDocumento12 pagineDu Lackierroboter en LowresKabil RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Gripper ArmDocumento4 pagineGripper ArmKabil RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Komfi - Delta Sinfgmbmgle SidedDocumento2 pagineKomfi - Delta Sinfgmbmgle SidedKabil RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Compumachine CNC Training VMCDocumento1 paginaCompumachine CNC Training VMCKabil RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Mastercam Transition: V9 To X5: Course DescriptionDocumento1 paginaMastercam Transition: V9 To X5: Course DescriptionKabil RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Bolt Load Analysis / Robotic Arm Simulation Engineering Methods, IncDocumento8 pagineBolt Load Analysis / Robotic Arm Simulation Engineering Methods, IncKabil RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparative Analysis For Link Cross-Section of Manipulator ArmsDocumento24 pagineComparative Analysis For Link Cross-Section of Manipulator ArmsKabil RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Precision Rail-to-Rail Input and Output Operational Amplifiers OP184/OP284/OP484Documento24 paginePrecision Rail-to-Rail Input and Output Operational Amplifiers OP184/OP284/OP484Kabil RajNessuna valutazione finora
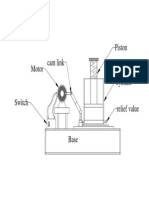
- Hydraulic Jack ModelDocumento1 paginaHydraulic Jack ModelKabil RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Modeling and Intelligent Control of A Robotic Gas Metal Arc Welding SystemDocumento19 pagineModeling and Intelligent Control of A Robotic Gas Metal Arc Welding SystemKabil RajNessuna valutazione finora
- NXDocumento6 pagineNXKabil RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Method For Throttle Holes Area of Telescopic Shock Absorber For Small Electric VehiclesDocumento7 pagineDesign Method For Throttle Holes Area of Telescopic Shock Absorber For Small Electric VehiclesKabil RajNessuna valutazione finora
- International Journal of Industrial Engineering ComputationsDocumento12 pagineInternational Journal of Industrial Engineering ComputationsKabil RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Ahmad Ridzuan Ibrahim (CD 5103)Documento24 pagineAhmad Ridzuan Ibrahim (CD 5103)Kabil RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Construction Companies in KazaksthanDocumento88 pagineConstruction Companies in KazaksthanNeetan SinglaNessuna valutazione finora
- T-90 Single Temp Installation ManualDocumento56 pagineT-90 Single Temp Installation ManualHeriberto Felix PereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Truck or Lorry Rest AreasDocumento5 pagineTruck or Lorry Rest AreasprasadNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamics AssignmentDocumento3 pagineDynamics AssignmentSid MenonNessuna valutazione finora
- TATA T.11 ULTRA DAY Overview - Specs, Features & ImagesDocumento2 pagineTATA T.11 ULTRA DAY Overview - Specs, Features & ImagesTata Light TrucksNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz For TT DriverDocumento8 pagineQuiz For TT DriverGulbarga DepotNessuna valutazione finora
- Travails of Cement TravelDocumento13 pagineTravails of Cement TravelRahul PinnamaneniNessuna valutazione finora
- Wilorton Hiws HybridDocumento20 pagineWilorton Hiws HybridAbdul HadiNessuna valutazione finora
- 14MY Defender Spec Sheet MEDIADocumento6 pagine14MY Defender Spec Sheet MEDIAjohanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2017 RV Trailer Towing GuideDocumento39 pagine2017 RV Trailer Towing GuidePron GoesNessuna valutazione finora
- Training Report of Sonaklika International HoshiarpurDocumento18 pagineTraining Report of Sonaklika International HoshiarpurSurinder palNessuna valutazione finora
- Port User Manual BahrainDocumento107 paginePort User Manual BahrainMohamed ElberryNessuna valutazione finora
- Handwheel To Road Wheel 730039V001Documento79 pagineHandwheel To Road Wheel 730039V001Dinesh Maheshwari100% (1)
- Body Builder Module Programming GuideDocumento50 pagineBody Builder Module Programming GuideAbhinandan PadhaNessuna valutazione finora
- KS 12-19.11.2019 PDFDocumento59 pagineKS 12-19.11.2019 PDFPrasann P'telNessuna valutazione finora
- Liebherr Truck Mounted Concrete Pumps en PDFDocumento16 pagineLiebherr Truck Mounted Concrete Pumps en PDFRidwanda HimawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cat Md6640 Key Specs - c10621591Documento2 pagineCat Md6640 Key Specs - c10621591Dutchie169100% (1)
- P-G-R-T / P-G-R-S Truck: Preventative Maintenance GuideDocumento2 pagineP-G-R-T / P-G-R-S Truck: Preventative Maintenance GuideKANG PRIYONessuna valutazione finora