Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Proper and Safe Use of Scissor Lift
Caricato da
Fajrin M. NatsirCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Proper and Safe Use of Scissor Lift
Caricato da
Fajrin M. NatsirCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Proper and Safe Use of Scissor Lifts
Here are some important tips to help ensure that you use scissor lifts properly:
O Close the platform's doors or chains.
O Never exceed the load-capacity limits of the manufacturer.
O Prevent unauthorized usage such as by locking the aerial lift
O Get written permission from the manufacturer of the scissor lift before making modifications
O Keep the operator's manual at the job site
O Use signs and cones to create work-zone warnings near high traffic areas
O Use proper restraining devices when required
O mplement correct fall-protection for operators
O Never lean over or climb on the guardrails
TOOL INSTALL/CLEAN ROOM SAFETY
1. OBJECTIVE
1.1. This document will outline the best know methods (BKM) Ior establishing and
maintaining tool install/clean room saIety programs during the installation oI process
equipment in a technology or manuIacturing environment.
2. SCOPE
2.1. All CP&E projects that involve tool install activities. As the project transitions Irom
base build to tool install, the emphasize needs to turn to tool install and clean room
saIety.
3. PROCEDURES/EXPECTATIONS
3.1. The tool install saIety program is divided into a number oI elements:
3.2. Subcontract Contracting - Ensure the unique nature oI working in a clean room and
around charged systems are clearly communicated during the contracting phase oI tool
install. SpeciIic procedures, training and equipment will diIIerent Irom standard
construction saIety. Review subcontractor EHS programs to veriIy they have worked in
this environment and have addressed it in their EHS programs and work practices.
3.3. Training - Initial construction saIety orientation training should be replaced with
training that will emphasize the unique hazards associated with operating clean rooms
and associated utility and process support systems. This can be accomplished by
modiIying the exiting construction saIety orientation to address these unique hazards and
expected co-occupancy issues. Depending on the timing oI the change the OP ready
message can also be added to the package at the same time.
3.4. !rocedures - Equipment related procedures need to be in place to ensure process
support systems are leak/pressure tested beIore systems can be turned over Ior use. A
signage system to identiIy when systems are charged needs to be put in place at
the same time. SpeciIic lock and tag protocols Ior electrically energized or charged
systems with chemicals needs to be put in place.
3.5. Work Coordination - As systems are charged and Iuture points oI connection
need to be made, some type oI work coordination meeting needs to be in place. This
may be satisIied through the SIPP process.
3.5.1. Specific Safety !rocedures - SpeciIic saIety procedures need to be put in
place as the tool install process takes place. This can include some oI the
Iollowing items:
3.5.1.1. Ladder use (Iall protection) in clean rooms
3.5.1.2. Working under the raised Iloor
3.5.1.3. Use oI scissors liIts
3.5.1.4. Energized electrical work
3.5.1.5. ConIined spaces
3.5.1.6. PPE
3.5.1.7. Working in and around charged utility systems
3.5.1.8. Material handling
3.5.1.9. Lock out/ tag out
3.5.1.10. Barricades, use oI tape, cones, handrails and toe boards
3.5.1.11. Hazardous materials
4. ROLES/RESPONSIBILITIES
4.1. !rofects EHS Representative - Participate in the development oI the contracting
strategy Ior the tool install general contractor. Ensure the general uses the BKM
contacting selection criteria when developing their bidding lists. Monitor the pre-bid
meetings to ensure the subcontractors clearly understand the unique environment they
will be asked to work in. Ensure contractor senior managers participate on site and chair
the various saIety committees (MAC, SLT).
4.2. General Contractor - The general contractor shall be prepared to demonstrate their
EHS program capability by way oI past projects. This would be speciIic to tool install
and clean room saIety. The overall
program shall include the injury Iree workplace philosophy along with EHS programs
that are outlined above. SpeciIic inIormation needs to be provided in the area oI training,
work place monitoring, equipment and indicators. Hold saIety meetings as needed.
4.3. Sub-contractors - When bidding the work they will address EHS specially in both
programs and dollars to ensure they can adequately support the necessary training,
personnel protective equipment and specialty equipment/materials they will need to make
their work as saIe as possible. They will provide the general contractor an overview oI
their training programs and procedures. They will include a copy oI their training records
Ior specialized training that will not be provided on the project. The subcontractor will
monitor the work area on a continues basis and work to eliminate and obvious hazards.
Each task will be support through planning and coordination with other subcontractors.
Hold saIety meetings as needed.
4.4. Site EHS - Participate in the various training and coordination meetings. This may
include the MAC, SLT, incident reviews as needed.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Heavy Equipment Safety Training HandbookDocumento22 pagineHeavy Equipment Safety Training HandbookFajrin M. Natsir100% (1)
- Working at Height Rescue Plan: WHS-FM-008Documento2 pagineWorking at Height Rescue Plan: WHS-FM-008Purwo PrihartonoNessuna valutazione finora
- Accident Investigation FormDocumento8 pagineAccident Investigation FormagusnurcahyoNessuna valutazione finora
- SWP-SF010A - 6 Daily Vibratory Roller Compactor Rev. ADocumento1 paginaSWP-SF010A - 6 Daily Vibratory Roller Compactor Rev. ACliffordNessuna valutazione finora
- Work Method Statement: Maxworks LTD Montebello, Pailles Mr. Georges Yueng Wye Kong 2086463Documento15 pagineWork Method Statement: Maxworks LTD Montebello, Pailles Mr. Georges Yueng Wye Kong 2086463Vinaye GopaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Brand Identity Style GuideDocumento34 pagineBrand Identity Style Guidesanal123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Falling Hazards in The Workplace - Protection & OSHA Standards PDFDocumento4 pagineFalling Hazards in The Workplace - Protection & OSHA Standards PDFMuhammad MalikNessuna valutazione finora
- Hvac Duct Work Installation Method StatementDocumento3 pagineHvac Duct Work Installation Method StatementSamer Ali0% (1)
- Design Hacking Checklist PDFDocumento2 pagineDesign Hacking Checklist PDFLia MooreNessuna valutazione finora
- Lifting Activity Permit To WorkDocumento1 paginaLifting Activity Permit To WorkBig ZaddyNessuna valutazione finora
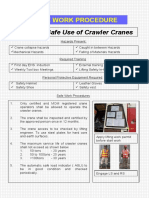
- 3 Safe Use of Crawler CranesDocumento2 pagine3 Safe Use of Crawler CranesSiewkuan LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- PDF Gi 0002721 2016 Arc Flash CompressDocumento23 paginePDF Gi 0002721 2016 Arc Flash CompressMark DingalNessuna valutazione finora
- Caretaker Risk Assessment - Working at HeightDocumento8 pagineCaretaker Risk Assessment - Working at HeightLina MarcelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Jardin Vs NLRCDocumento2 pagineJardin Vs NLRCEarvin Joseph BaraceNessuna valutazione finora
- MOS 2x15T EOTC Robotic ShopDocumento17 pagineMOS 2x15T EOTC Robotic ShopJohn Rey PerlasNessuna valutazione finora
- 8-22 Roller Shutter Door OHS TemplateDocumento11 pagine8-22 Roller Shutter Door OHS Templatemsc920138Nessuna valutazione finora
- Work Method Statements For Reed SelectDocumento53 pagineWork Method Statements For Reed SelectInoe InaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Komatsu Wheel Loader D21A - P-8E0 - D21P-8E0Documento6 pagineKomatsu Wheel Loader D21A - P-8E0 - D21P-8E0Fajrin M. Natsir100% (1)
- Doka FormworkDocumento124 pagineDoka FormworkTranタオNessuna valutazione finora
- DCL (Logo) : Hand BookDocumento16 pagineDCL (Logo) : Hand BookJahangir ShaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fall Prevention Plan: (Only Applicable To Contractor That Have Work Activities More Than 03 Meters and Above.)Documento21 pagineFall Prevention Plan: (Only Applicable To Contractor That Have Work Activities More Than 03 Meters and Above.)Md ShahinNessuna valutazione finora
- Proper and Safe Use of Scissor LiftsDocumento3 pagineProper and Safe Use of Scissor LiftsJulius SablayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Liebherr Floating Transfer Solutions OverviewDocumento16 pagineLiebherr Floating Transfer Solutions OverviewFajrin M. NatsirNessuna valutazione finora
- 37.2 Agreement Between Employer and MandatoryDocumento15 pagine37.2 Agreement Between Employer and MandatorykkNessuna valutazione finora
- Milling MachineDocumento1 paginaMilling MachineJeannie TimothyNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk Assessment MV Power Cables & Accessories InstallationDocumento10 pagineRisk Assessment MV Power Cables & Accessories InstallationAdil HasanovNessuna valutazione finora
- APPENDIX 1 Issues For Method Statements in Industrial Roof WorkDocumento3 pagineAPPENDIX 1 Issues For Method Statements in Industrial Roof WorkJulianna BakerNessuna valutazione finora
- Brochure Cutter Suction Dredger 01 2016Documento2 pagineBrochure Cutter Suction Dredger 01 2016Fajrin M. NatsirNessuna valutazione finora
- 675Documento2 pagine675Rameese MuhammedNessuna valutazione finora
- HPK Brochure English Reprint DCI III PDFDocumento6 pagineHPK Brochure English Reprint DCI III PDFFajrin M. NatsirNessuna valutazione finora
- p021.46 Db54 Mat Mep Mech 022 Ventilation FansDocumento95 paginep021.46 Db54 Mat Mep Mech 022 Ventilation Fansp4p7 projectsNessuna valutazione finora
- Method Ststement For Chiller ErectionDocumento7 pagineMethod Ststement For Chiller Erectionk md adnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Crown Rr5700 SpecsDocumento6 pagineCrown Rr5700 SpecsFajrin M. Natsir100% (1)
- TAKRAF Bulk Material Handling EngDocumento16 pagineTAKRAF Bulk Material Handling EngFajrin M. NatsirNessuna valutazione finora
- Toolboxtalk2 Housekeeping PDFDocumento2 pagineToolboxtalk2 Housekeeping PDFSajid HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Lifting Equipment at Work: A Brief GuideDocumento8 pagineLifting Equipment at Work: A Brief GuideEka KurniawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Samuk ForkliftDocumento14 pagineSamuk ForkliftFajrin M. NatsirNessuna valutazione finora
- Confined Spaces Standard Operating Procedure and Permit CombinedDocumento8 pagineConfined Spaces Standard Operating Procedure and Permit CombinedRaza Muhammad SoomroNessuna valutazione finora
- F 10Documento6 pagineF 10tonylundyNessuna valutazione finora
- Confined Space EntryDocumento8 pagineConfined Space EntryJoy WilsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Scissor Lift - HseDocumento4 pagineScissor Lift - HserassdriverNessuna valutazione finora
- Land PreparationDocumento2 pagineLand PreparationDiana Daina80% (5)
- Kathy Harris A Maturity Model For InnovationDocumento13 pagineKathy Harris A Maturity Model For InnovationUndecidedOne100% (1)
- BOMAQ BF 300 Finisher FinisherDocumento16 pagineBOMAQ BF 300 Finisher FinisherFajrin M. NatsirNessuna valutazione finora
- Index: Cv. Dira Utama SejahteraDocumento12 pagineIndex: Cv. Dira Utama SejahteraFreshop SurabayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Safe System of Work - Method StatementDocumento5 pagineSafe System of Work - Method StatementNishar BalkavadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Hse - The Selection and Management of Mobile Elevating Work PlatformsDocumento6 pagineHse - The Selection and Management of Mobile Elevating Work PlatformsrewmarineNessuna valutazione finora
- Evr J0100 Msra CL 02Documento10 pagineEvr J0100 Msra CL 02Marwan NizarNessuna valutazione finora
- Method Statement PDFDocumento2 pagineMethod Statement PDFAl Manar PetroleumNessuna valutazione finora
- WMS For Fire Fighting Line and SupportsDocumento4 pagineWMS For Fire Fighting Line and SupportsAbdul Rehman Sheikh100% (1)
- M.O.S DismantlingDocumento18 pagineM.O.S DismantlingAhmed Khaled100% (1)
- Working at HeightDocumento28 pagineWorking at HeighteustaquipaixaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Painting, Taping, Texturing or Epoxy CoatingsDocumento1 paginaPainting, Taping, Texturing or Epoxy CoatingsHenryOdohNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Scaffold Inspection ChecklistDocumento3 pagineMobile Scaffold Inspection Checklistanthony murphyNessuna valutazione finora
- SWP Working Safely at Height Version 2.01Documento7 pagineSWP Working Safely at Height Version 2.01marvinNessuna valutazione finora
- Building De-Dusting JSADocumento3 pagineBuilding De-Dusting JSAJayesh J PillaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Method Statement For Light Beacons and Buoys C04Documento93 pagineMethod Statement For Light Beacons and Buoys C04Olugbemiga James OlalekanNessuna valutazione finora
- Loto FormDocumento9 pagineLoto FormJoey GNessuna valutazione finora
- SOP For Working at HeightDocumento18 pagineSOP For Working at HeightWasim AkramNessuna valutazione finora
- Osh Communication: Document ID: MSP-005Documento7 pagineOsh Communication: Document ID: MSP-005Kingsley AhanonuNessuna valutazione finora
- Permit To Work Policy ProcedureDocumento7 paginePermit To Work Policy ProcedureChristian Auditor RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Tumbarumba Rail Trail Biosecurity Risk AssessmentDocumento9 pagineTumbarumba Rail Trail Biosecurity Risk AssessmentSimon McCarthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Njqs Core Audit Module - Rev1.6cDocumento14 pagineNjqs Core Audit Module - Rev1.6cNene UmohNessuna valutazione finora
- General Safety Inspection ChecklistDocumento1 paginaGeneral Safety Inspection ChecklistAyşe BalamirNessuna valutazione finora
- 42 Rigging 1. Procedure 1. Rigging SafetyDocumento15 pagine42 Rigging 1. Procedure 1. Rigging SafetyGopal ChoudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Work at Heights Self Assessment SheetDocumento4 pagineWork at Heights Self Assessment SheetBalogun IsaacNessuna valutazione finora
- Hot Work ProcedureDocumento6 pagineHot Work ProcedureSCOTTNessuna valutazione finora
- General Site Safety - SignDocumento1 paginaGeneral Site Safety - SignVũ GiangNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is The Difference Between TstiDocumento4 pagineWhat Is The Difference Between TstiFortuna HunilaNessuna valutazione finora
- 980 Behavior Based Safety Program PDFDocumento2 pagine980 Behavior Based Safety Program PDFherik0% (1)
- Ocp BatchingDocumento1 paginaOcp BatchingAarya Mishra TiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Method Statement For Gypsum Panels WorkDocumento8 pagineMethod Statement For Gypsum Panels WorkNikita KasyanovNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus Belt ConveyorDocumento3 pagineSyllabus Belt ConveyorFajrin M. NatsirNessuna valutazione finora
- Kumpulan Mesin PancangDocumento48 pagineKumpulan Mesin PancangFajrin M. NatsirNessuna valutazione finora
- Sellick Equipment Limited - S Series Rough Terrain Forklift - Standard FeaturesDocumento2 pagineSellick Equipment Limited - S Series Rough Terrain Forklift - Standard FeaturesFajrin M. Natsir100% (1)
- Silabus Pita Transport Kemenaker Ri 2009Documento1 paginaSilabus Pita Transport Kemenaker Ri 2009Fajrin M. NatsirNessuna valutazione finora
- Forklift PatriaDocumento4 pagineForklift Patriahasyim_dmkNessuna valutazione finora
- Rendez Scaffolding CatalogueDocumento40 pagineRendez Scaffolding CatalogueFajrin M. NatsirNessuna valutazione finora
- Canadian Boat Operator Competency Requirements For U.S. ResidentsDocumento1 paginaCanadian Boat Operator Competency Requirements For U.S. ResidentsFajrin M. NatsirNessuna valutazione finora
- Forklift - WikipediaDocumento10 pagineForklift - WikipediaFajrin M. NatsirNessuna valutazione finora
- Facts About Dredging and SafetyDocumento4 pagineFacts About Dredging and SafetyFajrin M. NatsirNessuna valutazione finora
- JCB Tracked Robot Loaders 190T1110TDocumento6 pagineJCB Tracked Robot Loaders 190T1110TFajrin M. NatsirNessuna valutazione finora
- Manitou 105VJR2 Manlift: General DescriptionDocumento4 pagineManitou 105VJR2 Manlift: General DescriptionFajrin M. NatsirNessuna valutazione finora
- Products Damen Com en Ranges Cutter Suction Dredger Csd650Documento17 pagineProducts Damen Com en Ranges Cutter Suction Dredger Csd650Fajrin M. NatsirNessuna valutazione finora
- Damen Cutter Suction Dredger 650Documento2 pagineDamen Cutter Suction Dredger 650Fajrin M. NatsirNessuna valutazione finora
- Production Planning Monthly Schedules: Value Stream MappingDocumento1 paginaProduction Planning Monthly Schedules: Value Stream MappingpranayNessuna valutazione finora
- The Core PrinciplesDocumento26 pagineThe Core PrinciplesAbed HossainNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Trading ICO Due DilligenceDocumento29 pagineAdvanced Trading ICO Due DilligenceciciyNessuna valutazione finora
- Data-Driven Insurance: Ready For The Next Frontier?Documento52 pagineData-Driven Insurance: Ready For The Next Frontier?Harry CerqueiraNessuna valutazione finora
- 2018 Q1 Net Lease Research Report - The Boulder GroupDocumento3 pagine2018 Q1 Net Lease Research Report - The Boulder GroupnetleaseNessuna valutazione finora
- CV - Bhupendra SinghDocumento3 pagineCV - Bhupendra SinghTejas LakhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Schedule Bsa II - ADocumento2 pagineSchedule Bsa II - AKier BatacNessuna valutazione finora
- Bulk SMS Service - SmsmenowDocumento2 pagineBulk SMS Service - Smsmenowsmsmenow jprNessuna valutazione finora
- Od428020695557784100 1Documento1 paginaOd428020695557784100 1Rájñîsh MôñdālNessuna valutazione finora
- Project - File of Electricity Biling SystemDocumento10 pagineProject - File of Electricity Biling SystemNiraj GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- b392 Tma - Summer 2023 - QQQQDocumento5 pagineb392 Tma - Summer 2023 - QQQQadel.dahbour97Nessuna valutazione finora
- Steven Lim & Associates ProfileDocumento6 pagineSteven Lim & Associates ProfileReika KuaNessuna valutazione finora
- GSIS TEMPLATE Fire Insurance Application Form (TRAD)Documento3 pagineGSIS TEMPLATE Fire Insurance Application Form (TRAD)Ronan MaquidatoNessuna valutazione finora
- CB Segmentation FinalDocumento18 pagineCB Segmentation FinalBipasha NayakNessuna valutazione finora
- Scholars Contract and LOIDocumento4 pagineScholars Contract and LOIMisha Madeleine GacadNessuna valutazione finora
- Ben & Jerrys AssignmentDocumento4 pagineBen & Jerrys AssignmentNgan Anh DoanNessuna valutazione finora
- CMR Technologies DriveDocumento4 pagineCMR Technologies DriveHunter UnitedNessuna valutazione finora
- FBKetjutekniikka - EN - 30102014 - Vedos Drag ChainDocumento13 pagineFBKetjutekniikka - EN - 30102014 - Vedos Drag ChainJona SiahaanNessuna valutazione finora
- Oracle Workforce Scheduling User Guide For Corporate ProfileDocumento29 pagineOracle Workforce Scheduling User Guide For Corporate ProfilejayNessuna valutazione finora
- PI-9003520-Mitali Fashions Limited - Self-SGS CTPAT-Announced-Iinitial-AC Fty.Documento1 paginaPI-9003520-Mitali Fashions Limited - Self-SGS CTPAT-Announced-Iinitial-AC Fty.Faruque UddinNessuna valutazione finora
- A Study On V-Guard Industries Limited With Special: Reference To Finance DepartmentDocumento5 pagineA Study On V-Guard Industries Limited With Special: Reference To Finance DepartmentSruthy psNessuna valutazione finora
- Ebusiness & Marketing Fundamentals - AssessmentDocumento6 pagineEbusiness & Marketing Fundamentals - AssessmentAhmed HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Loadstar Shipping vs. Pioneer AsiaDocumento7 pagineLoadstar Shipping vs. Pioneer AsiaKrisleen AbrenicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Viewtinet Presentación Big Data BIDocumento21 pagineViewtinet Presentación Big Data BIMari CarmenNessuna valutazione finora
- BRCGS - Baltic SticksDocumento2 pagineBRCGS - Baltic SticksClaudiaNessuna valutazione finora