Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Go Tsl3109
Caricato da
Muhammad Sanusi Bin IsmailDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Go Tsl3109
Caricato da
Muhammad Sanusi Bin IsmailCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT
TSL 3109
DEFINITIONS:
The idea that everyone should have equal rights and should be involved in making decision
DEMOCRATIC
ASSERTIVE
A form of communications in which needs of wishes are started clearly with respect for oneself and the other person in the interactions
Any of various devices designed to teach by presenting the student with a planned sequence of statements and questions and providing an immediate INSTRUCTIONAL response to his or her answers
Prepared by: TENGKU SYAKIRAH BT. TENGKU DZARIFF MUHAMMAD SANUSI B. ISMAIL
CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT
TSL 3109
Democratic Teaching - RUDOLF DREIKURS
Born in Vienna, Austria Educated at University Of Vienna Student and colleague of social psychiatrist, Alfred Alder. Immigrated to U.S in 1937. Founded the Alfred Alder institute of Chicago. Author of several books designed for parents and teacher on child behaviour and positive discipline. Pioneered Positive (Judicious) discipline.
Instructional Management - JACOB KOUNIN
Behaviourist theorist best known for his two studies done in 1970 he wrote the book, "Discipline And Group Management In Classrooms" worked to combined both discipline and learning in the classroom. believed that organization and planning are keys to engaging students. this relationship is characterized by proactive teacher behaviour along with the students involvement in learning.
Assertive Tactics - LEE AND MARLENE CANTER
Lee attended Californian State University. Then completed a master"s Degree in social work at the University of Southern California. 1970 - began serving as a psychiatric sovial worker for children in Southern California. Lee passion for helping children succeed in the classroom led to the research and development of his well-known Assertive Discipline Programe. Marlene worked with her husband,to help other educators address classroom management challenges. their strategies formed the basis for Lee Canter's groundbreaking book Assertive Discipline, and Ultimate of Canter And Associates in 1976
Prepared by: TENGKU SYAKIRAH BT. TENGKU DZARIFF MUHAMMAD SANUSI B. ISMAIL
CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT
TSL 3109
Descriptions Of Theories
ASSERTIVE TACTICS
a systematics and objectives way of ensuring a teacher controlled classroom. also called the "take - control" approach to teaching, as the teacher controls their classroom in a firm but positive manner. requires teachers to be assertive rather than passive or hostile (teacher-controlled) teacher creates a set of behaviour rules for the class and a set of negative consequences that result if the rules are not followed.
INSTRUCTIONAL MANAGEMENT
effective teaching includes group alerting and accountability, high participation and smooth transitions, effective teachers are "with it", use the ripple effect, overlapping, and they don't 'dangle' , 'flip-flop' or get distracted. "withitness" means the teacher knows what is going onat all times in the classroom. momentum keeps the students engaged. students may experience satiation when they have been over exposed to a certain topic or strategy. provide students with enjoyable and challenging lessons.
DEMOCRATIC TEACHING
classroom are democratic with appropriate teaching styles. mutual respect motivates pupils to behave constructively. praise supports completion. encouragement supports the process. logical consequences produce better results than punishment.
Prepared by: TENGKU SYAKIRAH BT. TENGKU DZARIFF MUHAMMAD SANUSI B. ISMAIL
CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT
TSL 3109
APPROACHES / STRATEGIES OF THEORIES
ASSERTIVE TACTICS
decide which rules ( 4 or 5 are best ) you wish to implement in your classroom for example ; raise up their hands when answering questions, do not disturb others, speak in english, be quiet when the teacher is speaking. determine negative consequences for noncompliance for example; time out or extra homework. determine positive consequences for appropriate behaviour such as verbal praise or giving stars. list the rules on the board along with the positive and negative consequences have the students write the rules and take them home to be signed by the parents and returned to the teacher.
DEMOCRATIC TEACHING
provide lessons with social interest in mind. provide a teaching environment that supports pupils sense of belonging. come up with a set of classroom rules as a group. support responsibility through freedom of choices in lesson plans. avoid power struggles and encourage pupils who display inadequacy. encourage pupils rather than praise them. provide pupils with logical consequences to "mistaken goals" to support responsibility and avoid punishment.
INSTRUCTIONAL MANAGEMENT
"whititness" - scan constantly, make notes of repeated behaviours, get to know the students on a personal level, keep moving through the classroom. do not follow for dead time during transitions. keep momentum by keeping the students engaged in some activity at all time. give lesson multiple times and assess yourself during the teaching. ask students questions to make sure they are not experiencing satiation. ask students their input before planning lessons - what interests them/ what they want to learn / what challenging techniques do they want to learn.
Prepared by: TENGKU SYAKIRAH BT. TENGKU DZARIFF MUHAMMAD SANUSI B. ISMAIL
CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT
TSL 3109
STRENGHTS AND WEAKNESSES OF THE THEORIES
ASSERTIVE TACTICS
STRENGTHS Foundation of mutual trust and positive relationship with students and earn their respect. Develop good class control. Students expectations are clearly stated. Rules and limitations are also clearly stated. No interruptions from students during teaching and learning session. Simple and wellstructured plan. Teachers are in power to control the students. Punishment will make students avoid breaking rules and positive reinforcement will encourage good behaviour. Positive , caring and productive classroom environment.
WEAKNESSES will not work without positive relationship and respect. Teaching style not fit the students needs. Can be bad way. Teacher might over controlling. Minimal students interactions. This approach fails to promote selfdirections in students. Students are not allowed to give ideas. negatives consequences or punishment stimulates rebellion. The practice of warning may entice some students to misbehave.
Prepared by: TENGKU SYAKIRAH BT. TENGKU DZARIFF MUHAMMAD SANUSI B. ISMAIL
CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT
TSL 3109
STRENGHTS AND WEAKNESSES OF THE THEORIES
INSTRUSCTIONAL MANAGEMENT
WEAKNESSES Teacher can lose track of time when performing a lesson. Teacher can get distracted by students or other outside variables (the phones rings, someone walks into the classroom) The teachers eye cannot be every student at all times. The teacher cannot always point out a students strength/weaknesse s. The teacher cannot always get every student involved in a lesson. The teacher can loose control over a disruptive students
STRENGTHS Present methods of withitness and organization that teachers can use in the classroom. Group alerting gains the attention of students. Overlapping provides teachers with control over several activities. Teachers that make lessons more interesting avoid satiation. Teachers develop a pace with their class to achieve a precise momentum to teach a lesson appropriately. Help extinguish misbehaviour.
Prepared by: TENGKU SYAKIRAH BT. TENGKU DZARIFF MUHAMMAD SANUSI B. ISMAIL
CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT
TSL 3109
STRENGHTS AND WEAKNESSES OF THE THEORIES
DEMOCRATIC TEACHING
WEAKNESSES STRENGTHS It promotes mutual respect between the teacher and students. It helps students to learn and correct their misbehaviour. This model incorporates a preventive approach to discipline. Relies on logical consequences instead of arbitrary punishments ( unreasonable or unfair punishment )and systematic reinforcement. clear logical consequences cant be arrived at for all behaviour for all students. Teachers have troubles determining the actual motives on their students. it takes a long time to build up students trust . teachers may have problem dealing with the complexity of engaging in a dialogue with their students.
Prepared by: TENGKU SYAKIRAH BT. TENGKU DZARIFF MUHAMMAD SANUSI B. ISMAIL
CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT
TSL 3109
PRACTICALITY OF THE THEORIES IN A LOCAL ESL CLASSROOM.
DEMOCRATIC TEACHING
ESL classes allow pupils to work in small groups and as a large group to support social group belonging. social group s can take place in criticism, aesthetic, and productions. allow time for each of these. encourage pupils who seem discouraged in the process of a product, rather than praising them for their completion. in group critiques, ask about process rather than focusing on the final product by itself.
INSTRUCTIONAL MANAGEMENT
in an ESL classroom, wiyhitness is very important because teacher is constantly scanning the classroom and observing whether pupils are using English Language while communicating with their friends. group work is a great time to move throughout the classroom and make sure that everyone is on task and understands the material. enjoyable and challenging lessons go hand in hand with ESL classes. teacher can ask pupils what challenges them the most and what they want to learn.
simple for applications. focus on teacher's desire. parents and administrators are involved in discipline process.
ASSERTIVE TACTICS
Prepared by: TENGKU SYAKIRAH BT. TENGKU DZARIFF MUHAMMAD SANUSI B. ISMAIL
CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT
TSL 3109
APPEAL
INSTRUCTIONAL MANAGEMENT
teacher prevent misbehaviours through awareness in the classroom and by using effective lesson management techniques (pupil movement, group awareness, smoothness of lesson delivery)to influence pupils behaviour.
DEMOCRATIC TEACHING
teachers promote pupils seldiscipline in a democratic classroom where pupils and teachers make a decisions on how the class will work pupil behaviour is goal directed and all pupils want to belong. pupils misbehae out of mistaken goal. teacher use logical consequences and encouragement instead of praise, and should never use punishment.
ASSERTIVE TACTICS
the teachers and pupils have right s in the classroom. clear rules of behaviour and expectations are written and enforced through a discipline hierarchy of consequences.
Prepared by: TENGKU SYAKIRAH BT. TENGKU DZARIFF MUHAMMAD SANUSI B. ISMAIL
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Theories of Democratic Teaching (Rudolf Dreikurs)Documento40 pagineTheories of Democratic Teaching (Rudolf Dreikurs)Hamizah Jaffar88% (8)
- Class Management 12Documento16 pagineClass Management 12Sasirekha RajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Rodolfo M. Evasco, JR.: Buhang NHS, Buhang, Bulusan, Sorsogon Secondary School Principal IIDocumento55 pagineRodolfo M. Evasco, JR.: Buhang NHS, Buhang, Bulusan, Sorsogon Secondary School Principal IIAlex Sanchez100% (1)
- Effective Classroom ManagementDocumento33 pagineEffective Classroom ManagementDENNIS RAMIREZNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom Management TheoriesDocumento16 pagineClassroom Management TheoriesRitchel PeterNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom Management EslDocumento37 pagineClassroom Management EslHariz SaveGazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Democratic Teaching (Rudolf Dreikurs)Documento14 pagineDemocratic Teaching (Rudolf Dreikurs)Farah Nadia100% (1)
- Classroom ManagementDocumento50 pagineClassroom ManagementGeorgia Benjamin100% (1)
- TSL 3109: Managing The Primary ESL ClassroomDocumento43 pagineTSL 3109: Managing The Primary ESL ClassroomNesamani Raja RetanamNessuna valutazione finora
- Tsl3109 GoDocumento6 pagineTsl3109 GosengihNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom Management Presentation 120712190047 Phpapp02Documento36 pagineClassroom Management Presentation 120712190047 Phpapp02Nazmul Al-deenNessuna valutazione finora
- Theories of Congruent CommunicationDocumento13 pagineTheories of Congruent CommunicationMuhammad Aman HasbullahNessuna valutazione finora
- 17 Conducve Learning EnvironmentDocumento101 pagine17 Conducve Learning EnvironmentZul Aiman Abd WahabNessuna valutazione finora
- Theories of Assertive TacticsDocumento24 pagineTheories of Assertive TacticsNursha- Irma50% (2)
- Tam2601 Assignment 2Documento7 pagineTam2601 Assignment 2Thembi AliceNessuna valutazione finora
- Teachers Lessons Disruptive Behavior Students: 11 Techniques For Better Classroom DisciplineDocumento12 pagineTeachers Lessons Disruptive Behavior Students: 11 Techniques For Better Classroom Disciplinejames christian castillonNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 Classroom Management and Instruction 7Documento27 pagine8 Classroom Management and Instruction 7khush sidhuNessuna valutazione finora
- The Teacher in The Classroom and CommunityDocumento21 pagineThe Teacher in The Classroom and Communitywarda mahumNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom Management YeniiiiiiDocumento39 pagineClassroom Management YeniiiiiiorkocamanNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom Management EnsonDocumento56 pagineClassroom Management EnsonorkocamanNessuna valutazione finora
- Competent TeachersDocumento2 pagineCompetent TeachersMicko Quinto100% (8)
- Written Report Educ 4aDocumento2 pagineWritten Report Educ 4aFlorian GutierrezNessuna valutazione finora
- 'Classroom Management Full Version - Part 2Documento33 pagine'Classroom Management Full Version - Part 2Amirah Najihah AzisNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom Management:: How To Be An Effective Teacher and Impact Student LivesDocumento27 pagineClassroom Management:: How To Be An Effective Teacher and Impact Student LivesSasirekha RajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Theories of Assertive TacticsDocumento24 pagineTheories of Assertive TacticsvickyktNessuna valutazione finora
- My Report - PPTX (Autosaved)Documento57 pagineMy Report - PPTX (Autosaved)ClaireXDNessuna valutazione finora
- Theories of Instructional Management: PISMP 5.08Documento35 pagineTheories of Instructional Management: PISMP 5.08TOMNessuna valutazione finora
- The Glasser Model of Student Choice and NeedsDocumento27 pagineThe Glasser Model of Student Choice and NeedsAdila FazleenNessuna valutazione finora
- General Methods of Teaching Semester: Autumn 2020 Program: B.Ed 1.5 Years Course Code: 8601Documento13 pagineGeneral Methods of Teaching Semester: Autumn 2020 Program: B.Ed 1.5 Years Course Code: 8601Waqas AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching English To Young LearnersDocumento42 pagineTeaching English To Young LearnersmarcelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Jacob Kounin-Instructional Management TheoryDocumento35 pagineJacob Kounin-Instructional Management TheoryTerrance Castro100% (35)
- Classroom Management StrategiesDocumento12 pagineClassroom Management StrategiesMuhammad AzfarNessuna valutazione finora
- Developing Classroom Management Skills in The Cooperative Language Learning ClassroomDocumento32 pagineDeveloping Classroom Management Skills in The Cooperative Language Learning ClassroomRinaldi AfriyantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Traditional and Contemporary EducationDocumento27 pagineTraditional and Contemporary Educationmary mae llorenteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.classroom ManagementDocumento28 pagine1.classroom ManagementHarley SulmanNessuna valutazione finora
- ESEIDocumento3 pagineESEINur Atikah NasrudinNessuna valutazione finora
- EDU105.19 Module1Documento17 pagineEDU105.19 Module1ROSEMARY K PNessuna valutazione finora
- Harry Wong ReadingDocumento8 pagineHarry Wong ReadingMsE2013100% (2)
- Classroom Discipline TechniquesDocumento10 pagineClassroom Discipline TechniquesvincentNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom MGT Theorists 2Documento125 pagineClassroom MGT Theorists 2Tay Hang CheanNessuna valutazione finora
- DeepenDocumento4 pagineDeepenlerma bisagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8Documento4 pagineChapter 8Lichelle Calicdan AlcantaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom ArrangementsDocumento20 pagineClassroom ArrangementsjuliuslapazNessuna valutazione finora
- Love and Logic 2Documento18 pagineLove and Logic 2nedaa aliNessuna valutazione finora
- Competent Teachers - Joan - Marissa ReportDocumento15 pagineCompetent Teachers - Joan - Marissa ReportMarissa Malobago - PascasioNessuna valutazione finora
- School ManagementDocumento4 pagineSchool ManagementFrancis D. MagsipocNessuna valutazione finora
- Social StudiesDocumento18 pagineSocial StudiesCRYSTAL JADE MUCASNessuna valutazione finora
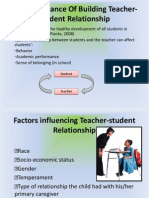
- Student Teacher RelationshipDocumento10 pagineStudent Teacher RelationshipNur Azimah LamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroon Management FINAL WORKDocumento17 pagineClassroon Management FINAL WORKleonardo dNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom Management Plan: Donna Muschamp, Francisco Ical & Ramiro Coc EDUC 324 UB-ToledoDocumento15 pagineClassroom Management Plan: Donna Muschamp, Francisco Ical & Ramiro Coc EDUC 324 UB-ToledochongssschNessuna valutazione finora
- Section 2 Professional Teachers Are Competent Chapter 4Documento29 pagineSection 2 Professional Teachers Are Competent Chapter 4Carmelli Ann GallardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom management techniques for engaged learningDocumento10 pagineClassroom management techniques for engaged learninglily100% (2)
- Task 2. Critical AnalysisDocumento8 pagineTask 2. Critical AnalysisHulk Hijau100% (1)
- The Kounin Model of DisciplineDocumento28 pagineThe Kounin Model of DisciplineNurulFatihahAzemi0% (1)
- IdeasDocumento9 pagineIdeasAshrafNessuna valutazione finora
- The Teacher's Role in and Beyond the ClassroomDocumento25 pagineThe Teacher's Role in and Beyond the ClassroomTimoy CajesNessuna valutazione finora
- A.T.A.P How to Achieve a Workable Classroom Environment: In a Core Curriculum Classroom (Grades Pre-K Through 8Th and Special Education) (A Book of Strategies and Research)Da EverandA.T.A.P How to Achieve a Workable Classroom Environment: In a Core Curriculum Classroom (Grades Pre-K Through 8Th and Special Education) (A Book of Strategies and Research)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Top Ten Strategies for Student Engagement: How to Make the Most of Your Time with Your StudentsDa EverandTop Ten Strategies for Student Engagement: How to Make the Most of Your Time with Your StudentsNessuna valutazione finora
- Social ExpressionsDocumento17 pagineSocial ExpressionsMuhammad Sanusi Bin IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- 1000 Cuvinte EnglezaDocumento10 pagine1000 Cuvinte EnglezaNotar SorinNessuna valutazione finora
- WorksheetDocumento1 paginaWorksheetMuhammad Sanusi Bin IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Go Tsl3109Documento9 pagineGo Tsl3109Muhammad Sanusi Bin IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Match The Picture With The Correct SoundsDocumento4 pagineMatch The Picture With The Correct SoundsMuhammad Sanusi Bin IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- ClassDocumento13 pagineClassBeni LanuzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dilly Duck Has A Doll. Dino Dog Digs A Hole. Dino Takes Dilly's Dol Dilly Duck Is Sad and MadDocumento2 pagineDilly Duck Has A Doll. Dino Dog Digs A Hole. Dino Takes Dilly's Dol Dilly Duck Is Sad and MadMuhammad Sanusi Bin IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- TSL 3109Documento27 pagineTSL 3109Muhammad Sanusi Bin IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- PosterDocumento7 paginePosterMuhammad Sanusi Bin IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Sekolah Kebangsaan Pauh Sembilan, Bachok, Kel: Activity Teaching and Learning Strategies Impact Picture StimulusDocumento4 pagineSekolah Kebangsaan Pauh Sembilan, Bachok, Kel: Activity Teaching and Learning Strategies Impact Picture StimulusMuhammad Sanusi Bin IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- January THN 2Documento2 pagineJanuary THN 2Muhammad Sanusi Bin IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Sekolah Kebangsaan Pauh Sembilan, Bachok, Kel.: Activity Teaching and Learning Strategies Impact Picture StimulusDocumento4 pagineSekolah Kebangsaan Pauh Sembilan, Bachok, Kel.: Activity Teaching and Learning Strategies Impact Picture StimulusMuhammad Sanusi Bin IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Calf Cow: Iama - The Is My MotherDocumento7 pagineCalf Cow: Iama - The Is My MotherMuhammad Sanusi Bin IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Bachok Kelantan.: Activity T & L Strategies Notes Sing A SongDocumento3 pagineBachok Kelantan.: Activity T & L Strategies Notes Sing A SongMuhammad Sanusi Bin IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Peta MindaDocumento2 paginePeta MindaMuhammad Sanusi Bin IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- Thinking Assignment 3 - Piaget's Developmental StagesDocumento9 pagineThinking Assignment 3 - Piaget's Developmental StagesJena Bailey NymanNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Management 12th Edition by Schermerhorn Sample ChapterDocumento26 pagineTest Bank For Management 12th Edition by Schermerhorn Sample ChapterAndrea NovillasNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 Applied Social ScienceDocumento3 pagineChapter 1 Applied Social ScienceTrisha DoriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Appreciating Artistry in Chekhov's "A Day in the CountryDocumento4 pagineAppreciating Artistry in Chekhov's "A Day in the CountryJohnny Xavier Dee100% (2)
- Module 1 Concept and Nature of SelfDocumento10 pagineModule 1 Concept and Nature of SelfKrizha SisonNessuna valutazione finora
- FS 1 - Topic 1 The School As A Learning EnvironmentDocumento5 pagineFS 1 - Topic 1 The School As A Learning EnvironmentMa. Arnelyn AniNessuna valutazione finora
- Mental Health Nursing GuideDocumento32 pagineMental Health Nursing GuideMegha V Kurian60% (5)
- Premature Termination in Psychotherapy PDFDocumento221 paginePremature Termination in Psychotherapy PDFDAN NICOLAE MORAR100% (1)
- Reading Module at University of Eastern PhilippinesDocumento13 pagineReading Module at University of Eastern PhilippinesBernard CegarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Study of Quality of Work Life (QWL) : G Nasl Saraji, H DargahiDocumento7 pagineStudy of Quality of Work Life (QWL) : G Nasl Saraji, H DargahiVaishnavi RamanujanNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment of Learning 1 PPT 1 DelivaDocumento26 pagineAssessment of Learning 1 PPT 1 DelivaRey LeoninNessuna valutazione finora
- Personal Development Insights Help Career ChoicesDocumento11 paginePersonal Development Insights Help Career ChoicesLynette LicsiNessuna valutazione finora
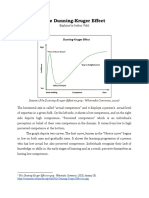
- What Is Dunning-Kruger EffectDocumento5 pagineWhat Is Dunning-Kruger EffectJoshua VidalNessuna valutazione finora
- Placebo EffectDocumento3 paginePlacebo EffectMarnee BrowerNessuna valutazione finora
- Boosting Long-Term Retention Without Extra Study TimeDocumento4 pagineBoosting Long-Term Retention Without Extra Study TimeFranciane AraujoNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom Observation Report Robin Pegg 11Documento4 pagineClassroom Observation Report Robin Pegg 11api-337384040Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Streetcar Named Desire As A Brilliant Implacable Play About The Disintegration of WomenDocumento3 pagineA Streetcar Named Desire As A Brilliant Implacable Play About The Disintegration of WomenIJELS Research JournalNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study On Individual DifferencesDocumento3 pagineCase Study On Individual DifferencesTUMMALAPENTA BHUVAN SAI KARTHIKNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 - The Analytic ThirdDocumento25 pagine3 - The Analytic ThirdRob100% (1)
- L5 U5 - Lessons 1-2 - 2022Documento33 pagineL5 U5 - Lessons 1-2 - 2022Adriana SalgadoNessuna valutazione finora
- LIST OF ONLINE SHORT COURSES - UWI Open Campus Semester 2 2022 - 2023Documento39 pagineLIST OF ONLINE SHORT COURSES - UWI Open Campus Semester 2 2022 - 2023Suelin LumfaiNessuna valutazione finora
- UPDATED-PAQ-Questionnaire - BURI1991-G07Documento5 pagineUPDATED-PAQ-Questionnaire - BURI1991-G07Charlhyn BisnarNessuna valutazione finora
- Homeschooling and Social Skill DevelopmentDocumento6 pagineHomeschooling and Social Skill Developmentapi-666596583Nessuna valutazione finora
- Field Practice Module 1Documento4 pagineField Practice Module 1Jake BascoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hall's Care, Cure, Core Nursing TheoryDocumento8 pagineHall's Care, Cure, Core Nursing TheoryAlex AlegreNessuna valutazione finora
- Maximizing Student Potential Through Understanding DiversityDocumento2 pagineMaximizing Student Potential Through Understanding DiversityGellaine FernandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Munich Chronotype Questionnaire (MCTQ)Documento3 pagineMunich Chronotype Questionnaire (MCTQ)Monica CusniriucNessuna valutazione finora
- 6traits Template Diff MotivationDocumento3 pagine6traits Template Diff Motivationapi-250000527Nessuna valutazione finora
- Avon Case StudyDocumento55 pagineAvon Case Studyremon4hrNessuna valutazione finora
- TNA Competency BasedDocumento59 pagineTNA Competency BasedaishwaryaasnNessuna valutazione finora