Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Cefaclor, Salbutamol, Paracetamol and NCP
Caricato da
Ariane Rose Saria CedronDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Cefaclor, Salbutamol, Paracetamol and NCP
Caricato da
Ariane Rose Saria CedronCopyright:
Formati disponibili
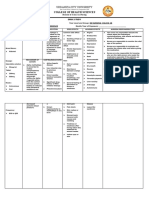
DRUG STUDY Name of Patient Initial: N.N.
B Age: 1 year and 10 months old Sex: Male Date of Admission: August 27, 2013 Diagnosis: BFC secondary to AURTI Date Medication Started: August 27, 2013
DRUG(20) Generic Name(2) Cefaclor Brand Name(2) Classification(2) Antibiotic, Cephalosporin Dosage(4) 250/5ml = 5ml Route(3) Oral Frequency(3) q8 Form(2) suspension Color(2) red
MECHANISM OF ACTION(10) Bactericidal: inhibits synthesis of bacterial cell wall, causing cell death.
INDICATION(10) Lower respiratory infections caused by S. pneumonia, S. aureus, E. coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, H. influenza, S. pyogenes Dermatologic infections caused by S. aureus, S. pyogenes, E. coli, K. pneumonia, Enterobacter UTIs caused by E. coli, K. pneumonia Uncomplicated and disseminated
CONTRAINDICATIONS(1 0) Contraindicated with allergy to cephalosporins or penicillins Use continuously with renal failure, lactation, pregnancy
EFFECTS(10)
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES(40) Determine history of hypersensitivity reactions to cephalosporins, penicillins, and history of allergies, particularly to drugs, before therapy is initiated. Lab tests: Perform culture and sensitivity tests before initiation of therapy and periodically during therapy if indicated. Therapy may be instituted pending test results. Monitor periodically BUN and creatinine clearance. Inspect IV injection sites frequently for signs of phlebitis. Report onset of loose stools or diarrhea.
Side Effects Diarrhea, stomach upset Difficulty of breathing Anusual tiredness or fatigue Pain at injection site
Adverse Effect CNS: headache, dizziness, lethargy, paresthesias GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia,
gonorrhea caused by N. gonorrhoeae Septicimia caused by S. pneumonia, S. aureus, E. coli, K pneumonia, H. influenza Meningitis caused by S. pneumoniae, H. influenza, S. aureus, N. meningitides Bone and joint infections due to S. aureus Perioperative prophylaxis Treatment of acute bacterial maxillary sinusitis in patients 3-mo 12yr
abdominal pain, Although flatulence, pseudomembranous pseudomenbran colitis rarely occurs, ouse colitis, this potentially lifehepatotoxicity threatening complication should be GU: ruled out as the cause Nephrotoxicity of diarrhea during and Hematologic: after antibiotic Bone marrow therapy. depression Monitor for Hypersensitivity: manifestations of ranging from hypersensitivity. rash to fever to Discontinue drug and anaphylaxis; report their serum sickness appearance promptly. reaction Monitor I&O rates and Local: pain, pattern: Especially abcess at important in severely ill injection site, patients receiving high phlebitis, doses. Report any inflammation of significant changes. IV site Others: Patient & Family Education superinfection, disulfram- like reaction with Report loose stools or alcohol diarrhea promptly. Report any signs or symptoms of hypersensitivity
Submitted by: Ariane Rose S.Cedron Year& Section Grp. : BSN3-1 Group 3 Date: August 30, 2013
Submitted to: Mr.Rolly Antonio
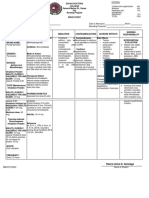
DRUG STUDY Name of Patient Initial: N.N.B Age: 1 year and 10 months old Sex: Male Date of Admission: August 27, 2013 Diagnosis: BFC secondary to AURTI Date Medication Started: August 27, 2013
DRUG(20) Generic Name(2) Salbutamol Guaifenesin Brand Name(2) Ventolin Classification(2) Expectorant/ Antiasthma Dosage(4) 5ml, 12mg Route(3) Oral Frequency(3) TID Form(2) Syrup Color(2) White
MECHANISM OF ACTION(10) It relieves nasal congestion and reversible bronchospasm by relaxing the smooth muscles of the bronchioles. The relief from nasal congestion and bronchospasm is made possible by the following mechanism that takes place when Salbutamol is administered. First, it binds to the beta2adrenergic receptors in the airway of the smooth muscle which then leads to the activation of the adenyl cyclase and increased levels of cyclic- 35-
INDICATION(10) To control and prevent reversible airway obstruction caused by asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) Quick relief for bronchospasm For the prevention of exercise-induced bronchospasm Long-term control agent for patients with chronic or persistent bronchospasm
CONTRAINDICATIONS(10) Hypersensitivity to adrenergic amines Hypersensitivity to fluorocarbons
EFFECTS(10) Nervousness Restlessness Tremor Headache Insomnia Chest pain Palpitations Angina Arrhythmias Hypertension Nausea and vomiting Hyperglycemia Hypokalemia
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES(40) Assess lung sounds, PR and BP before drug administration and during peak of medication. Observe fore paradoxical spasm and withhold medication and notify physician if condition occurs Administer PO medications with meals to minimize gastric irritation. Extended-release tablet should be swallowed-whole. It should not be crushed or chewed. If administering medication through inhalation, allow at least 1 minute between
adenosine monophospha te (cAMP). When cAMP increases, kinases are activated. Kinases inhibit the phosphorylati on of myosin and decrease intracellular calcium. Decreased in intracellular calcium will result to the relaxation of the smooth muscle airways.
inhalation of aerosol medication. Advise the patient to rinse mouth with water after each inhalation to minimize dry mouth. Inform the patient that Albuterol may cause an unusual or bad taste.
Submitted by: Ariane Rose S.Cedron Year& Section Grp. : BSN3-1 Group 3 Date: August 30, 2013
Submitted to: Mr.Rolly Antonio
DRUG STUDY
Name of Patient Initial: N.N.B Age: 1 year and 10 months old Sex: Male
Date of Admission: August 27, 2013 Diagnosis: BFC secondary to AURTI Date Medication Started: August 27, 2013
DRUG(20) Generic Name(2) Paracetamol Brand Name(2) Calpol Classification (2) Analgesic, Non- opioid Antipyretic Dosage(4) 250mg/ 5ml= 1.5ml Route(3) P.O Frequency(3) q4 for temp 37.8 C Form(2) Suspension Color(2) orange
MECHANISM OF ACTION(10) Decreases fever by a hypothalamic effect leading to sweating and vasodilation Inhibits pyrogen effect on the hypothalamicheat-regulating centers Inhibits CNS prostaglandin synth esis with minimal effects on peripheral prostaglandin synthesis Does not cause ulceration of the GI tract and causes no anticoagulant action
INDICATION(10) Control of pain due to headache, earache,dysmen orrhea, arthralgia, myalgia, musculoskeletal pain, arthritis, immun izations, teething, tonsillectomy Reduce fever in viral and bacterial inf ections As a substitute for aspirin in upper GI disease, bleeding disorders clients in anticoagulant therapy and gouty arthritis
CONTRAINDICATIONS (10) Anemia, cardiac & pulmonary disease. Hepatic or severe renal disease. Liver toxicity (hepatocyte necrosis) may occur with doses not far beyond labeled dosing.
EFFECTS(10)
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES(40) Do not exceed 4gm/24hr. in adults and 75mg/kg/day in children. Do not take for >5days for pain in children, 10 days for pain in adults, or more than 3 days for fever in adults. Extended-Release tablets are not to be chewed. Monitor CBC, liver and renal functions. Assess for fecal occult blood and nephritis. Avoid using OTC drugs with Acetaminophen . Take with food or milk to minimize GI upset. Report N&V. cyanosis, shortness of breath and abdominal pain as these are signs of toxicity.
Side Effects Minimal GI upset,methemogl obinemia,hemoly tic anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopeni a, pancytopenia, leucopenia,urtica ria, CNS stimulation, hypoglycemic coma, jaundice, glissitis, drowsiness, liver damage
Adverse Effect Allergic skin reactions & GI disturbances.
Report paleness, weakness and heart beat skips Report abdominal pain, jaundice, dark urine, itchiness or clay-colored stools. Phenmacetin may cause urine to become dark brown or winecolored. Report pain that persists for more than 3-5 days This drug is not for regular use with any form of liver disease.
Submitted by: Ariane Rose S.Cedron Year& Section Grp. : BSN3-1 Group 3 Date: August 30, 2013
Submitted to: Mr.Rolly Antonio
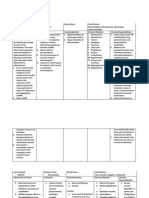
NURSING CARE PLAN Name of Patient Initial: N.N.B Age: 1 year and 10 months old Sex: Male ASSESSMENT NURSING DIAGNOSIS Risk for imbalanced nutrition less than body requirements related to inadequate nutritional intake due to decreased appetite. SCIENTIFIC RATIONALE When a person get sick, all his/ her senses are affected, even the sense of taste, and some have an after taste with the medication. Thats the reason why people loss their appetite when sick. OBJECTIVE NURSING INTERVENTION 1. Assess nutritional history, including a preferred food. 2. Observation and record the patient's food intake. Date of Admission: August 27, 2013 Diagnosis: BFC secondary to AURTI Surgery (if any): None SCIENTIFIC RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective cues: Wala ako masyadong ganang kumain, halos mga isang lingo na po. As verbalized by the client. Objective cues: Loss of appetite for a week Anorexia Thin body frame
After 8hrs of nursing intervention the client will identify the importance of eating nutritious foods that will help his body to recover.
1. Identify deficiencies, suspect the possibility of intervention 2. Observing caloric intake / lack of quality food consumption.
The patient identifies the importance of eating nutritious food. The patient shows behavior to improve his eating habits.
3.
Measure body weight per day (if possible).
3. Observing weight loss / observe the effectiveness of the intervention. 4. Little food can reduce vulnerabilities and increase input also prevent gastric distention.
4. Give food a little but often and or eat between meals.
5.
Give and Help oral hygiene.
6. Avoid foods
5. Increased appetite and
that stimulate and gassy. Rational:
oral input. 6. Lowering distention and gastric irritation.
Submitted by: Ariane Rose S.Cedron Year& Section Grp. : BSN3-1 Group 3 Date: August 30, 2013
Submitted to: Mr.Rolly Antonio
NURSING CARE PLAN Name of Patient Initial: N.N.B Age: 1 year and 10 months old Sex: Male ASSESSMENT NURSING DIAGNOSIS Ineffective Airway Clearance related to thick tenacious secretions and airway obstruction as manifested by shallow respiration, tachypnea and fever. SCIENTIFIC RATIONALE OBJECTIVE NURSING INTERVENTION 1. Monitor VS every 2 hrs. 2. Encourage patient to position in high-Fowlers or semi-Fowlers positon. 3. 3. turn patient every2 hrs and prn. 4. teach client to maintain adequate hydration by drinking at least 8-10 glasses of fluid/day ( if not contraindicated) 5. teach andsupervise effective coughing techniques.. 6. perform Chest Physical therapy 7. instruct on splinting abdomen with pillow during coughing efforts.. 8. monitor airway for patency Date of Admission: August 27, 2013 Diagnosis: BFC secondary to AURTI Surgery (if any): None SCIENTIFIC RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective: Nahihirapan siyang huminga, kaya naka oxygen siya. As stated by the mother Objective: inability to cough effectively shallow respiratio ns febrile T= 38.1 anxiety restlessne ss adventitio us breath sounds use of accessory muscle while brea thing tachypnea
After 8 hours of nursing intervention, the client will be able to cough effectively andclear own secretions.
1. to assess baseline data. 2. promotes maximal lungfunction. 3. repositioning pro motes drainage o f pulmonary secretions and enhances ventilation to decrease potential of atelectasis. 4. to help thin secretions. 5. To conserve energy and to reduce airway collapse. 6. CPT techniques utilizes forces of gravity and motionto facilitate secretion removal
After 8hours of nursing intervention, the client had beenable to cougheffectively andclear own secretions. Goal was met
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15. 16.
and provide artificial airways as warranted. administer bron chodilators as ordered. instruct client/family to notify nurse if the client is experiencing shortness of breath or air hunger instruct client/family regarding medications, effects, side effects and symptoms of adverse effects to nurse or physician promotes increased expiratory pressu re.8.requires if patient cannot maintain airway patency. to improve ventilation and maximizes air exchange. may indicate bronchial tubes are blocked with mucus, leading tohypoxia andhypoxemia. promotes prompt
identification of potential adverse reaction to facilitate timely intervention
Submitted by: Ariane Rose S.Cedron Year& Section Grp. : BSN3-1 Group 3 Date: August 30, 2013
Submitted to: Mr.Rolly Antonio
NURSING CARE PLAN Name of Patient Initial: N.N.B Age: 1 year and 10 months old Sex: Male ASSESSMENT NURSING DIAGNOSIS Hyperthermia related to BFC secondary to AURTI SCIENTIFIC RATIONALE A fever occurs when t he body sets the core temperature to a higher temperature, through the action of the pre-optic region of the anterior hypothalamus. For example, in response to a bacterial or viral infection, the body will raise its temperature, much like raising the temperature setting on a thermostat. OBJECTIVE NURSING INTERVENTION Provide tepid sponge bath. Assess fluidloss & facilitate oral intake. Promote bed rest. Provide cool circulating air usinga fan. Assist patient in changing into dry clothing. Provide oral hygiene. Monitor vital signs. Maintain IVfluids as orderedby physician. Administer antipyretic as ordered. Administer antibiotic as ordered. Interdepende nt: Monitor Date of Admission: August 27, 2013 Diagnosis: BFC secondary to AURTI Surgery (if any): None SCIENTIFIC RATIONALE Enhances heat loss by evaporation& conduction. Increases metabolic rate &diaphoresis. Reduces body heat Production. Dissipates heat by convection. Increases comfort. Prevents herpetic lesions of the mouth. Notes progress & changes of condition. Prevents de hydration. Reduces fever. Treats underlying cause. EVALUATION
Subjective cues: Baba, taas ang lagnat nang anak ko hanggang ngayon as stated by the patients mother. Objective cues: Warm to touch Drooping eyes Irritability Mild eyes redness Dry lips Flashed skin V/S T= 38.1C CR= 144 RR= 44
After 8 hours of nursing intervention, the patient temperature will lower downto37.5 C
After 8 hours of nursing intervention, the patient as a temperature of 37C
hematologic test &other pertinent lab records Discuss condition of the patient withother members of the health care team.
Indicates presence of infection &dehydration. Ensures continuous intervention
Submitted by: Ariane Rose S.Cedron Year& Section Grp. : BSN3-1 Group 3 Date: August 30, 2013
Submitted to: Mr.Rolly Antonio
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Drug Study OrthoDocumento4 pagineDrug Study OrthoJhessa Curie Pitagan100% (1)
- Generic Name: Classification: Indication:: Candida InfectionsDocumento1 paginaGeneric Name: Classification: Indication:: Candida Infectionscen janber cabrillos0% (1)
- Drug Study AzithromycinDocumento2 pagineDrug Study Azithromycinkuro hanabusaNessuna valutazione finora
- SHEENA Clomid Drug StudyDocumento3 pagineSHEENA Clomid Drug StudyNur SetsuNessuna valutazione finora
- Generic Name:: Norgestimate and Ethinyl EstradiolDocumento5 pagineGeneric Name:: Norgestimate and Ethinyl EstradiolJay VillasotoNessuna valutazione finora
- FINAL Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineFINAL Drug StudycasedraftNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study: AmoxicillinDocumento3 pagineDrug Study: AmoxicillinKrzia TehNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Sudy Format MethyldopaDocumento3 pagineDrug Sudy Format MethyldopaBianca Marithè RejanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Generic Name: - Ceftazidime Brand Name: - Tazidime ClassificationDocumento2 pagineGeneric Name: - Ceftazidime Brand Name: - Tazidime ClassificationRadicalRayNessuna valutazione finora
- Terramycin - Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineTerramycin - Drug StudyBolasoc, HazelNessuna valutazione finora
- Generic Name: Metoclopramide Brand Name: Reglan and Metozolv ODTDocumento2 pagineGeneric Name: Metoclopramide Brand Name: Reglan and Metozolv ODTJohn Paolo Tamayo OrioNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineDrug StudyemmanuelmyagokayeNessuna valutazione finora
- Silver Sulfadiazine Drug StudyDocumento3 pagineSilver Sulfadiazine Drug StudyKenn Siasar100% (1)
- Drug Study SulfasalazineDocumento2 pagineDrug Study SulfasalazineBunnie AlphaNessuna valutazione finora
- Senokot-S (Senna Concentrate 8.6mg + Docusate Sodium 50mg)Documento2 pagineSenokot-S (Senna Concentrate 8.6mg + Docusate Sodium 50mg)E100% (1)
- Tapazole and Calcium GluconateDocumento3 pagineTapazole and Calcium Gluconatekuro hanabusaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cephalexin Drug Study RNpedia ComDocumento2 pagineCephalexin Drug Study RNpedia ComKatyana Cesar100% (1)
- Dazomet DrugDocumento2 pagineDazomet Drugashley11Nessuna valutazione finora
- Amlodipine CPDocumento2 pagineAmlodipine CPRose EchevarriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento7 pagineDrug StudyOlive Keithy Ascaño ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- CetirizineDocumento2 pagineCetirizineDanielle Marie SamblacenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study Ceftriaxone SodiumDocumento3 pagineDrug Study Ceftriaxone SodiumPrincess Queenie OlarteNessuna valutazione finora
- Cefprozil (Drug Study)Documento2 pagineCefprozil (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888Nessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaDrug StudyElisha Faith Sevilla EspineliNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study: MontelukastDocumento3 pagineDrug Study: Montelukastunkown userNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study Cushing's SyndromeDocumento5 pagineDrug Study Cushing's SyndromeSelena MarieNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study AzithromycinDocumento4 pagineCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study AzithromycinhahahahaaaaaaaNessuna valutazione finora
- LOPERAMIDEDocumento3 pagineLOPERAMIDEfaye kimNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Name Indication Action Adverse EffectsDocumento4 pagineDrug Name Indication Action Adverse EffectsMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- PrioritizationDocumento1 paginaPrioritizationJLAZRONessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study: I Loilo Doctors' College College of NursingDocumento6 pagineDrug Study: I Loilo Doctors' College College of NursingAudrie Allyson GabalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Formoterol Gonzaga.Documento2 pagineFormoterol Gonzaga.Sheryl Anne GonzagaNessuna valutazione finora
- TerramycinDocumento2 pagineTerramycinChoox PriiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mupirocin DSDocumento2 pagineMupirocin DSArnzz AgbulosNessuna valutazione finora
- Sodium ChlorideDocumento1 paginaSodium ChlorideMark Christian M. GonzagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug SDocumento2 pagineDrug SJane CasiquinNessuna valutazione finora
- DS - Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS)Documento2 pagineDS - Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS)Celline Isabelle ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentDocumento1 paginaDrug Study: Nursing Departmentgiselle chloeNessuna valutazione finora
- Asian College of Science and Technology College of Nursing Drug StudyDocumento7 pagineAsian College of Science and Technology College of Nursing Drug StudynizabangxNessuna valutazione finora
- FluticasoneDocumento4 pagineFluticasonevanNessuna valutazione finora
- DRUGSTUDY Tetanus ToxoidDocumento1 paginaDRUGSTUDY Tetanus ToxoidMicaela Andrea CieloNessuna valutazione finora
- Nahco3 Vancomycin AmlodipineDocumento3 pagineNahco3 Vancomycin AmlodipineShan Dave TupasNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study Table OkDocumento29 pagineDrug Study Table OkRifa'atul Mahmudah100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY LevetiracetamDocumento3 pagineDRUG STUDY LevetiracetamMaria Althea NajorraNessuna valutazione finora
- Metronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayDocumento4 pagineMetronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayCrisyl LipawenNessuna valutazione finora
- BNP (C)Documento2 pagineBNP (C)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNessuna valutazione finora
- Mupirocin Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaMupirocin Drug StudyArthur Christopher Corpuz0% (1)
- Drug Study DoxycylineDocumento3 pagineDrug Study DoxycylineMethaGod GameNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study DoxoburicinDocumento1 paginaDrug Study DoxoburicinkyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug AnalysisDocumento18 pagineDrug AnalysisArt Christian RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento4 pagineDrug StudyAilah Mae Dela Cruz0% (1)
- DRUG STUDY-LidocaineDocumento3 pagineDRUG STUDY-LidocaineCarissa Mae Tapec Estrada100% (1)
- Name of Drug Dosage/Frequency/ Timing/Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento2 pagineName of Drug Dosage/Frequency/ Timing/Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitieskyleNessuna valutazione finora
- Generic Name: Classification: IndicationDocumento2 pagineGeneric Name: Classification: IndicationKristine YoungNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study EntecavirDocumento4 pagineDrug Study EntecavirClarimae AwingNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentDocumento1 paginaDrug Study: Nursing Departmentgiselle chloeNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study LoperamideDocumento2 pagineDrug Study LoperamideBunnie AlphaNessuna valutazione finora
- V. Laboratory Result and Diagnostic ExaminationDocumento23 pagineV. Laboratory Result and Diagnostic ExaminationAvigael Gabriel AvilesNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento13 pagineDrug StudyAbdullah Mascardo BarabagNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento9 pagineDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloNessuna valutazione finora
- E01723 Yogic Asanas For Health and Vigour TextDocumento138 pagineE01723 Yogic Asanas For Health and Vigour TextAnonymous nKVk2VC2VENessuna valutazione finora
- 1289 - Andrology Labratory ManualDocumento245 pagine1289 - Andrology Labratory ManualJuragang PotilNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymers in Medicine and Surgery 1975 PDFDocumento336 paginePolymers in Medicine and Surgery 1975 PDFVidvendu GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- BLS Provider Manual PDFDocumento21 pagineBLS Provider Manual PDFAmany Al Mahgoob100% (1)
- 10752-02 CH02 Final PDFDocumento28 pagine10752-02 CH02 Final PDFDejan MilenkovicNessuna valutazione finora
- Panic Away EbookDocumento61 paginePanic Away Ebooknobi_69100% (2)
- Anatomia de BufalosDocumento24 pagineAnatomia de BufalosTrilce ClaroNessuna valutazione finora
- Zincum ValerianicumDocumento3 pagineZincum ValerianicumKamalNessuna valutazione finora
- Finding BalanceDocumento56 pagineFinding BalanceVersoza Nel100% (2)
- Liberation From Mechanical VentilationDocumento21 pagineLiberation From Mechanical VentilationRins Chacko50% (2)
- The+O2+Awakening+ +O2+Daily+Practice+GuideDocumento3 pagineThe+O2+Awakening+ +O2+Daily+Practice+GuidetonalbadassNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro To EndoDocumento18 pagineIntro To EndoGareth DoodyNessuna valutazione finora
- Observations During Fundus ExaminationDocumento3 pagineObservations During Fundus ExaminationAn'umillah Arini ZidnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Recognizing and Treating Breathing DisordersDocumento302 pagineRecognizing and Treating Breathing DisordersJun Kim100% (2)
- Notes - Human GeneticsDocumento68 pagineNotes - Human GeneticsiwennieNessuna valutazione finora
- Pex 05 05Documento4 paginePex 05 05Lesly Castellano50% (2)
- BS EN 00138-1994 (1995) Scan PDFDocumento24 pagineBS EN 00138-1994 (1995) Scan PDFShan Sandaruwan AbeywardeneNessuna valutazione finora
- Methyldopa DYNAMED 2014Documento19 pagineMethyldopa DYNAMED 2014Lalo AngelesNessuna valutazione finora
- 1,4-Butanediol: From Formaldehyde + AcetyleneDocumento14 pagine1,4-Butanediol: From Formaldehyde + AcetyleneRisa HashimotoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Structure and Function of Proteins Chapter 5 (Continued)Documento27 pagineThe Structure and Function of Proteins Chapter 5 (Continued)Rabi MehrNessuna valutazione finora
- 12575277461737Documento29 pagine12575277461737Chintan ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Esthetics of Artificial GingivaDocumento13 pagineEsthetics of Artificial GingivaSorabh JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Regulation of BPDocumento17 pagineRegulation of BPLemon CatbaganNessuna valutazione finora
- ISMST Shockwave Medical Papers 2012Documento24 pagineISMST Shockwave Medical Papers 2012Dr-Gehad Samy Halwagy100% (1)
- Carlson (7E) : Powerpoint Lecture OutlineDocumento26 pagineCarlson (7E) : Powerpoint Lecture Outlinechat gazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Food Tambola: Department of Food Science & TechnologyDocumento183 pagineFood Tambola: Department of Food Science & TechnologyManu BhatiaNessuna valutazione finora
- C - Syiam Amalia Rahmah - Topik 4Documento7 pagineC - Syiam Amalia Rahmah - Topik 4Syiam Amalia RahmahNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentasi Penjelasan 1Documento17 paginePresentasi Penjelasan 1sri wulan100% (1)
- Mandibular Fracture: Pembimbing: Drg. Henry Setiawan, M.Kes, SP - BMDocumento33 pagineMandibular Fracture: Pembimbing: Drg. Henry Setiawan, M.Kes, SP - BMSilvestri PurbaNessuna valutazione finora
- 67Documento57 pagine67Neeruam Ellehcim Aled ZurcNessuna valutazione finora