Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Caricato da
Rai HanahDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Caricato da
Rai HanahCopyright:
Formati disponibili
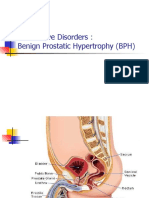
BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA (ENLARGED PROSTATE) It is gradual enlargement of the prostate gland with hypertrophy and hyperplasia of normal
l tissues. The cause is unknown. It usually occurs among men over 50 years of age. Aging process in males results to hormonal imbalances. The estrogen levels become higher than androgen levels. This cause hyperplasia of the prostate gland The enlargement causes compression of the urethra and base of the bladder. This leads to urinary obstruction. If untreated, it results to a serious complication Clinical Manifestations NOCTURIA (frequent voiding during the night). Is usually the initial manifestations. The other manifestations are: Frequency, urgency, hesitancy (difficulty in initiating urination, takes few minutes before urine flows), decreased caliber of urinary stream and force, increased residual urine, hematuria, UTI. Collaborative Management Surgery is the only successful management of BPH The different surgical procedures of BPH: 1. Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) Prostatic tissues are excised through a resectoscope. There is no incision. Continuous bladder irrigation (CBI) or cystoclysis is done post-op to irrigate the bladder and remove blood clots. This is done through 3-way Foley catheter.
The surgery does not cause inconsistence or impotence post-op.
2. Suprapubic Prostactectomy It involves the removal of the prostate gland through abdominal and bladder incision. The client will have cystostomy tube and 2-way Foley catheter. To drain urine adequately and prevent leakage though the incision. (Whenever bladder incision is done, cystostomy tube will be in place). CBI is prescribed and administered to keep urine pink.
3. Retropublic Prostactectomy Is removal of the prostate gland through a lower abdominal incision. There is no incision into the bladder. CBI may be done. 4. Perineal Prostactectomy Is removal of the prostate gland through an incision made between the scrotum and the anus. The procedure causes inconsistence and sterility. Avoid inserting rectal tube, taking rectal temperature, or administering enemas. Post-op Care of the Client who had undergone Prostactectomy 1. Care of the client with CBI Maintain patency of the catheter. If the drainage is reddish, increase the flow rate as the drainage becomes clear. Practice asepsis. To prevent infection Use sterile NS (normal saline). To prevent infection and water intoxication. Repeated administration of hypotonic solution e.g., sterile water, may cause water intoxication. Monitor the client for hemorrhage. Monitor urinary output. Expect red to light pink urine for the first 24 hours; then it becomes amber in 3 days post-op.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- BPH - TextDocumento7 pagineBPH - TextSomesh GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- BPH GuideDocumento7 pagineBPH GuideSomesh GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy: Pathophysiology and EtiologyDocumento4 pagineBenign Prostatic Hypertrophy: Pathophysiology and EtiologyErnestomalamionNessuna valutazione finora
- BPHDocumento20 pagineBPHHerly KakaNessuna valutazione finora
- BENGIN PROSTATE HYPERPLASIA (BPH) GUIDEDocumento31 pagineBENGIN PROSTATE HYPERPLASIA (BPH) GUIDENipul MondolNessuna valutazione finora
- TURBT Procedure GuideDocumento80 pagineTURBT Procedure GuideWindelyn GamaroNessuna valutazione finora
- Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocumento9 pagineBenign Prostatic HyperplasiaElizabeth Mapa100% (1)
- INCONTINENCE3Documento12 pagineINCONTINENCE3allthingali217Nessuna valutazione finora
- Obstructive Disorders: Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy (BPH)Documento24 pagineObstructive Disorders: Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy (BPH)Pahlevie RezhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Storing A Urine SampleDocumento8 pagineStoring A Urine SampleMarz DempseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Wa0038.Documento5 pagineWa0038.sham gowliNessuna valutazione finora
- Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocumento28 pagineBenign Prostatic HyperplasiaFedrick MasatuNessuna valutazione finora
- Benigna Prostat Hiperplasia (BPH) Basic Concepts of Illness 2.1 DefinitionsDocumento9 pagineBenigna Prostat Hiperplasia (BPH) Basic Concepts of Illness 2.1 DefinitionsMade Va RaiyawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary RetentionDocumento24 pagineUrinary RetentionMuhammad Amri Kautsar100% (1)
- Care for Urinary Problems & InfectionsDocumento7 pagineCare for Urinary Problems & InfectionsJosephine NavarroNessuna valutazione finora
- BPH DefinitionDocumento5 pagineBPH DefinitionMadhu Sudhan PandeyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary System by Carmelita ChavezDocumento16 pagineUrinary System by Carmelita ChaveztankmpNessuna valutazione finora
- Bladder Atony/Urinary RetentionDocumento11 pagineBladder Atony/Urinary RetentionAngela CaguitlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary DiversionDocumento2 pagineUrinary DiversionWendy EscalanteNessuna valutazione finora
- Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocumento4 pagineBenign Prostatic HyperplasiaAdelle Fortunato100% (2)
- Retensio Urine Sapkom FixDocumento22 pagineRetensio Urine Sapkom FixBagus Wanda HabibullahNessuna valutazione finora
- CSS Urinary Retention: Davie Muhamad Ferzy Awwali FadhilaDocumento22 pagineCSS Urinary Retention: Davie Muhamad Ferzy Awwali FadhilaBagus Wanda HabibullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary System DisordersDocumento14 pagineUrinary System DisordersGideon P. CasasNessuna valutazione finora
- Female Incontinence: DR Alin CiopecDocumento51 pagineFemale Incontinence: DR Alin CiopecalinciopecNessuna valutazione finora
- Cystoscopy Guide: Examines Bladder & UrethraDocumento17 pagineCystoscopy Guide: Examines Bladder & UrethraMichael Angelo PangiliganNessuna valutazione finora
- Stress IncontinenceDocumento44 pagineStress IncontinenceswatisinghnigeriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Repro System NotesDocumento13 pagineRepro System NotesAraw GabiNessuna valutazione finora
- Elimination Needs 04Documento52 pagineElimination Needs 04Kishore RathoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Urology Guide to Kidney, Bladder and ProstateDocumento34 pagineUrology Guide to Kidney, Bladder and ProstateaddelinsNessuna valutazione finora
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Presented By: 2BSN2 - Group 6Documento34 pagineBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Presented By: 2BSN2 - Group 6Hazel Ann MolinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Instrumentations: Presented byDocumento27 pagineInstrumentations: Presented byOmar AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- EliminationDocumento128 pagineEliminationhailye mitikeNessuna valutazione finora
- Null - PDF 2Documento30 pagineNull - PDF 2مهند حسام محمد سعيد عبدNessuna valutazione finora
- BPH Symptoms, Risk Factors, and Treatment OptionsDocumento60 pagineBPH Symptoms, Risk Factors, and Treatment OptionsMaddox EdeyajNessuna valutazione finora
- LP BPH HasanuddinDocumento21 pagineLP BPH Hasanuddinahmad yusufNessuna valutazione finora
- Benign Prostate HyperthropyDocumento3 pagineBenign Prostate Hyperthropyzmae23Nessuna valutazione finora
- Elimination Review: Urinary Function and Nursing CareDocumento27 pagineElimination Review: Urinary Function and Nursing Careالموعظة الحسنه chanelNessuna valutazione finora
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : By, Ms. Ekta. S. Patel, I Yr M.SC NursingDocumento71 pagineBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : By, Ms. Ekta. S. Patel, I Yr M.SC NursingannisanabilaasNessuna valutazione finora
- Bladder DiverticulaDocumento23 pagineBladder DiverticulaJeanette CallejasNessuna valutazione finora
- BPH 180828154943Documento42 pagineBPH 180828154943Amandeep SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- TURP Procedure Guide for Prostate RemovalDocumento4 pagineTURP Procedure Guide for Prostate RemovalJylme Keziah Manzano DoronioNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Review: Managing Urinary Incontinence in Older PeopleDocumento15 pagineClinical Review: Managing Urinary Incontinence in Older PeopleMatthias WollfNessuna valutazione finora
- CystosDocumento19 pagineCystosneenuj_5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocumento6 pagineBenign Prostatic HyperplasiaHenny HansengNessuna valutazione finora
- Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocumento36 pagineBenign Prostatic Hyperplasiapooja9688Nessuna valutazione finora
- Evidence Based Research Related To The Disease: Suprapubic Bladder CatheterizationDocumento3 pagineEvidence Based Research Related To The Disease: Suprapubic Bladder CatheterizationManjiro SanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal Trauma and Surgeries ExplainedDocumento49 pagineRenal Trauma and Surgeries ExplainedsanthiyasandyNessuna valutazione finora
- LP Tifoid FeverDocumento15 pagineLP Tifoid FeverAghaYamaichiRyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Kidney InjuyDocumento36 pagineKidney InjuySK TalkNessuna valutazione finora
- The neuropathic lower urinary tractDocumento4 pagineThe neuropathic lower urinary tractBarez AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary Tract Obstruction: Zheng Xuepei MDDocumento66 pagineUrinary Tract Obstruction: Zheng Xuepei MDapi-19916399Nessuna valutazione finora
- Arianna Mabunga BSN-3B Urinary Diversion DeffinitionDocumento5 pagineArianna Mabunga BSN-3B Urinary Diversion DeffinitionArianna Jasmine Mabunga0% (1)
- 0616 SCuDocumento18 pagine0616 SCuYolanda Dwi OktaviyaniNessuna valutazione finora
- EliminationDocumento20 pagineEliminationHasan A AsFour100% (2)
- Transurethral Resection of The ProstateDocumento48 pagineTransurethral Resection of The Prostateralf_dolanNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary Incontinence Types and TreatmentsDocumento8 pagineUrinary Incontinence Types and Treatmentswzeer mohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- UTI Disorder PDFDocumento23 pagineUTI Disorder PDFMonarahayuNessuna valutazione finora
- Hematuria, (Blood in Urine) A Simple Guide to The Condition, Related Diseases And Use in Diagnosis of DiseasesDa EverandHematuria, (Blood in Urine) A Simple Guide to The Condition, Related Diseases And Use in Diagnosis of DiseasesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Prostatitis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesDa EverandProstatitis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- CDI-500 Specialized Crime Investigation and Legal MedicineDocumento20 pagineCDI-500 Specialized Crime Investigation and Legal MedicineCherry Len FaroniloNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 SM PDFDocumento14 pagine1 SM PDFSiti HamsyiahNessuna valutazione finora
- Parameters Governing Predicted and Actual RQD Estimation - FINAL - PUBLISHED - VERSIONDocumento14 pagineParameters Governing Predicted and Actual RQD Estimation - FINAL - PUBLISHED - VERSIONKristian Murfitt100% (1)
- Engineering Mechanics Lectures PDFDocumento83 pagineEngineering Mechanics Lectures PDFluay adnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Terminal BlockDocumento12 pagineTerminal BlockAlmaforNessuna valutazione finora
- Shop Math PDFDocumento29 pagineShop Math PDFKen LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 s2.0 S2210803316300781 MainDocumento8 pagine1 s2.0 S2210803316300781 MainGilang Aji P. EmonNessuna valutazione finora
- ###Questions Model PDFDocumento2 pagine###Questions Model PDFDave DMNessuna valutazione finora
- Approach To Malabsorption (SANJAY)Documento58 pagineApproach To Malabsorption (SANJAY)Sanjay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Manoeuvrability Final EditedDocumento12 pagineManoeuvrability Final EditedSaptarshi BasuNessuna valutazione finora
- LirikDocumento537 pagineLirikMuhamad Iqbal FahmiNessuna valutazione finora
- HistorydylaneditDocumento6 pagineHistorydylaneditapi-19858424Nessuna valutazione finora
- VGHV NBV GH fc7fvbn BN NGCJHGDocumento16 pagineVGHV NBV GH fc7fvbn BN NGCJHGRahul GNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Blyden: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (Copd)Documento63 pagineDr. Blyden: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (Copd)Blyden NoahNessuna valutazione finora
- อัตราภาษีของไทยที่ลดให้เปรูDocumento124 pagineอัตราภาษีของไทยที่ลดให้เปรูDante FilhoNessuna valutazione finora
- EAGLE TUGS - Parts Service ManualDocumento72 pagineEAGLE TUGS - Parts Service ManualDave MilnerNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied Acoustics: André M.N. Spillere, Augusto A. Medeiros, Julio A. CordioliDocumento13 pagineApplied Acoustics: André M.N. Spillere, Augusto A. Medeiros, Julio A. CordioliAbdelali MoumenNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydraulic Power Steering System Design PDFDocumento16 pagineHydraulic Power Steering System Design PDFAdrianBirsan100% (1)
- Soal ReadingDocumento3 pagineSoal ReadingSendi PuspaNessuna valutazione finora
- CERT Basic Training Participant Manual - 2011Documento332 pagineCERT Basic Training Participant Manual - 2011jegodfreyNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice: Circles and ArcsDocumento2 paginePractice: Circles and ArcsTIANA ARILENessuna valutazione finora
- Integrating Kuleana Rights and Land Trust PrioritesDocumento50 pagineIntegrating Kuleana Rights and Land Trust PrioritesKeala Rodenhurst-JamesNessuna valutazione finora
- ASIAN LIVESTOCK PERSPECTIVESDocumento18 pagineASIAN LIVESTOCK PERSPECTIVESMuadz AbdurrahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Series: Mechanical Style Pressure SwitchDocumento15 pagineSeries: Mechanical Style Pressure SwitchPhúc Phan TiếnNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 10 Trigonometry and Application of TrigonometryDocumento1 paginaClass 10 Trigonometry and Application of TrigonometryTanmay SanchetiNessuna valutazione finora
- Nest Installation GuideDocumento8 pagineNest Installation GuideOzzyNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 s2.0 S2214860417301148 Main PDFDocumento16 pagine1 s2.0 S2214860417301148 Main PDFQuy Hoang KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual of Curatorship: A Guide To Museum PracticeDocumento7 pagineManual of Curatorship: A Guide To Museum PracticeLuísa MenezesNessuna valutazione finora
- Modeling Vessel Impacts for Lock Wall DesignDocumento15 pagineModeling Vessel Impacts for Lock Wall DesignSalam FaithNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal Risna YantiDocumento14 pagineJurnal Risna YantiRisnayantiNessuna valutazione finora